信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1570-1578.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.008
大语言模型在安全托管服务误报处理中的应用研究
- 1.中南大学计算机学院,长沙 410083
2.深信服科技股份有限公司,深圳 518052
-
收稿日期:2025-03-03出版日期:2025-10-10发布日期:2025-11-07 -
通讯作者:宋虹 E-mail:songhong@csu.edu.cn -
作者简介:胡隆辉(2001—),男,湖南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络安全、大语言模型|宋虹(1975—),女,江西,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为操作系统安全、信息安全|王伟平(1969—),女,江苏,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为网络安全态势感知、互联网应用安全|易佳(1992—),男,湖南,硕士,主要研究方向为大语言模型、AI智能体|张智雄(1993—),男,湖南,硕士,主要研究方向为大语言模型、网络安全 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFB3106903)
Research on the Application of Large Language Model in False Positive Handling for Managed Security Services
HU Longhui1, SONG Hong1( ), WANG Weiping1, YI Jia2, ZHANG Zhixiong2
), WANG Weiping1, YI Jia2, ZHANG Zhixiong2
- 1. School of Computer Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
2. Sangfor Technologies Co., Ltd., Shenzhen 518052, China
-
Received:2025-03-03Online:2025-10-10Published:2025-11-07 -
Contact:SONG Hong E-mail:songhong@csu.edu.cn
摘要:
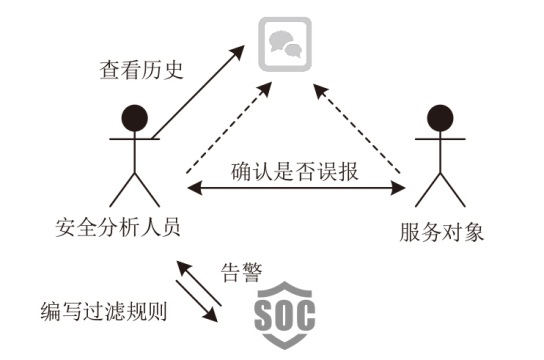
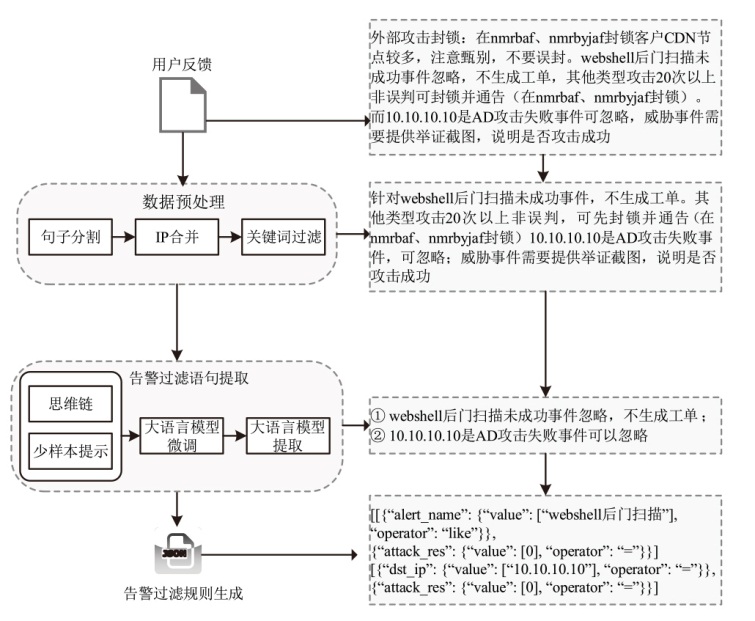
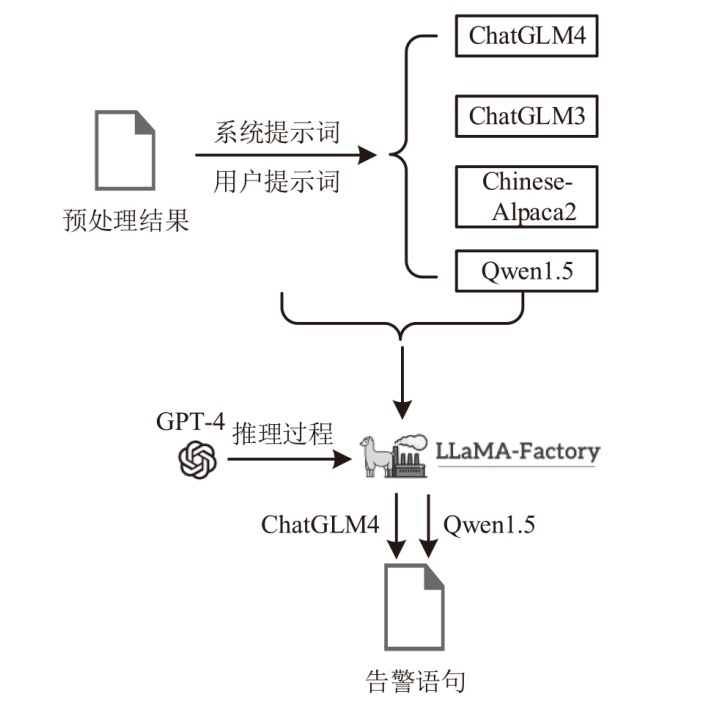
当安全托管服务由第三方提供时,由于企业用户环境的差异,部署统一的安全检测规则容易导致误报,通常需要依据用户反馈人工调整安全规则或对告警进行过滤。针对该应用场景,文章提出一种自动化处理用户反馈语句的方法,从用户反馈语句中自动提取与告警过滤相关的语句,并将其转化为安全设备的告警过滤规则。该方法基于大语言模型,结合思维链和少样本提示两种提示工程技术,从用户反馈中提取告警过滤语句。为进一步提升提取效果,该方法使用GPT-4生成的安全语料对表现最优的ChatGLM4和Qwen1.5大语言模型进行指令微调。实验结果表明,该方法在告警过滤相关语句的提取任务中,Rouge-L指标达92.208%,可有效减少人工审核用户反馈的工作量。
中图分类号:
引用本文
胡隆辉, 宋虹, 王伟平, 易佳, 张智雄. 大语言模型在安全托管服务误报处理中的应用研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1570-1578.
HU Longhui, SONG Hong, WANG Weiping, YI Jia, ZHANG Zhixiong. Research on the Application of Large Language Model in False Positive Handling for Managed Security Services[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1570-1578.
表2
大语言模型微调参数
| 参数名 | 参数值 | 参数名 | 参数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| preprocessing_num_workers | 16 | learning_rate | 5×10-5 |
| lr_scheduler_type | cosine | cutoff_len | 2048 |
| finetuning_type | LoRA | save_steps | 100 |
| per_device_train_batch_size | 2 | max_samples | 1×105 |
| gradient_accumulation_steps | 8 | fp16 | True |
| max_grad_norm | 1.0 | logging_steps | 5 |
| num_train_epochs | 3.0 | lora_rank | 8 |
| optim | adamw_torch | lora_alpha | 16 |
表5
提示工程消融实验结果
| 大语言模型 | 提示工程技术 | Rouge-L |
|---|---|---|
| ChatGLM4 | CoT + Few Shot | 86.322% |
| CoT | 80.415% | |
| Few Shot | 84.243% | |
| Zero Shot | 79.558% | |
| ChatGLM3 | CoT + Few Shot | 79.088% |
| CoT | 51.188% | |
| Few Shot | 83.725% | |
| Zero Shot | 58.590% | |
| Chinese-Alpaca2 | CoT + Few Shot | 66.785% |
| CoT | 54.743% | |
| Few Shot | 69.468% | |
| Zero Shot | 21.675% | |
| Qwen1.5 | CoT + Few Shot | 85.664% |
| CoT | 80.099% | |
| Few Shot | 81.235% | |
| Zero Shot | 80.495% |
| [1] | KOKULU F B, SONEJI A, BAO T, et al. Matched and Mismatched SOCs: A Qualitative Study on Security Operations Center Issues[C]// ACM. The 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 1955-1970. |
| [2] | HASSAN W U, NOUREDDINE M A, DATTA P, et al. OmegaLog: High-Fidelity Attack Investigation via Transparent Multi-Layer Log Analysis[EB/OL]. (2020-02-23)[2025-03-01]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/ndss-paper/omegalog-high-fidelity-attack-investigation-via-transparent-multi-layer-log-analysis/. |
| [3] | YU Le, MA Shiqing, ZHANG Zhuo, et al. ALchemist: Fusing Application and Audit Logs for Precise Attack Provenance Without Instrumentation[EB/OL]. (2021-02-21)[2025-03-01]. https://dx.doi.org/10.14722/ndss.2021.24445. |
| [4] |
ZHONG Chen, LIN Tao, LIU Peng, et al. A Cyber Security Data Triage Operation Retrieval System[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 76: 12-31.
doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2018.02.011 URL |
| [5] | HASSAN W U, GUO Shengjian, LI Ding, et al. NoDoze: Combatting Threat Alert Fatigue with Automated Provenance Triage[EB/OL]. (2019-02-22)[2025-03-01]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348915407_NoDoze_Combatting_Threat_Alert_Fatigue_with_Automated_Provenance_Triage. |
| [6] |
DAS S, SAHA S, PRIYOTI A T, et al. Network Intrusion Detection and Comparative Analysis Using Ensemble Machine Learning and Feature Selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2022, 19(4): 4821-4833.
doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2021.3138457 URL |
| [7] |
ATEFINIA R, AHMADI M. Network Intrusion Detection Using Multi-Architectural Modular Deep Neural Network[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2021, 77(4): 3571-3593.
doi: 10.1007/s11227-020-03410-y |
| [8] | ZHANG Changlin, TONG Xin, TONG Hui, et al. A Survey of Large Language Models in the Domain of Cybersecurity[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(5): 778-793. |
| 张长琳, 仝鑫, 佟晖, 等. 面向网络安全领域的大语言模型技术综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5):778-793. | |
| [9] | CUI Yiming, YANG Ziqing, YAO Xin. Efficient and Effective Text Encoding for Chinese Llama and Alpaca[EB/OL]. (2024-02-23)[2025-03-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.08177. |
| [10] | ZENG Aohan, XU Bin, WANG Bowen, et al. ChatGLM: A Family of Large Language Models from GLM-130b to GLM-4 All Tools[EB/OL]. (2024-07-30)[2025-03-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.12793. |
| [11] | BAI Jinze, BAI Shuai, CHU Yunfei, et al. Qwen Technical Report[EB/OL]. (2023-09-28)[2025-03-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2309.16609. |
| [12] | BROWN T, MANN B, RYDER N, et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners[J]. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020(33): 1877-1901. |
| [13] | WEI J, WANG Xuezhi, SCHUURMANS D, et al. Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models[J]. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2022(35): 24824-24837. |
| [14] | LIN C Y. ROUGE: A Package for Automatic Evaluation of Summaries[C]// ACL. 2004 Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2004: 74-81. |
| [15] | ACHIAM J, ADLER S, AGARWAL S, et al. GPT-4 Technical Report[EB/OL]. (2023-03-15)[2025-03-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.08774. |
| [16] | ZHENG Yaowei, ZHANG Richong, ZHANG Junhao, et al. LlamaFactory: Unified Efficient Fine-Tuning of 100+ Language Models[EB/OL]. (2024-06-27)[2025-03-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.13372. |
| [17] | LYU Kai, YANG Yuqing, LIU Tengxiao, et al. Full Parameter Fine-Tuning for Large Language Models with Limited Resources[C]// ACL. The 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 8187-8198. |
| [18] |
ZHANG Qintong, WANG Yuchao, WANG Hexi, et al. Comprehensive Review of Large Language Model Fine-Tuning[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(17): 17-33.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2312-0035 |
|
张钦彤, 王昱超, 王鹤羲, 等. 大语言模型微调技术的研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(17): 17-33.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2312-0035 |
|
| [19] | HU E J, SHEN Yelong, WALLIS P, et al. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models[EB/OL]. (2021-10-16)[2025-03-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2106.09685. |
| [1] | 胡雨翠, 高浩天, 张杰, 于航, 杨斌, 范雪俭. 车联网安全自动化漏洞利用方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1348-1356. |
| [2] | 刘会, 朱正道, 王淞鹤, 武永成, 黄林荃. 基于深度语义挖掘的大语言模型越狱检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1377-1384. |
| [3] | 王磊, 陈炯峄, 王剑, 冯袁. 基于污点分析与文本语义的固件程序交互关系智能逆向分析方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1385-1396. |
| [4] | 张燕怡, 阮树骅, 郑涛. REST API设计安全性检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(8): 1313-1325. |
| [5] | 陈平, 骆明宇. 云边端内核竞态漏洞大模型分析方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1007-1020. |
| [6] | 酆薇, 肖文名, 田征, 梁中军, 姜滨. 基于大语言模型的气象数据语义智能识别算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1163-1171. |
| [7] | 张学旺, 卢荟, 谢昊飞. 基于节点中心性和大模型的漏洞检测数据增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 550-563. |
| [8] | 顾欢欢, 李千目, 刘臻, 王方圆, 姜宇. 基于虚假演示的隐藏后门提示攻击方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 619-629. |
| [9] | 解梦飞, 傅建明, 姚人懿. 基于LLM的多媒体原生库模糊测试研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 403-414. |
| [10] | 秦中元, 王田田, 刘伟强, 张群芳. 大语言模型水印技术研究进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 177-193. |
| [11] | 胡斌, 黑一鸣, 吴铁军, 郑开发, 刘文忠. 大模型安全检测评估技术综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1477-1492. |
| [12] | 焦诗琴, 张贵杨, 李国旗. 一种聚焦于提示的大语言模型隐私评估和混淆方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1396-1408. |
| [13] | 陈昊然, 刘宇, 陈平. 基于大语言模型的内生安全异构体生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1231-1240. |
| [14] | 项慧, 薛鋆豪, 郝玲昕. 基于语言特征集成学习的大语言模型生成文本检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1098-1109. |
| [15] | 郭祥鑫, 林璟锵, 贾世杰, 李光正. 针对大语言模型生成的密码应用代码安全性分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(6): 917-925. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||