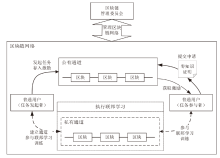
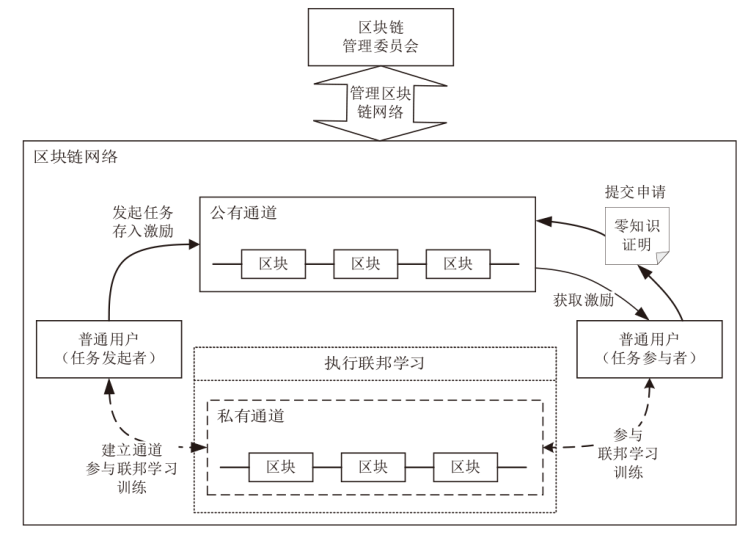
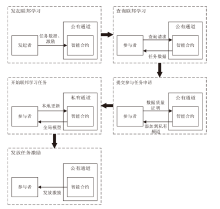
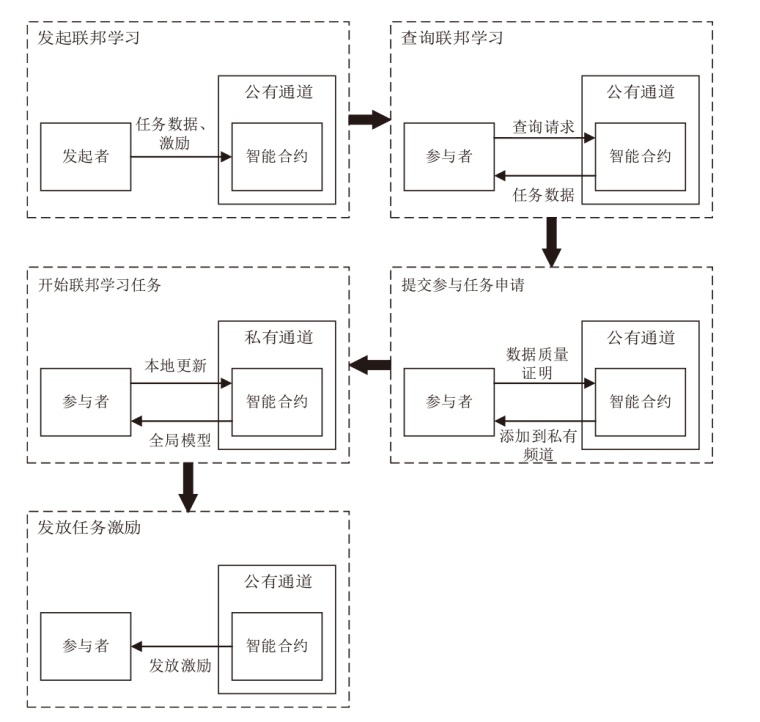
Netinfo Security ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 1-13.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.01.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Federated Learning Incentive Scheme Based on Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Blockchain
WU Haotian1, LI Yifan1, CUI Hongyan2, DONG Lin3( )
)
- 1. School of Computer Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
2. Zhengzhou Xinda Institute of Advanced Technology, Zhengzhou 450001, China
3. National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team/Coordination Center of China, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2023-08-26Online:2024-01-10Published:2024-01-24 -
Contact:DONG Lin E-mail:donglin@cert.org.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WU Haotian, LI Yifan, CUI Hongyan, DONG Lin. Federated Learning Incentive Scheme Based on Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Blockchain[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 1-13.
share this article
| [1] | KONECNY J, MCMAHAN H B, RAMAGE D. Federated Optimization: Distributed Optimization Beyond the Datacenter[EB/OL]. (2015-11-11) [2022-10-20]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.03575. |
| [2] | KONECNY J, MCMAHAN H B, RAMAGE D, et al. Federated Optimization: Distributed Machine Learning for On-Device Intelligence[EB/OL]. (2016-10-08) [2022-10-20]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1610.02527. |
| [3] |
KAIROUZ P, MCMAHAN H B, AVENT B, et al. Advances and Open Problems in Federated Learning[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2021, 14(1-2): 1-210.
doi: 10.1561/2200000083 URL |
| [4] | YU Han, LIU Zelei, LIU Yang, et al. A Sustainable Incentive Scheme for Federated Learning[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2020, 35(4): 58-69. |
| [5] |
LYU Lingjuan, YU Jiangshan, NANDAKUMAR K, et al. Towards Fair and Privacy-Preserving Federated Deep Models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2020, 31(11): 2524-2541.
doi: 10.1109/TPDS.71 URL |
| [6] | WENG Jiasi, WENG Jian, ZHANG Jilian, et al. DeepChain: Auditable and Privacy-Preserving Deep Learning with Blockchain-Based Incentive[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019, 18(5): 2438-2455. |
| [7] | TOYODA K, ZHANG A N. Mechanism Design for An Incentive-Aware Blockchain-Enabled Federated Learning Platform[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data). New York: IEEE, 2019: 395-403. |
| [8] | MA Shuaicheng, CAO Yang, LI Xiong. Transparent Contribution Evaluation for Secure Federated Learning on Blockchain[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW). New York: IEEE, 2021: 88-91. |
| [9] | HU Qiwei, WANG Wei, BAI Xiang, et al. Blockchain Enabled Federated Slicing for 5G Networks with AI Accelerated Optimization[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(6): 46-52. |
| [10] |
WU Haotian, ZHENG Yuncong, ZHAO Benbo, et al. An Anonymous Reputation Management System for Mobile Crowdsensing Based on Dual Blockchain[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(9): 6956-6968.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3113997 URL |
| [11] |
LI Yijing, TAO Xiaofeng, ZHANG Xuefei, et al. Privacy-Preserved Federated Learning for Autonomous Driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 8423-8434.
doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3081560 URL |
| [12] | KUMAR S, DUTTA S, CHATTURVEDI S, et al. Strategies for Enhancing Training and Privacy in Blockchain Enabled Federated Learning[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM). New York: IEEE, 2020: 333-340. |
| [13] | WU L, GUO S, LIU Y, et al. Sustainable Federated Learning with Long-Term Online VCG Auction Mechanism[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE 42nd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS). Bologna: IEEE, 2022: 895-905. |
| [14] | LING X, LI R, OUYANG T, et al. Time is Gold: A Time-Dependent Incentive Mechanism Design for Fast Federated Learning[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC). Foshan: IEEE, 2022: 1038-1043. |
| [15] | KUMARESAN R, BENTOV I. How to Use Bitcoin to Incentivize Correct Computations[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2014: 30-41. |
| [16] |
KANG Jiawen, XIONG Zehui, NIYATO D, et al. Incentive Mechanism for Reliable Federated Learning: A Joint Optimization Approach to Combining Reputation and Contract Theory[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10700-10714.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2940820 |
| [17] | FANG Minghong, CAO Xiaoyu, JIA Jinyuan, et al. Local Model Poisoning Attacks to Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning[C]// USENIX. 29th USENIX Security Symposium. New York: USENIX, 2020: 1623-1640. |
| [18] |
ZHANG Weishan, LU Qinghua, YU Qiuyu, et al. Blockchain-Based Federated Learning for Device Failure Detection in Industrial IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(7): 5926-5937.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3032544 URL |
| [19] |
KIM H, PARK J, BENNIS M, et al. Blockchained On-Device Federated Learning[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(6): 1279-1283.
doi: 10.1109/COML.4234 URL |
| [20] |
QU Y, POKHREL S R, GARG S, et al. A Blockchained Federated Learning Framework for Cognitive Computing in Industry 4.0 Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(4): 2964-2973.
doi: 10.1109/TII.9424 URL |
| [21] | LI Yuzheng, CHEN Chuan, LIU Nan, et al. A Blockchain-Based Decentralized Federated Learning Framework with Committee Consensus[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(1): 234-241. |
| [22] | WANG Shufen. BlockFedML: Blockchained Federated Machine Learning Systems[C]// IEEE. 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Automation and Systems (ICICAS). Chongqing: IEEE, 2019: 751-756. |
| [23] | WANG Peng, MA Wengqiang, ZHANG Haibin, et al. A Dynamic Contribution Measurement and Incentive Mechanism for Energy-Efficient Federated Learning in 6G[C]// IEEE. ICC 2022-IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2022: 1-6. |
| [24] | LI Beibei, SHI Yaxin, GUO Yuqing, et al. Incentive and Knowledge Distillation Based Federated Learning for Cross-Silo Applications[C]// IEEE. 2022IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS). New York: IEEE, 2022: 1-6. |
| [25] | GHODSI Z, GU Tianyu, GARG S. SafetyNets: Verifiable Execution of Deep Neural Networks on an Untrusted Cloud[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 2017: 4673-4682. |
| [26] | KEUFFER J, MOLVA R, CHABANNE H. Efficient Proof Composition for Verifiable Computation[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 2018, 11098 LNCS(Vc): 152-171. |
| [27] | LEE S, KO H, KIM J, et al. vCNN: Verifiable Convolutional Neural Network Based on zk-SNARKs[EB/OL]. (2020-12-18) [2022-10-20]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/584. |
| [28] | LIU T, XIE X, ZHANG Y. zkCNN: Zero Knowledge Proofs for Convolutional Neural Network Predictions and Accuracy[C]// ACM.Proceedings of the 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2021: 2968-2985. |
| [29] | FENG B, QIN L, ZHANG Z, et al. ZEN: An Optimizing Compiler for Verifiable, Zero-Knowledge Neural Network Inferences[EB/OL]. (2021-05-15) [2022-10-20]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2021/087. |
| [30] | SHEEHAN M. Swiss Re Partners with Tencent’s WeBank to Research AI Use in Reinsurance[EB/OL]. (2019-05-24) [2022-10-20]. https://www.reinsurancene.ws/swiss-re-partners-with-tencents-webank-to-research-ai-use-in-reinsurance/. |
| [31] | FRANCE O. MachinE Learning Ledger Orchestration for Drug Discovery[EB/OL]. (2019-06-01) [2022-10-20]. https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/831472. |
| [32] | LIM W Y B, LUONG N C, HOANG D T, et al. Federated Learning in Mobile Edge Networks: A Comprehensive Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(3): 2031-2063. |
| [33] | NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[EB/OL]. (2008-10-31) [2022-10-20]. http://www.bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf. |
| [34] | BHOWMIK D, FENG Tian. The Multimedia Blockchain: A Distributed and Tamper-Proof Media Transaction Framework[C]// IEEE. 2017 22nd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing. London: IEEE, 2017: 1-5. |
| [35] | XU R, ZHANG L, ZHAO H, et al. Design of Network Media’s Digital Rights Management Scheme Based on Blockchain Technology[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Autonomous Decentralized System (ISADS). Bangkok: IEEE, 2017: 128-133. |
| [36] | BUTERIN V. On Public and Private Blockchains[EB/OL]. (2015-08-07) [2022-10-20]. https://blog.ethereum.org/2015/08/07/on-public-and-private-blockchains/. |
| [37] | Hyperledger Foundation. Hyperledger[EB/OL]. [2022-10-20]. https://www.hyperledger.org/. |
| [38] | ENTERPRISE. Enterprise on Ethereum Mainnet[EB/OL]. [2022-10-20]. https://ethereum.org/en/enterprise/. |
| [39] | LI Weihan, ZHANG Zongyang, ZHOU Zibo, et al. An Overview on Succinct Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Proofs[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2022, 9(3): 379-447. |
|
李威翰, 张宗洋, 周子博, 等. 简洁非交互零知识证明综述[J]. 密码学报, 2022, 9(3): 379-447.
doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000525 |
|
| [40] | GROTH J. On the Size of Pairing-Based Non-interactive Arguments[C]// Spriuger Advances in Cryptology- EUROCRYPT 2016. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 305-326. |
| [41] | CUBUK E D, ZOPH B, MANE D, et al. AutoAugment: Learning Augmentation Strategies from Data[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach: IEEE, 2019: 113-123. |
| [42] | LECUN Y, CORTES C, BURGES C J C. MNIST Handwritten Digit Database, Yann LeCun, Corinna Cortes and Chris Burges[EB/OL]. (1998)[2023-01-09]. http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/. |
| [43] | XIAO Han, RASUL K, VOLLGRAF R. Fashion-MNIST: A Novel Image Dataset for Benchmarking Machine Learning Algorithms[EB/OL]. (2017-08-25) [2022-10-20]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1708.07747. |
| [44] | CLANUWAT T, BOBER-IRIZAR M, KITAMOTO A, et al. Deep Learning for Classical Japanese Literature[EB/OL]. (2018-12-03) [2022-12-25]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1812.01718. |
| [45] | PEDERSEN T P. Non-Interactive and Information-Theoretic Secure Verifiable Secret Sharing[M]// Feigenbaum J. Advances in Cryptology - CRYPTO ’91. Heidelberg: Springer, 1992: 129-140. |
| [46] |
ZHAN Yufeng, LI Peng, QU Zhihao, et al. A Learning-Based Incentive Mechanism for Federated Learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(7): 6360-6368.
doi: 10.1109/JIoT.6488907 URL |
| [1] | ZHU Guocheng, HE Debiao, AN Haoyang, PENG Cong. The Proxy Voting Scheme Based on the Blockchain and SM9 Digital Signature [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 36-47. |
| [2] | ZHAO Jia, YANG Bokai, RAO Xinyu, GUO Yating. Design and Implementation of Tor Traffic Detection Algorithm Based on Federated Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 60-68. |
| [3] | XU Ruzhi, DAI Lipeng, XIA Diya, YANG Xin. Research on Centralized Differential Privacy Algorithm for Federated Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 69-79. |
| [4] | LAI Chengzhe, ZHAO Yining, ZHENG Dong. A Privacy Preserving and Verifiable Federated Learning Scheme Based on Homomorphic Encryption [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 93-105. |
| [5] | GONG Pengfei, XIE Sijiang, CHENG Andong. The Multi-Leader Consensus Algorithm Based on Improvements to HotStuff [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(9): 108-117. |
| [6] | ZHOU Quan, CHEN Minhui, WEI Kaijun, ZHENG Yulong. Blockchain Access Control Scheme with SM9-Based Attribute Encryption [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(9): 37-46. |
| [7] | ZHAO Jiahao, JIANG Jiajia, ZHANG Yushu. Cross-Chain Data Consistency Verification Model Based on Dynamic Merkle Hash Tree [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(9): 95-107. |
| [8] | SHAO Zhenzhe, JIANG Jiajia, ZHAO Jiahao, ZHANG Yushu. An Improved Weighted Byzantine Fault Tolerance Algorithm for Cross-Chain System [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 109-120. |
| [9] | QIN Sihang, DAI Weiqi, ZENG Haiyan, GU Xianjun. Secure Sharing of Power Application Data Based on Blockchain [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 52-65. |
| [10] | PENG Hanzhong, ZHANG Zhujun, YAN Liyue, HU Chenglin. Research on Intrusion Detection Mechanism Optimization Based on Federated Learning Aggregation Algorithm under Consortium Chain [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 76-85. |
| [11] | YU Huifang, QIAO Yifan, MENG Ru. Attribute-Based Anti-Quantum Threshold Ring Signcryption Scheme for Blockchain-Based Finance [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(7): 44-52. |
| [12] | CHEN Jing, PENG Changgen, TAN Weijie, XU Dequan. A Multi-Server Federation Learning Scheme Based on Differential Privacy and Secret Sharing [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(7): 98-110. |
| [13] | LIU Changjie, SHI Runhua. A Smart Grid Intrusion Detection Model for Secure and Efficient Federated Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(4): 90-101. |
| [14] | GUO Rui, WEI Xin, CHEN Li. An Outsourceable and Policy-Hidden Attribute-Based Encryption Scheme in the IIoT System [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(3): 1-12. |
| [15] | LI Chunxiao, WANG Yaofei, XU Enliang, ZHAO Yu. Enabling Privacy-Preserving Range Queries in Blockchain-Based Collaborative Databases with Bilinear Pairings [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(3): 22-34. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||