信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 249-259.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.02.006
改进Simon32/64和Simeck32/64神经网络差分区分器
- 1.西安电子科技大学通信工程学院,西安 710071
2.河南省网络密码技术重点实验室,郑州 450001
3.陕西师范大学计算机科学学院,西安 710119
-
收稿日期:2024-05-22出版日期:2025-02-10发布日期:2025-03-07 -
通讯作者:陈杰 E-mail:jchen@mail.xidian.edu.cn -
作者简介:武浩莹(2000—),女,河北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为分组密码分析|陈杰(1979—),女,湖南,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为密码算法设计与分析|刘君(1993—),女,陕西,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为分组密码算法设计与分析 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62302285);河南省网络密码技术重点实验室研究课题(LNCT2022-A08)
Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64
WU Haoying1, CHEN Jie1,2( ), LIU Jun3
), LIU Jun3
- 1. School of Telecommunications Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
2. Henan Key Laboratory of Network Cryptography Technology, Zhengzhou 450001, China
3. School of Computer Science, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an 710119, China
-
Received:2024-05-22Online:2025-02-10Published:2025-03-07
摘要:
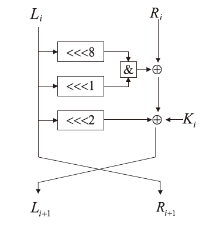
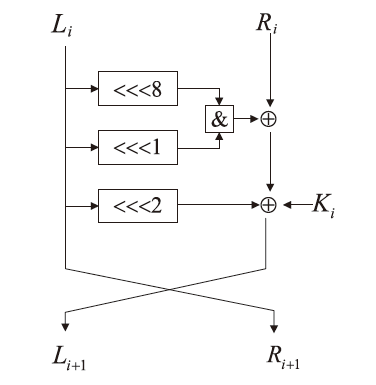
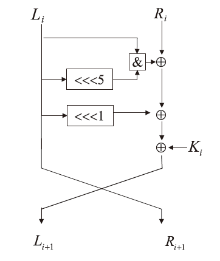
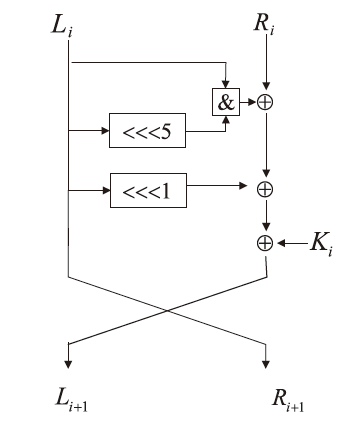
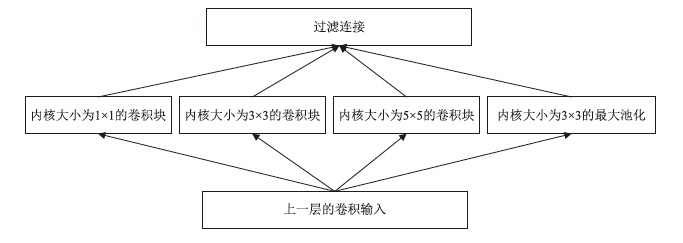
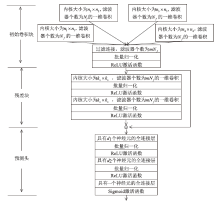
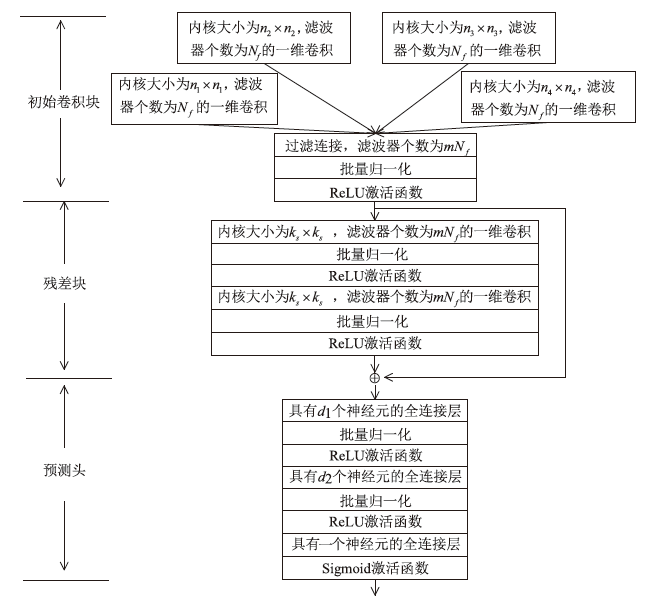
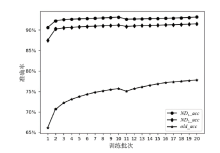
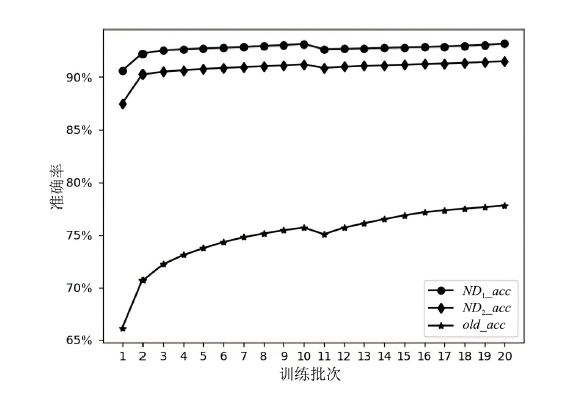
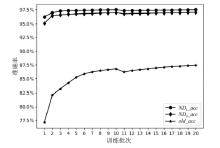
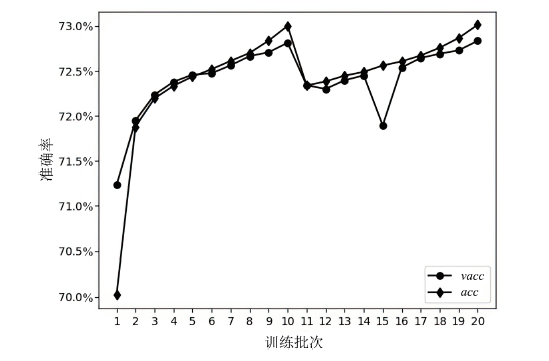
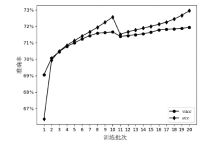
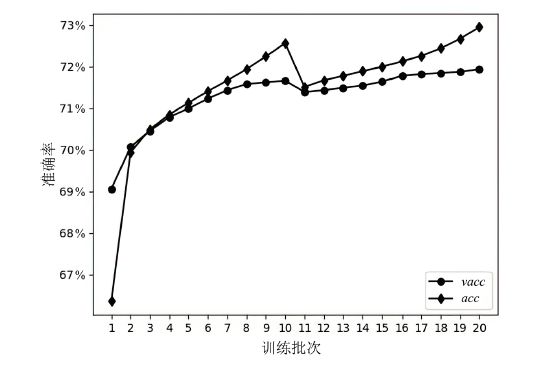
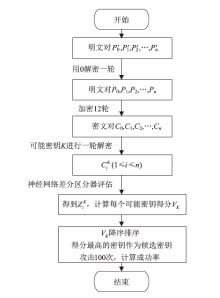
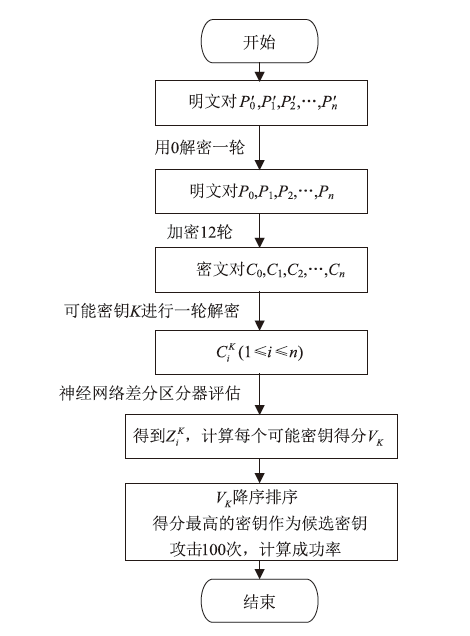
神经网络差分区分器具备良好的泛化能力和强大的学习能力,但目前仍缺乏完善且具有普适性的神经网络差分区分模型。为提升Simon32/64和Simeck32/64神经网络差分区分器的准确率和普适性,文章提出3个改进方向。首先,采用多密文对作为Simon32/64和Simeck32/64的输入,并将Inception网络模块引入神经网络模型,以改善过拟合现象。然后,将Simon32/64和Simeck32/64倒数第二轮的差分信息加入多密文对输入样本中,构造7~10轮和7~11轮神经网络差分区分器。最后,将多密文对与多面体差分结合,根据Simon32/64和Simeck32/64两种密码构造改进多面体差分区分器,提高已有多面体神经网络差分区分器的准确率。实验结果表明,8轮Simon32/64和Simeck32/64新型多面体神经网络差分区分器的准确率分别达到99.54%和99.67%。此外,利用10轮神经网络差分区分器对12轮Simon32/64和Simeck32/64开展最后一轮子密钥恢复攻击,在100次攻击实验中,攻击成功率分别达到86%和97%。
中图分类号:
引用本文
武浩莹, 陈杰, 刘君. 改进Simon32/64和Simeck32/64神经网络差分区分器[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 249-259.
WU Haoying, CHEN Jie, LIU Jun. Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 249-259.
使用本文
表1
Simon32/64和Simeck32/64多密文对神经网络差分区分器的准确率对比
| 密码 | 轮数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simon32/64 | 7 | 96.73 % | 99.22 % | 99.51 % | 99.16 % | 99.12 % |
| Simon32/64 | 8 | 76.76 % | 77.36 % | 80.38 % | 85.46 % | 89.21 % |
| Simon32/64 | 9 | 62.70 % | 64.38 % | 67.17 % | 62.84 % | 62.50 % |
| Simeck32/64 | 7 | 98.75 % | 99.78 % | 99.81 % | 99.96 % | 99.99 % |
| Simeck32/64 | 8 | 86.77 % | 91.38 % | 97.13 % | 97.31 % | 97.92 % |
| Simeck32/64 | 9 | 67.26 % | 68.58 % | 67.95 % | 66.98 % | 66.90 % |
| [1] | BOGDANOV A, KNUDSEN L R, LEANDER G, et al. PRESENT: An Ultra-Lightweight Block Cipher[C]// Springer. Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems-CHES 2007. Heidelberg: Springer, 2007: 450-466. |
| [2] | WU Wenling, ZHANG Lei. LBlock: A Lightweight Block Cipher[C]// Springer. Applied Cryptography and Network Security (ACNS 2011). Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 327-344. |
| [3] | BEAULIEU R, SHORS D, SMITH J, et al. The Simon and Speck Families of Lightweight Block Ciphers[C]// IEEE. 2015 52nd ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-6. |
| [4] | YANG Gangqiang, ZHU Bo, SUDER V, et al. The Simeck Family of Lightweight Block Ciphers[C]// Springer. Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems-CHES 2015. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 307-329. |
| [5] | WANG Meiqin. Differential Cryptanalysis of Reduced-Round PRESENT[C]// Springer. Progress in Cryptology-AFRICACRYPT 2008. Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 40-49. |
| [6] | WANG Ning, WANG Xiaoyun, JIA Keting. Improved Impossible Differential Attack on Reduced-Round LBlock[C]// Springer. Information Security and Cryptology-ICISC 2015. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 136-152. |
| [7] | LI Mingming, GUO Jiansheng, CUI Jingyi, et al. Impossible Differential Cryptanalysis of SPECK[C]// Springer. Trusted Computing and Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 16-31. |
| [8] | SUN Ling, FU Kai, WANG Meiqin. Improved Zero-Correlation Cryptanalysis on SIMON[C]// Springer. Information Security and Cryptology. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 125-143. |
| [9] | QIAO Kexin, HU Lei, SUN Siwei. Differential Analysis on Simeck and SIMON with Dynamic Key-Guessing Techniques[C]// Springer. Information Systems Security and Privacy. Heidelberg: Springer, 2017: 64-85. |
| [10] | GOHR A. Improving Attacks on Round-Reduced Speck32/64 Using Deep Learning[C]// Springer. Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO 2019. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 150-179. |
| [11] | PAL D, MANDAL U, DAS A, et al. Deep Learning Based Differential Classifier of PRIDE and RC5[C]// Springer. Applications and Techniques in Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2023: 46-58. |
| [12] | JAIN A, KOHLI V, MISHRA G. Deep Learning-Based Differential Distinguisher for Lightweight Cipher PRESENT[EB/OL]. (2020-07-12)[2024-04-30]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/846, 2020-07-12/2023-1-17. |
| [13] | HOU Zezhou, CHEN Shaozhen, REN Jiongjiong. Research and Application of Deep Learning on Differential Distinguisher of Block Cipher[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(5): 1893-1906. |
| 侯泽洲, 陈少真, 任炯炯. 深度学习在分组密码差分区分器上的研究应用[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(5): 1893-1906. | |
| [14] | ZHANG Liu, WANG Zilong, WANG Baocang. Improving Differential-Neural Cryptanalysis with Inception[EB/OL]. (2022-02-20)[2024-04-30]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2022/183, 2022-02-10/2023-1-17. |
| [15] | BENAMIRA A, GERAULT D, PEYRIN T, et al. A Deeper Look at Machine Learning-Based Cryptanalysis[C]// Springer. Cryptology-EUROCRYPT 2021. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 805-835. |
| [16] | BAKSI A. Machine Learning-Assisted Differential Distinguishers for Lightweight Ciphers[C]// Springer. Classical and Physical Security of Symmetric Key Cryptographic Algorithms. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 141-162. |
| [17] | HOU Zezhou, REN Jiongjiong, CHEN Shaozhen. Improve Neural Distinguisher for Cryptanalysis[EB/OL]. (2021-08-06)[2024-04-30]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2021/1017, 2021-08-06/2023-1-17. |
| [18] | CHEN Yi, SHEN Yantian, YU Hongbo, et al. A New Neural Distinguisher Considering Features Derived from Multiple Ciphertext Pairs[J]. The Computer Journal, 2023, 66(6): 1419-1433. |
| [19] | FU Chaohui, DUAN Ming, WEI Qiang, et al. Polytopic Differential Attack Based on Deep Learning and Its Application[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2021, 8(4): 591-600. |
| [20] | BIHAM E, SHAMIR A. Differential Cryptanalysis of DES-Like Cryptosystems[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 1991, 4(1): 63-72. |
| [21] | TIESSEN T. Polytopic Cryptanalysis[C]// Springer. Cryptology-EUROCRYPT 2016. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 214-239. |
| [22] | SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going Deeper with Convolutions[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-9. |
| [23] | YANG Xiaoxue, CHEN Jie, HAN Lidong. Application of Deep Learning in Differential Cryptanalysis of ARX Block Ciphers[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2022, 9(5): 923-935. |
| [24] | SU Hengchuan, ZHU Xuanyong, MING Duan.Polytopic Attack on Round-Reduced Simon32/64 Using Deep Learning[C]// Springer. Information Security and Cryptology. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 3-20. |
| [1] | 李海龙, 崔治安, 沈燮阳. 网络流量特征的异常分析与检测方法综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [2] | 金地, 任昊, 唐瑞, 陈兴蜀, 王海舟. 基于情感辅助多任务学习的社交网络攻击性言论检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [3] | 陈晓静, 陶杨, 吴柏祺, 刁云峰. 面向骨骼动作识别的优化梯度感知对抗攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [4] | 徐茹枝, 张凝, 李敏, 李梓轩. 针对恶意软件的高鲁棒性检测模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [5] | 田钊, 牛亚杰, 佘维, 刘炜. 面向车联网的车辆节点信誉评估方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [6] | 张光华, 刘亦纯, 王鹤, 胡勃宁. 基于JSMA对抗攻击的去除深度神经网络后门防御方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [7] | 徐子荣, 郭焱平, 闫巧. 基于特征恶意度排序的恶意软件对抗防御模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| [8] | 杨志鹏, 刘代东, 袁军翼, 魏松杰. 基于自注意力机制的网络局域安全态势融合方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 398-410. |
| [9] | 江荣, 刘海天, 刘聪. 基于集成学习的无监督网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [10] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [11] | 赵鹏程, 于俊清, 李冬. 一种基于深度学习的SRv6网络流量调度优化算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 272-281. |
| [12] | 金志刚, 丁禹, 武晓栋. 融合梯度差分的双边校正联邦入侵检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 293-302. |
| [13] | 张选, 万良, 罗恒, 杨阳. 基于两阶段图学习的僵尸网络自动化检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(12): 1933-1947. |
| [14] | 印杰, 陈浦, 杨桂年, 谢文伟, 梁广俊. 基于人工智能的物联网DDoS攻击检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1615-1623. |
| [15] | 魏金侠, 黄玺章, 付豫豪, 李婧, 龙春. 基于全局特征学习的挖矿流量检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1506-1514. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 45
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 70
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||