信息网络安全 ›› 2026, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 91-101.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2026.01.008
一种基于分层强化学习的网络防御自主决策研究
- 1.北京宇航系统工程研究所,北京 100076
2.中国运载火箭技术研究院,北京 100076
-
收稿日期:2025-03-17出版日期:2026-01-10发布日期:2026-02-13 -
通讯作者:姚琳元linyuan_yao@126.com -
作者简介:王焕臻(2000—),男,吉林,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络主动防御|徐洪平(1969—),男,河南,研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为飞行器总体设计|李旷代(1984—),男,黑龙江,研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为指挥信息系统|刘洋(1994—),男,安徽,高级工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为网络安全|姚琳元(1988—),男,天津,高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为网络安全 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFB3101900)
A Study on Autonomous Decision-Making for Network Defense Based on Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
WANG Huanzhen1, XU Hongping2, LI Kuangdai1, LIU Yang1, YAO Linyuan1( )
)
- 1. Beijing Institute of Astronautical System Engineering, Beijing 100076, China
2. China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, Beijing 100076, China
-
Received:2025-03-17Online:2026-01-10Published:2026-02-13
摘要:
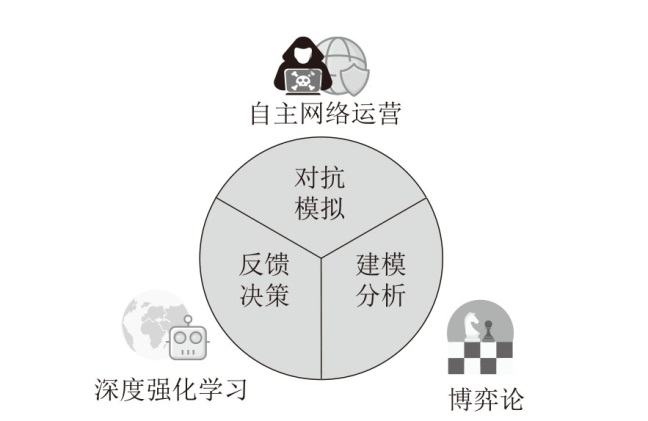
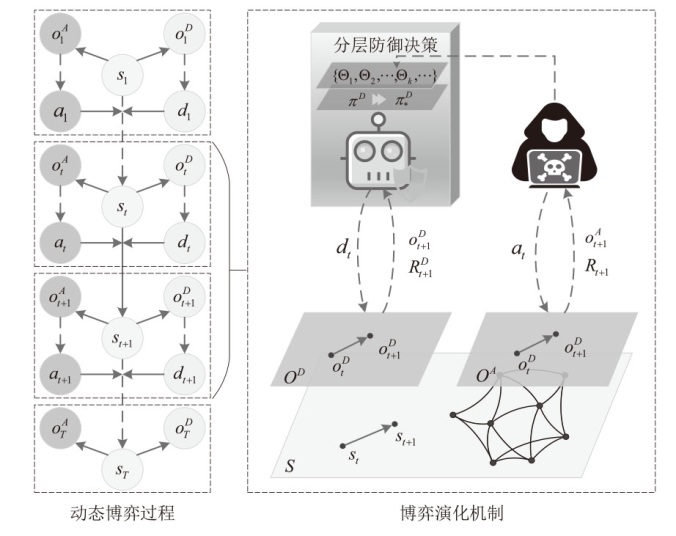
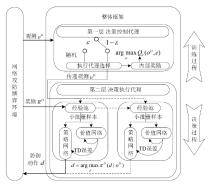
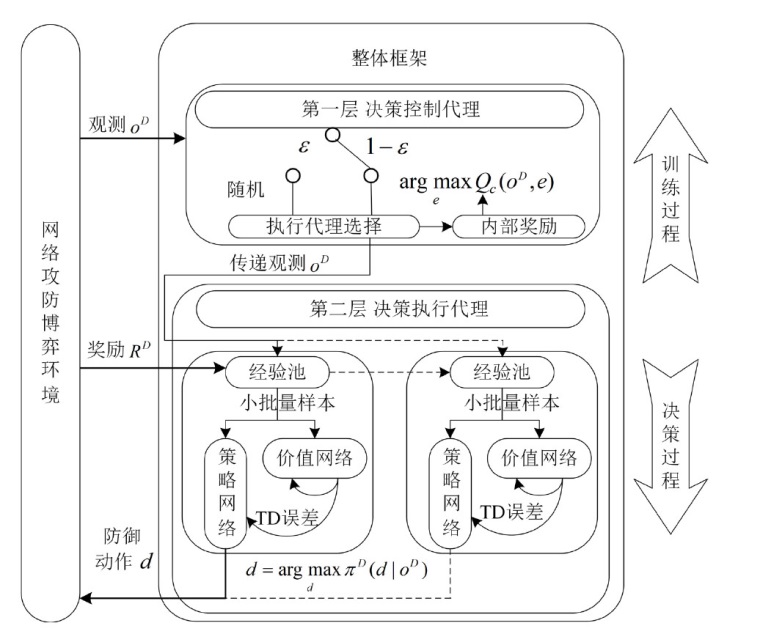
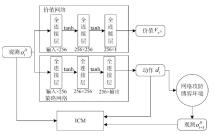
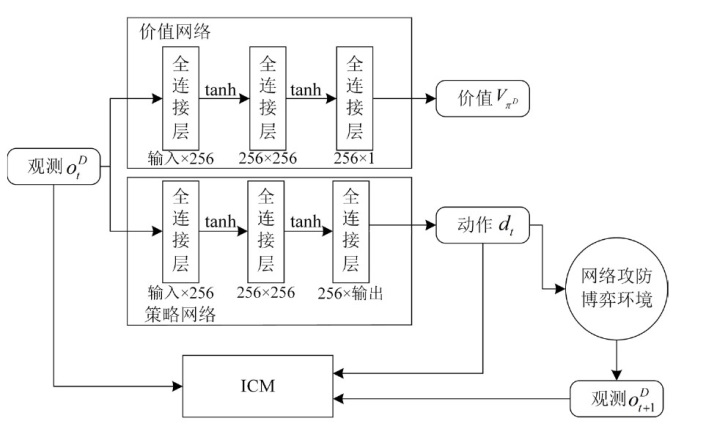
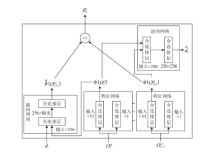
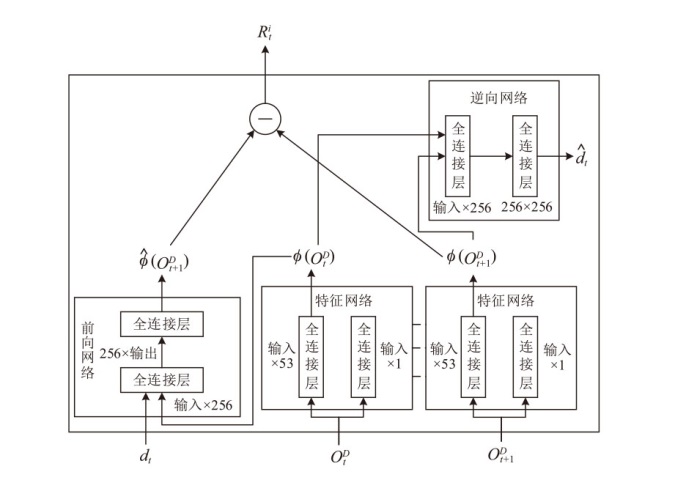
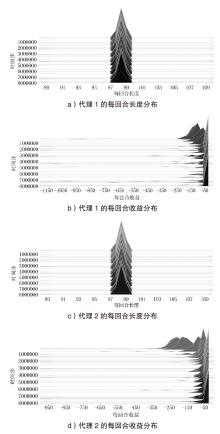
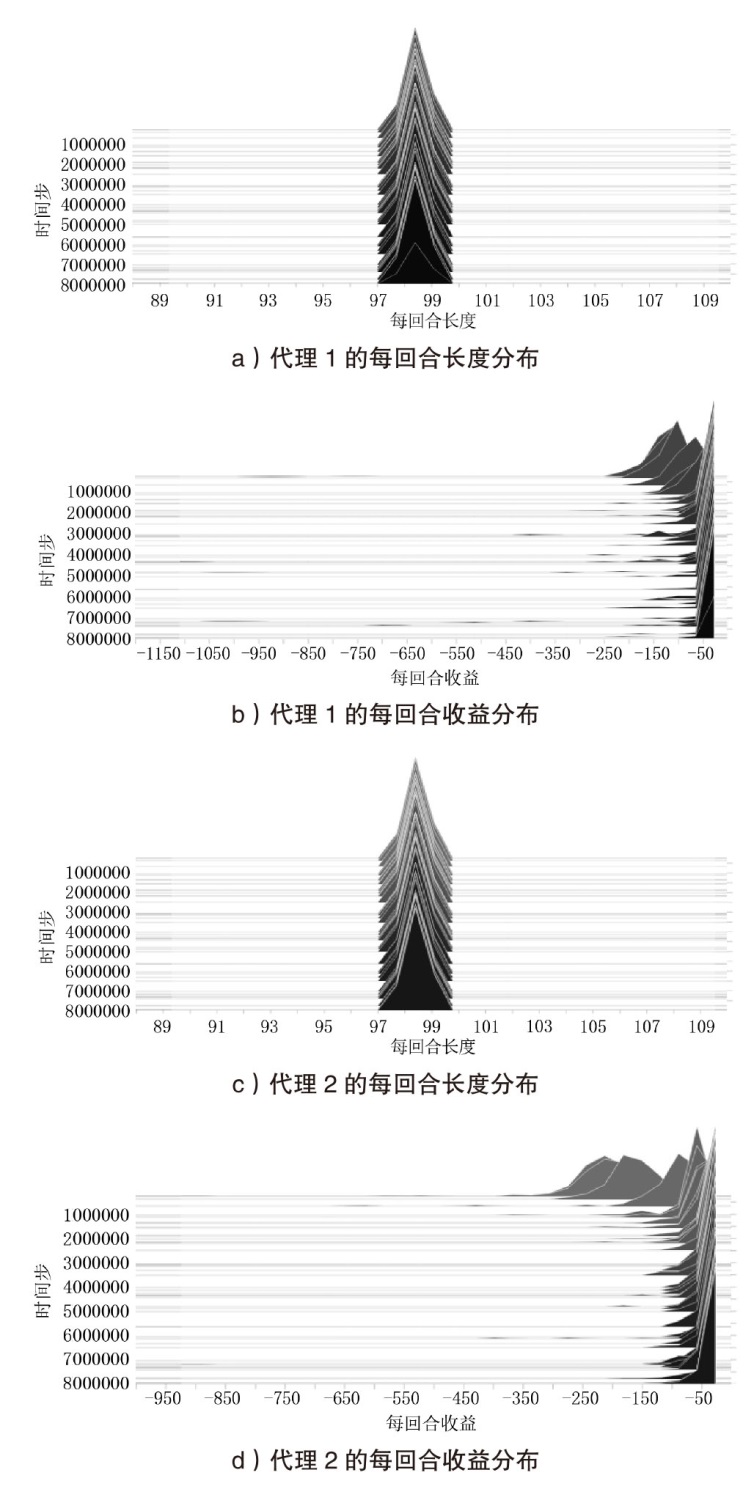
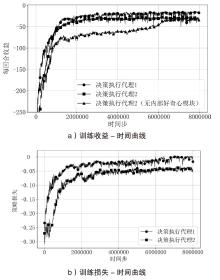
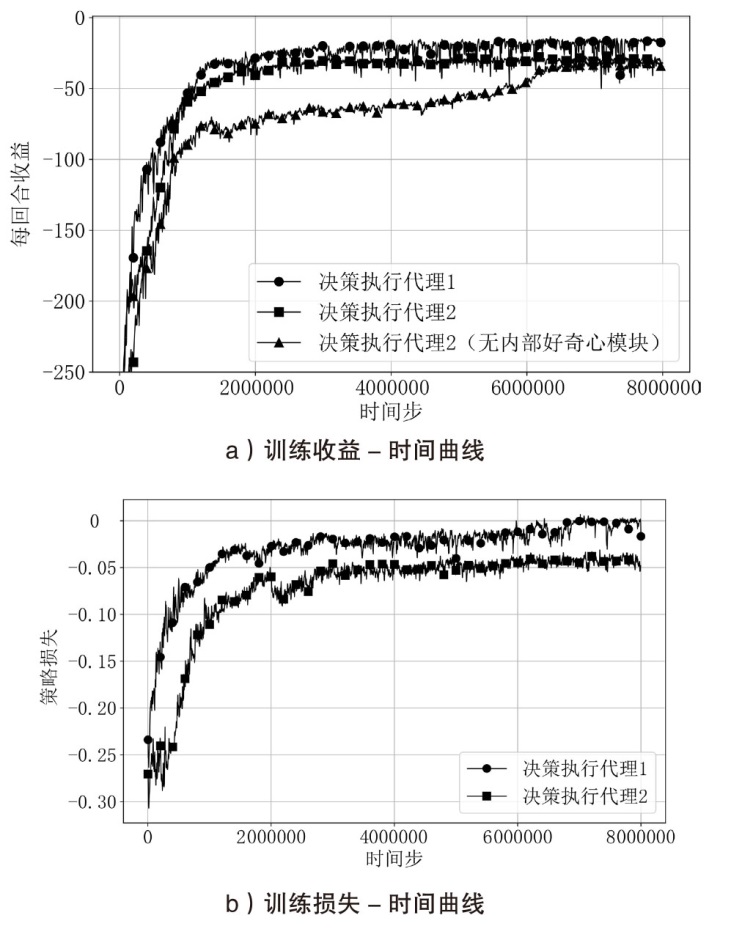
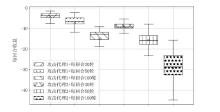
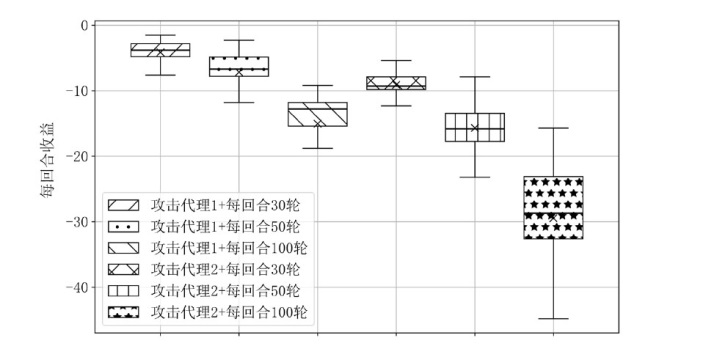
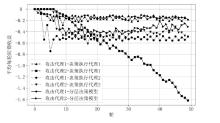
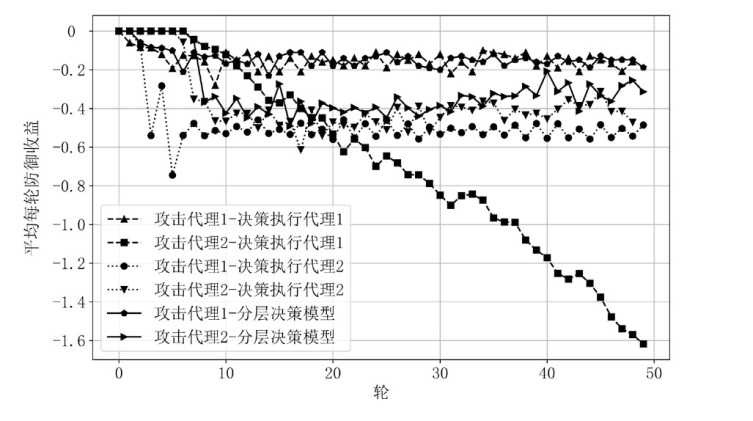
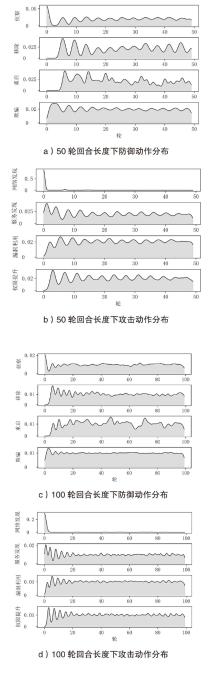
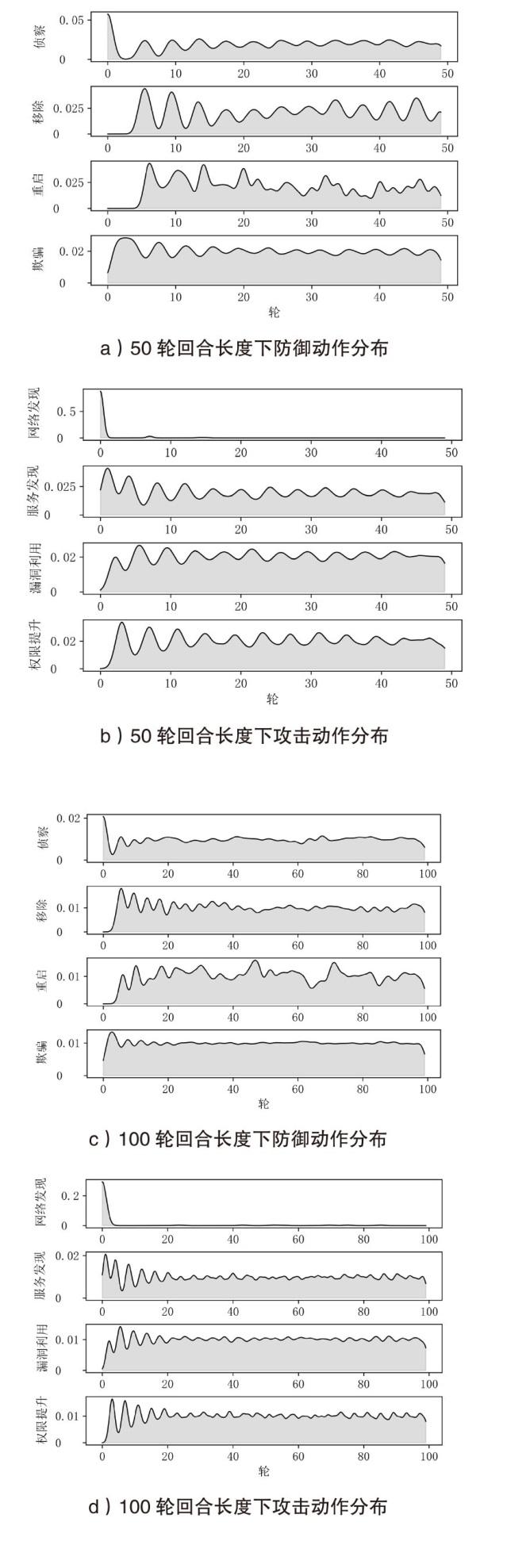
针对传统网络防御决策方法难以有效应对复杂动态的网络环境和多样化网络攻击的问题,结合高保真网络攻防仿真环境,文章提出一种基于分层强化学习的网络防御自主决策方法。通过构建一个基于不完全信息的马尔可夫网络攻防博弈模型,分析攻防双方的动态交互过程,形式化表示最优防御策略。通过顶层控制代理与底层执行代理的协同工作,分解了由于攻击者类型未知所造成的复杂防御决策任务。不同攻防场景下的仿真实验结果表明,该方法对两类渗透攻击模式均能进行灵活且高效的决策响应,维持弹性防御并生成可解释的动作分布。与现有相关工作的对比分析进一步证实了该方法在防御效能方面的优越性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王焕臻, 徐洪平, 李旷代, 刘洋, 姚琳元. 一种基于分层强化学习的网络防御自主决策研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 91-101.
WANG Huanzhen, XU Hongping, LI Kuangdai, LIU Yang, YAO Linyuan. A Study on Autonomous Decision-Making for Network Defense Based on Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2026, 26(1): 91-101.
| [1] | CrowdStrike. CrowdStrike 2024 Threat Hunting Report[EB/OL]. (2024-08-15)[2025-02-02]. ://crowdstrike.com/explore/crowdstrike-2024-threat-hunting-report/crowdstrike-2024-threat-hunting-report. |
| [2] |
MIAO Li, LI Shuai, WU Xiangjuan, et al. Mean-Field Stackelberg Game-Based Security Defense and Resource Optimization in Edge Computing[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(9): 3406-3417.
doi: 10.3390/app14083406 URL |
| [3] |
WU Huici, GAO Qiuyue, TAO Xiaofeng, et al. Differential Game Approach for Attack-Defense Strategy Analysis in Internet of Things Networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 9(12): 10340-10353.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3122115 URL |
| [4] | LIU Liang, TANG Chuhao, ZHANG Lei, et al. A Generic Approach for Network Defense Strategies Generation Based on Evolutionary Game Theory[EB/OL]. (2024-08-15)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2024.120875. |
| [5] | SUN Pengyu, TAN Jinglei, LI Chenwei, et al. Network Security Defense Decision-Making Method Based on Time Differential Game[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(5): 64-74. |
| 孙鹏宇, 谭晶磊, 李晨蔚, 等. 基于时间微分博弈的网络安全防御决策方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 64-74. | |
| [6] | HAMMAR K, STADLER R. Finding Effective Security Strategies through Reinforcement Learning and Self-Play[C]// IEEE. The 16th International Conference on Network and Service Management. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-9. |
| [7] |
HAMMAR K, STADLER R. Intrusion Prevention through Optimal Stopping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2021, 19: 2333-2348.
doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2022.3176781 URL |
| [8] | ALSHAMRANI A, ALSHAHRANI A. Adaptive Cyber Defense Technique Based on Multiagent Reinforcement Learning Strategies[J]. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing, 2023, 36(3): 2757-2771. |
| [9] | SELMONAJ A, SZEHR O, DEL R G, et al. Hierarchical Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Air Combat Maneuvering[C]// IEEE. 2023 International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications. New York: IEEE, 2023: 1031-1038. |
| [10] | TANG Yunlong, SUN Jing, WANG Huan, et al. A Method of Network Attack-Defense Game and Collaborative Defense Decision-Making Based on Hierarchical Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning[EB/OL]. (2024-07-01)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2024.103871. |
| [11] | CHEAH M, STONE J, HAUBRICK P, et al. CO-DECYBER: Cooperative Decision Making for Cybersecurity Using Deep Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning[C]// Springer. The 29th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2023: 628-643. |
| [12] | STANDEN M, LUCAS M, BOWMAN D, et al. Cyborg: A Gym for the Development of Autonomous Cyber Agents[EB/OL]. (2021-08-20)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2108.09118. |
| [13] | WIEBE J, MALLAH R A, LI L. Learning Cyber Defence Tactics from Scratch with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning[EB/OL]. (2023-08-25)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.05939. |
| [14] | PALMER G, PARRY C, HARROLD D J B, et al. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Cyber Operations: A Survey[EB/OL]. (2024-09-17)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.07745. |
| [15] | LIU Xiaohu, ZHANG Hengwei, DONG Shuqin, et al. Network Defense Decision-Making Based on a Stochastic Game System and a Deep Recurrent Q-Network[EB/OL]. (2021-12-01)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102480. |
| [16] |
WAHAB O A, BENTAHAR J, OTROK H, et al. Resource-Aware Detection and Defense System against Multi-Type Attacks in the Cloud: Repeated Bayesian Stackelberg Game[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019, 18(2): 605-622.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.8858 URL |
| [17] | SLIVKINS A. Introduction to Multi-Armed Bandits[EB/OL]. (2019-04-15)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1904.07272. |
| [18] | SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal Policy Optimization Algorithms[EB/OL]. (2019-04-15)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1707.06347. |
| [19] | PATHAK D, AGRAWAL P, EFROS A A, et al. Curiosity-Driven Exploration by Self-Supervised Prediction[C]// PMLR. International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: PMLR, 2017: 2778-2787. |
| [20] | KIELY M, BOWMAN D, STANDEN M, et al. On Autonomous Agents in a Cyber Defence Environment[EB/OL]. (2023-09-02)[2025-02-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2309.07388. |
| [21] | OASIS Open. OpenC 2 Language Specification Version 2.0[EB/OL]. (2024-05-15)[2025-02-02]. https://docs.oasis-open.org/openc2/oc2ls/v2.0/oc2ls-v2.0.pdf. |
| [22] | HANNAY J. Champion Award of CAGE Challenge 2[EB/OL]. (2023-06-06)[2025-02-02]. https://github.com/john-cardiff/-cyborg-cage-2. |
| [23] | RASHID T, SAMVELYAN M, DE W C S, et al. Monotonic Value Function Factorisation for Deep Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2020, 21(178): 1-51. |
| [1] | 郭毅, 李旭青, 张子蛟, 张宏涛, 张连成, 张香丽. 基于区块链的数据安全共享研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 1-23. |
| [2] | 郑开发, 骆振鹏, 刘嘉奕, 刘志全, 王赜, 吴云坤. 支持属性更新的轻量级联邦学习节点动态参与方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 102-114. |
| [3] | 李冬, 高源, 于俊清, 曾木虹, 陈俊鑫. 一种基于P4的多模态网络控制与安全检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 115-124. |
| [4] | 董佳瑜, 高宏民, 马兆丰, 赖冠辉. 多重签名机制在区块链中的研究及实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 125-138. |
| [5] | 钮可, 胡方锰, 李军. 基于非局部机制的可逆神经网络视频隐写研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 139-149. |
| [6] | 邓钰洋, 芦天亮, 李知皓, 孟昊阳, 马远声. 融合GAT与可解释DQN的SQL注入攻击检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 150-167. |
| [7] | 仝鑫, 焦强, 王靖亚, 袁得嵛, 金波. 公共安全领域大语言模型的可信性研究综述:风险、对策与挑战[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 24-37. |
| [8] | 王亚杰, 陆锦标, 谭冬黎, 范青, 祝烈煌. 面向胶囊网络的成员推理风险评估[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 38-48. |
| [9] | 施寅生, 包阳, 庞晶晶. 一种对抗GAN攻击的联邦隐私增强方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 49-58. |
| [10] | 吴越, 张雅雯, 程相然. 基于动态安全管理模式的信息系统安全防御策略研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 59-68. |
| [11] | 张慎明, 梁金洁, 许新桥, 冯戈, 邹添华, 胡志林. 基于博弈论的地址跳变系统时间策略研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 69-78. |
| [12] | 徐一凡, 程光, 周余阳. 抽样情况下复杂LDoS攻击检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 79-90. |
| [13] | 韩益亮, 彭一轩, 吴旭光, 李鱼. 基于图变分自编码器的多模态特征融合加密流量分类模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(12): 1914-1926. |
| [14] | 张雪锋, 王柯航. 一种基于SM9的代理环签名方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(12): 1901-1913. |
| [15] | 解相朋, 邵邢晨. 基于双域多项式框架的随机非线性CPS安全增益调度方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(12): 1889-1900. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||