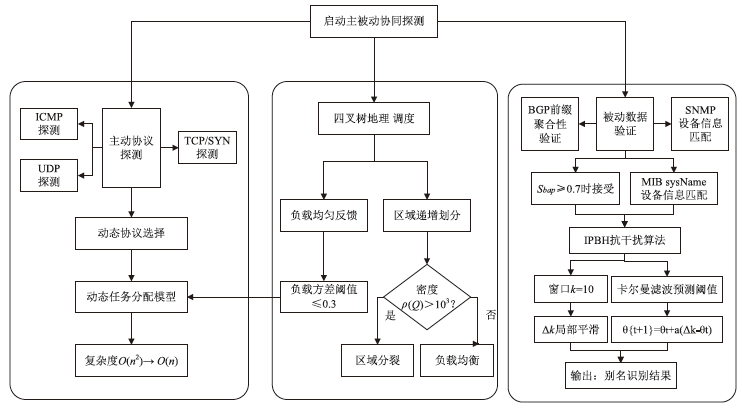
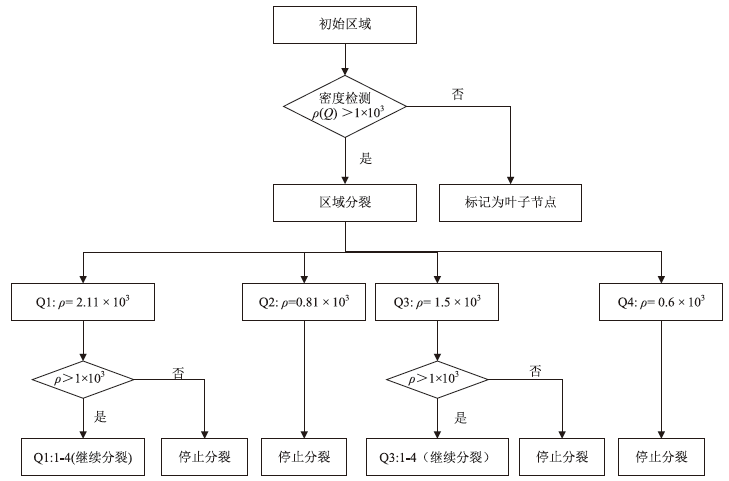
Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1863-1877.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.12.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
An Efficient Method for Router Alias Identification with Active-Passive Collaboration
- 1. College of Information Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266160, China
2. Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100093, China
3. Beijing Zhidao Chuangyu Information Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100020, China
-
Received:2025-10-10Online:2025-12-10Published:2026-01-06 -
Contact:HU Dan E-mail:hudan@stu.ouc.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HU Dan, YANG Jilong. An Efficient Method for Router Alias Identification with Active-Passive Collaboration[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1863-1877.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.12.003
| 类型 | 核心原理 | 优势 | 局限性 | 代表方法 | 假阳率 | 复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主动 探测法 | 发送定制探测包分析IPID/TTL等特征 | 接口覆盖率高(大于85%) | 受ECMP干扰假阳率高 | MBT[ Ally [ | 1.8%~ 3.5% | O(n2) |
| 被动 监测法 | 解析BGP/SNMP日志构建别名关系 | 无需主动流量注入 | 数据碎片化 (覆盖率小于60%) | BGP-Miner[ | — | O(n) |
| 混合 方法 | 融合主被动数据互补验证,动态阈值调整/自适应路径探测 | 抗路径跳变干扰,噪声鲁棒性提升 | 任务调度低(负载方差大于等于0.65),实时性不足(延迟大于等于15ms) | Hybrid Alias[ | 1.20% | O(n2) |
| 分类 | 具体内容 |
|---|---|
| 硬件平台 | 集群配置:8台Intel Xeon Platinum 8375C服务器(32核/64线程,主频3.6 GHz);内存:512 GB DDR4(ECC校验); 网络:10 Gbps双网卡(RDMA支持); 存储:NVMe SSD阵列(200 TB,IOPS 1M) |
| 软件工具 | 主动探测:Python 3.10 + Scapy 2.4.5(四协议探测包定制); 被动监测:BGPStream 2.0(BGP更新解析)+ Net-SNMP 5.9(SNMPv3加密查询); 数据处理:PostgreSQL 14(拓扑关系存储)+ Redis 6.2(实时任务队列)+ Spark 3.3(分布式计算) |
| 数据集与 基准真值 | 数据集:CAIDA2023公开数据集(120万路由器接口,IPv4占比92%),注入25%均匀分布IPID噪声(模拟Linux RFC7739); 基准真值:RIPE Atlas平台(10,000+全球探针)主动探测 + IRR数据库(路由前缀聚合性验证) + 人工标注5%高置信度别名对 |
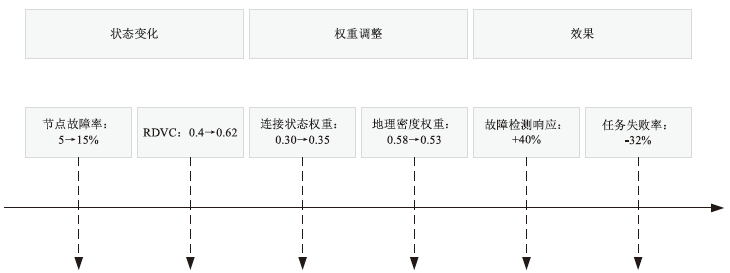
| 噪声与干扰模拟 | 动态负载均衡:配置3条ECMP等价路径,每5 min修改哈希种子强制路径切换; IPID随机化:在25%接口响应中随机替换IPID值(δ=???,均匀分布U(-δ,δ)); 突发流量:基线1 Gbps + 瞬时3 Gbps DDoS流量(持续10 min) |
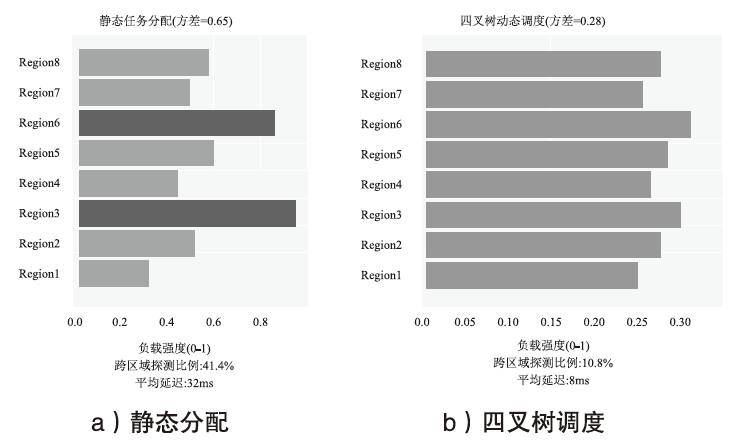
| 指标 | 静态分配 | 四叉树调度 (本文) | 提升率 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 跨区域探测 比例 | 41.40%±1.20% | 10.80%±0.80% | 73.9% | 本文实验(3次均值±标准差) |
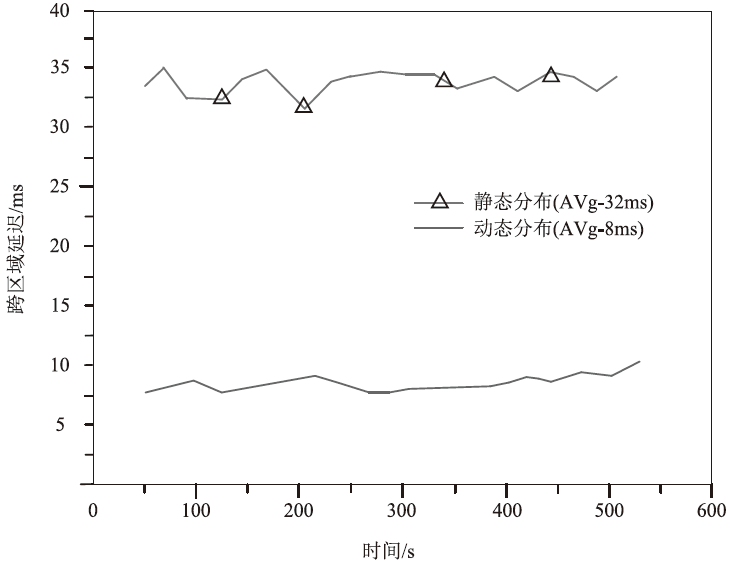
| 平均延迟/ms | 32±3 | 8±1 | 75.0% | CAIDA2023数据集(子集抽样) |
| ECMP假阳率 | 1.80%±0.20% | 0.90%±0.10% | 50.0% | 文献[3]对比实验(p<0.01) |
| 任务分配耗时 /s/万设备 | 42.3±2.5 | 12.3±0.9 | 70.9% | 文献[24]优化验证(O(n2)→O(n)) |
| 负载均衡度 (方差) | 0.65±0.05 | 0.28±0.03 | 56.9% | 公式(2-4)计算结果(负载反馈模型) |
| 设备覆盖率 | 85.10%±0.70% | 98.50%±0.40% | 13.4% | CAIDA2023数据集(全量验证) |
| 故障节点 剔除率 | 未实现 | 90%±2% | 新增 | 文献[24]异常清洗 |
| 带宽资源消耗 | 100% | 82%±3% | 18.0% | 本文实验 |
| 方法 | 假阳率 | 效率(s/万设备) | 准确率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBT [ | 1.8%±?.?% | 42.3±1.5 | 72.0%±?.?% |
| RadarGun [ | 2.5%±?.?% | 28.9±1.2 | 75.0%±?.?% |
| BGP-Miner [ | 1.5%±?.?% | - | 65.0%±?.?% |
| Hybrid Alias [ | 1.2%±?.?% | 28.9±1.0 | 78.0%±?.?% |
| DynaMap[18] | 1.0%±?.?% | 35.6.±1.8 | 76.8%±?.6% |
| FastAlias2023 [ | 1.5%±?.?% | 15.6±0.8 | 76.3%±?.?% |
| NoiseShield [ | 0.8%±?.?% | 15.6±0.9 | 83.0%±?.?% |
| GNN4Route[ | 1.0%±?.?% | 11.5±0.7 | 85.3%±?.?% |
| FedAlias[ | 1.1%±?.?% | 9.8±0.5 | 85.1%±?.?% |
| PathAttn[ | 0.9%±?.?% | 28.9±1.2 | 83.7%±?.?% |
| 本文方法 | 0.9%±?.?% | 4.1±0.3 | 90.1%±?.?% |
| 权重策略 | 参数范围 | 负载均衡度(方差) | 冗余 探测率 | 任务耗时 (s/万设备) | 实验条件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 传统静态 分配 | 0.50:0.20:0.20 | 0.65±0.05 | 41.4%±1.5% | 42.3±2.5 | 固定轮询调度,无地理优化 |
| 基础动态 分配 | 0.50:0.30:0.20 | 0.42±0.03 | 22.5%±0.8% | 12.3±0.9 | 四叉树索引,无负载反馈 |
| 负载优先 | 0.60:0.20:0.20 | 0.35±0.02 | 18.3%±0.6% | 10.9±0.7 | 网格搜索(α∈[0.5, 0.7]) |
| 延迟优先 | 0.20:0.60:0.20 | 0.41±0.04 | 21.4%±1.0% | 9.7±0.5 | 网格搜索(β∈[0.2 0.4]) |
| 本文动态 优化 | 0.58:0.30:0.12 | 0.28±0.01 | 10.8%±0.5% | 4.1±0.3 | 自适应调整(反馈机制) |
| 方法 | 准确率 | 假阳率 | 任务耗时 (s/万设备) | 关键抗干扰 机制 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBT[4] | 72.0%± 1.2% | 1.8%± 0.2% | 42.3±2.5 | IPID全局 连续性 | 静态调度 |
| RadarGun[6] | 75.0%± 0.9% | 2.5%± 0.3% | 28.9±1.2 | IPID局部 相似性 | (O(n2)复杂度) |
| APAR[9] | 68.3%± 1.5% | 2.1%± 0.4% | 36.7±1.8 | 多路径探测 | 混合方法 |
| DynaMap[18] | 76.8%± 0.6% | 1.0%± 0.2% | 35.6±1.8 | 动态调整探测 | 混合方法 |
| FastAlias2023[19] | 76.3%± 0.6% | 1.5%± 0.3% | 15.6±0.8 | 自适应路径 探测 | 混合方法 |
| NoiseShield[20] | 83.0%± 0.8%* | 0.8%± 0.1%* | 15.6±0.9 | 静态噪声过滤 | 随机森林 模型 |
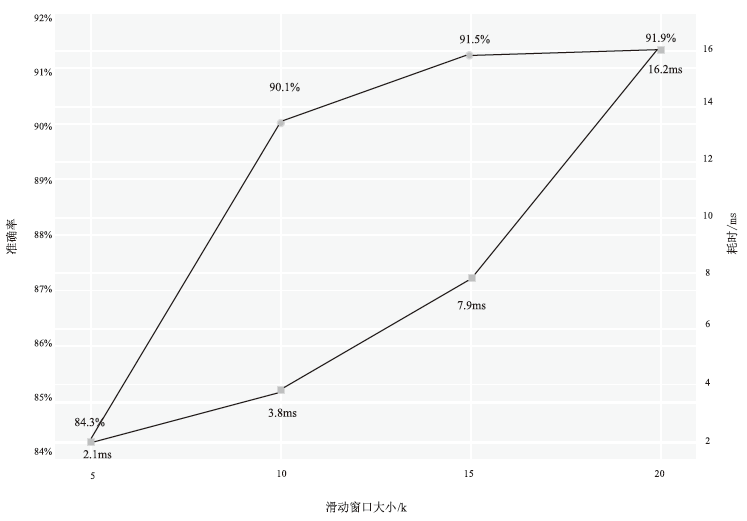
| IPBH算法 (本文) | 90.1%± 0.4%*** | 0.9%± 0.1% | 4.1±0.3 | 滑动窗口(k=10)+动态阈值 | 本文实验 |
| [1] |
SPRING N, MAHAJAN R, WETHERALL D. Measuring ISP Topologies with Rocketfuel[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2002, 32(4): 133-145.
doi: 10.1145/964725.633039 URL |
| [2] | KUMAR A, LEE T, KATTA N, et al. ECMP Load Balancing in the Wild: A Measurement Study of Path Instability in SDN[C]// ACM.The 2020 Conference on Emerging Networking Experiments and Technologies (CoNEXT). New York: ACM, 2020: 1-14. |
| [3] | FELDMANN A, LUCKIE M, REXFORD J, et al. The Economic Cost of Internet Infrastructure Misconfigurations: A Global ISP Perspective[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2019, 49(4): 2-10. |
| [4] | BRENNER-BARR A, BEN-ARTZI A, RAMI G, et al. Detecting and Mapping Routers with Monotonic Bounds Test[C]// USENIX. The 2011 ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. Berkeley: USENIX, 2011: 387-400. |
| [5] | BEVERLY R, BERGER A. Leveraging IP Identifier for Coarse Router Classification[C]// Springer. Passive and Active Measurement Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 183-192. |
| [6] | SHERWOOD R, SPRING N. Touring the Internet in a TCP Sidecar[C]// ACM. The 6th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. New York: ACM, 2006: 339-344. |
| [7] |
KEYS K, HYUN Y, LUCKIE M, et al. Internet-Scale IPv4 Alias Resolution with MIDAR[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2013, 21(2): 383-399.
doi: 10.1109/TNET.2012.2198887 URL |
| [8] | ZHOU Jun, ZHANG Jian, YANG Shunfeng. Stochastic Modeling and Convergence Analysis of Internet Routers[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(2): 207-214. |
| [9] | YUAN Fuxiang. Analysis of Network Characteristics for IP Positioning[D]. Zhengzhou: Information Engineering University, 2020. |
| 袁福祥. 面向IP定位的网络特性分析[D]. 郑州: 战略支援部队信息工程大学, 2020. | |
| [10] | DONNET B, FRIEDMAN T. Internet Topology Discovery: A Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2007, 9(4): 56-69. |
| [11] | KOUNTOURIS A, KINTIS P, CHEN P, et al. Exposed! A Large-Scale Analysis of Cloud Service Misconfigurations[C]// USENIX.The 29th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2020: 2545-2562. |
| [12] | YUAN Fuxiang, LIU Fenlin, LIU Chong, et al. MLAR: Large-Scale Network Alias Resolution for IP Positioning[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2020, 6(4): 77-94. |
| 袁福祥, 刘粉林, 刘翀, 等. MLAR:面向IP定位的大规模网络别名解析[J]. 网络与信息安全学报, 2020, 6(4):77-94. | |
| [13] | MUHLBAUER W, FELDMANN A, MAENNEL O, et al. Building an AS-Topology Model that Captures Route Diversity and Its Applications[C]// ACM. The 2007 ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. New York: ACM, 2007: 1-14. |
| [14] | LIU Zheng, ZHANG Yang, WU Qiang, et al. AutoTopo: SNMP-Based Topology Discovery with Active Learning[C]// ACM. The SIGCOMM Workshop on Network Data Analytics (NDA’22). New York: ACM, 2022: 1-8. |
| [15] |
WANG Zhanfeng, CHENG Guang, HU Chao, et al. Research Progress of Alias Resolution Technology[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(7): 169-185.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019134 |
|
王占丰, 程光, 胡超, 等. 别名解析技术研究进展[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(7):169-185.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019134 |
|
| [16] | ALI S, QURESHI K N, RANA L, et al. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and Its Challenges: A Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(3): 1559-1587. |
| [17] | HE Heng, CHEN Kai, JIN Hai, et al. HybridAlias: A Hybrid Active-Passive Approach for Scalable Router Alias Resolution[C]// ACM. The ACM SIGCOMM Conference. New York: ACM, 2022: 456-470. |
| [18] | LIU Yang, ZHANG Ming, LI Dong, et al. DynaMap: Dynamic IP Alias Mapping with High Accuracy and Efficiency[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2019, 27(3): 1024-1037. |
| [19] | LIU Xiaobo, GUO Li, CHENG Guang, et al. APAR: Adaptive Path Probing for Fast and Accurate Router Alias Resolution[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2023, 31(2): 812-827. |
| [20] | LIU Xiangyang, JIN Yier, VAN DER MERWE J, et al. Towards a Lightweight Solution for Low-Rate DoS Attack Detection[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2022, 30(4): 1789-1802. |
| [21] | CHEN Min, LIU Yong, LIU Zimu, et al. GAP: A General Framework for Graph Alignment in Network Topology Inference[C]// IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications(INFOCOM 2022). New York: IEEE, 2022: 270-279. |
| [22] | CHENG Guang, WANG Zhanfeng, HU Chao, et al. FedAlias: A Federated Learning Framework for Privacy-Preserving and Collaborative Router Alias Resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18: 1526-1540. |
| [23] | WANG Zihao, LIU Yang, CHEN Min, et al. APAR: Adaptive Path Selection for Alias Resolution with Attention Mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2023, 20(1): 512-525. |
| [24] |
ZHOU Xuan, CHEN Min, LIU Yang, et al. Scalable Internet-Wide Alias Resolution with Global-Local Analysis[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2023, 31(5): 2101-2114.
doi: 10.1109/TNET.2022.3233908 URL |
| [25] | BEVERLY R, BERGER A. Leveraging IP Identifier for Coarse Router Classification[C]// IFIP. The 15th International Conference on Passive and Active Measurement. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 183-192. |
| [26] | SHERRY J, KATZ-BASSETT E. A Survey of Router Aliasing and a New Approach Using Geographic Diversity[C]// ACM.The 2012 ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. New York: ACM, 2012: 1-14. |
| [27] | ZHANG Wei, LI Hang, WANG Zhi. An Active Probing-Based Detection Method for Anomalous Nodes in Internet Topology[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(3): 45-53. |
| 张伟, 李航, 王智. 基于主动探测的互联网拓扑异常节点检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3):45-53. | |
| [28] | CHEN Gang, LIU Yang, ZHOU Yue. Construction Technology of Network Device Fingerprint Library Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(7): 12-20. |
| 陈刚, 刘洋, 周悦. 多源数据融合的网络设备指纹库构建技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7):12-20. | |
| [29] | XU Zhen, WANG Xiaofeng, LI Ning. Router Alias Resolution Algorithm Based on Probabilistic Graphical Model[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2023, 60(2): 334-345. |
| 徐震, 王晓峰, 李宁. 基于概率图模型的路由器别名解析算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2023, 60(2):334-345. |
| [1] | JIN Zhigang, LUO Houyang, LIU Zepei, DING Yu. Semantic Communication Security: Multi-Layered Threats and Countermeasures [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1827-1846. |
| [2] | YANG Liqun, LI Zhen, WEI Chaoren, YAN Zhimin, QIU Yongxin. Research on Protocol Fuzzing Technology Guided by Large Language Models [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1847-1862. |
| [3] | PANG Shuchao, LI Zhengxiao, QU Junyi, MA Ruhao, CHEN Hechang, DU Anan. Detecting Poisoned Samples for Untargeted Backdoor Attacks [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1878-1888. |
| [4] | XIE Xiangpeng, SHAO Xingchen. Secure Gain-Scheduling Method for Stochastic Nonlinear CPS Based on Dual-Domain Polynomial Framework [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1889-1900. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xuefeng, WANG Kehang. A Proxy Ring Signature Scheme Based on SM9 Algorithm [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1901-1913. |
| [6] | HAN Yiliang, PENG Yixuan, WU Xuguang, LI Yu. Multimodal Feature Fusion Encrypted Traffic Classification Model Based on Graph Variational Auto-Encoder [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1914-1926. |
| [7] | FU Zhangjie, CHEN Tianyu, CUI Qi. Dynamic Handwritten Signature Verification Models Protection Method Based on Contrastive Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1927-1935. |
| [8] | LIU Dahe, XIU Jiapeng, YANG Zhengqiu. Research on Community Detection and Core Node Discovery Based on Improved Louvain Algorithm [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1936-1947. |
| [9] | ZHANG Guanping, WEI Fushan, CHEN Xi, GU Chunxiang. Blockchain-Based Privacy-Preserving Cross-Domain Authentication Protocol [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1948-1960. |
| [10] | QIN Siying, SUN Bing, FU Shaojing, TANG Xiaomei. Key Switching for Somewhat Homomorphic Encryption Based on RLWR [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1961-1974. |
| [11] | WANG Houzhen, JIANG Haolang, LIU Jichen, TU Hang. Privacy-Preserving Sorting Scheme Based on Paillier Homomorphic Encryption [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1975-1989. |
| [12] | MENG Hui, MAO Linlin, PENG Juzhi. Sanitize Processing and Recognition Method Driven by Large Language Model [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1990-1998. |
| [13] | ZHU Hui, FANG Yunyi, WANG Fengwei, XU Wei. Research Progress on Data Security Processing Integrating Confidential Computing [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1643-1657. |
| [14] | HAO Meng, LI Jiayong, YANG Hongwei, ZHANG Weizhe. Heterogeneous CPU-GPU System Confidential Computing Survey [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1658-1672. |
| [15] | GUAN Zhi, HU Jianbin, LI Yue, CHEN Zhong. A Comprehensive Survey of Blockchain Technologies and Applications Based on Trusted Execution Environments [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1673-1690. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||