信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1554-1569.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.007
基于累积量与深度学习融合的水下调制识别模型
- 1.东南大学网络空间安全学院,南京 211189
2.网络通信与安全紫金山实验室,南京 211111
-
收稿日期:2025-07-02出版日期:2025-10-10发布日期:2025-11-07 -
通讯作者:张子豪 E-mail:220235436@seu.edu.cn -
作者简介:李古月(1989—),女,江苏,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为物理层安全、无线通信安全|张子豪(2000—),男,江苏,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为水声通信、射频指纹|毛承海(2005—),男,山东,本科,主要研究方向为图像处理、深度学习|吕锐(1986—),男,江苏,博士研究生,主要研究方向为网络信息安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62171121)
A Cumulant-Deep Learning Fusion Model for Underwater Modulation Recognition
LI Guyue1,2, ZHANG Zihao1( ), MAO Chenghai1, LYU Rui1
), MAO Chenghai1, LYU Rui1
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China
2. Purple Mountain Laboratories for Network Communication and Security, Nanjing 211111, China
-
Received:2025-07-02Online:2025-10-10Published:2025-11-07 -
Contact:ZHANG Zihao E-mail:220235436@seu.edu.cn
摘要:
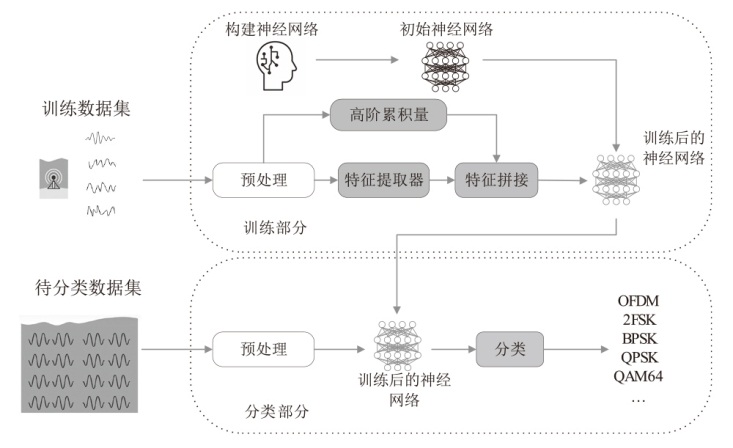
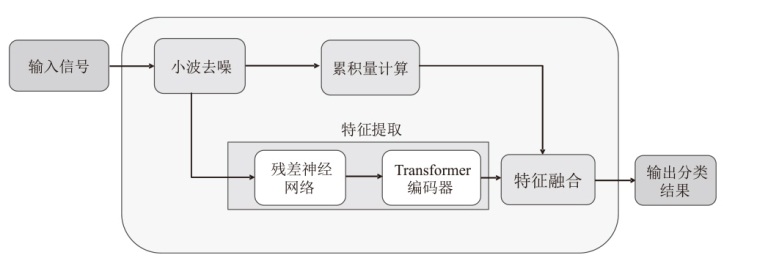
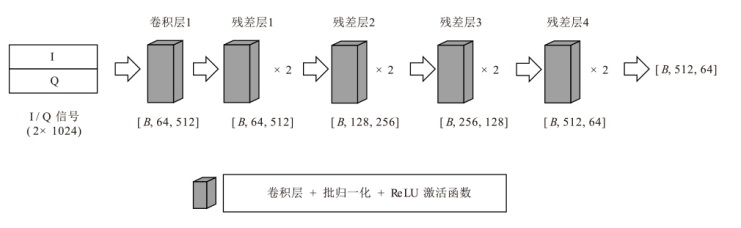
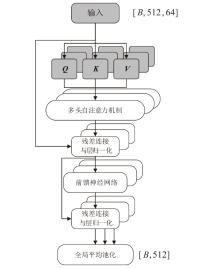
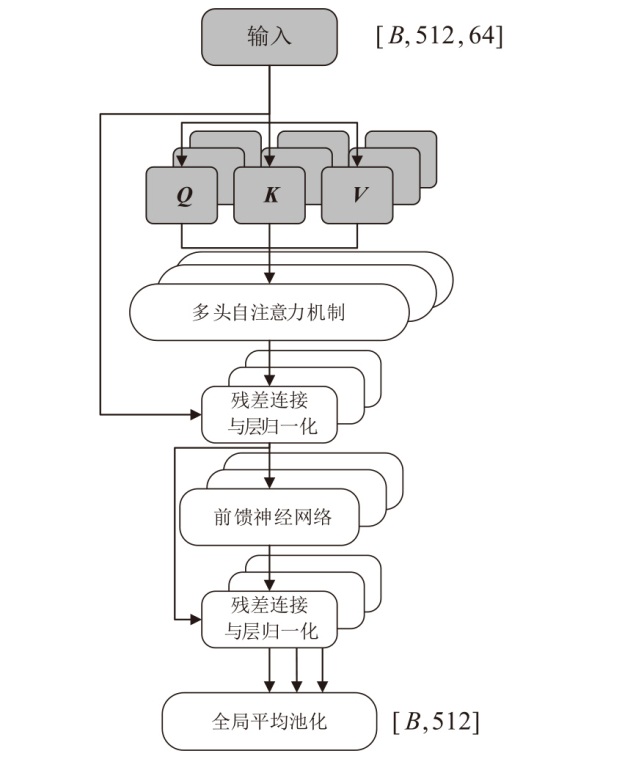
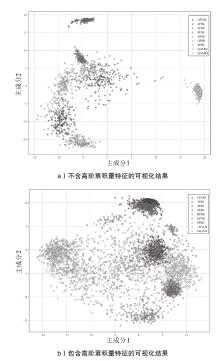
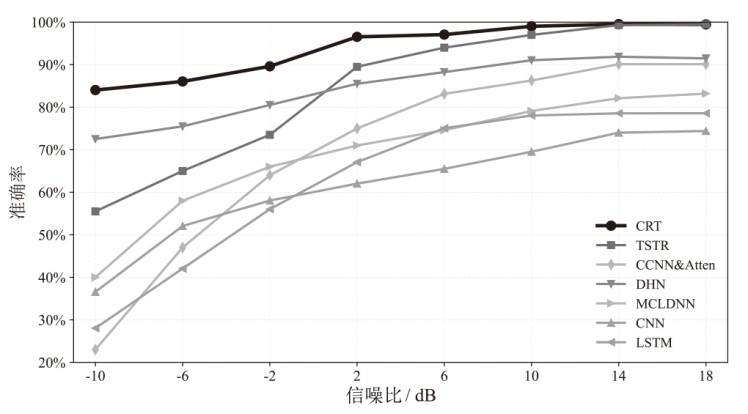
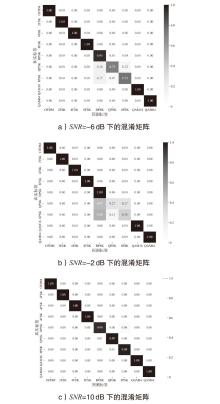
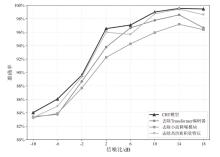
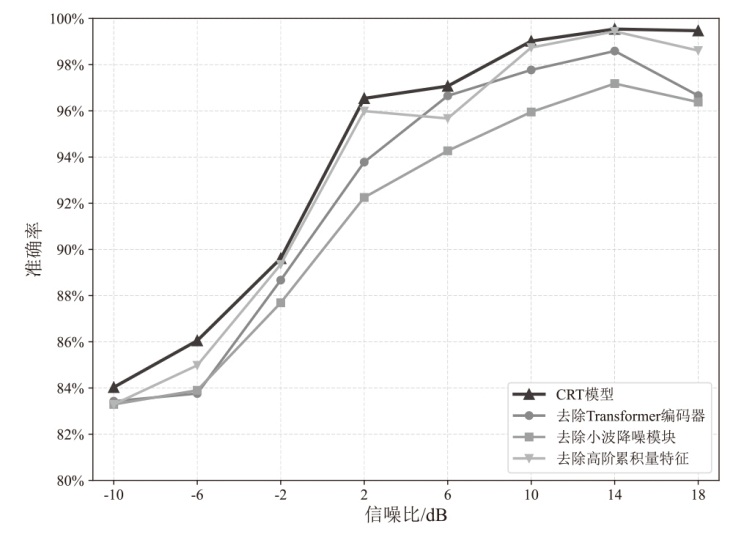
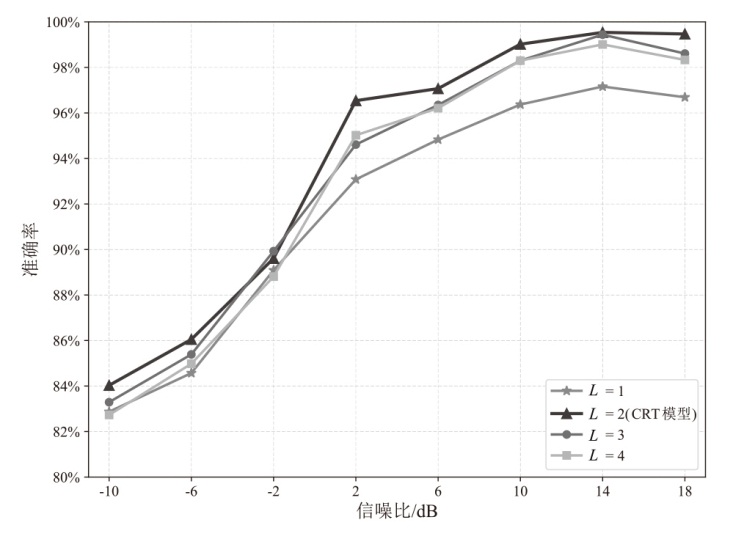
在复杂严苛的水声通信环境中,调制识别技术对于提升水下通信系统的抗截获能力和信息安全具有重要意义。然而,水声信道中的非线性、多径效应与强噪声干扰对自动调制识别任务构成了严峻挑战。为应对这些挑战,文章提出了一种融合小波去噪与高阶累积量特征的深度调制识别模型(CRT)。该模型通过优化残差网络与Transformer编码器结构,分别构建局部与全局时序频域特征模型,并基于水声信号时频分布特性融合高阶累积量特征,在9类典型水下调制方式下实现了93.56%的平均识别准确率,较当前最优模型提升了2.4%。特别是在-10 dB~-2 dB的低信噪比环境下,CRT模型识别准确率提升超过10%,验证了该模型在复杂水声场景下的有效性与实用价值。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李古月, 张子豪, 毛承海, 吕锐. 基于累积量与深度学习融合的水下调制识别模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1554-1569.
LI Guyue, ZHANG Zihao, MAO Chenghai, LYU Rui. A Cumulant-Deep Learning Fusion Model for Underwater Modulation Recognition[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1554-1569.
| [1] |
SONG Aijun, STOJANOVIC M, CHITRE M. Editorial Underwater Acoustic Communications: Where We Stand and What is Next?[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 44(1): 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2018.2883872 |
| [2] | JIANG Shengming. On Securing Underwater Acoustic Networks: A Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 21(1): 729-752. |
| [3] | JIANG Shengming. On Reliable Data Transfer in Underwater Acoustic Networks: A Survey from Networking Perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(2): 1036-1055. |
| [4] |
HUANG Jianchun, DIAMANT R. Adaptive Modulation for Long-Range Underwater Acoustic Communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6844-6857.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3006230 URL |
| [5] |
ALI M F, JAYAKODY D N K, CHURSIN Y A, et al. Recent Advances and Future Directions on Underwater Wireless Communications[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2020, 27(5): 1379-1412.
doi: 10.1007/s11831-019-09354-8 |
| [6] | GHOREYSHI S M, SHAHRABI A, BOUTALEB T. Void-Handling Techniques for Routing Protocols in Underwater Sensor Networks: Survey and Challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(2): 800-827. |
| [7] | ZHAO Caidan, CHEN Jingqian, WU Zhiqiang. Automatic Modulation Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Channel Joint Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(4): 20-29. |
| 赵彩丹, 陈璟乾, 吴志强. 基于多通道联合学习的自动调制识别网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4):20-29. | |
| [8] |
XU J L, SU Wei, ZHOU Mengchu, Likelihood-Ratio Approaches to Automatic Modulation Classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2010, 41(4): 455-469.
doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2010.2076347 URL |
| [9] | LI Yuxing, TANG Bingzhao, JIAO Shangbin. SO-Slope Entropy Coupled with SVMD: A Novel Adaptive Feature Extraction Method for Ship-Radiated Noise[EB/OL]. (2023-05-01)[2025-06-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114677. |
| [10] | MENG Qingxin, YANG Shie. A Wave Structure Based Method for Recognition of Marine Acoustic Target Signals[EB/OL]. (2015-04-01)[2025-06-30]. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4920186. |
| [11] |
ZHU Daimei, MATHEWS V J, DETIENNE D H. A Likelihood-Based Algorithm for Blind Identification of QAM and PSK Signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(5): 3417-3430.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2811802 URL |
| [12] | HONG Feng, LIU Chengwei, GUO Lijuan, et al. Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition with Resnet18 on Shipsear Dataset[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET). New York: IEEE, 2021: 1240-1244. |
| [13] | JIANG Zenghui, ZENG Weijun, CHEN Pu, et al. Review of Adversarial Samples for Modulation Recognition[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(6): 74-90. |
| 蒋曾辉, 曾维军, 陈璞, 等. 面向调制识别的对抗样本研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6):74-90. | |
| [14] | WANG Yan, ZHANG Hao, SANG Zhanliang, et al. Modulation Classification of Underwater Communication with Deep Learning Network[EB/OL]. (2019-04-01)[2025-06-30]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31065254/. |
| [15] | HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[C]// IEEE. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| [16] | TIAN Xiao, CHEN Chao. Modulation Pattern Recognition Based on Resnet50 Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing (ICICSP). New York: IEEE, 2019: 34-38. |
| [17] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[EB/OL]. (2017-09-02)[2025-06-30]. https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf. |
| [18] |
CAI Jingjing, GAN Fengming, CAO Xianghai, et al. Signal Modulation Classification Based on the Transformer Network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2022, 8(3): 1348-1357.
doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2022.3176640 URL |
| [19] | LI Bing, CUI Wei, WANG Wei, et al. Two-Stream Convolution Augmented Transformer for Human Activity Recognition[C]// AAAI. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2021: 286-293. |
| [20] | ZHANG Rui, YIN Zhendong, WU Zhilu, et al. A Novel Automatic Modulation Classification Method Using Attention Mechanism and Hybrid Parallel Neural Network[EB/OL]. (2021-01-02)[2025-06-30]. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031327. |
| [21] | YU Yang, CAO Xu, ZHANG Xiaomin. Underwater Target Classification Using Deep Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2018 Oceans-Mts/IEEE Kobe Techno-Oceans (Oto). New York: IEEE, 2018: 1-5. |
| [22] | STOJANOVIC M, PREISIG J. Underwater Acoustic Communication Channels: Propagation Models and Statistical Characterization[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2009, 47(1): 84-89. |
| [23] | CAO Xu, ZHANG Xiaomin, YU Yang, et al. Deep Learning-Based Recognition of Underwater Target[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP). New York: IEEE, 2016: 89-93. |
| [24] |
PENG Shengliang, SUN Shujun, YAO Yudong. A Survey of Modulation Classification Using Deep Learning: Signal Representation and Data Preprocessing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 33(12): 7020-7038.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3085433 URL |
| [25] |
CHANG Shuo, HUANG Sai, ZHANG Ruiyun, et al. Multitask-Learning-Based Deep Neural Network for Automatic Modulation Classification[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 9(3): 2192-2206.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3091523 URL |
| [26] |
PENG Shengliang, JIANG Hanyu, WANG Huaxia, et al. Modulation Classification Based on Signal Constellation Diagrams and Deep Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 30(3): 718-727.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2850703 URL |
| [27] |
ZHANG Zufan, LUO Hao, WANG Chun, et al. Automatic Modulation Classification Using CNN-LSTM Based Dual-Stream Structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 13521-13531.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3030018 |
| [28] |
KE Ziqi, VIKALO H. Real-Time Radio Technology and Modulation Classification via an LSTM Auto-Encoder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 21(1): 370-382.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3095855 URL |
| [29] |
GHASEMZADEH P, HEMPEL M, SHARIF H. GS-QRNN: A High-Efficiency Automatic Modulation Classifier for Cognitive Radio IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(12): 9467-9477.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3141032 URL |
| [30] |
XU Jialang, LUO Chunbo, PARR G, et al. A Spatiotemporal Multi-Channel Learning Framework for Automatic Modulation Recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(10): 1629-1632.
doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2999453 |
| [31] | YUE Zhou, WEI Kong, QING Xu. A Novel Modeling and Recognition Method for Underwater Sound Based on HMT in Wavelet Domain[C]// Springer. Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Heidelberg: Springer, 2004: 332-343. |
| [32] | SAFI S, FRIKEL M, ZEROUAL A, et al. Higher Order Cumulants for Identification and Equalization of Multicarrier Spreading Spectrum Systems[J]. Journal of Telecommunications and Information Technology, 2011 (2): 74-84. |
| [33] |
ZHANG Ruoyun, CHANG Shuo, WEI Zhiqing, et al. Modulation Classification of Active Attacks in Internet of Things: Lightweight MCBLDN with Spatial Transformer Network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(19): 19132-19146.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3163892 URL |
| [34] |
LIANG Zhi, TAO Mingliang, XIE Jian, et al. A Radio Signal Recognition Approach Based on Complex-Valued CNN and Self-Attention Mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2022, 8(3): 1358-1373.
doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2022.3179450 URL |
| [35] |
ZHANG Weilong, YANG Xinghai, LENG Changli, et al. Modulation Recognition of Underwater Acoustic Signals Using Deep Hybrid Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(8): 5977-5988.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3144608 URL |
| [36] |
LI Juan, JIA Qingning, CUI Xuerong, et al. Automatic Modulation Recognition of Underwater Acoustic Signals Using a Two-Stream Transformer[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(10): 18839-18851.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3367852 URL |
| [1] | 徐茹枝, 武晓欣, 吕畅冉. 基于Transformer的超分辨率网络对抗样本防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1367-1376. |
| [2] | 陈咏豪, 蔡满春, 张溢文, 彭舒凡, 姚利峰, 朱懿. 多尺度多层次特征融合的深度伪造人脸检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1456-1464. |
| [3] | 王新猛, 陈俊雹, 杨一涛, 李文瑾, 顾杜娟. 贝叶斯优化的DAE-MLP恶意流量识别模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1465-1472. |
| [4] | 金志刚, 李紫梦, 陈旭阳, 刘泽培. 面向数据不平衡的网络入侵检测系统研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(8): 1240-1253. |
| [5] | 王钢, 高雲鹏, 杨松儒, 孙立涛, 刘乃维. 基于深度学习的加密恶意流量检测方法研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(8): 1276-1301. |
| [6] | 张兴兰, 陶科锦. 基于高阶特征与重要通道的通用性扰动生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(5): 767-777. |
| [7] | 李敬有, 席晓天, 魏荣乐, 张光妲. 基于小波分解与动态密集空洞卷积的双分支神经网络水印算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(5): 828-839. |
| [8] | 金增旺, 江令洋, 丁俊怡, 张慧翔, 赵波, 方鹏飞. 工业控制系统安全研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 341-363. |
| [9] | 陈红松, 刘新蕊, 陶子美, 王志恒. 基于深度学习的时序数据异常检测研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 364-391. |
| [10] | 李海龙, 崔治安, 沈燮阳. 网络流量特征的异常分析与检测方法综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [11] | 武浩莹, 陈杰, 刘君. 改进Simon32/64和Simeck32/64神经网络差分区分器[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [12] | 金地, 任昊, 唐瑞, 陈兴蜀, 王海舟. 基于情感辅助多任务学习的社交网络攻击性言论检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [13] | 梁凤梅, 潘正豪, 刘阿建. 基于共性伪造线索感知的物理和数字人脸攻击联合检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1604-1614. |
| [14] | 陈晓静, 陶杨, 吴柏祺, 刁云峰. 面向骨骼动作识别的优化梯度感知对抗攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [15] | 徐茹枝, 张凝, 李敏, 李梓轩. 针对恶意软件的高鲁棒性检测模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||