信息网络安全 ›› 2026, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 24-37.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2026.01.002
公共安全领域大语言模型的可信性研究综述:风险、对策与挑战
- 1.中国人民公安大学信息网络安全学院,北京 100038
2.公安部科技信息化局,北京 100741
3.公安部第三研究所,上海 200031
-
收稿日期:2025-10-10出版日期:2026-01-10发布日期:2026-02-13 -
通讯作者:金波jinbo@gass.cn -
作者简介:仝鑫(1995—),男,河南,博士研究生,CCF会员,主要研究方向为大语言模型安全|焦强(1981—),男,河北,硕士,主要研究方向为大数据和人工智能|王靖亚(1966—),女,北京,教授,硕士,主要研究方向为自然语言处理|袁得嵛(1986—),男,河北,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为信息内容安全与人工智能安全|金波(1970—),男,上海,研究员,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为行业大模型 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFB3107105);北京市教育委员会科研计划(KM202414019003);中国人民公安大学研究生科研创新项目(2025yjsky006)
A Survey on the Trustworthiness of Large Language Models in the Public Security Domain: Risks, Countermeasures, and Challenges
TONG Xin1, JIAO Qiang2, WANG Jingya1, YUAN Deyu1, JIN Bo3( )
)
- 1. School of Information and Cyber Security, People’s Public Security University of China, Beijing 100038, China
2. Bureau of Science and Technology Information, Ministry of Public Security of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing 100741, China
3. The Third Research Institute of the Ministry of Public Security of China, Shanghai 200031, China
-
Received:2025-10-10Online:2026-01-10Published:2026-02-13
摘要:
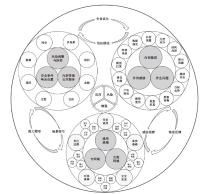
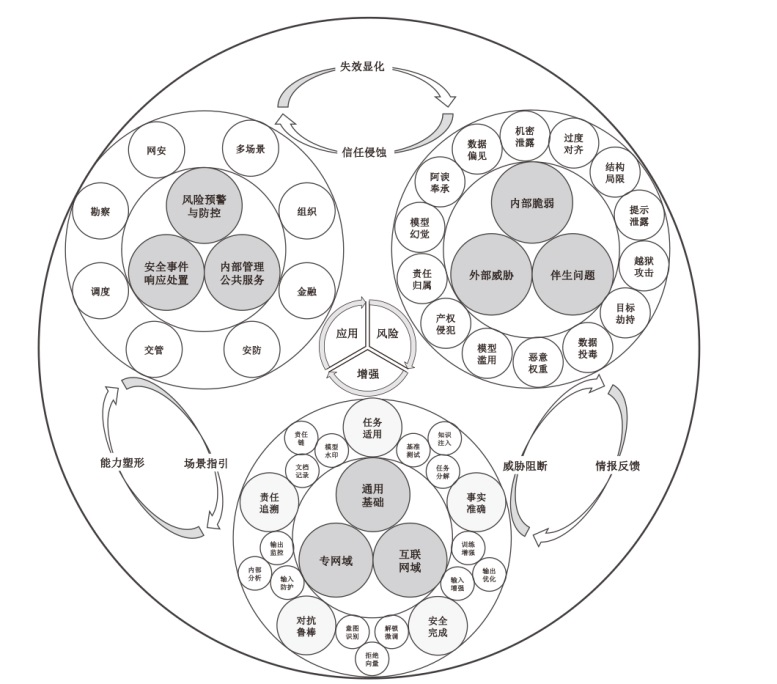
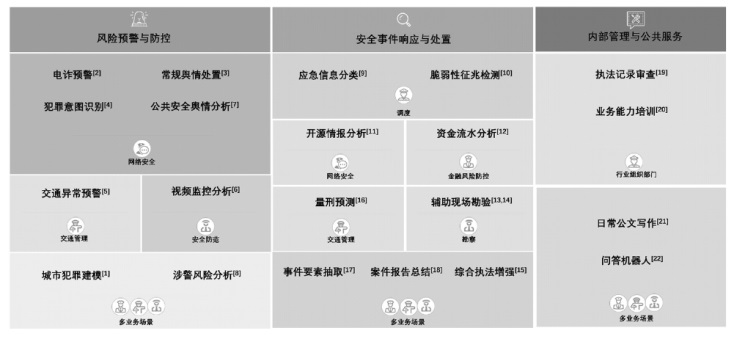
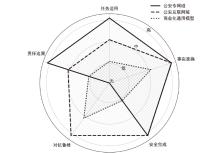
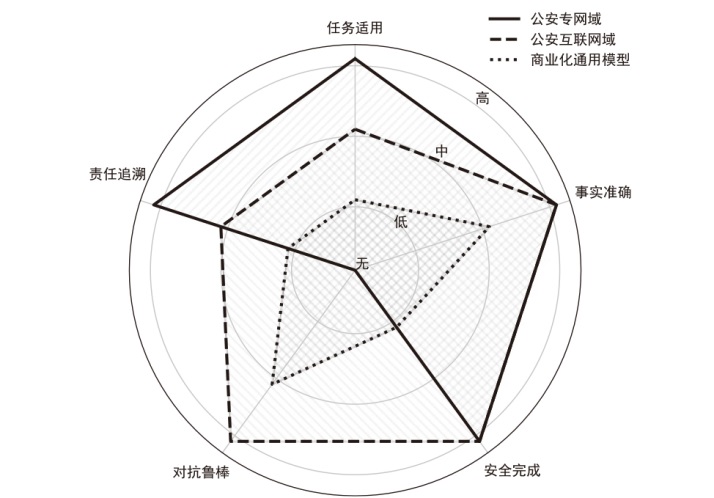
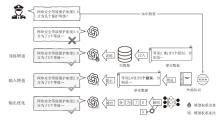
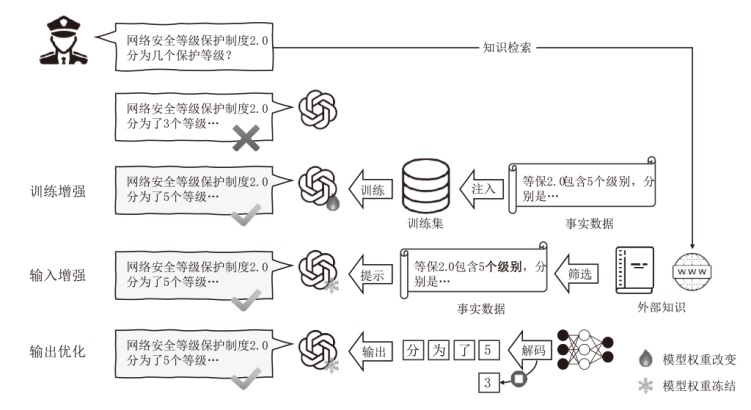
随着大语言模型(LLMs)的快速发展,其在公共安全领域的应用潜力不断凸显。然而,能力透明度不足、过度对齐导致可用性弱、幻觉生成及安全威胁等问题使其难以满足公共安全场景的高敏感性、高风险性和高精度需求。文章系统综述了公共安全领域LLMs的可信性问题:梳理其在风险预警、安全事件响应、内部管理与公共服务等任务中的应用现状,明确可信性定义并归纳出内部脆弱、外部威胁和伴生问题这3类风险;结合通用基础、专网域与互联网域的特点,提出任务适用、事实准确、安全完成、对抗鲁棒和责任追溯这5个可信维度,并以此为顺序综述了相应的增强策略与挑战,旨在推动LLMs在公共安全领域的可靠、安全与可控应用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
仝鑫, 焦强, 王靖亚, 袁得嵛, 金波. 公共安全领域大语言模型的可信性研究综述:风险、对策与挑战[J]. 信息网络安全, 2026, 26(1): 24-37.
TONG Xin, JIAO Qiang, WANG Jingya, YUAN Deyu, JIN Bo. A Survey on the Trustworthiness of Large Language Models in the Public Security Domain: Risks, Countermeasures, and Challenges[J]. Netinfo Security, 2026, 26(1): 24-37.
表2
公共安全领域应用LLMs潜在的外部威胁
| AT 编号 | 渠道 | 风险点 | 攻击向量 | 典型影响 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT-1 | 线上 交互 | 提示词 泄露 | 差分探针问句、翻译迭代 | 系统指令与过滤规则外泄,助攻后续攻击 |
| AT-2 | 线上 交互 | 越狱攻击 | 复杂提示拆词、编码、隐喻注入 | 输出暴恐、涉黄或内部规程,威胁内容 安全 |
| AT-3 | 线上 交互 | 目标劫持 | 上下文覆写、角色标签插入 | 将法律咨询重定向为其他非法目标 |
| AT-4 | 供应链 | 数据投毒 | 在回收的对话对或微调集插入后门样本 | 将触发词映射为非法输出,且随在线学习逐步放大 |
| AT-5 | 供应链 | 恶意 权重、LoRA | 发布带隐藏逻辑的微调权重或插件 | 内网加载后门模型,出现系统性偏向或泄密通道 |
| [1] | ZENG Qingbin, ZHAO Ruotong, MAO Jinzhu, et al. CrimeMind: Simulating Urban Crime with Multi-Modal LLM Agents[EB/OL]. [2025-07-19]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.05981. |
| [2] | LEE J, LIM P, HOOI B, et al. Multimodal Large Language Models for Phishing Webpage Detection and Identification[C]// IEEE.2024 APWG Symposium on Electronic Crime Research (eCrime). New York: IEEE, 2024: 1-13. |
| [3] | LIU Min, ZHANG Luxiang, PING Weiying, et al. Research on Multi-Stage Online Public Opinion-Driven Group Consensus Decision-Making Method Based on Large Language Model[J]. Chinese Journal of Management, 2025, 22(4): 750-759. |
| 刘敏, 张露祥, 平卫英, 等. 基于大语言模型的多阶段网络舆情驱动群体共识决策方法研究[J]. 管理学报, 2025, 22(4): 750-759. | |
| [4] | BOKOLO B G, ONYEHANERE P, OGEGBENE-ISE E, et al. Leveraging Machine Learning for Crime Intent Detection in Social Media Posts[C]// Springer Nature. International Conference on AI-Generated Content. Singapore: Springer Nature, 2023: 224-236. |
| [5] | LI Yanying, WANG Xinyu, WANG Xiao, et al. Traffic Anomaly Event Detection and Auxiliary Decision-Making Based on Large Language Models[J]. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology, 2024, 6(3): 347-355. |
| 李炎英, 王新宇, 王晓, 等. 基于大语言模型的交通异常事件检测与辅助决策[J]. 智能科学与技术学报, 2024, 6(3): 347-355. | |
| [6] | CHEN Haoran, YI Dong, CAO Moyan, et al. A Benchmark for Crime Surveillance Video Analysis with Large Models[EB/OL]. [2025-07-03]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.09325. |
| [7] | CROWL L, DUTTA S, KHUDABUKHSH A R, et al. Measuring Criticism of the Police in the Local News Media Using Large Language Models[EB/OL]. [2025-09-20]. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2418821122. |
| [8] | HALFORD E, WEBSTER A. Using ChatGPT to Evaluate Police Threats, Risk and Harm[EB/OL]. [2025-09-23]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlcj.2024.100686. |
| [9] | XING Xintao, CHEN Peng. Entity Extraction of Key Elements in 110 Police Reports Based on Large Language Models[EB/OL]. [2025-08-21]. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177819. |
| [10] | RELINS S, BIRKS D, LLOYD C. Using Instruction-Tuned Large Language Models to Identify Indicators of Vulnerability in Police Incident Narratives[J]. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 2025, 41(4): 1-38. |
| [11] | SCHWARTZ Y, BEN-SHIMOL L, MIMRAN D, et al. LLMcloudhunter: Harnessing LLMs for Automated Extraction of Detection Rules from Cloud-Based CTI[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2025. New York: ACM, 2025: 1922-1941. |
| [12] | LEGG P, RYDER N, BOURTON S, et al. Advancements in Cyber Crime Investigations and Modern Data Analytics[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2024. |
| [13] | SHAHID A R, HASAN S M, KANKANAMGE M W, et al. WatchOverGPT: A Framework for Real-Time Crime Detection and Response Using Wearable Camera and Large Language Model[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE 48th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC). New York: IEEE, 2024: 2189-2194. |
| [14] |
FARBER S. AI as a Decision Support Tool in Forensic Image Analysis: A Pilot Study on Integrating Large Language Models into Crime Scene Investigation Workflows[J]. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 2025, 70(3): 932-943.
doi: 10.1111/jfo.v70.3 URL |
| [15] | KIM H, KIM D, LEE J, et al. LAPIS: Language Model-Augmented Police Investigation System[C]// ACM. The 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. New York: ACM, 2024: 4637-4644. |
| [16] | MIN H, NOH B. TRACS-LLM: LLM-Based Traffic Accident Criminal Sentencing Prediction Focusing on Imprisonment, Probation, and Fines[EB/OL]. [2025-08-26]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10506-025-09472-8. |
| [17] | PEI Bingsen, LI Xin, JIANG Zhangtao, et al. Research on Public Security Professional Small Sample Knowledge Extraction Method Based on Large Language Model[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2024, 18(10): 2630-2642. |
|
裴炳森, 李欣, 蒋章涛, 等. 基于大语言模型的公安专业小样本知识抽取方法研究[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2024, 18(10): 2630-2642.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2403039 |
|
| [18] | ADAMS I T. Large Language Models and Artificial Intelligence for Police Report Writing[EB/OL]. [2025-09-06]. https://www.crimrxiv.com/pub/c5lj2rmy/release/1. |
| [19] | SRBINOVSKA A, SENTHIL V, et al. Towards AI-Driven Policing: Interdisciplinary Knowledge Discovery from Police Body-Worn Camera Footage[EB/OL]. [2025-08-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.20007. |
| [20] | VIOLAKIS P. Leveraging Large Language Models for Enhanced Simulation-Based Learning in Police and Law Enforcement[EB/OL]. [2025-09-12]. https://doi.org/10.1093/police/paaf012. |
| [21] | LIANG Ruiwei, CAI Zijie, FANG Hui, et al. Instruction Tuning of Large Language Models for Official Document Generation[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2025, 39(5): 164-176. |
| 梁瑞威, 蔡子杰, 方荟, 等. 基于大模型指令微调的公文生成方法[J]. 中文信息学报, 2025, 39(5): 164-176. | |
| [22] |
WANG Yun, HU Min, TA Na, et al. Large Language Models and Their Application in Government Affairs[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2024, 64(4): 649-658.
doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2023.26.042 |
|
王昀, 胡珉, 塔娜, 等. 大语言模型及其在政务领域的应用[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 64(4): 649-658.
doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2023.26.042 |
|
| [23] | TENG Jie, HE Huanglan, HU Guangwei, et al. A Fine-Grained Sentiment Recognition Method for Online Government-Public Interaction Texts Based on Large Language Models[J]. Journal of Modern Information, 2025, 45(9): 58-70, 107. |
| 滕婕, 贺荒兰, 胡广伟, 等. 基于大语言模型的网络问政文本细粒度情感识别方法[J]. 现代情报, 2025, 45(9): 58-70, 107. | |
| [24] | ISO/IEC TS 5723: 2022. Trustworthiness—Vocabulary[EB/OL]. [2025-08-26]. https://www.iso.org/standard/81608.html. |
| [25] | European Commission. Ethics Guidelines For Trustworthy AI[EB/OL]. [2025-07-29]. https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/ethics-guidelines-trustworthy-ai. |
| [26] | NIST. Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework (AI RMF 1.0)[EB/OL]. [2025-08-23]. https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.AI.100-1. |
| [27] | Cyberspace Administration of China. Interim Measures for the Administration of Generative Artificial Intelligence Services. [EB/OL]. [2025-07-06]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202311/content_6917778.htm. |
| 国家互联网信息办公室. 生成式人工智能服务管理暂行办法[EB/OL]. [2025-07-06]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202311/content_6917778.htm. | |
| [28] | HUANG Lei, YU Weijiang, MA Weitao, et al. A Survey on Hallucination in Large Language Models: Principles, Taxonomy, Challenges, and Open Questions[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2025, 43(2): 1-55. |
| [29] | LI Tianle, ZHANG Ge, DO Q D, et al. Long-Context LLMs Struggle with Long In-Context Learning[EB/OL]. [2025-09-29]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.02060. |
| [30] | RANALDI L, PUCCI G. When Large Language Models Contradict Humans? Large Language Models’ Sycophantic Behaviour[EB/OL]. [2025-09-03]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.09410. |
| [31] | BYUN J, LIN Xiaofeng, WARD J, et al. Risk In Context: Benchmarking Privacy Leakage of Foundation Models in Synthetic Tabular Data Generation[EB/OL]. [2025-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.17066. |
| [32] | NAVIGLI R, CONIA S, ROSS B. Biases in Large Language Models: Origins, Inventory, and Discussion[J]. ACM Journal of Data and Information Quality, 2023, 15(2): 1-21. |
| [33] | OUYANG Long, WU J, JIANG Xu, et al. Training Language Models to Follow Instructions with Human Feedback[C]// NeurIPS Foundation. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates Inc., 2022: 27730-27744. |
| [34] | LIN Yong, LIN Hangyu, XIONG Wei, et al. Mitigating the Alignment Tax of RLHF[C]// ACL. The 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 580-606. |
| [35] |
TONG Xin, JIN Bo, LIN Zhi, et al. CPSDbench: A Large Language Model Evaluation Benchmark and Baseline for Chinese Public Security Domain[J]. International Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 2025, 20(4): 3205-3234.
doi: 10.1007/s41060-024-00652-4 |
| [36] | PEREZ F, RIBEIRO I. Ignore Previous Prompt: Attack Techniques for Language Models[EB/OL]. [2025-09-03]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09527. |
| [37] | CARLINI N, TRAMER F, WALLACE E, et al. Extracting Training Data from Large Language Models[C]// USENIX. The 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 21). Berkeley: USENIX, 2021: 2633-2650. |
| [38] | WAN A, WALLACE E, SHEN Sheng, et al. Poisoning Language Models during Instruction Tuning[C]// International Machine Learning Society. International Conference on Machine Learning. Cambridge: JMLR, 2023: 35413-35425. |
| [39] | KURITA K, MICHEL P, NEUBIG G. Weight Poisoning Attacks on Pretrained Models[C]// ACL. The 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2020: 2793-2806. |
| [40] | LIU Hongyi, ZHONG Shaocheng, SUN Xintong, et al. LoRATK: LoRA Once, Backdoor Everywhere in the Share-and-Play Ecosystem[EB/OL]. [2025-09-03]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.00108. |
| [41] | HU Beizhe, SHENG Qiang, CAO Juan, et al. LLM-Generated Fake News Induces Truth Decay in News Ecosystem: A Case Study on Neural News Recommendation[C]// ACM.The 48th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. New York: ACM, 2025: 435-445. |
| [42] | OECD. AI Principles[EB/OL]. [2025-09-03]. https://www.oecd.org/en/topics/sub-issues/ai-principles.html. |
| [43] | EUR-Lex. REGULATION (EU) 2024/1689 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL[EB/OL]. [2025-08-30]. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=OJ:L_202401689. |
| [44] | ISO. ISO/IEC 42001: 2023 Information Technology — Artificial Intelligence — Management System[EB/OL]. [2025-09-09]. https://www.iso.org/standard/42001. |
| [45] | DENG Chunyuan, ZHAO Yilun, TANG Xiangru, et al. Benchmark Probing: Investigating Data Leakage In Large Language Models[ EB/OL]. [2025-09-13]. https://openreview.net/pdf?id=a34bgvner1. |
| [46] | TONG Xin, JIN Bo, WANG Jingya, et al. IDE: A Multi-Agent-Driven Iterative Framework for Dynamic Evaluation of LLMs[C]// IEEE. 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). New York: IEEE, 2025: 1-5. |
| [47] | HU E J, WALLIS P, ALLEN-ZHU Z, et al. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models[EB/OL]. [2025-09-25]. https://openreview.net/forum?id=nZeVKeeFYf9. |
| [48] | WANG Mingyang, STOLL A, LANGE L, et al. Bring Your Own Knowledge: A Survey of Methods for LLM Knowledge Expansion[EB/OL]. [2025-09-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.12598. |
| [49] | LI Xinyi, WANG Sai, ZENG Siqi, et al. A Survey on LLM-Based Multi-Agent Systems: Workflow, Infrastructure, and Challenges[EB/OL]. [2025-09-29]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44336-024-00009-2. |
| [50] | TONG Xin, XIA Tian, YANG Menghui, et al. Research on Factuality Issues in Large Language Models: Evaluation, Enhancement, and Prospects[J]. Information Studies: Theory & Application, 2025, 48(7): 81-93. |
|
仝鑫, 夏天, 杨孟辉, 等. 大语言模型的事实性问题研究:评估、增强和展望[J]. 情报理论与实践, 2025, 48(7): 81-93.
doi: 10.16353/j.cnki.1000-7490.2025.07.010 |
|
| [51] | LI Yuanzhi, BUBECK S, ELDAN R, et al. Textbooks are All You Need ii:Phi-1.5 Technical Report[EB/OL]. [2025-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.05463. |
| [52] | BORGEAUD S, MENSCH A, HOFFMANN J, et al. Improving Language Models by Retrieving from Trillions of Tokens[C]// International Machine Learning Society. International Conference on Machine Learning. Cambridge: JMLR, 2022: 2206-2240. |
| [53] | HU Minda, HE Bowei, WANG Yufei, et al. Mitigating Large Language Model Hallucination with Faithful Finetuning[EB/OL]. [2025-09-02]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.11267. |
| [54] | SUN Zhiqing, SHEN Sheng, CAO Shengcao, et al. Aligning Large Multimodal Models with Factually Augmented RLHF[C]// ACL. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics ACL 2024. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 13088-13110. |
| [55] | WEI J, HUANG Da, LU Yifeng, et al. Simple Synthetic Data Reduces Sycophancy in Large Language Models[EB/OL]. [2025-08-16]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.03958. |
| [56] | PAPADATOS H, FREEDMAN R. Linear Probe Penalties Reduce LLM Sycophancy[EB/OL]. [2025-09-06]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.00967. |
| [57] | LIU Xiao, LAI Hanyu, YU Hao, et al. WebGLM: Towards an Efficient Web-Enhanced Question Answering System with Human Preferences[C]// ACM.The 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2023: 4549-4560. |
| [58] | LI L, CHEN Zhenhao, CHEN Guangyi, et al. Confidence Matters: Revisiting Intrinsic Self-Correction Capabilities of Large Language Models[EB/OL]. [2025-08-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.12563. |
| [59] | DASH S, REYMOND A, SPIRO E S, et al. Persona-Assigned Large Language Models Exhibit Human-Like Motivated Reasoning[EB/OL]. [2025-09-07]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.009672506. |
| [60] | STRONG J, MEN Qianhui, NOBLE A. Towards Human-AI Collaboration in Healthcare: Guided Deferral Systems with Large Language Models[C]// International Machine Learning Society. ICML 2024 Workshop on LLMs and Cognition. Cambridge: JMLR, 2024. |
| [61] | DAS S, JIN Lifeng, SONG Linfeng, et al. Entropy Guided Extrapolative Decoding to Improve Factuality in Large Language Models[C]// ACL.The 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2025: 6589-6600. |
| [62] | KRISHNA K, RAMPRASAD S, GUPTA P, et al. GenAudit: Fixing Factual Errors in Language Model Outputs with Evidence[EB/OL]. [2025-09-19]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.12566. |
| [63] | ARDITI A, OBESO O, SYED A, et al. Refusal in Language Models is Mediated by a Single Direction[C]// NeurIPS Foundation. The 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates Inc., 2024: 136037-136083. |
| [64] | ONG I, ALMAHAIRI A, WU V, et al. RouteLLM: Learning to Route LLMs from Preference Data[EB/OL]. [2025-09-23]. https://openreview.net/forum?id=8sSqNntaMr. |
| [65] | RAHMAN M A, SHAHRIAR H, WU Fan, et al. Applying Pre-Trained Multilingual BERT in Embeddings for Improved Malicious Prompt Injection Attacks Detection[C]// IEEE. 2024 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, and Internet of Things (AIBThings). New York: IEEE, 2024: 1-7. |
| [66] | INAN H, UPASANI K, CHI J, et al. Llama Guard: LLM-Based Input-Output Safeguard for Human-AI Conversations[EB/OL]. [2025-08-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.06674. |
| [67] | HUNG K H, KO C Y, RAWAT A, et al. Attention Tracker: Detecting Prompt Injection Attacks in LLMs[EB/OL]. [2025-01-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.00348. |
| [68] | XUAN Zitao, MAO Xiaofeng, CHEN Da, et al. ShieldHead: Decoding-Time Safeguard for Large Language Models[C]// ACL.Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics ACL 2025. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2025: 18129-18143. |
| [69] | TONG Xin, LIN Zhi, YUAN Lining, et al. An Agent Driven Framework for Enhancing Risk Instruction Mining in Large Language Models[EB/OL]. [2025-08-08]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/10.1478.G2.20250704.1005.002. |
| 仝鑫, 林智, 袁立宁, 等. 智能体驱动的大语言模型风险指令挖掘增强方法[EB/OL]. [2025-08-08]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/10.1478.G2.20250704.1005.002. | |
| [70] | RENAN S, AMAL G, et al. PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking AI Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows[EB/OL]. [2025-08-06]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.02866. |
| [71] | PAN Leyi, LIU Aiwei, HE Zhiwen, et al. MarkLLM: An Open-Source Toolkit for LLM Watermarking[C]// ACL. The 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing:System Demonstrations. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 61-71. |
| [1] | 胡雨翠, 高浩天, 张杰, 于航, 杨斌, 范雪俭. 车联网安全自动化漏洞利用方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1348-1356. |
| [2] | 刘会, 朱正道, 王淞鹤, 武永成, 黄林荃. 基于深度语义挖掘的大语言模型越狱检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1377-1384. |
| [3] | 王磊, 陈炯峄, 王剑, 冯袁. 基于污点分析与文本语义的固件程序交互关系智能逆向分析方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1385-1396. |
| [4] | 张燕怡, 阮树骅, 郑涛. REST API设计安全性检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(8): 1313-1325. |
| [5] | 陈平, 骆明宇. 云边端内核竞态漏洞大模型分析方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1007-1020. |
| [6] | 酆薇, 肖文名, 田征, 梁中军, 姜滨. 基于大语言模型的气象数据语义智能识别算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1163-1171. |
| [7] | 张学旺, 卢荟, 谢昊飞. 基于节点中心性和大模型的漏洞检测数据增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 550-563. |
| [8] | 顾欢欢, 李千目, 刘臻, 王方圆, 姜宇. 基于虚假演示的隐藏后门提示攻击方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 619-629. |
| [9] | 解梦飞, 傅建明, 姚人懿. 基于LLM的多媒体原生库模糊测试研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 403-414. |
| [10] | 秦中元, 王田田, 刘伟强, 张群芳. 大语言模型水印技术研究进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 177-193. |
| [11] | 杨立群, 李镇, 韦超仁, 闫治敏, 仇勇鑫. 大语言模型引导的协议模糊测试技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(12): 1847-1862. |
| [12] | 孟辉, 毛琳琳, 彭聚智. 大语言模型驱动的无害化处理识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(12): 1990-1998. |
| [13] | 胡斌, 黑一鸣, 吴铁军, 郑开发, 刘文忠. 大模型安全检测评估技术综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1477-1492. |
| [14] | 胡隆辉, 宋虹, 王伟平, 易佳, 张智雄. 大语言模型在安全托管服务误报处理中的应用研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1570-1578. |
| [15] | 焦诗琴, 张贵杨, 李国旗. 一种聚焦于提示的大语言模型隐私评估和混淆方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1396-1408. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||