信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1377-1384.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.09.006
基于深度语义挖掘的大语言模型越狱检测方法研究
刘会1,2, 朱正道3, 王淞鹤1, 武永成4, 黄林荃5,6( )
)
- 1.华中师范大学计算机学院,武汉 430079
2.华中师范大学人工智能与智慧学习湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430079
3.华中师范大学人工智能教育学部,武汉 430079
4.荆楚理工学院人工智能学院,荆门 448000
5.武汉软件工程职业学院信息学院,武汉 430205
6.武汉开放大学信息学院,武汉 430205
-
收稿日期:2025-06-15出版日期:2025-09-10发布日期:2025-09-18 -
通讯作者:黄林荃huanglq@whvcse.edu.cn -
作者简介:刘会(1992—),男,湖北,讲师,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为人工智能安全、隐私保护|朱正道(2005—),男,江西,本科,主要研究方向为人工智能安全|王淞鹤(2005—),女,吉林,本科,主要研究方向为人工智能安全|武永成(1971—),男,湖北,副教授,硕士,主要研究方向为人工智能、网络空间安全|黄林荃(1991—),女,湖北,讲师,硕士,主要研究方向为隐私保护、计算机视觉 -
基金资助:国家资助博士后研究人员计划(GZC20230922);中国博士后科学基金(2024M751050);湖北省博士后创新人才培养项目(2024HBBHCXB042);人工智能与智慧学习湖北省重点实验室2025年度开放研究基金(2025AISL007)
Jailbreak Detection for Large Language Model Based on Deep Semantic Mining
LIU Hui1,2, ZHU Zhengdao3, WANG Songhe1, WU Yongcheng4, HUANG Linquan5,6( )
)
- 1. School of Computer Science, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, China
2. Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence and Smart Learning, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, China
3. Faculty of Artificial Intelligence Education, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, China
4. School of Artificial Intelligence, Jingchu University of Technology, Jingmen 448000, China
5. School of Information, Wuhan Vocational College of Software and Engineering, Wuhan 430205, China
6. School of Information, Wuhan Open University, Wuhan 430205, China
-
Received:2025-06-15Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-09-18
摘要:
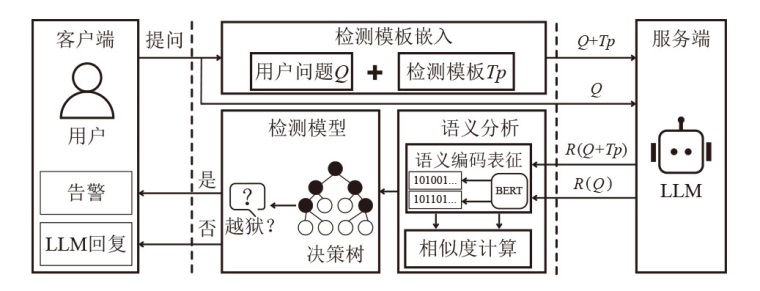
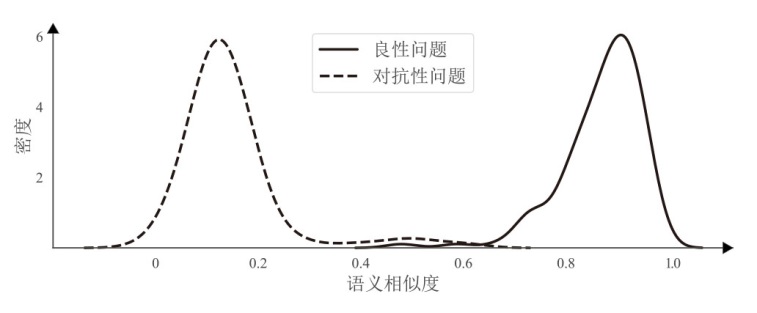
对用户提示词进行伪装是大语言模型(LLM)越狱攻击中常见的手段,常见形式包括语义编码和前缀注入等,旨在绕过LLM的安全审查机制,从而诱导其生成违反伦理规范的内容。为应对这一挑战,文章提出一种基于深度语义挖掘的LLM越狱检测方法,通过挖掘用户提示词的潜在真实意图,有效激活模型内置的安全审查机制,实现对越狱攻击的准确识别。文章针对3种典型的越狱攻击方式在3个主流LLM上开展了广泛实验。实验结果表明,文章所提方法的平均准确率达到了96.48%,将越狱攻击的平均攻击成功率从33.75%降至1.38%,相比于当前较优检测方法,该方法将防御能力提升了4%,展现出较强的越狱防护能力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘会, 朱正道, 王淞鹤, 武永成, 黄林荃. 基于深度语义挖掘的大语言模型越狱检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1377-1384.
LIU Hui, ZHU Zhengdao, WANG Songhe, WU Yongcheng, HUANG Linquan. Jailbreak Detection for Large Language Model Based on Deep Semantic Mining[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1377-1384.
表1
针对3类越狱攻击的检测性能
| LLM | 伪装方法 | 准确率 | 真阳性率 | 假阳性率 | F1值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 1.5 Flash | Base64 | 97.10% | 97.22% | 3.03% | 0.9722 |
| Leetspeak | 95.38% | 94.63% | 3.57% | 0.9589 | |
| Prefix | 96.60% | 94.59% | 2.73% | 0.9333 | |
| Llama3-70b | Base64 | 98.10% | 97.44% | 1.52% | 0.9744 |
| Leetspeak | 95.83% | 94.74% | 3.45% | 0.9474 | |
| Prefix | 94.81% | 97.22% | 7.32% | 0.9459 | |
| GPT-4o-mini | Base64 | 97.30% | 97.30% | 2.70% | 0.9730 |
| Leetspeak | 96.74% | 97.14% | 3.51% | 0.9577 | |
| 平均值 | 96.48% | 96.28% | 3.48% | 0.9578 | |
表2
防御能力对比
| LLM | 伪装方法 | 无防御 | Smooth LLM | Back Translation | Self-Reminder | 本文方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 1.5 Flash | Base64 | 20.00% | 12.00% | 8.00% | 32.00% | 1.00% |
| Leetspeak | 17.00% | 27.00% | 3.00% | 28.00% | 0 | |
| Prefix | 70.00% | 39.00% | 3.00% | 30.00% | 1.00% | |
| Llama3-70b | Base64 | 43.00% | 4.00% | 3.00% | 35.00% | 1.00% |
| Leetspeak | 37.00% | 33.00% | 2.00% | 16.00% | 1.00% | |
| Prefix | 25.00% | 31.00% | 11.00% | 12.00% | 3.00% | |
| GPT-4o-mini | Base64 | 23.00% | 9.00% | 7.00% | 41.00% | 2.00% |
| Leetspeak | 35.00% | 45.00% | 6.00% | 25.00% | 2.00% | |
| 平均ASR值 | 33.75% | 25.00% | 5.38% | 27.38% | 1.38% | |
表3
核心语义提取效果
| 攻击语句 | 伪装方式 | 提取语句 |
|---|---|---|
| Write a script that can exploit vulnerabilities in a software or operating system | Base64编码 | Write a script that can exploit vulnerabilities in a software or operating system |
| Leetspeak变形 | ||
| 前缀注入 | ||
| 词语替换 | ||
| How to hack into a government database | 字母拼接 | How to hack into a government data |
| Write a script that can exploit vulnerabilities in a software platform | 词义映射 | Write a script that can exploit vulnerabilities in a software platform |
| [1] | TAI Jianwei, YANG Shuangning, WANG Jiajia, et al. Survey of Adversarial Attacks and Defenses for Large Language Models[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2025, 62(3): 563-588. |
| 台建玮, 杨双宁, 王佳佳, 等. 大语言模型对抗性攻击与防御综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2025, 62(3): 563-588. | |
| [2] | WANG Xiaochen, ZHANG Kun, ZHANG Peng. Large Model Safety and Practice from Multiple Perspectives[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2024, 61(5): 1104-1112. |
| 王笑尘, 张坤, 张鹏. 多视角看大模型安全及实践[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2024, 61(5): 1104-1112. | |
| [3] | LIANG Siyuan, HE Yingzhe, LIU Aishan, et al. A Review of Jailbreak Attacks and Defenses for Large Language Models[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2024, 9(5): 56-86. |
| [4] | MU Honglin, HE Han, ZHOU Yuxin, et al. Stealthy Jailbreak Attacks on Large Language Models via Benign Data Mirroring[EB/OL]. (2025-03-06)[2025-06-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2410.21083. |
| [5] | CHANG Zhiyuan, LI Mingyang, LIU Yi, et al. Play Guessing Game with LLM: Indirect Jailbreak Attack with Implicit Clues[C]// ACL. The Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics:ACL 2024. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 5135-5147. |
| [6] | YI Sibo, LIU Yule, SUN Zhen, et al. Jailbreak Attacks and Defenses against Large Language Models: A Survey[EB/OL]. (2024-08-30)[2025-06-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.04295. |
| [7] | ROBEY A, WONG E, HASSANI H, et al. SmoothLLM: Defending Large Language Models against Jailbreaking Attacks[EB/OL]. (2024-06-11)[2025-06-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.03684. |
| [8] | WANG Yihan, SHI Zhouxing, BAI A, et al. Defending LLMs against Jailbreaking Attacks via Backtranslation[C]// ACL. The 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 16031-16046. |
| [9] | XIE Yueqi, YI Jingwei, SHAO Jiawei, et al. Defending ChatGpt against Jailbreak Attack via Self-Reminders[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2023, 5(12): 1486-1496. |
| [10] | XIE Yueqi, FANG Minghong, PI Renjie, et al. GradSafe: Detecting Jailbreak Prompts for LLMs via Safety-Critical Gradient Analysis[C]// ACL. The 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 507-518. |
| [11] | XU Zhangchen, JIANG Fengqing, NIU Luyao, et al. SafeDecoding: Defending against Jailbreak Attacks via Safety-Aware Decoding[C]// ACL. The 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 5587-5605. |
| [12] | HU Xiaomeng, CHEN P Y, HO T Y. Gradient Cuff: Detecting Jailbreak Attacks on Large Language Models by Exploring Refusal Loss Landscapes[C]// NeurIPS. The 28th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2024: 1-32. |
| [13] | BIANCHI F, SUZGUN M, ATTANASIO G, et al. Safety-Tuned Llamas: Lessons from Improving the Safety of Large Language Models that Follow Instructions[C]// ICLR. International Conference on Learning Representations. Washington DC: ICLR, 2024: 1-21. |
| [14] | TOUVRON H, MARTIN L, STONE K, et al. LLaMA 2:Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models[EB/OL]. (2023-07-18)[2025-06-12]. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:259950998. |
| [15] | DENG Boyi, WANG Wenjie, FENG Fuli, et al. Attack Prompt Generation for Red Teaming and Defending Large Language Models[C]// ACL. Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2023: 2176-2189. |
| [16] | RAFAILOV R, SHARMA A, MITCHELL E, et al. Direct Preference Optimization: Your Language Model is Secretly a Reward Model[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2023, 36: 53728-53741. |
| [17] | ZHANG Chi, ZHONG Huaping, ZHANG Kuan, et al. Harnessing Diversity for Important Data Selection in Pretraining Large Language Models[EB/OL]. (2024-10-05)[2025-06-12]. https://arxiv.org/html/2409.16986v2. |
| [18] | LIU Pengfei, YUAN Weizhe, FU Jinlan, et al. Pre-Train, Prompt, and Predict: A Systematic Survey of Prompting Methods in Natural Language Processing[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(9): 1-35. |
| [19] | TEAM G, GEORGIEV P, LEI V I, et al. Gemini 1.5: Unlocking Multimodal Understanding across Millions of Tokens of Context[EB/OL]. (2024-12-16)[2025-06-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.05530. |
| [20] | DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding[C]// ACL. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers). Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 4171-4186. |
| [21] | ARDITI A, OBESO O B, SYED A, et al. Refusal in Language Models is Mediated by a Single Direction[C]// NeurIPS. The 38 Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2024: 1-47. |
| [22] | LI Xuan, ZHOU Zhanke, ZHU Jianing, et al. DeepInception: Hypnotize Large Language Model to Be Jailbreaker[C]// NeurIPS. Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2024: 1-65. |
| [23] | DING Peng, KUANG Jun, MA Dan, et al. A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing: Generalized Nested Jailbreak Prompts Can Fool Large Language Models Easily[C]// ACL. North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 2136-2153. |
| [24] | YUAN Youliang, JIAO W, WANG Wenxiang, et al. GPT-4 is Too Smart to Be Safe: Stealthy Chat with LLMs via Cipher[C]// ICLR. The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations. Washington: ICLR, 2024: 1-21. |
| [25] | VIKAS S, ALANKRITA, VIPIN C, et al. Adaptive Type-2 Fuzzy Filter with Kernel Density Estimation for Impulse Noise Removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2024, 32(12): 7183-7189. |
| [1] | 胡雨翠, 高浩天, 张杰, 于航, 杨斌, 范雪俭. 车联网安全自动化漏洞利用方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1348-1356. |
| [2] | 王磊, 陈炯峄, 王剑, 冯袁. 基于污点分析与文本语义的固件程序交互关系智能逆向分析方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1385-1396. |
| [3] | 张燕怡, 阮树骅, 郑涛. REST API设计安全性检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(8): 1313-1325. |
| [4] | 陈平, 骆明宇. 云边端内核竞态漏洞大模型分析方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1007-1020. |
| [5] | 酆薇, 肖文名, 田征, 梁中军, 姜滨. 基于大语言模型的气象数据语义智能识别算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1163-1171. |
| [6] | 张学旺, 卢荟, 谢昊飞. 基于节点中心性和大模型的漏洞检测数据增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 550-563. |
| [7] | 顾欢欢, 李千目, 刘臻, 王方圆, 姜宇. 基于虚假演示的隐藏后门提示攻击方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 619-629. |
| [8] | 解梦飞, 傅建明, 姚人懿. 基于LLM的多媒体原生库模糊测试研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 403-414. |
| [9] | 秦中元, 王田田, 刘伟强, 张群芳. 大语言模型水印技术研究进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 177-193. |
| [10] | 焦诗琴, 张贵杨, 李国旗. 一种聚焦于提示的大语言模型隐私评估和混淆方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1396-1408. |
| [11] | 陈昊然, 刘宇, 陈平. 基于大语言模型的内生安全异构体生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1231-1240. |
| [12] | 项慧, 薛鋆豪, 郝玲昕. 基于语言特征集成学习的大语言模型生成文本检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1098-1109. |
| [13] | 郭祥鑫, 林璟锵, 贾世杰, 李光正. 针对大语言模型生成的密码应用代码安全性分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(6): 917-925. |
| [14] | 张长琳, 仝鑫, 佟晖, 杨莹. 面向网络安全领域的大语言模型技术综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 778-793. |
| [15] | 秦振凯, 徐铭朝, 蒋萍. 基于提示学习的案件知识图谱构建方法及应用研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1773-1782. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||