信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 54-63.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.02.007
一种使用Bi-ADMM优化深度学习模型的方案
- 南京信息工程大学软件学院,南京 210044
-
收稿日期:2022-10-21出版日期:2023-02-10发布日期:2023-02-28 -
通讯作者:程洛飞 E-mail:20201221009@nuist.edu.cn -
作者简介:徐占洋(1975—),男,江苏,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为区块链、大数据智能分析与处理|程洛飞(1996—),男,安徽,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为分布式凸优化和联邦学习|程建春(1998—),男,山东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为联邦学习|许小龙(1988—),男,江苏,教授,博士,主要研究方向为大数据、知识图谱、边缘计算和服务计算 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62272236)
A Scheme of Optimizing Deep Learning Model Using Bi-ADMM
XU Zhanyang, CHENG Luofei( ), CHENG Jianchun, XU Xiaolong
), CHENG Jianchun, XU Xiaolong
- School of Software, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2022-10-21Online:2023-02-10Published:2023-02-28 -
Contact:CHENG Luofei E-mail:20201221009@nuist.edu.cn
摘要:
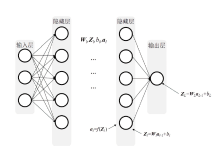
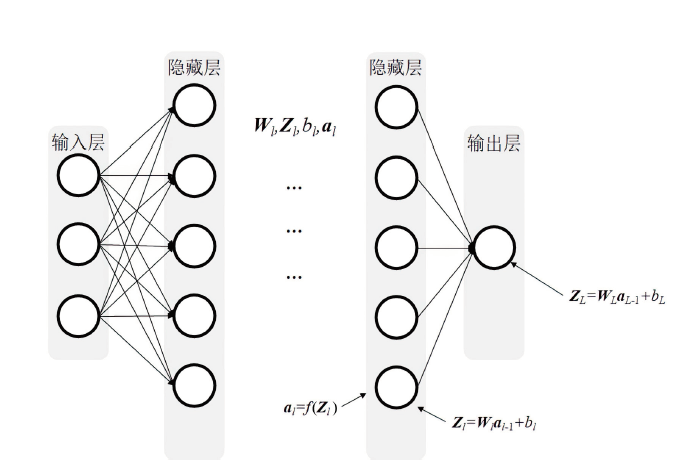
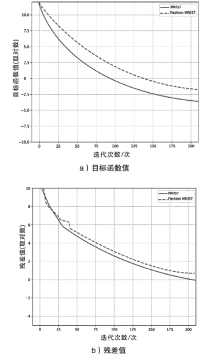
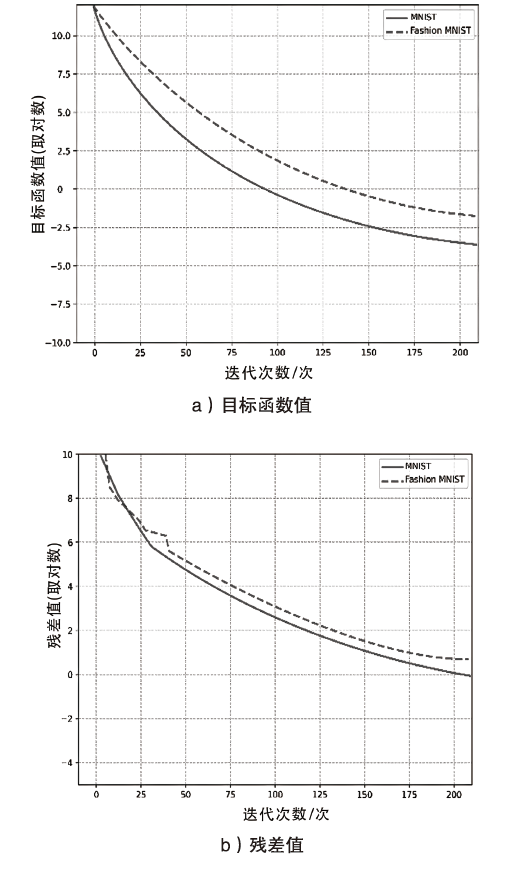
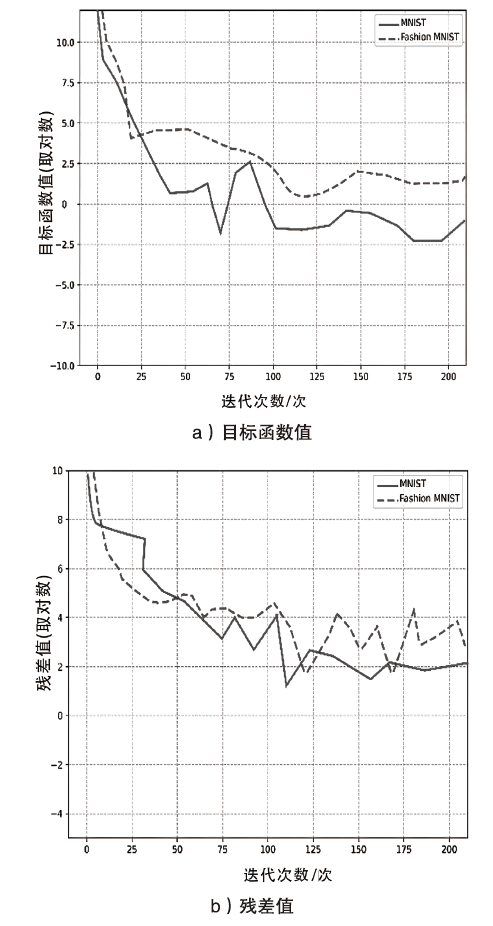
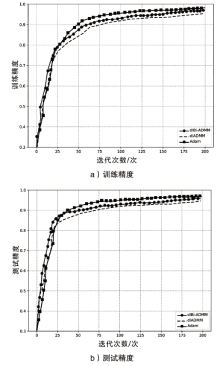
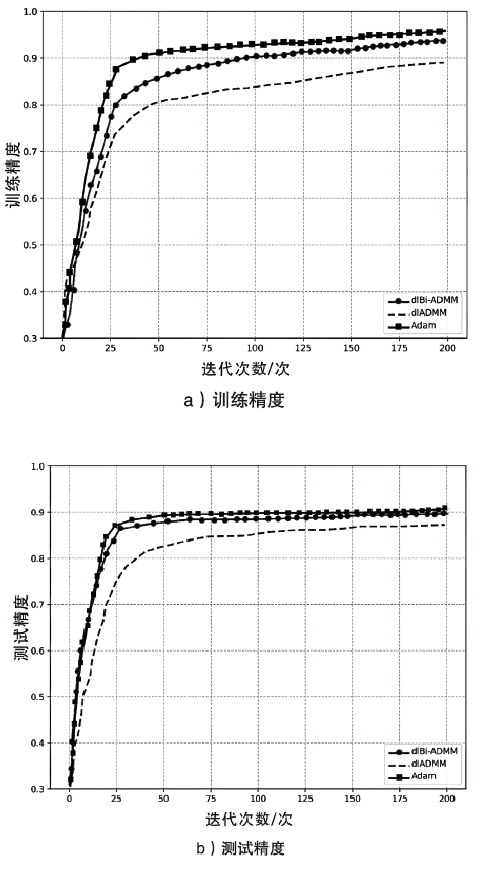
ADMM算法被广泛应用于传统机器学习模型优化领域,它解决了某些深度学习的优化问题。该算法在优化深度学习模型方面的表现已经超过了大多数基于梯度的优化算法,而Bi-ADMM算法比ADMM算法的收敛速度更快、更稳定。文章提出了一种优化深度学习模型方案dlBi-ADMM算法,并用该算法来训练深度学习模型。首先,文章采用加速近端梯度算法优化耦合变量来降低矩阵求逆运算的复杂度;然后,详细给出每个变量的优化子问题的具体函数;最后,通过实验证明文章所提dlBi-ADMM算法优化的结果比dlADMM优化的结果更能提高模型的精度,且dlBi-ADMM算法比dlADMM算法在时间效率上表现更好。
中图分类号:
引用本文
徐占洋, 程洛飞, 程建春, 许小龙. 一种使用Bi-ADMM优化深度学习模型的方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 54-63.
XU Zhanyang, CHENG Luofei, CHENG Jianchun, XU Xiaolong. A Scheme of Optimizing Deep Learning Model Using Bi-ADMM[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(2): 54-63.
| [1] | BOTTOU L. Large-Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent[C]// Springer. Proceedings of COMPSTAT' 2010. Berlin:Springer, 2010: 177-186. |
| [2] | DUCHI J, HAZAN E, SINGER Y. Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning research, 2011, 12(7): 257-269. |
| [3] | LIN Jiadong, SONG Chuanbiao, HE Kun, et al. Nesterov Accelerated Gradient and Scale Invariance for Adversarial Attacks[EB/OL]. (2020-02-03)[2022-10-05]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2976752987. |
| [4] | ZEILER M D. Adadelta: An Adaptive Learning Rate Method[EB/OL]. (2012-12-22)[2022-10-05]. http://export.arxiv.org/pdf/1212.5701. |
| [5] | WANG Bao, NGUYEN T, SUN Tao, et al. Scheduled Restart Momentum for Accelerated Stochastic Gradient Descent[EB/OL]. (2020-04-26)[2022-10-05]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3007093918. |
| [6] | ZOU Fangyu, SHEN Li, JIE Zequn, et al. A Sufficient Condition for Convergences of Adam and RMSprop[C]// IEEE. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). New York:IEEE, 2018: 11127-11135. |
| [7] | KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimizationt[EB/OL]. (2017-01-30)[2022-10-05]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980. |
| [8] | TAYLOR G, BURMERISTER R, XU Zheng, et al. Training Neural Networks without Gradients: A Scalable Admm Approach[C]// ACM. International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2016: 2722-2731. |
| [9] | WANG Junxiang, YU Fuxun, CHEN Xiang, et al. Admm for Efficient Deep Learning with Global Convergence[C]// ACM. 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2019: 111-119. |
| [10] | HONG Mingyi, LUO Zhiquan, RAZAVIYAYN M. Convergence Analysis of Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers for a Family of Nonconvex Problems[C]// IEEE. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP). New York:IEEE, 2015: 337-364. |
| [11] |
GOLDSTEIN T, O'DONOGHUE B, SETZER S, et al. Fast Alternating Direction Optimization Methods[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2014, 7(3): 1588-1623.
doi: 10.1137/120896219 URL |
| [12] | ZHANG Guoqiang, HEUADENS R. Bi-Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers over Graphs[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. New York: IEEE, 2013: 3317-3321. |
| [13] | ZHANG Guoqiang, HEUADENS R, KLEIJN W B. On the Convergence Rate of the Bi-Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers[C]// IEEE. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). New York:IEEE, 2014: 3869-3873. |
| [14] |
BECK A, TEBOULLE M. A Fast Iterative ShrinkageTthresholding Algorithm for Linear Inverse Problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183-202.
doi: 10.1137/080716542 URL |
| [15] |
SCHEINBERG K, GOLDFARB D, BAI Xi. Fast First-Order Methods for Composite Convex Optimization with Backtracking[J]. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 2014, 14(3): 389-417.
doi: 10.1007/s10208-014-9189-9 URL |
| [16] |
Wang Huahua, Banerjee A. Bregman Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers[EB/OL]. (2014-07-08) [2022-10-05]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1306.3203.
doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1306.3203 |
| [17] | ZHOU Xingyu. On the Fenchel Duality Between Strong Convexity and Lipschitz Continuous Gradient[EB/OL]. (2018-03-17)[2022-10-05]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2793948820. |
| [18] | HUTZENTHALER M, JENTZEN A, KRUSE T, et al. Multilevel Picard Approximations for High-Dimensional Semilinear Second-Order PDEs with Lipschitz Nonlinearitiest[EB/OL]. (2018-03-17)[2022-10-05].https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.02484. |
| [19] |
BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine learning, 2011, 3(1): 1-122.
doi: 10.1561/2200000016 URL |
| [20] |
DOMBI J, JONAS T. The Generalized Sigmoid Function and its Connection with Logical Operators[J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2022, 143(4): 121-138.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2022.01.006 URL |
| [21] |
NAYEF B H, ABDULLAH S N H S, SULAIMAN R, et al. Optimized Leaky ReLU for Handwritten Arabic Character Recognition Using Convolution Neural Networks[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(2): 2065-2094.
doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11593-6 URL |
| [22] |
LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324.
doi: 10.1109/5.726791 URL |
| [23] | XIAO Han, RASUL K, VOLLGRAF R. Fashion-MNIST: A Novel Image Dataset for Benchmarking Machine Learning Algorithms[EB/OL]. (2017-09-15)[2022-10-05]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.07747. |
| [24] | GOLDSBOROUGH P. A Tour of Tensorflow[EB/OL]. (2016-10-01)[2022-10-05]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1610.01178. |
| [25] | PASZKE A, GROSS S, MASSA F, et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 32: 1-12. |
| [1] | 谭柳燕, 阮树骅, 杨敏, 陈兴蜀. 基于深度学习的教育数据分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 96-102. |
| [2] | 陈得鹏, 刘肖, 崔杰, 仲红. 一种基于双阈值函数的成员推理攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 64-75. |
| [3] | 贾凡, 康舒雅, 江为强, 王光涛. 基于NLP及特征融合的漏洞相似性算法评估[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(1): 18-27. |
| [4] | 高博, 陈琳, 严迎建. 基于CNN-MGU的侧信道攻击研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 55-63. |
| [5] | 郑耀昊, 王利明, 杨婧. 基于网络结构自动搜索的对抗样本防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 70-77. |
| [6] | 郭森森, 王同力, 慕德俊. 基于生成对抗网络与自编码器的网络流量异常检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(12): 7-15. |
| [7] | 张郅, 李欣, 叶乃夫, 胡凯茜. 融合多重风格迁移和对抗样本技术的验证码安全性增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 129-135. |
| [8] | 刘烁, 张兴兰. 基于双重注意力的入侵检测系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 80-86. |
| [9] | 朱新同, 唐云祁, 耿鹏志. 基于特征融合的篡改与深度伪造图像检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 70-81. |
| [10] | 路宏琳, 王利明. 面向用户的支持用户掉线的联邦学习数据隐私保护方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 64-71. |
| [11] | 马瑞, 蔡满春, 彭舒凡. 一种基于改进的Xception网络的深度伪造视频检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 109-117. |
| [12] | 潘孝勤, 杜彦辉. 基于混合特征和多通道GRU的伪造语音鉴别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 1-7. |
| [13] | 徐国天, 盛振威. 基于融合CNN与LSTM的DGA恶意域名检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 41-47. |
| [14] | 吴警, 芦天亮, 杜彦辉. 基于Char-RNN改进模型的恶意域名训练数据生成技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 6-11. |
| [15] | 王文华, 郝新, 刘焱, 王洋. AI系统的安全测评和防御加固方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 87-91. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||