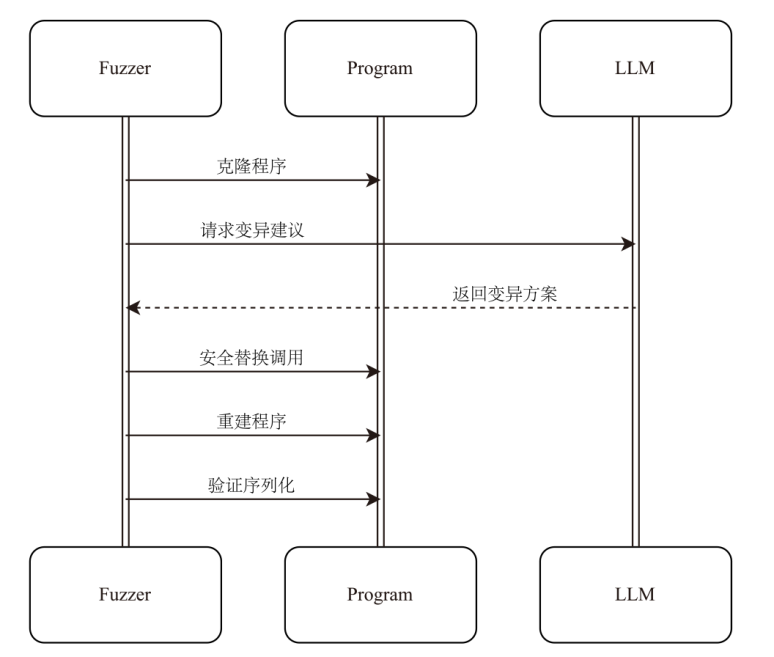
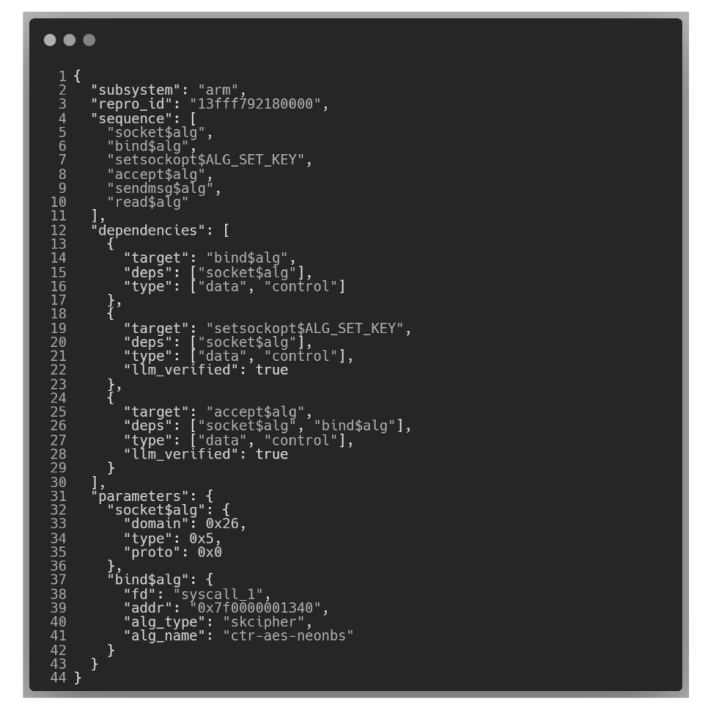
| [1] |
UPADHYAY A, LAXMI V, NAVAL S. Navigating the Concurrency Landscape: A Survey of Race Condition Vulnerability Detectors[EB/OL]. (2023-12-22) [2025-04-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.14479.
|
| [2] |
DRYSDALE D. Coverage-Guided Kernel Fuzzing with Syzkaller[EB/OL]. [2025-04-30]. https://lwn.net/Articles/677764/.
|
| [3] |
SUN Hao, SHEN Yuheng, LIU Jianzhong, et al. KSG: Augmenting Kernel Fuzzing with System Call Specification Generation[C]// USENIX. 2022 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 22). Berkeley: USENIX, 2022: 351-366.
|
| [4] |
CHEN M, TWOREK J, JUN H, et al. Evaluating Large Language Models Trained on Code[EB/OL]. (2021-07-07) [2025-04-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.03374.
|
| [5] |
BROWN T, MANN B, RYDER N, et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 1877-1901.
|
| [6] |
YAO Dongyu, ZHANG Jianshu, HARRIS I G, et al. FuzzLLM: A Novel and Universal Fuzzing Framework for Proactively Discovering Jailbreak Vulnerabilities in Large Language Models[C]// IEEE. ICASSP 2024-2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). New York: IEEE, 2024: 4485-4489.
|
| [7] |
YANG Chenyuan, ZHAO Zijie, ZHANG Lingming. KernelGPT: Enhanced Kernel Fuzzing via Large Language Models[EB/OL]. (2024-01-02) [2025-04-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.00563.
|
| [8] |
DENG Yinlin, XIA C S, PENG Haoran, et al. Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Fuzzers: Fuzzing Deep-Learning Libraries via Large Language Models[C]// ACM. The 32nd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis. New York: ACM, 2023: 423-435.
|
| [9] |
XIA C S, PALTENGHI M, LE T J, et al. Fuzz4all: Universal Fuzzing with Large Language Models[C]// ACM. The 46th International Conference on Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2024: 1-13.
|
| [10] |
ZHANG Cen, ZHENG Yaowen, BAI Mingqiang, et al. How Effective are They? Exploring Large Language Model Based Fuzz Driver Generation[C]// ACM. The 33rd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis. New York: ACM, 2024: 1223-1235.
|
| [11] |
ENGLER D, ASHCRAFT K. RacerX: Effective, Static Detection of Race Conditions and Deadlocks[J]. ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review, 2003, 37(5): 237-252.
|
| [12] |
MANÈS V J M, HAN H S, HAN C, et al. The Art, Science, and Engineering of Fuzzing: A Survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2019, 47(11): 2312-2331.
|
| [13] |
LIANG Hongliang, PEI Xiaoxiao, JIA Xiaodong, et al. Fuzzing: State of the Art[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2018, 67(3): 1199-1218.
|
| [14] |
SCHUMILO S, ASCHERMANN C, GAWLIK R, et al. kAFL: Hardware-Assisted Feedback Fuzzing for OS Kernels[C]// USENIX. The 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17). Berkeley: USENIX, 2017: 167-182.
|
| [15] |
JEONG D R, KIM K, SHIVAKUMAR B, et al. Razzer: Finding Kernel Race Bugs through Fuzzing[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2019: 754-768.
|
| [16] |
XU Meng, KASHYAP S, ZHAO Hanqing, et al. Krace: Data Race Fuzzing for Kernel File Systems[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1643-1660.
|
| [17] |
PAILOOR S, ADAY A, JANA S. MoonShine: Optimizing OS Fuzzer Seed Selection with Trace Distillation[C]// USENIX. 27th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 18). Berkeley: USENIX, 2018: 729-743.
|
| [18] |
ODENA A, OLSSON C, ANDERSEN D, et al. Tensorfuzz: Debugging Neural Networks with Coverage-Guided Fuzzing[C]// PMLR. International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: PMLR, 2019: 4901-4911.
|