信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1847-1862.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.12.002
大语言模型引导的协议模糊测试技术研究
杨立群1,2,3( ), 李镇1, 韦超仁1, 闫治敏1, 仇勇鑫1
), 李镇1, 韦超仁1, 闫治敏1, 仇勇鑫1
- 1.北京航空航天大学网络空间安全学院,北京 100191
2.中国民用航空飞行学院民航安全工程学院,广汉 618307
3.四川省全电通航飞行器关键技术工程研究中心,广汉 618307
-
收稿日期:2025-08-23出版日期:2025-12-10发布日期:2026-01-06 -
通讯作者:杨立群 E-mail:lqyang@buaa.edu.cn -
作者简介:杨立群(1990—),男,河北,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为网络信息安全、工业互联网和工控安全|李镇(1995—),男,山东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络信息安全、模糊测试|韦超仁(2002—),男,四川,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为模糊测试、大语言模型|闫治敏(2003—),男,内蒙古,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为大语言模型、模糊测试|仇勇鑫(2001—),男,山西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为模糊测试 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62302025);国家自然科学基金(62572027);国家自然科学基金(U2333205);四川省全电通航飞行器关键技术工程研究中心开放课题(CAFUC 202401KF003)
Research on Protocol Fuzzing Technology Guided by Large Language Models
YANG Liqun1,2,3( ), LI Zhen1, WEI Chaoren1, YAN Zhimin1, QIU Yongxin1
), LI Zhen1, WEI Chaoren1, YAN Zhimin1, QIU Yongxin1
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Technology, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2. School of Civil Aviation Safety Engineering, Civil Aviation Flight University of China, Guanghan 618307, China
3. Engineering Research Center of Key Technologies for All-Electric General Aviation Aircraft of Sichuan Province, Guanghan 618307, China
-
Received:2025-08-23Online:2025-12-10Published:2026-01-06 -
Contact:YANG Liqun E-mail:lqyang@buaa.edu.cn
摘要:
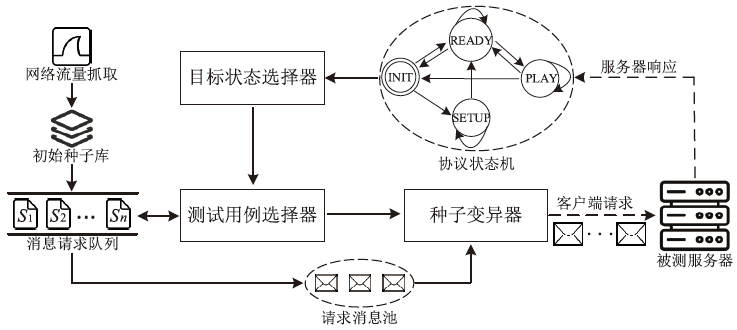
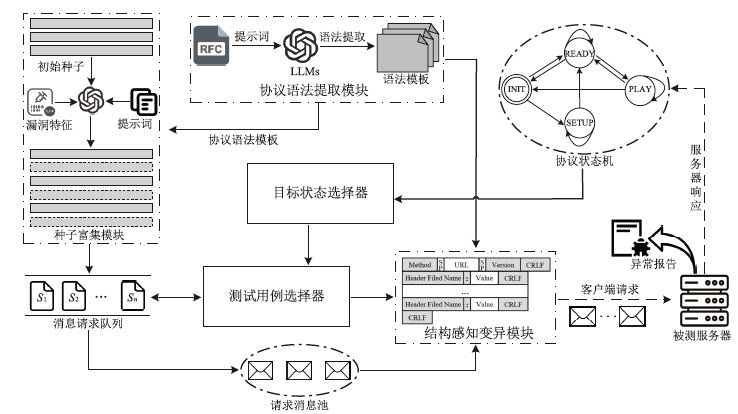
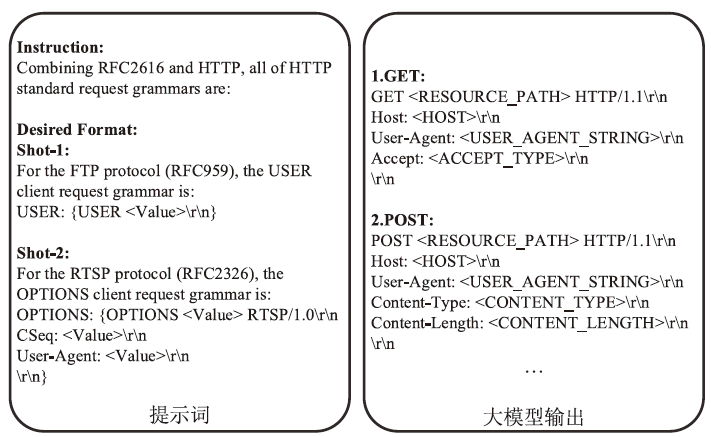
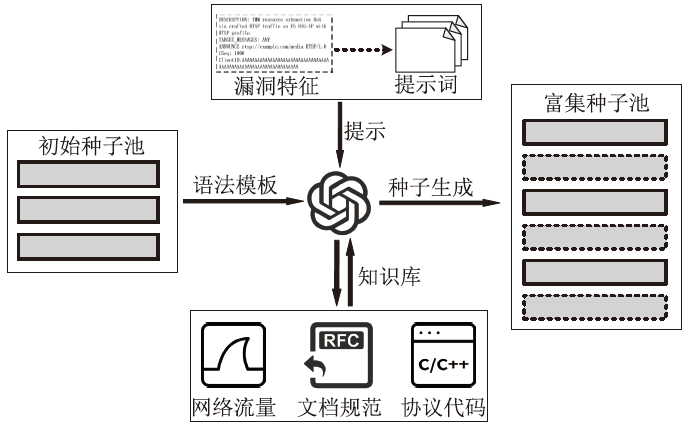
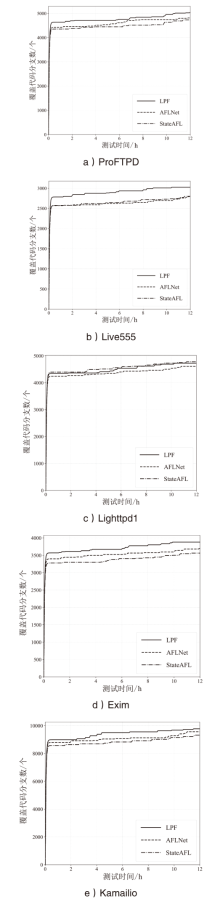
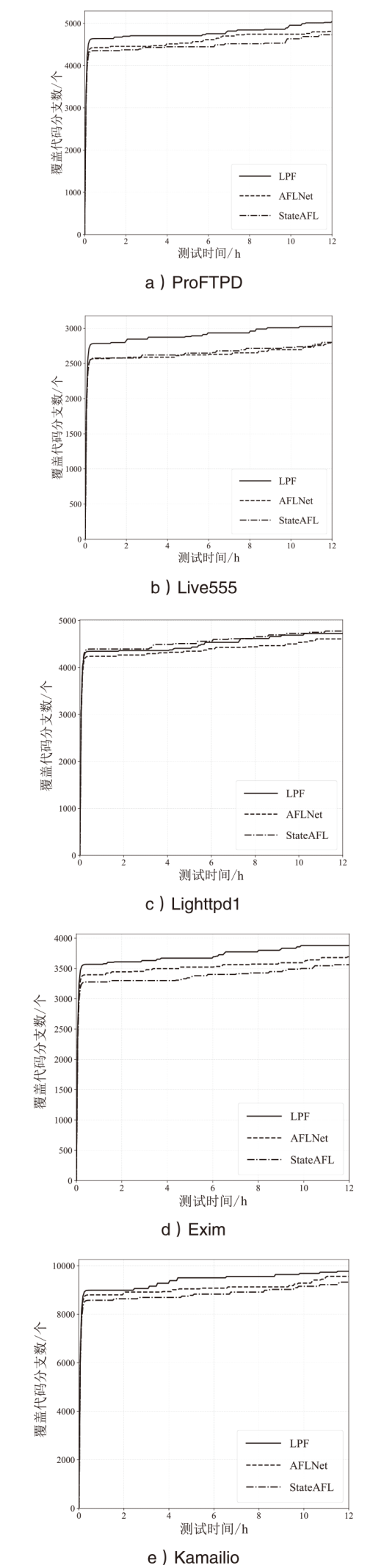
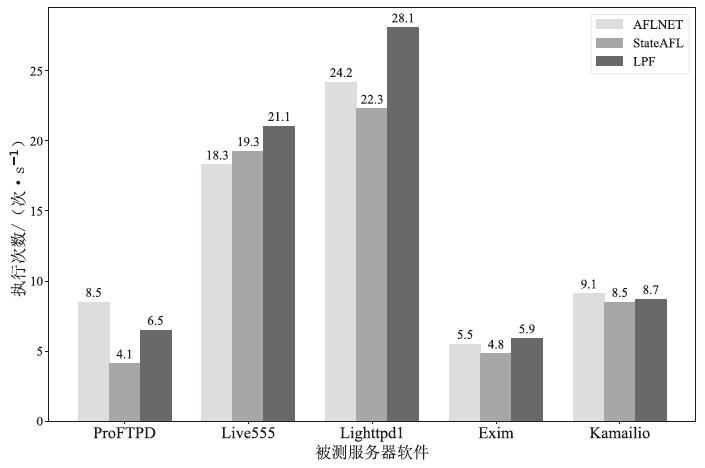
网络协议软件漏洞频发,严重威胁网络空间安全。以AFLNet为代表的灰盒协议模糊测试工具通过引入覆盖率反馈与状态建模机制提升了漏洞挖掘能力,但受限于“语义屏障”,此类工具难以理解协议的语法结构与上下文逻辑,测试效率较低。近年来,大语言模型在语义建模、上下文推理与代码生成等任务中展现出强大的泛化与理解能力,为打破这一屏障提供了关键技术路径。文章提出了一种由大语言模型引导的协议模糊测试框架(LLMProFuzz,LPF),在以下3个层面克服传统方法的局限性:一是利用少样本提示工程自动提取协议语法模板;二是基于历史漏洞特征设计种子富集机制,生成覆盖边界场景和异常逻辑的高价值初始用例;三是引入结构感知的变异位置选择策略,提高有效测试用例的生成比例。在HTTP、FTP、RTSP等典型协议栈中的实验结果表明,LPF在代码覆盖率、状态覆盖率和测试效率等方面均显著优于AFLNet与StateAFL等基准工具。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨立群, 李镇, 韦超仁, 闫治敏, 仇勇鑫. 大语言模型引导的协议模糊测试技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(12): 1847-1862.
YANG Liqun, LI Zhen, WEI Chaoren, YAN Zhimin, QIU Yongxin. Research on Protocol Fuzzing Technology Guided by Large Language Models[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1847-1862.
| [1] | BA J, BÖHME M, MIRZAMOMEN Z, et al. Stateful Greybox Fuzzing[C]// USENIX. The 31st USENIX Security Symposium. Berkely: USENIX Association, 2022: 3255-3272. |
| [2] | LU Liyu, LIU Yuan, HONG Chao, et al. Screening Method of Fuzzy Test Seeds Based on Impact Orientation[J]. Network Security Technology & Application, 2024(2): 44-46. |
| 陆力瑜, 刘媛, 洪超, 等. 基于影响性导向的模糊测试种子筛选方法[J]. 网络安全技术与应用, 2024(2):44-46. | |
| [3] |
MILLER B P, ZHANG Mengxiao, HEYMANN E R. The Relevance of Classic Fuzz Testing: Have We Solved this One?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2022, 48(6): 2028-2039.
doi: 10.1109/TSE.2020.3047766 URL |
| [4] |
MANÈS V J M, HAN H, HAN C, et al. The Art, Science, and Engineering of Fuzzing: A Survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2021, 47(11): 2312-2331.
doi: 10.1109/TSE.2019.2946563 URL |
| [5] | ZHANG Xiaohan, ZHANG Cen, LI Xinghua, et al. A Survey of Protocol Fuzzing[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2024, 57(2): 1-36. |
| [6] |
ZHAO Yiru, GAO Long, WEI Qiang, et al. Towards Tightly-Coupled Hybrid Fuzzing via Excavating Input Specifications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2024, 21(5): 4801-4814.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2024.3361008 URL |
| [7] | PHAM V, BÖHME M, ROYCHOUDHURY A. AFLNet: A Greybox Fuzzer for Network Protocols[C]// IEEE. The 13th IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation (ICST). New York: IEEE, 2020: 460-465. |
| [8] |
LUO Zhengxiong, YU Junze, DU Qingpeng, et al. Parallel Fuzzing of IoT Messaging Protocols through Collaborative Packet Generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2024, 43(11): 3431-3442.
doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2024.3444705 URL |
| [9] |
MENG Ruijie, PHAM V-T, BÖHME M, et al. AFLNet Five Years Later: On Coverage-Guided Protocol Fuzzing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2025, 51(4): 960-974.
doi: 10.1109/TSE.2025.3535925 URL |
| [10] | Website. American Fuzzy Lop (AFL) Fuzzer[EB/OL]. [2025-07-30]. http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/afl. |
| [11] |
LI Junqiang, LI Senyi, SUN Gang, et al. SNPSFuzzer: A Fast Greybox Fuzzer for Stateful Network Protocols Using Snapshots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 2673-2687.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3192991 URL |
| [12] | ANDRONIDIS A, CADAR C. SnapFuzz: High-Throughput Fuzzing of Network Applications[C]// ACM. The 31st ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis. New York: ACM, 2022: 340-351. |
| [13] | QIN Shisong, HU Fan, MA Zheyu, et al. NSFuzz: Towards Efficient and State-Aware Network Service Fuzzing[J]. ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology, 2023, 32(6): 1-26. |
| [14] |
HUANG Tao, GAO Yansong, ZHENG Yifeng, et al. FineBID: Fine-Grained Protocol Reverse Engineering for Bit-Level Field Identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2025, 22(3): 2670-2686.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2024.3521592 URL |
| [15] |
KIM J, SEO M, MARIN E, et al. Ambusher: Exploring the Security of Distributed SDN Controllers through Protocol State Fuzzing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 6264-6279.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2024.3402967 URL |
| [16] |
ZHANG Qingyu, LIN Jiayi, SUN Chenxin, et al. CherryPicker: A Parallel Solving and State Sharing Hybrid Fuzzing System[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2025, 22(4): 3324-3336.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2025.3530010 URL |
| [17] | HONG Xuanquan, JIA Peng, LIU Jiayong. AFLNeTrans: Fuzzing of Protocols with State Relationship Awareness[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 121-132. |
| 洪玄泉, 贾鹏, 刘嘉勇. AFLNeTrans:状态间关系感知的网络协议模糊测试[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1):121-132. | |
| [18] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[C]// ACM. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’17). New York: ACM, 2017: 6000-6010. |
| [19] | BROWN T, MANN B, RYDER N, et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners[C]// ACM. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS ‘20). New York: ACM, 2020: 1877-1901. |
| [20] |
ZHU Xiaogang, ZHOU Wei, HAN Q, et al. When Software Security Meets Large Language Models: A Survey[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2025, 12(2): 317-334.
doi: 10.1109/JAS.2024.124971 URL |
| [21] | LEMIEUX C, INALA J, LAHIRI S, et al. Codamosa: Escaping Coverage Plateaus in Test Generation with Pre-Trained Large Language Models[C]// IEEE. The 45th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE). New York: IEEE, 2023: 919-931. |
| [22] | DENG Yinlin, XIA C S, PENG Haoran, et al. Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Fuzzers: Fuzzing Deep-Learning Libraries via Large Language Models[C]// ACM. The 32nd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis(ISSTA 2023). New York: ACM, 2023: 423-435. |
| [23] | DENG Yinlin, XIA C S, YANG Chenyuan, et al. Large Language Models are Edge-Case Generators: Crafting Unusual Programs for Fuzzing Deep Learning Libraries[C]// ACM. The IEEE/ACM 46th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE’24). New York: ACM, 2024: 1-13. |
| [24] |
ZHANG Qiang, SHEN Yuheng, LIU Jianzhong, et al. ECG: Augmenting Embedded Operating System Fuzzing via LLM-Based Corpus Generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2024, 43(11): 4238-4249.
doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2024.3447220 URL |
| [25] |
SHAHRIAR A, HISHAM S J, RAHMAN K M A, et al. 5GPT: 5G Vulnerability Detection by Combining Zero-Shot Capabilities of GPT-4 with Domain Aware Strategies through Prompt Engineering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025, 20: 7045-7060.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2025.3586480 URL |
| [26] |
ZHENG Tao, SHAO Jiang, DAI Jinqiao, et al. RESTLess: Enhancing State-of-the-Art REST API Fuzzing with LLMs in Cloud Service Computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2024, 17(6): 4225-4238.
doi: 10.1109/TSC.2024.3489441 URL |
| [27] | WANG Jincheng, YU Le, LUO Xiapu. LLMIF: Augmented Large Language Model for Fuzzing IoT Devices[C]// IEEE. The 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2024: 881-896. |
| [28] | YANG Liqun, WEI Chaoren, YANG Jian, et al. Code Large Language Model-Based Fuzz Testing for Industrial IoT Programs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024: 1-11. |
| [29] | PIYUSH J, JOSEPH S, JAYA S G, et al. BertRLFuzzer: A BERT and Reinforcement Learning Based Fuzzer[C]// ACM. The Thirty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirty-Sixth Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Fourteenth Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence (AAAI’24/IAAI’24/EAAI’24). New York: ACM, 2024: 23521-23522. |
| [30] | YANG Chenyuan, DENG Yinlin, LU Runyu, et al. WhiteFox: White-Box Compiler Fuzzing Empowered by Large Language Models[C]// ACM. The ACM on Programming Languages. New York: ACM, 2024, 8(2): 709-735. |
| [31] | EOM J, JEONG S, KWON T. Fuzzing JavaScript Interpreters with Coverage-Guided Reinforcement Learning for LLM-Based Mutation[C]// ACM. The 33rd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis (ISSTA 2024). New York: ACM, 2024: 1656-1668. |
| [32] | XIA C S, PALTENGHI M, TIAN Jiale, et al. Fuzz4All: Universal Fuzzing with Large Language Models[C]// ACM. The 46th International Conference on Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2024: 1-13. |
| [33] |
YE Kai, ZHU Xiaogang, XIAO Xi, et al. BazzAFL: Moving Fuzzing Campaigns towards Bugs via Grouping Bug-Oriented Seeds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2025, 22(1): 179-191.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2024.3391795 URL |
| [34] |
LI Yuwei, JI Shouling, LYU Chenyang, et al. V-Fuzz: Vulnerability Prediction-Assisted Evolutionary Fuzzing for Binary Programs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(5): 3745-3756.
doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3013675 URL |
| [1] | 胡雨翠, 高浩天, 张杰, 于航, 杨斌, 范雪俭. 车联网安全自动化漏洞利用方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1348-1356. |
| [2] | 刘会, 朱正道, 王淞鹤, 武永成, 黄林荃. 基于深度语义挖掘的大语言模型越狱检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1377-1384. |
| [3] | 王磊, 陈炯峄, 王剑, 冯袁. 基于污点分析与文本语义的固件程序交互关系智能逆向分析方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1385-1396. |
| [4] | 张燕怡, 阮树骅, 郑涛. REST API设计安全性检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(8): 1313-1325. |
| [5] | 陈平, 骆明宇. 云边端内核竞态漏洞大模型分析方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1007-1020. |
| [6] | 酆薇, 肖文名, 田征, 梁中军, 姜滨. 基于大语言模型的气象数据语义智能识别算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1163-1171. |
| [7] | 张学旺, 卢荟, 谢昊飞. 基于节点中心性和大模型的漏洞检测数据增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 550-563. |
| [8] | 韦超仁, 夏万煦, 屈刚, 白万荣, 杨立群. 面向智能系统开源模糊测试框架优化技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 587-597. |
| [9] | 顾欢欢, 李千目, 刘臻, 王方圆, 姜宇. 基于虚假演示的隐藏后门提示攻击方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 619-629. |
| [10] | 常振轩, 郑之涵, 梅傲寒, 谭毓安. 一种面向固件网络应用的高效灰盒模糊测试方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 654-663. |
| [11] | 金增旺, 江令洋, 丁俊怡, 张慧翔, 赵波, 方鹏飞. 工业控制系统安全研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 341-363. |
| [12] | 解梦飞, 傅建明, 姚人懿. 基于LLM的多媒体原生库模糊测试研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 403-414. |
| [13] | 秦中元, 王田田, 刘伟强, 张群芳. 大语言模型水印技术研究进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 177-193. |
| [14] | 孟辉, 毛琳琳, 彭聚智. 大语言模型驱动的无害化处理识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(12): 1990-1998. |
| [15] | 胡斌, 黑一鸣, 吴铁军, 郑开发, 刘文忠. 大模型安全检测评估技术综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1477-1492. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||