信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 341-363.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.03.001
工业控制系统安全研究综述
金增旺1,2, 江令洋1, 丁俊怡1, 张慧翔1( ), 赵波1, 方鹏飞3
), 赵波1, 方鹏飞3
- 1.西北工业大学网络空间安全学院,西安 710072
2.西北工业大学太仓长三角研究院,太仓 215400
3.国家工业信息安全发展研究中心,北京 100040
-
收稿日期:2024-12-25出版日期:2025-03-10发布日期:2025-03-26 -
通讯作者:张慧翔 E-mail:zhanghuixiang@nwpu.edu.cn -
作者简介:金增旺(1990—),男,福建,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为工业协议安全分析和工业控制系统安全分析|江令洋(1999—),男,河南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为工业控制安全和模糊测试|丁俊怡(2003—),女,安徽,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为工业控制安全和模糊测试|张慧翔(1981—),男,陕西,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络与系统安全|赵波(1992—),男,山东,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为无人系统安全分析、空天地一体化网络安全传输协议|方鹏飞(1986-),男,北京,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为协议逆向分析、工业控制系统安全 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2022YFB3104005);太仓市基础研究计划(TC2022JC17)
A Review of Research on Industrial Control System Security
JIN Zengwang1,2, JIANG Lingyang1, DING Junyi1, ZHANG Huixiang1( ), ZHAO Bo1, FANG Pengfei3
), ZHAO Bo1, FANG Pengfei3
- 1. School of Cybersecurity, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China
2. Yangtze River Delta Research Institute, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Taicang 215400, China
3. China Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team, Beijing 100040, China
-
Received:2024-12-25Online:2025-03-10Published:2025-03-26 -
Contact:ZHANG Huixiang E-mail:zhanghuixiang@nwpu.edu.cn
摘要:
随着工业4.0和智能制造的快速发展,工业控制系统的安全性成为关键问题。工业控制协议作为工业控制系统的核心通信机制,其安全性直接关系到系统的稳定性和数据保护。然而,许多工业控制协议在设计时缺乏充分的网络安全考虑,导致系统容易受到恶意软件、拒绝服务等攻击,可能危及企业利益甚至国家安全。当前,研究者们正积极探索工业控制协议的安全问题,并提出了多种解决方案。文章综述了工业控制协议的安全现状、主要挑战和发展趋势。首先,介绍了工业控制协议的基本概念和分类,分析了其安全特性及脆弱性。然后,重点讨论了符号执行、逆向分析和模糊测试在漏洞挖掘中的应用,这些技术在应对复杂工业协议时尤为有效。而且还探讨了加密认证、入侵检测及深度防御等安全防护措施。最后,文章探索了生成式大语言模型在工业控制系统安全中的应用,涉及代码生成、网络防护及自动化控制等领域,助力工业控制系统从被动防御向主动防护转变。通过本研究,期望能够提升对工业控制协议安全性的认识,为工业控制系统的可靠性和安全性提供坚实的基础和实用的解决方案,以有效保护关键信息基础设施免受潜在威胁和攻击。
中图分类号:
引用本文
金增旺, 江令洋, 丁俊怡, 张慧翔, 赵波, 方鹏飞. 工业控制系统安全研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 341-363.
JIN Zengwang, JIANG Lingyang, DING Junyi, ZHANG Huixiang, ZHAO Bo, FANG Pengfei. A Review of Research on Industrial Control System Security[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 341-363.
使用本文
表1
历史工业控制安全事件
| 事件日期 | 事件描述 | 影响 |
|---|---|---|
| 2010年6月 | Stuxnet蠕虫病毒攻击了西门子为伊朗铀浓缩设施设计的工业控制系统 | 伊朗核计划受到影响 |
| 2014年12月 | 德国钢铁厂因网络攻击导致控制系统失灵,造成熔炉损坏 | 钢铁生产受损 |
| 2015年12月 | 乌克兰西部两州电网遭到黑客攻击 | 乌克兰部分地区供电中断 |
| 2017年6月 | NotPetya勒索软件在全球范围内爆发 | 多家公司经济损失 |
| 2020年2月 | 一家未公开名字的美国天然气管道商遭到网络攻击,不得不关闭其压缩设施 | 美国天然气输送受到影响 |
| 2021年5月 | 美国科洛尼尔管道系统遭受勒索软件网络攻击,影响了负责管理管道的计算机系统 | 美国东南部的燃油供应受影响 |
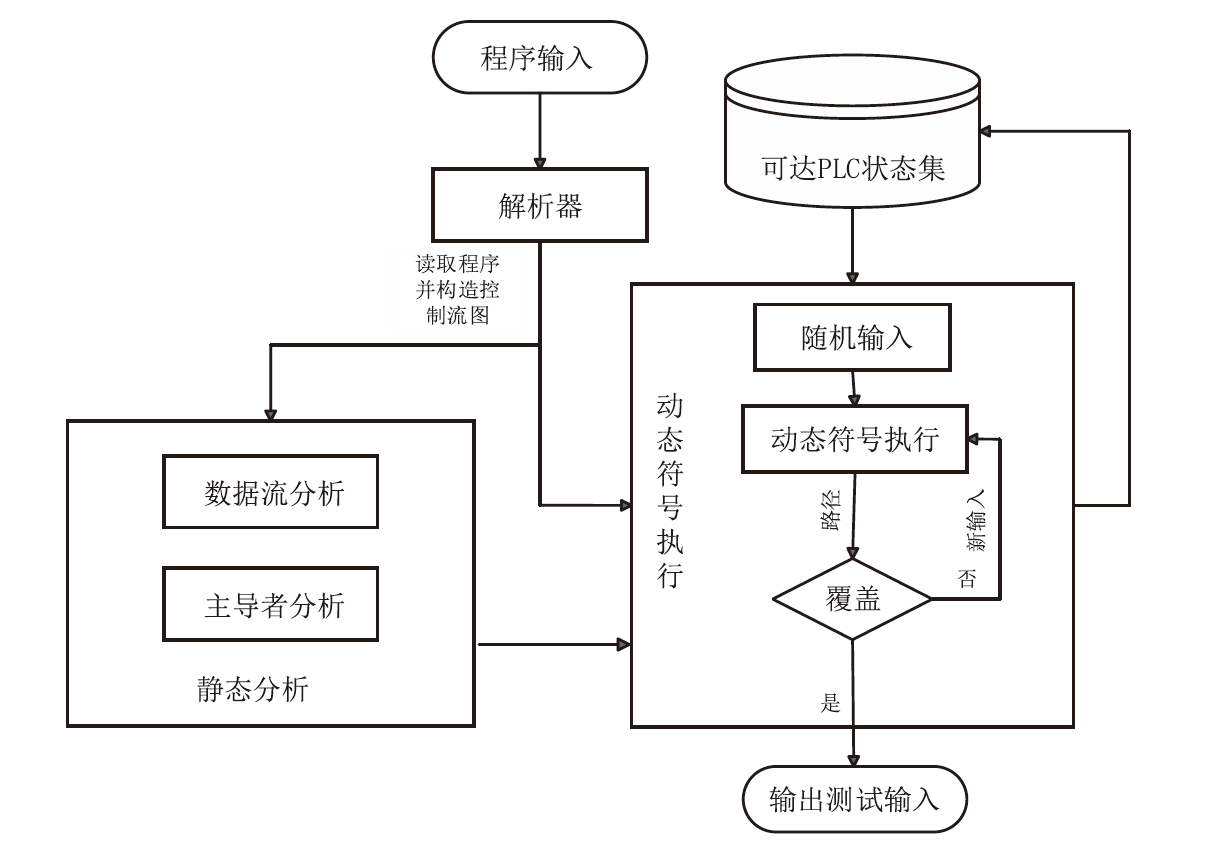
| 2022年6月 | 德克萨斯州一家液化天然气厂遭黑客攻击导致爆炸 | 影响自由港液化天然气的运营 |
| 2023年6月 | 加拿大最大的合成原油生产商之一的Suncor Energy遭受了网络攻击 | 官网瘫痪,用户数据泄露 |
| 2023年8月 | 美国芝加哥贝尔特铁路公司遭遇勒索软件攻击 | 85 GB的数据被泄露 |
| 2024年9月 | 黎巴嫩发生BB机(寻呼机)爆炸事件,导致至少42人死亡,数千人受伤 | 通信中断,公众安全受到威胁 |
表5
ICP逆向分析现有工作对比
| 分类 | 文献 | 方法名称 | 技术要点 | 协议 | 主要应用场景/优势 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 静态 分析 | 文献[ | 静态逆向分析方法 | 关键字模糊匹配识别函数调用 关系 | — | 适用于电力工业控制软件的静态逆向分析 |
| 文献[ | ARES 自动逆向工程方法 | 对 PLC 程序中变量的语义进行逆向工程 | PLC code | 不需要领域知识即可逆向 工程 | |
| 动态 分析 | 文献[ | 黑盒动态分析工具 | 从控制器寄存器内存扫描中推导模型 | Modbus | 适用于已有控制器日志数据的情况 |
| 文献[ | ICSPRF 工业控制系统协议逆向工程 框架 | 监控程序执行,收集 BBL 组数据 | DNP3, Modbus, S7, IEC104 | 适用于已知执行上下文的 信息 | |
| 文献[ | Reditus 框架 | 集成反编译器恢复控制逻辑源代码 | Modbus | 从网络流量中恢复二进制控制逻辑 | |
| 聚类和序列 比对 | 文献[ | 网络跟踪技术 | Pair-HMM 对关键字段进行序列 比对 | Modbus, ICS 61850 | 有效表示私有协议的重要 字段 |
| 文献[ | 消息聚类方法 | 基于大小和相似性的两步聚类 | Modbus/TCP, Ethernet/IP, FTP | 减少计算复杂度,提高聚类准确性 | |
| 文献[ | V-gram 方法 | XGBoost 提取特征词构建 FSM 模型 | S7 | 利用ICP的周期性和结构固定性 | |
| 文献[ | REInPro 方法 | 利用控制字段确定ICP结构,进行聚类推断关键字段语义 | Modbus, Dnp3, S7, PCCC, Omron_Fins, Delta_P, Hollysys_P | 识别准确率高,适应性强 | |
| 无监督学习和深度 学习 | 文献[ | IPART 无监督工具 | 扩展的投票专家算法推断字段 边界 | Modbus, IEC104 | 自动逆向工业协议格式 |
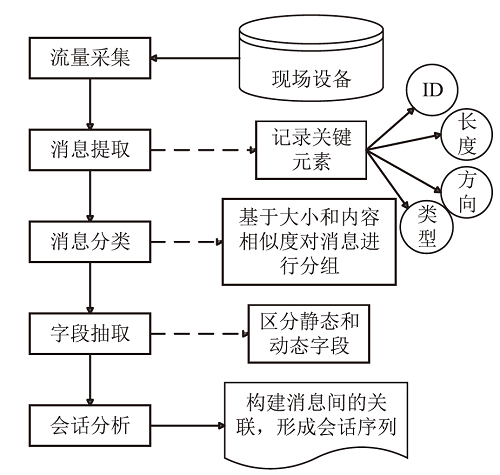
| 文献[ | PREIUD 工具 | 注意机制的双向 LSTM-CRF 进行分类 | Modbus/TCP, Ethernet/IP, DNP3, IEC104 | 结合无监督学习和深度神经网络,提高分类准确性 | |
| 启发式方法 | 文献[ | MSERA 多阶段集成反向分析方法 | 使用 Needleman-Wunsch 算法进行序列比对 | DNP3, Modbus, S7Comm | 识别特定语义字段,提高逆向分析结果 |
| 文献[ | PREE 启发式构建器 | 创建启发式方法识别字段 | Modbus TCP, UMAS, ENIP | 便于控制工程师快速识别新协议 | |
| 文献[ | Spenny 框架 | 字段覆盖度量标准,高效路径优先策略 | DNP3, Modbus, IEC104, UMAS | 缓解路径爆炸问题,提高逆向分析准确性 | |
| 子消息提取 技术 | 文献[ | 子消息提取算法 | 模板迭代形成消息格式推理框架 | Modbus/TCP, Ethernet/IP, CIP, DNP3, EtherCAT | 提高消息格式推断的准确性 |
表6
工业控制协议模糊测试现有工作对比
| 分类 | 研究名称 | 主要方法 | 应用协议 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基于协议格式和字段依赖 关系 | Across-field [ | 区分长度字段、内容字段和常规 字段 | MMS | 提高协议格式适应性和测试准确性 |
| 专有协议 | FieldFuzz[ | 反向工程解析专有协议 | Codesys 运行时环境 | 在运行时环境中直接模糊测试,扩大对专有系统的覆盖面 |
| Information Theory[ | 结合信息论解析协议 | — | 识别拒绝服务漏洞,有生成式测试潜力 | |
| 功能码感知和状态引导 | Polar[ | 自动提取语义信息 | Modbus、IEC104、IEC61850 | 加速安全漏洞检测,优化模糊测试过程 |
| Mutation Tree[ | 模糊突变树剪枝优化 | — | 解决突变算子效率低的问题 | |
| PCFuzzer[ | 流量驱动协议测试 | S7Comm、SRTP、Ethernet/IP | 状态引导,网络/物理状态监控 | |
| Cross State[ | 跨状态代码覆盖率 | RTPS、IEC61850-MMS | 发掘不同状态间的安全隐患 | |
| 模糊测试工具改进 | Improved Boofuzz[ | 并行化测试 | IEC 60870-5-104 | 提升模糊测试性能,自动检测硬件漏洞 |
| Peach Fuzzer[ | 覆盖率引导功能 | Profinet-DCP | 插件支持,增强模糊测试性能 | |
| Peach*[ | 覆盖率反馈优化 | Modbus、DNP3 | 通过覆盖率反馈提升测试用例质量 | |
| MTF[ | 基于状态引导的优化 | Modbus、TCP | 侦察阶段,针对性和高效的测试 | |
| MSGFuzzer[ | 基于消息序列的优化 | 工业机器人协议 | 减少状态引导时间,精准测试用例 | |
| 深度学习 | SeqFuzzer[ | 基于Seq2seq | EtherCAT | 生成接受率高的测试用例 |
| GANFuzz[ | 基于SeqGAN | Modbus/TCP | 优于以往的模糊测试工具 | |
| CGFuzzer[ | 基于CGGAN | DNP3 | 将 UCT 与 SeqGAN 相结合,提高通过率和代码覆盖率 | |
| NCMFuzzer[ | 基于SeqGAN | Modbus/TCP | 通过非关键字段进行变异和组合测试案例,提高了模糊测试的效率 | |
| WGANFuzz[ | 基于WGAN | Modbus/TCP、EtherCAT | 提出了一种广义的模糊处理过程 | |
| WGGFuzz[ | 基于WGAN和VAE | Modbus/TCP | 通过数据帧处理模块对种子进行优化,以提供高质量的训练 数据 | |
| MaskFuzzer[ | 基于MaskGAN | Modbus/TCP | 与基于 GAN 的方法和 Peach 方法相比,能提供更好的测试 结果 | |
| BLSTM-DCNNFuzz[ | 基于BLSTM和DCGAN | Modbus/TCP、EtherCAT | 在便利性、有效性和效率方面优于以往的模糊方法 | |
| ICPFuzzer[ | 基于LSTM | Modbus/TCP | 使用LSTM自动学习协议特征并生成测试数据,减少对协议先验知识的依赖 | |
| PSMFuzzer[ | 变换器和协议相似性 | Modbus/TCP | 用Transformer学习Modbus/TCP协议 | |
| DiffusionFuzz[ | 基于DDPM | Modbus/TCP、S7Comm、Ethernet/IP | 提出了基于去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)的自动模糊测试方法 |
表7
工业控制系统入侵检测现有工作对比
| 分类 | 文献 | 方法名称 | 特点 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 机器学习和深度学习 | 文献[ | 深度防御架构的入侵检测机制 | 实时异常行为检测,考虑网络通信中的消息序列和软件执行 轨迹 | 需要全面防护的ICS和SCADA网络环境,能够及时检测异常 行为 |
| 文献[ | 基于深度学习的网络入侵检测 | 识别SCADA流量中的时间模式,检测网络攻击,通过加入攻击记录扩展模型 | 保护SCADA网络免受传统网络攻击及特制SCADA协议攻击 | |
| 文献[ | 基于深度自编码器的NIDS | 分析网络流量数据检测异常行为,无人监督学习环境下训练,高检测率、低误报率 | 检测ICS中的DDoS攻击,不需要了解网络拓扑或底层协议 | |
| 文献[ | 基于实例的ICS入侵检测 | 数据缩放、降维、重采样,基于实例的学习器识别攻击向量 | 需要从被攻击数据中识别有害向量的SCADA网络环境,提高检测效率 | |
| 文献[ | SAIN | 通过状态感知不变量自动生成与实时监控,提供紧密边界条件的攻击检测 | 在关键基础设施中能有效识别和防御针对PLC的隐秘攻击 | |
| 文献[ | IFinger检测方法 | 观察寄存器状态值,生成设备指纹,主动与被动检测策略,预测未来流量 | 需要获取不可见寄存器状态信息的ICS环境,减少主动探测 影响 | |
| 基于网络数据特征 | 文献[ | SENAMI | 监控PLC变量,无明显计算开销,避免轮询大量上下文冗余值,控制网络负载 | 老旧设备环境,减少网络负载,适用于秘密改变PLC行为的攻击检测 |
| 文献[ | 基于网络遥测数据的入侵检测 | 区分正常流量和攻击流量,缩短数据捕获窗口时间,提高分类器准确性 | 快速响应和高准确性的ICS环境,特别是在区分工程师与攻击者活动时 | |
| 文献[ | ZOE | 计算流相似度,建立正常流模型,未知流与模型对比 | 需要精确检测未知流与正常流区别的ICS环境 | |
| 文献[ | 基于Snort的入侵检测 机制 | 测试以太网攻击向量,定义Snort新规则,展示工业现场总线级别入侵检测 可行性 | EtherCAT协议环境 |
表8
大语言模型应用现有工作对比
| 分类 | 文献 | 研究名称 | 主要贡献 | 技术特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 代码生成与 验证 | 文献[ | Agents-4PLC | 基于多代理的 LLM 系统自动生成和验证 PLC 代码,实现从自然语言需求到形式化规范和参考代码的全流程自动化 | 利用 LLM 进行自然语言到编程语言的转换,多代理协作生成代码 |
| 文献[ | LLM-4PLC | 扩展了 LLM 在 PLC 代码生成中的应用,通过用户反馈和外部验证工具优化生成代码 | 结合外部工具如语法检查器、编译器和 SMV 验证器辅助 LLM 优化代码 | |
| 文献[ | — | LLM 可以直接生成符合 IEC 61131-3 标准的结构化 文本代码 | 生成符合国际标准的代码,提供智能提示和代码生成支持 | |
| 生产自动化与优化 | 文献[ | — | 开发了基于 LLM 的智能工业生产自动化系统,通过实时数据分析优化生产线运行 | 集成 Langchain 和 METAGPT 框架,数据驱动的智能决策 |
| 文献[ | Control-Agent | 优化控制系统设计过程,根据实时反馈迭代优化控制器参数 | LLM 代理与控制专业知识的融合,自动调整控制器 | |
| 网络安全防护 | 文献[ | LLMPot | 将 LLM 应用于 ICS 蜜罐设计,自动化配置真实蜜罐环境 | 自动化配置,高效模拟工业协议和设备特性 |
| 建筑自动化与生产控制 | 文献[ | — | 探索在建筑 HVAC 系统中应用 LLM 的可能性 | 处理异构任务和应对动态变化的能力更强 |
| 文献[ | — | 通过数字孪生系统为生产过程的智能化控制提供基础 | 建立细粒度和粗粒度控制接口,支持生产任务的动态规划和控制 |
| [1] | BHAMARE D, ZOLANVARI M, ERBAD A, et al. Cybersecurity for Industrial Control Systems: A Survey[EB/OL]. (2019-11-19)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404819302172. |
| [2] | ASGHAR M R, HU Qinwen, ZEADALLY S. Cybersecurity in Industrial Control Systems: Issues, Technologies, and Challenges[EB/OL]. (2019-12-24)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1389128619306292. |
| [3] | CONTI M, DONADEL D, TURREN F. A Survey on Industrial Control System Testbeds and Datasets for Security Research[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(4): 2248-2294. |
| [4] | KNOWLES W, PRINCE D, HUTCHISON D, et al. A Survey of Cyber Security Management in Industrial Control Systems[J]. International Journal of Critical Infrastructure Protection, 2015, 9: 52-80. |
| [5] | MCLAUGHLIN S, KONSTANTINOU C, WANG X, et al. The Cybersecurity Landscape in Industrial Control Systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(5): 1039-1057. |
| [6] |
LAI Yingxu, LIU Zenghui, CAI Xiaotian, et al. Research on Intrusion Detection of Industrial Control System[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(2): 143-156.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017036 |
| [7] | SU W, ANTONIOU A, EAGLE C. Cyber Security of Industrial Communication Protocols[C]// IEEE. The 22nd IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA). New York: IEEE, 2017: 1-4. |
| [8] | MODBUS. Modbus Application Protocol Specification[EB/OL]. (2012-04-26)[2024-11-15]. https://www.modbus.org/docs/Modbus_Application_Protocol_V1_1b3.pdf. |
| [9] | MODBUS. MODBUS/TCP Security, Protocol Specification[EB/OL]. (2021-07-30)[2024-11-15]. https://www.modbus.org/docs/MB-TCP-Security-v36_2021-07-30.pdf. |
| [10] | SHAHZAD A, LEE M, LEE Y K, et al. Real Time MODBUS Transmissions and Cryptography Security Designs and Enhancements of Protocol Sensitive Information[J]. Symmetry, 2015, 7(3): 1176-1210. |
| [11] | CURTIS K. A DNP3 Protocol Primer[EB/OL]. (2005-03-20)[2024-11-15]. https://www.dnp.org/Portals/0/AboutUs/DNP3%20Primer%20Rev%20A.pdf. |
| [12] | GE H. Overview of DNP3 Security Version 6[EB/OL]. (2020-01-21)[2024-11-15]. https://www.dnp.org/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket=hyvYMYugaQI%3D&tabid=66&portalid=0&mid=447&forcedownload=true. |
| [13] | MAJDALAWIEH M, PARISI-PRESICCE F, WIJESekera D. DNP Sec: Distributed Network Protocol Version 3 (DNP3) Security Framework[J]. Computer, Information, and Systems Sciences, and Engineering, 2006(1): 227-234. |
| [14] | KLEINMANN A, WOOL A. Accurate Modeling of the Siemens S7 SCADA Protocol for Intrusion Detection and Digital Forensics[J]. Journal of Digital Forensics, Security and Law, 2014, 9(2): 37-50. |
| [15] | CHENG Lei, LI Donghong, MA Liang. The Spear to Break the Security Wall of S7 CommPlus[J]. Blackhat USA, 2017, 17: 1-12. |
| [16] | DIAS A L, SESTITO G S, TURCATO A C, et al. Panorama, Challenges and Opportunities in PROFINET Protocol Research[C]// IEEE. The 13th IEEE International Conference on Industry Applications (INDUSCON). New York: IEEE, 2018: 186-193. |
| [17] | NIEMANN K H. IT Security Extensions for PROFINET[C]// IEEE. The 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN). New York: IEEE, 2019: 407-412. |
| [18] | SHIREY R. Internet Security Glossary(Version 2)[EB/OL]. (2007-07-08)[2024-11-15]. https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/pdfrfc/rfc4949.txt.pdf. |
| [19] | MOORE S, YAMPOLSK I M, GATLIN J, et al. Buffer Overflow Attack’s Power Consumption Signatures[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Software Security, Protection, and Reverse Engineering. New York: ACM, 2016: 1-7. |
| [20] | HOFFMAN M. Vulnerabilities on the Wire: Mitigations for Insecure ICS Device Communication[J]. Cyber Security: A Peer-Reviewed Journal, 2020, 4(2): 160-181. |
| [21] | THOMAS R J, CHOTHIA T. Learning from Vulnerabilities-Categorising, Understanding and Detecting Weaknesses in Industrial Control Systems[C]//Springer. Computer Security:ESORICS 2020 International Workshops, CyberICPS, SECPRE, and ADIoT. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 100-116. |
| [22] | GONZALEZ D, ALHENAKI F, MIRAKHORLI M. Architectural Security Weaknesses in Industrial Control Systems (ICS) an Empirical Study Based on Disclosed Software Vulnerabilities[C]// IEEE. International Conference on Software Architecture (ICSA). New York: IEEE, 2019: 31-40. |
| [23] | ALI S, AL B T, NADIR Z, et al. ICS/SCADA System Security for CPS[J]. Cyber Security for Cyber Physical Systems, 2018, 768: 89-113. |
| [24] | UPADHYAY D, SAMPALLI S. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Systems: Vulnerability Assessment and Security Recommendations[EB/OL]. (2019-11-13)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404819302068. |
| [25] | WANG Zibo, ZHANG Yaofang, CHEN Yilu, et al. A Survey on Programmable Logic Controller Vulnerabilities, Attacks, Detections, and Forensics[EB/OL]. (2023-03-17)[2024-11-15]. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9717/11/3/918. |
| [26] | QASSIM Q S, JAMIL N, DAUD M, et al. A Review of Security Assessment Methodologies in Industrial Control Systems[J]. Information & Computer Security, 2019, 27(1): 47-61. |
| [27] | EL-KADY A H, HALIM S, EL-HALWAGI M M, et al. Analysis of Safety and Security Challenges and Opportunities Related to Cyber-Physical Systems[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 173: 384-413. |
| [28] | MEKDAD Y, BERNIERI G, CONTI M, et al. A Threat Model Method for ICS Malware: The TRISIS Case[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Computing Frontiers. New York: ACM, 2021: 221-228. |
| [29] | YILMAZ E N, CIYLAN B, GONEN S, et al. Cyber Security in Industrial Control Systems: Analysis of DoS Attacks Against PLCs and the Insider Effect[C]// IEEE. The 6th International Istanbul Smart Grids and Cities Congress and Fair (ICSG). New York: IEEE, 2018: 81-85. |
| [30] | YANG Kai, WANG Haining, SUN Limin. An Effective Intrusion-Resilient Mechanism for Programmable Logic Controllers Against Data Tampering Attacks[EB/OL]. (2022-02-23)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166361522000082. |
| [31] | WLAZLO P, SAHU A, MAO Z, et al. Man in the Middle Attacks and Defence in A Power System Cyber Physical Testbed[J]. IET Cyber Physical Systems: Theory & Applications, 2021, 6(3): 164-177. |
| [32] | RAJESH L, SATYANARAYANA P. Detection and Blocking of Replay, False Command, and False Access Injection Commands in Scada Systems with Modbus Protocol[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 21: 1-15. |
| [33] | HE Weigang, MAO Xia, SU Ting, et al. Data Flow Testing for PLC Programs via Dynamic Symbolic Execution[C]// IEEE. 28th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC). New York: IEEE, 2021: 152-160. |
| [34] | LI Haonan, HAO Yu, ZHAI Yizhuo, et al. Enhancing Static Analysis for Practical Bug Detection: An LLM-Integrated Approach[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Programming Languages, 2024, 8: 474-499. |
| [35] | RAJPUT P H N, DOUMANIDIS C, MANIATAKOS M. {ICSPatch}: Automated Vulnerability Localization and {Non-Intrusive} Hotpatching in Industrial Control Systems Using Data Dependence Graphs[C]//USENIX. 32nd USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 23). Berkeley: USENIX, 2023: 6861-6876. |
| [36] | BALDONI R, COPPA E, D’ELIA D C, et al. A Survey of Symbolic Execution Techniques[J]. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2018, 51(3): 1-39. |
| [37] | SHI Jianqi, CHEN Yinghao, LI Qin, et al. Automated Test Cases Generator for IEC 61131-3 Structured Text Based Dynamic Symbolic Execution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2024, 73(4): 1048-1059. |
| [38] | HE Weigang, SHI Jianqi, SU Ting, et al. Automated Test Generation for IEC 61131-3 ST Programs via Dynamic Symbolic Execution[EB/OL]. (2021-02-11)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167642321000010. |
| [39] | GUO Shengjian, WU Meng, WANG Chao. Symbolic Execution of Programmable Logic Controller Code[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2017 11th Joint Meeting on Foundations of Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2017: 326-336. |
| [40] | KURIAN E, BRIOLA D, BRAIONE P, et al. Automatically Generating Test Cases for Safety-Critical Software via Symbolic Execution[EB/OL]. (2023-02-02)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121223000249. |
| [41] | SUBRAMANYAN P, MALIK S, KHATTRI H, et al. Verifying Information Flow Properties of Firmware Using Symbolic Execution[C]// IEEE. 2016 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE). New York: IEEE, 2016: 337-342. |
| [42] | CHEN Jinshan, YU Sihang, XIE Xuanxuan, et al. Research on Static Reverse Analysis Technology for Security Detection of Power Industrial Control Software[C]// IEEE. 2023 the 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Power and Systems (ICIPS). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-9. |
| [43] | YANG Zeyu, HE Liang, YU Hua, et al. Reverse Engineering Physical Semantics of PLC Program Variables Using Control Invariants[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 20th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems. New York: ACM, 2022: 548-562. |
| [44] | CECCATO M, DRIOUICH Y, LANOTTE R, et al. Towards Reverse Engineering of Industrial Physical Processes[C]// Springer. European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 273-290. |
| [45] | MA Rongkuan, ZHENG Hao, WANG Jingyi, et al. Automatic Protocol Reverse Engineering for Industrial Control Systems with Dynamic Taint Analysis[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2022, 23(3): 351-360. |
| [46] | QASIM S A, SMITH J M, AHMED I. Control Logic Forensics Framework Using Built-in Decompiler of Engineering Software in Industrial Control Systems[EB/OL]. (2020-09-30)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666281720302626. |
| [47] | WU Zewei, SHU Min, SHI Junzheng, et al. How to Reverse Engineer ICS Protocols using Pair-HMM[C]// Springer. Information and Communication Technology for Intelligent Systems:Proceedings of ICTIS 2018. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 115-125. |
| [48] | SHIM K S, GOO Y H, LEE M S, et al. Clustering Method in Protocol Reverse Engineering for Industrial Protocols[EB/OL]. (2020-06-24)[2024-11-15]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/nem.2126. |
| [49] | WANG Rui, SHIYijie, DING Jinkou. Reverse Engineering of Industrial Control Protocol by XGBoost with V-Gram[C]// IEEE. IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC). New York: IEEE, 2020: 172-176. |
| [50] | QIN Zhen, YANG Zeyu, GENG Yangyang, et al. Reverse Engineering Industrial Protocols Driven by Control Fields[C]// IEEE. IEEE INFOCOM 2024-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. New York: IEEE, 2024: 2408-2417. |
| [51] | WANG Xiaowei, LYU Kezhi, LI Bo. IPART: An Automatic Protocol Reverse Engineering Tool Based on Global Voting Expert for Industrial Protocols[J]. International Journal of Parallel, Emergent and Distributed Systems, 2020, 35(3): 376-395. |
| [52] | NING Bowei, ZONG Xuejun, HE Kan, et al. PREIUD: An Industrial Control Protocols Reverse Engineering Tool Based on Unsupervised Learning and Deep Neural Network Methods[EB/OL]. (2023-03-11)[2024-11-15]. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-8994/15/3/706. |
| [53] | WANG Qun, SUN Zhonghao, WANG Zhangquan, et al. A Practical Format and Semantic Reverse Analysis Approach for Industrial Control Protocols[EB/OL]. (2021-03-13)[2024-11-15]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1155/2021/6690988. |
| [54] | QASIM S A, JO W, AHMED I. Pree: Heuristic Builder for Reverse Engineering of Network Protocols in Industrial Control Systems[EB/OL]. (2023-07-07)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666281723000744. |
| [55] | SUN Yue, LI Zhi, LYU Shichao, et al. Spenny: Extensive ICS Protocol Reverse Analysis via Field Guided Symbolic Execution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 20(6): 4502-4518. |
| [56] | LIU Yuhuan, ZHANG Fengyun, DING Yulong, et al. Sub-Messages Extraction for Industrial Control Protocol Reverse Engineering[J]. Computer Communications, 2022, 194: 1-14. |
| [57] | KIM J S, SHON T. Field Classification-Based Novel Fuzzing Case Generation for ICS Protocols[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2018, 74(9): 4434-4450. |
| [58] | BYTES A, RAJPUT P H N, DOUMANIDIS C, et al. FieldFuzz: In Situ Blackbox Fuzzing of Proprietary Industrial Automation Runtimes via the Network[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and Defenses. New York: ACM, 2023: 499-512. |
| [59] | CHE Xin, GENG Yangyang, ZHANG Ge, et al. Fuzzing Technology Based on Information Theory for Industrial Proprietary Protocol[EB/OL]. (2023-07-11)[2024-11-15]. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/12/14/3041. |
| [60] | LUO Zhengxiong, ZUO Feilong, JIANG Yu, et al. Polar: Function Code Aware Fuzz Testing of ICS Protocol[J]. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 2019, 18(5): 1-22. |
| [61] | DONG Guofang, SUN Pu, SHI Wenbo, et al. A Novel Valuation Pruning Optimization Fuzzing Test Model Based on Mutation Tree for Industrial Control Systems[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 70: 896-902. |
| [62] | LIU Puzhuo, ZHENG Yaowen, SONG Zhanwei, et al. Fuzzing Proprietary Protocols of Programmable Controllers to Find Vulnerabilities That Affect Physical Control[EB/OL]. (2022-04-09)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1383762122000625. |
| [63] | ZUO Feilong, LUO Zhengxiong, YU Junze, et al. Vulnerability Detection of ICS Protocols via Cross-State Fuzzing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2022, 41(11): 4457-4468. |
| [64] | ILGNER P, FUJDIAK R. Fuzzing Framework for IEC 60870-5-104 Protocol[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2022: 190-194. |
| [65] | ZHANG Dianbo, WANG Jianfei, ZHANG Hua. Peach Improvement on Profinet-DCP for Industrial Control System Vulnerability Detection[C]// Atlantis Press. 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Computer Engineering and Electronics. Paris: Atlantis Press, 2015: 1622-1627. |
| [66] | LUO Zhengxiong, ZUO Feilong, SHEN Yuheng, et al. ICS Protocol Fuzzing: Coverage-Guided Packet Crack and Generation[C]// IEEE. 57th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-6. |
| [67] | VOYIATZIS A G, KATSIGINIS K, KOUBIAS S. A Modbus/TCP Fuzzer for Testing Internetworked Industrial Systems[C]// IEEE. 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-6. |
| [68] | ZHANG Yang, FANG Dongliang, LIU Puzhuo, et al. MSGFuzzer: Message Sequence Guided Industrial Robot Protocol Fuzzing[C]// IEEE. Conference on Software Testing Verification and Validation (ICST). New York: IEEE, 2024: 140-150. |
| [69] | ZHAO Hui, LI Zhihui, WEI Hansheng, et al. SeqFuzzer: An Industrial Protocol Fuzzing Framework from a Deep Learning Perspective[C]// IEEE. The 12th IEEE Conference on Software Testing, Validation and Verification (ICST). New York: IEEE, 2019: 59-67. |
| [70] | HU Zhicheng, SHI Jianqi, HUANG Yanhong, et al. GANFuzz: A GAN-Based Industrial Network Protocol Fuzzing Framework[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 15th ACM International Conference on Computing Frontiers. New York: ACM, 2018: 138-145. |
| [71] | YU Zhenhua, WANG Haolu, WANG Dan, et al. CGFuzzer: A Fuzzing Approach Based on Coverage-Guided Generative Adversarial Networks for Industrial IoT Protocols[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(21): 21607-21619. |
| [72] | WANYAN Hanxiao, LAI Yingxu, LIU Jing, et al. NCMFuzzer: Using Non-Critical Field Mutation and Test Case Combination to Improve the Efficiency of ICS Protocol Fuzzing[EB/OL]. (2024-03-16)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404824001123. |
| [73] |
LI Zhihui, ZHAO Hui, SHI Jianqi, et al. An Intelligent Fuzzing Data Generation Method Based on Deep Adversarial Learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 49327-49340.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2911121 |
| [74] | YANG Hongsen, HUANG Yuezhen, ZHANG Zhiyong, et al. A Novel Generative Adversarial Network-Based Fuzzing Cases Generation Method for Industrial Control System Protocols[EB/OL]. (2024-05-10)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045790624001964. |
| [75] | SUN Weifeng, ZHANG Bowei, DING Jianqiao, et al. MaskFuzzer: A MaskGAN-Based Industrial Control Protocol Fuzz Testing Framework[C]// IEEE. International Conference on Smart Internet of Things (SmartIoT). New York: IEEE, 2022: 51-57. |
| [76] | LYU Wanyou, XIONG Jiawen, SHI Jianqi, et al. A Deep Convolution Generative Adversarial Networks Based Fuzzing Framework for Industry Control Protocols[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2021, 32(2): 441-457. |
| [77] | LIN Peiyi, TIEN Chiawei, HUANG Tingchun, et al. ICPFuzzer: Proprietary Communication Protocol Fuzzing by Using Machine Learning and Feedback Strategies[J]. Cybersecurity, 2021, 4: 1-15. |
| [78] | WANG Wenpeng, CHEN Zhixiang, ZHENG Ziyang, et al. An Adaptive Fuzzing Method Based on Transformer and Protocol Similarity Mutation[EB/OL]. (2023-03-22)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404823001074. |
| [79] | ZONG Xuejun, LUO Wenjie, NING Bowei, et al. DiffusionFuzz: Fuzzing Framework of Industrial Control Protocols Based on Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 67795-67808. |
| [80] | SHAHZAD A A, MUSA S, et al. Industrial Control Systems (ICSs) Vulnerabilities Analysis and SCADA Security Enhancement Using Testbed Encryption[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication. New York: ACM, 2014: 1-6. |
| [81] | CHEN Yanru, YIN Fengming, HU Shunfang, et al. ECC-Based Authenticated Key Agreement Protocol for Industrial Control System[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 10(6): 4688-4697. |
| [82] | XU Jian, MENG Qingyu, WU Jun, et al. Efficient and Lightweight Data Streaming Authentication in Industrial Control and Automation Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 17(6): 4279-4287. |
| [83] | GUPTA D S, MAZUMDAR N, NAG A, et al. Secure Data Authentication and Access Control Protocol for Industrial Healthcare System[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2023, 14(5): 4853-4864. |
| [84] | GAICEANU M, STANCULESCU M, ANDREI P C, et al. Intrusion Detection on ICS and SCADA Networks[J]. Recent Developments on Industrial Control Systems Resilience, 2020, 255: 197-262. |
| [85] | YANG Huan, CHENG Liang, CHUAH M C. Deep-Learning-Based Network Intrusion Detection for SCADA Systems[C]// IEEE. Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1-7. |
| [86] | ORTEGA-FERNANDEZ I, SESTELO M, BURGUILLO J C, et al. Network Intrusion Detection System for DDoS Attacks in ICS Using Deep Autoencoders[J]. Wireless Networks, 2024, 30(6): 5059-5075. |
| [87] | ALI B S, ULLAH I, AL SHLOUL T, et al. ICS-IDS: Application of Big Data Analysis in AI-Based Intrusion Detection Systems to Identify Cyberattacks in ICS Networks[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2024, 80(6): 7876-7905. |
| [88] | ABBAS S G, OZMEN M O, ALSAHEEL A, et al. {SAIN}: Improving {ICS} Attack Detection Sensitivity via {State-Aware} Invariants[C]//USENIX. 33rd USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 24). Berkeley: USENIX, 2024: 6597-6613. |
| [89] | YANG Kai, LI Qiang, LIN Xiaodong et al. IFinger: Intrusion Detection in Industrial Control Systems via Register-Based Fingerprinting[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(5): 955-967. |
| [90] | JARDINE W, FREY S, GREEN B, et al. Senami: Selective Non-Invasive Active Monitoring for ICS Intrusion Detection[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Workshop on Cyber-Physical Systems Security and Privacy. New York: ACM, 2016: 23-34. |
| [91] | PONOMAREV S, ATKISON T. Industrial Control System Network Intrusion Detection by Telemetry Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2015, 13(2): 252-260. |
| [92] | LI Huiping, WANG Bin, XIE Xin. An Improved Content-Based Outlier Detection Method for ICS Intrusion Detection[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2020, 20: 1-15. |
| [93] | GRANAT A, HOFKEN H, SCHUBA M. Intrusion Detection of the ICS Protocol EtherCAT[C]// Springer. 2nd International Conference on Computer, Network Security and Communication Engineering. Heidelberg: Springer, 2017: 113-117. |
| [94] | MA Xinyin, FANG Gongfan, WANG Xinchao. LLM-Pruner: On the Structural Pruning of Large Language Models[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2023, 36: 21702-21720. |
| [95] | YAO Yifan, DUAN Jinhao, XU Kaidi, et al. A Survey on Large Language Model (LLM) Security and Privacy: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly[EB/OL]. (2024-03-01)[2024-11-15]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266729522400014X. |
| [96] | LIU Zihan, ZENG Ruinan, WANG Dongxia, et al. Agents4PLC: Automating Closed-Loop PLC Code Generation and Verification in Industrial Control Systems Using LLM-Based Agents[EB/OL]. (2024-10-18)[2024-11-15]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.14209. |
| [97] | FAKIH M, DHARMAJI R, MOGHADDAS Y, et al. LLM4PLC: Harnessing Large Language Models for Verifiable Programming of PLCs in Industrial Control Systems[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 46th International Conference on Software Engineering:Software Engineering in Practice. New York: ACM, 2024: 192-203. |
| [98] | KOZIOLEK H, GRUENER S, ASHIWAL V. ChatGPT for PLC/DCS Control Logic Generation[C]// IEEE. 28th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-8. |
| [99] | WANG Zihao, QIN Huijian. Intelligent Industrial Production Process Automatic Regulation System Based on LLM Agents[C]// IEEE. The 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Electromechanical Automation (AIEA). New York: IEEE, 2024: 133-137. |
| [100] | GUO Xingang, KEIVAN D, SYED U, et al. ControlAgent: Automating Control System Design via Novel Integration of LLM Agents and Domain Expertise[EB/OL]. (2024-10-17)[2024-11-15]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.19811. |
| [101] | VASILATOS C, MAHBOOBEH D J, LAMRI H, et al. LLMPot: Automated LLM-Based Industrial Protocol and Physical Process Emulation for ICS Honeypots[EB/OL]. (2024-05-09)[2024-11-15]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.05999. |
| [102] | SONG Lei, ZHANG Chuheng, ZHAO Li, et al. Pre-Trained Large Language Models for Industrial Control[EB/OL]. (2023-08-06)[2024-11-15]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.03028. |
| [103] | XIA Yuchen, SHENOY M, JAZDI N, et al. Towards Autonomous System: Flexible Modular Production System Enhanced with Large Language Model Agents[C]// IEEE. 28th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-8. |
| [1] | 陈红松, 刘新蕊, 陶子美, 王志恒. 基于深度学习的时序数据异常检测研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 364-391. |
| [2] | 解梦飞, 傅建明, 姚人懿. 基于LLM的多媒体原生库模糊测试研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 403-414. |
| [3] | 刘晨飞, 万良. 基于时空图神经网络的CAN总线入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 478-493. |
| [4] | 李海龙, 崔治安, 沈燮阳. 网络流量特征的异常分析与检测方法综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [5] | 武浩莹, 陈杰, 刘君. 改进Simon32/64和Simeck32/64神经网络差分区分器[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [6] | 金地, 任昊, 唐瑞, 陈兴蜀, 王海舟. 基于情感辅助多任务学习的社交网络攻击性言论检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [7] | 王鹃, 张勃显, 张志杰, 谢海宁, 付金涛, 王洋. 基于模糊测试的Java反序列化漏洞挖掘[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(1): 1-12. |
| [8] | 陈晓静, 陶杨, 吴柏祺, 刁云峰. 面向骨骼动作识别的优化梯度感知对抗攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [9] | 刘联海, 黎汇业, 毛冬晖. 基于图像凸包特征的CBAM-CNN网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1422-1431. |
| [10] | 徐茹枝, 张凝, 李敏, 李梓轩. 针对恶意软件的高鲁棒性检测模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [11] | 陈昊然, 刘宇, 陈平. 基于大语言模型的内生安全异构体生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1231-1240. |
| [12] | 张立强, 路梦君, 严飞. 一种基于函数依赖的跨合约模糊测试方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1038-1049. |
| [13] | 田钊, 牛亚杰, 佘维, 刘炜. 面向车联网的车辆节点信誉评估方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [14] | 张浩, 谢大智, 胡云晟, 叶骏威. 基于半监督学习的网络异常检测研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 491-508. |
| [15] | 张光华, 刘亦纯, 王鹤, 胡勃宁. 基于JSMA对抗攻击的去除深度神经网络后门防御方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 27
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 34
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||