信息网络安全 ›› 2026, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 69-78.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2026.01.006
基于博弈论的地址跳变系统时间策略研究
张慎明1, 梁金洁2, 许新桥2( ), 冯戈2, 邹添华2, 胡志林2
), 冯戈2, 邹添华2, 胡志林2
- 1.中国科学院大学网络空间安全学院,北京 100049
2.国家林业和草原局信息中心,北京 100714
-
收稿日期:2025-08-06出版日期:2026-01-10发布日期:2026-02-13 -
通讯作者:许新桥341802378@qq.com -
作者简介:张慎明(1999—),男,山东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为移动目标防御|梁金洁(1993—),女,山西,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为林草信息化、数据处理|许新桥(1972—),男,山东,正高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为林草信息化|冯戈(1987—),女,陕西,高级工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为网络安全、数据治理|邹添华(1998—),男,安徽,助理工程师,本科,主要研究方向为网络安全、信息系统管理|胡志林(1997—),男,河南,助理研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为林草信息化建设与管理
Research on Time Strategy of IP Hopping System Based on Game Theory
ZHANG Shenming1, LIANG Jinjie2, XU Xinqiao2( ), FENG Ge2, ZOU Tianhua2, HU Zhilin2
), FENG Ge2, ZOU Tianhua2, HU Zhilin2
- 1. School of Cyber Security, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
2. Information Center, National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Beijing 100714, China
-
Received:2025-08-06Online:2026-01-10Published:2026-02-13
摘要:
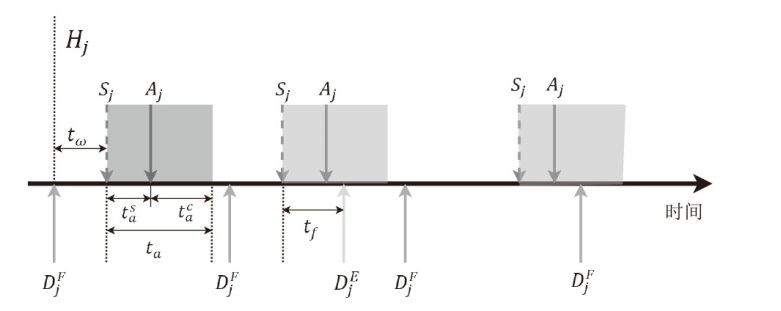
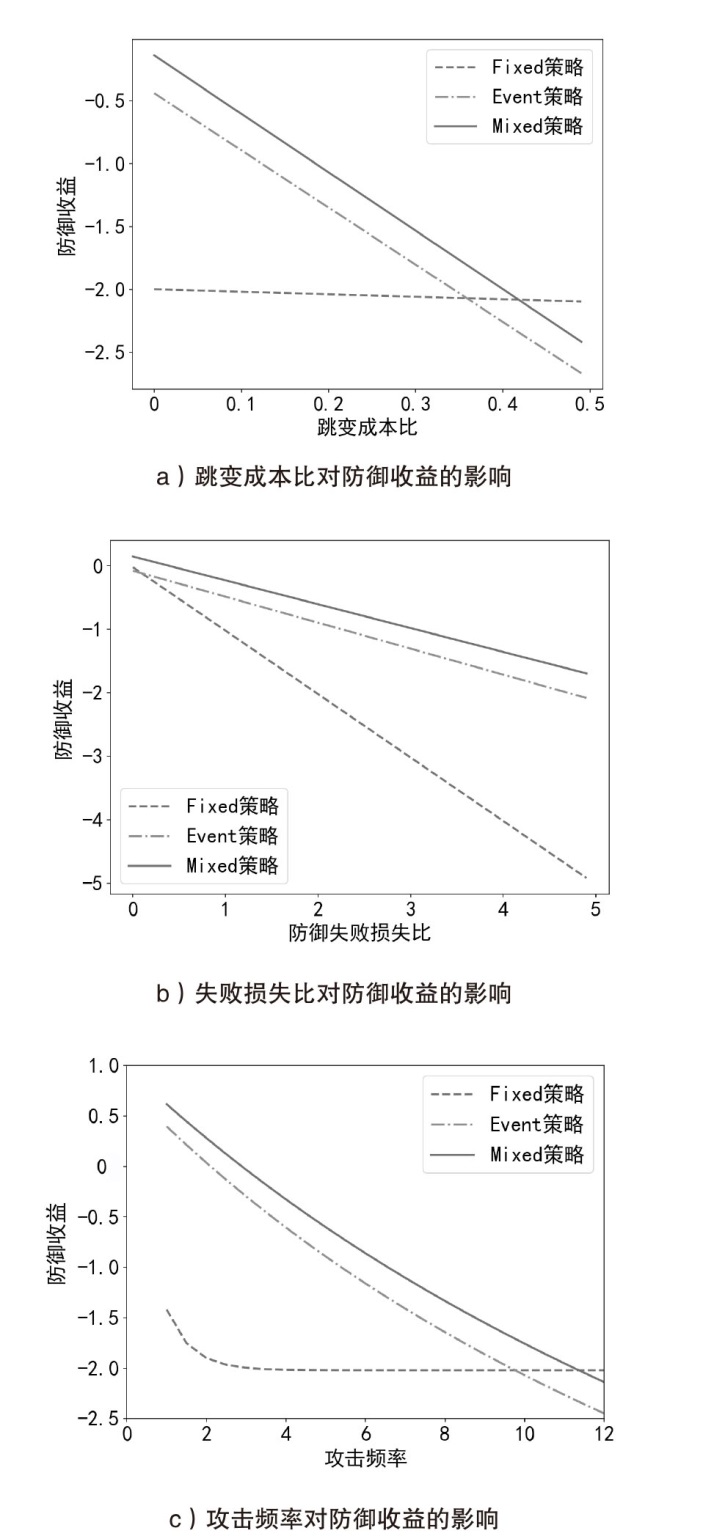
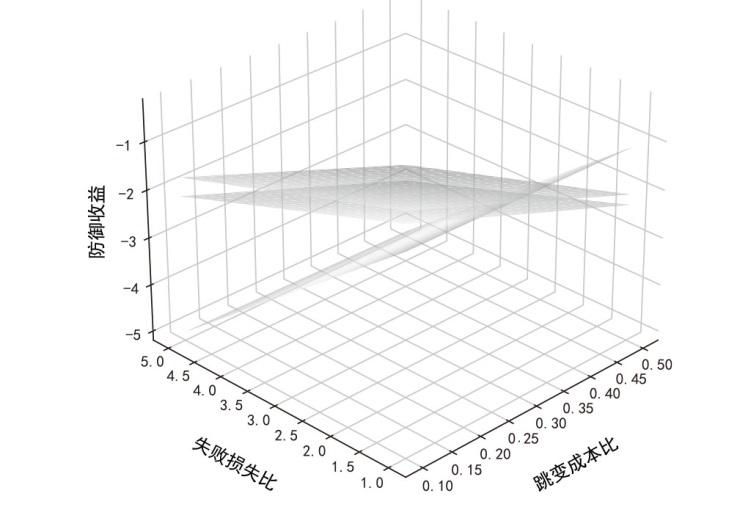
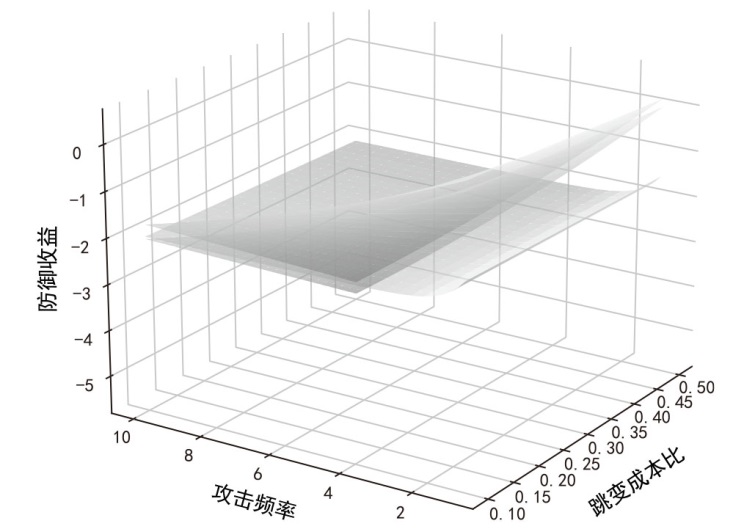
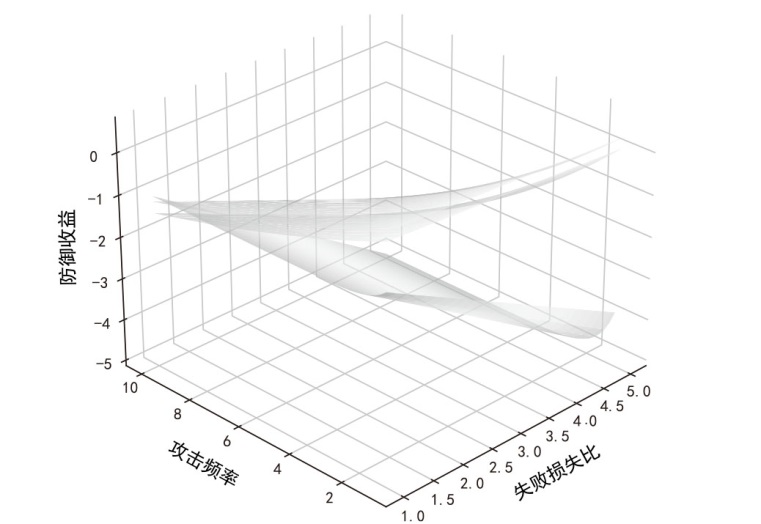
文章旨在探究移动目标防御中地址跳变系统的最优时间策略,针对网络攻防非对称性问题,提出基于博弈论的动态防御决策模型。研究围绕周期性、事件驱动和混合驱动3种地址跳变策略展开,量化其防御收益并比较策略选择效果。通过构建单阶段完全信息零和博弈模型,推导出各策略对应的防御成功概率、跳变次数与收益函数,并采用无因次化方法对跳变成本比、防御失败损失比、攻击频率等关键参数进行实验分析。实验结果表明,混合驱动策略在多数场景下防御收益较高,但在高跳变成本比或高防御失败损失比条件下,周期性策略更具优势。文章为移动目标防御时间策略的优化选择提供了理论依据,揭示了攻防参数耦合效应对策略决策的影响机制,提升了动态防御系统的自适应能力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张慎明, 梁金洁, 许新桥, 冯戈, 邹添华, 胡志林. 基于博弈论的地址跳变系统时间策略研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 69-78.
ZHANG Shenming, LIANG Jinjie, XU Xinqiao, FENG Ge, ZOU Tianhua, HU Zhilin. Research on Time Strategy of IP Hopping System Based on Game Theory[J]. Netinfo Security, 2026, 26(1): 69-78.
表1
参数及基准值
| 参数 | 符号 | 基准值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 防御成功收益 | 1 | 基准收益单位 | |
| 攻击时间 | 1 | 基准时间单位 | |
| 检测准确率 | 0.9 | Event策略的流量检测准确率 | |
| 误报率 | 0.05 | 单位时间误报触发跳变次数 | |
| Fixed策略跳变周期比 | 5 | Fixed策略中周期性跳变周期与攻击时间的比值 | |
| Mixed策略跳变周期比 | 10 | Mixed策略中周期性跳变周期与攻击时间的比值 | |
| 检测成本比 | 0.01 | 单位时间内检测流量消耗的资源与防御成功收益的比值 | |
| 风险损失比 | 0.2 | Event策略在单位时间内由于检测器不稳定造成的损失与防御成功收益的比值 | |
| 攻击频率 | 5 | 单位时间内攻击次数 |
| [1] | YANG Wentao. A Study on the Attacks to Networks[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2004. |
| 杨文涛. 网络攻击技术研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2004. | |
| [2] | TANG Hong, LUO Zhiqiang, SHEN Jun. Research and Application of Active Defense Technology for DDoS Attacks in Zombie Networks[J]. Telecommunications Technology, 2014(11): 76-80. |
| 唐宏, 罗志强, 沈军. 僵尸网络DDoS攻击主动防御技术研究与应用[J]. 电信技术, 2014(11): 76-80. | |
| [3] | GUO Xiangxin, LIN Jingqiang, JIA Shijie, et al. Security Analysis of Cryptographic Application Code Generated by Large Language Model[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(6): 917-925. |
| 郭祥鑫, 林璟锵, 贾世杰, 等. 针对大语言模型生成的密码应用代码安全性分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(6): 917-925. | |
| [4] | CAI Guilin, WANG Baosheng, XING Qianqian. Game Theoretic Analysis for the Mechanism of Moving Target Defense[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2017, 18(12): 2017-2034. |
| [5] |
NAVAS R E, CUPPENS F, BOULAHIA C N, et al. MTD,Where Art Thou? A Systematic Review of Moving Target Defense Techniques for IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(10): 7818-7832.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3040358 URL |
| [6] | CHEN Zhihao, WU Xinming, CAO Miao. Research on Active Defense of Deep Level Network Security under Attack and Defense Games[J]. Computer Simulation, 2024, 41(12): 482-486. |
| 陈志浩, 吴昕铭, 曹淼. 攻防博弈下深层次网络安全主动防御研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2024, 41(12): 482-486. | |
| [7] | CAI Guilin. Research on Several Key Issues of Mobile Target Defense Technology[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2016. |
| 蔡桂林. 移动目标防御技术若干关键问题研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2016. | |
| [8] | JUDY R L, FUCHS Z E, CASBEER D W. High-Value Target Escort and Defense Scenario with Differential Subgame Cost[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE 63rd Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). New York: IEEE, 2024: 16-29. |
| [9] | CARTER K M, RIORDAN J F, OKHRAVI H. A Game Theoretic Approach to Strategy Determination for Dynamic Platform Defenses[C]// ACM. The First ACM Workshop on Moving Target Defense. New York: ACM, 2014: 21-30. |
| [10] | LIU Xiaohu, ZHANG Hengwei, DONG Shuqin, et al. Network Defense Decision-Making Based on a Stochastic Game System and a Deep Recurrent Q-Network[EB/OL]. (2021-12-01)[2025-04-16]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102480. |
| [11] | GE Mengmeng, CHO J H, KIM D, et al. Proactive Defense for Internet-of-Things: Moving Target Defense with Cyberdeception[J]. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology, 2022, 22(1): 1-31. |
| [12] |
TAN Jinglei, JIN Hui, HU Hao, et al. WF-MTD: Evolutionary Decision Method for Moving Target Defense Based on Wright-Fisher Process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2023, 20(6): 4719-4732.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2022.3232537 URL |
| [13] |
ZHANG Tao, XU Changqiao, ZOU Ping, et al. How to Mitigate DDoS Intelligently in SD-IoV: A Moving Target Defense Approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(1): 1097-1106.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3190556 URL |
| [14] |
LAKSHMINARAYANA S, BELMEGA E V, POOR H V. Moving-Target Defense against Cyber-Physical Attacks in Power Grids via Game Theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12(6): 5244-5257.
doi: 10.1109/TSG.2021.3095083 URL |
| [15] | LEI Cheng, MA Duohe, ZHANG Hongqi. Optimal Strategy Selection for Moving Target Defense Based on Markov Game[J]. IEEE Access, 2017(5): 156-169. |
| [16] | QIU Yihui, CHEN Zhide, XU Li. Active Defense Model of Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Evolutionary Game Theory[C]// IEEE. 2010 6th International Conference on Wireless Communications Networking and Mobile Computing (WiCOM). New York: IEEE, 2010: 1-4. |
| [17] | LEITMANN G. Two-Person Zero-Sum Games[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 1974. |
| [18] |
GUPTA A, LANGBORT C, BASAR T. Dynamic Games with Asymmetric Information and Resource Constrained Players with Applications to Security of Cyberphysical Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2017, 4(1): 71-81.
doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2016.2584183 URL |
| [19] | ZHAI Lijing, VAMVOUDAKIS K G. A Data-Based Moving Target Defense Framework for Switching Zero-Sum Games[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA). New York: IEEE, 2021: 931-936. |
| [20] |
YU Jian, LI Qiang. Optimal Deployment in Moving Target Defense against Coordinated Cyber-Physical Attacks via Game Theory[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(11): 2484-2508.
doi: 10.3390/electronics12112484 URL |
| [1] | 耿致远, 许泽轩, 张恒巍. 基于随机博弈和DQN算法的云原生移动目标防御决策方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(6): 967-976. |
| [2] | 宋丽华, 张津威, 张少勇. 基于博弈论对手建模的物联网SSH自适应蜜罐策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 38-47. |
| [3] | 于克辰, 郭莉, 阴宏伟, 燕雪松. 面向数据中心场景的基于区块链与博弈论的高价值数据共享模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(6): 73-85. |
| [4] | 胡瑞钦, 谭晶磊, 彭心荷, 张红旗. 面向SDN数据层的双虚假IP地址动态跳变技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 76-85. |
| [5] | 任航, 程相国, 张睿, 夏辉. 基于议价贝叶斯博弈模型的防欺诈策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(4): 81-88. |
| [6] | 李朝阳, 谭晶磊, 胡瑞钦, 张红旗. 基于双重地址跳变的移动目标防御方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(2): 24-33. |
| [7] | 杨雪君, 陈宁江. 基于Swarm平台的理性密码协议建模与仿真[J]. 信息网络安全, 2014, 14(8): 34-39. |
| [8] | 郎为民;苏泽友. 无线认知传感器网络数据伪造攻击博弈研究[J]. , 2013, 13(9): 0-0. |
| [9] | 郎为民;张国峰. 无线认知传感器网络主用户模拟攻击博弈研究[J]. , 2013, 13(7): 0-0. |
| [10] | 顾巧云;孙玉龙;高丰. 基于博弈论的网络攻防对抗模型及应用研究[J]. , 2013, 13(1): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||