信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (12): 69-90.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.12.008
联邦学习与攻防对抗综述
- 西安电子科技大学网络与信息安全学院,西安 710126
-
收稿日期:2023-10-24出版日期:2023-12-10发布日期:2023-12-13 -
通讯作者:朱凌波 E-mail:zlb326511@163.com -
作者简介:杨丽(1994—),女,安徽,博士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全和隐私计算|朱凌波(1999—),男,安徽,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络安全和机器学习|于越明(1998—),女,河北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络安全和机器学习|苗银宾(1989—),男,河南,教授,博士,主要研究方向为云计算、数据安全和隐私保护 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62072361);陕西省重点研发计划(2022GY-019);陕西省数理基础科学研究项目(22JSY019)
Review of Federal Learning and Offensive-Defensive Confrontation
YANG Li, ZHU Lingbo( ), YU Yueming, MIAO Yinbin
), YU Yueming, MIAO Yinbin
- School of Cyber Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710126, China
-
Received:2023-10-24Online:2023-12-10Published:2023-12-13
摘要:
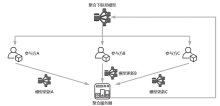
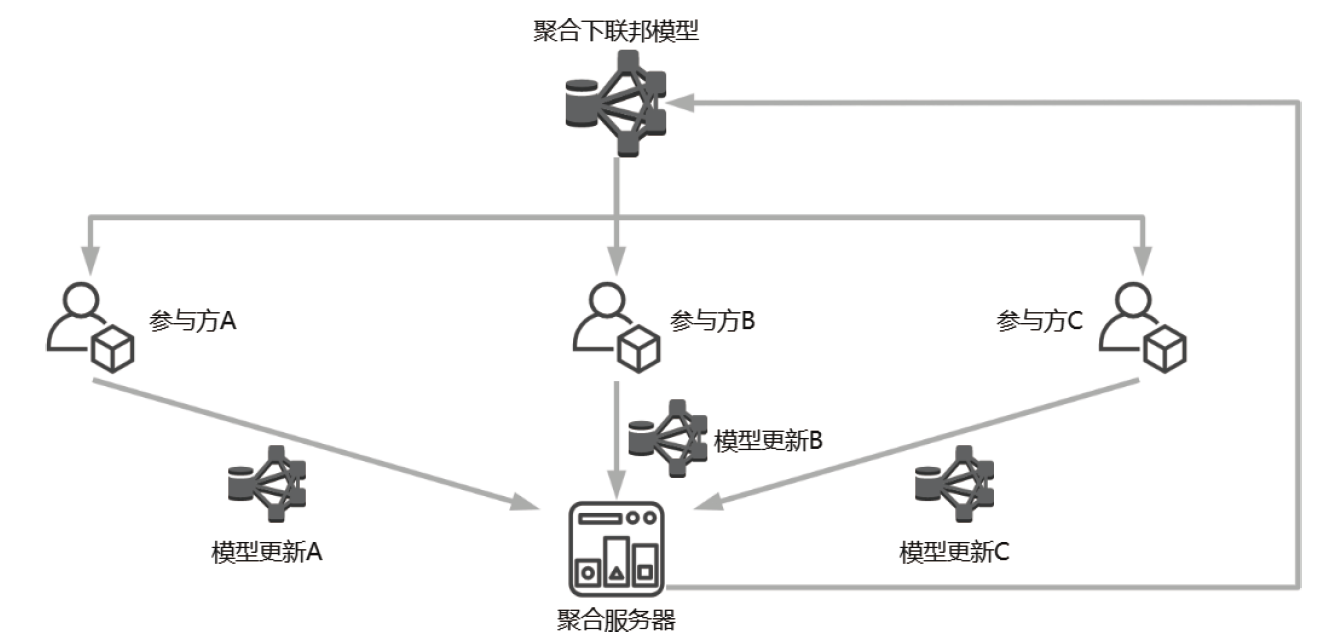
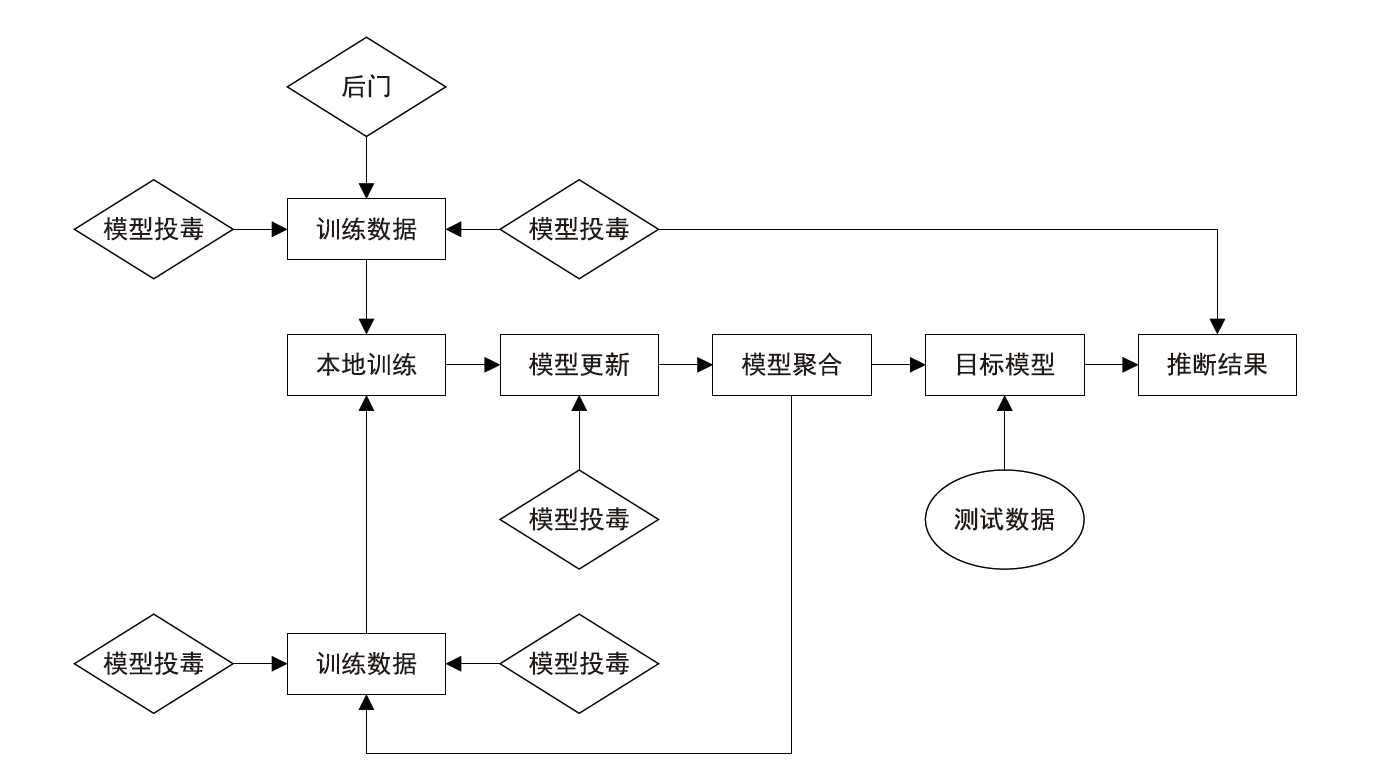
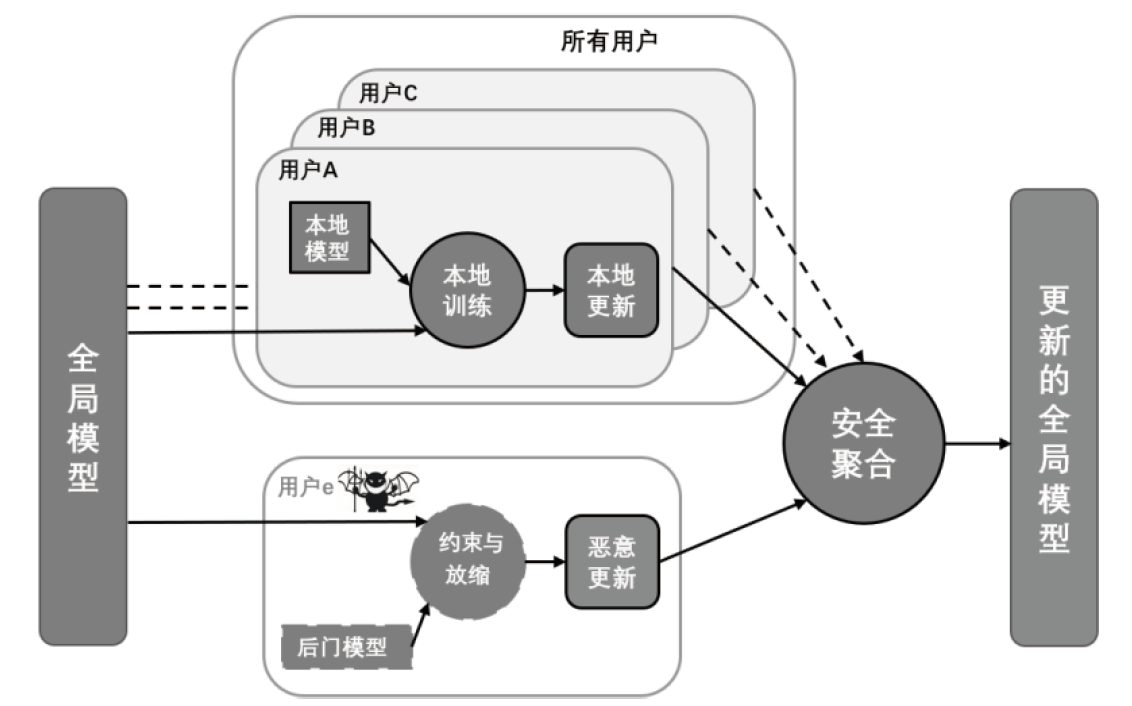
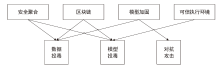
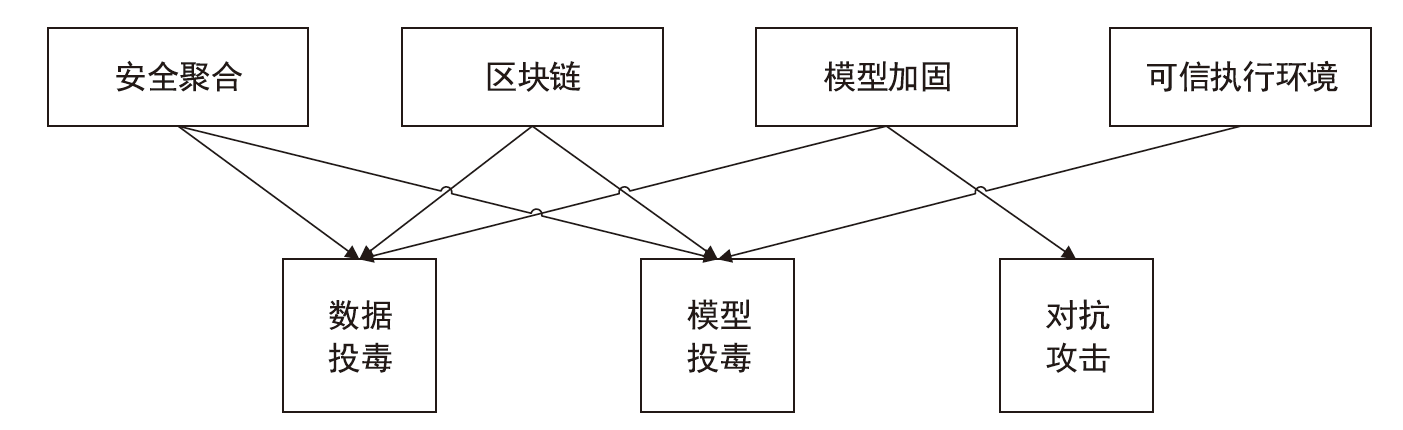
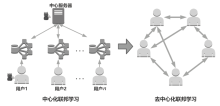
随着机器学习技术的不断发展,个人隐私问题被广泛重视。由于用户数据被发送至中心节点导致集中学习受到相当程度的制约,所以联邦学习作为一个数据不出本地便可以完成模型训练的框架应运而生。但联邦学习机制依旧会受到各种攻击的影响而导致安全性和隐私性降低。文章先从联邦学习的基本定义入手,再对机密性和完整性两个方面进行重点分析、总结联邦学习中的威胁和防御手段,最后结合这些问题来讨论该领域在未来的发展方向。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨丽, 朱凌波, 于越明, 苗银宾. 联邦学习与攻防对抗综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12): 69-90.
YANG Li, ZHU Lingbo, YU Yueming, MIAO Yinbin. Review of Federal Learning and Offensive-Defensive Confrontation[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(12): 69-90.
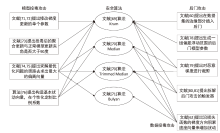
表1
数据投毒方法主流方法总结
| 投毒方式 | 投毒思路 |
|---|---|
| 基于标签 反转[ | 通过直接修改目标类别的训练数据的标签信息,而数据的特征保持不变 |
| 基于目标 优化[ | 将要解决的目标转化为一系列最优解问题。在数据投毒中,目标问题通常是制作最有效的中毒样本,既可以用于计算标签中毒的最佳数据点集,也可用于找到最有效的数据修改方案 |
| 基于梯度 优化[ | 使中毒样本朝着对抗目标函数 |
| 基于干净 标签[ | 干净标签数据投毒攻击中,中毒图像的标签与视觉感官是一致的,但测试图像会被错误分类 |
表1
表2
基于特征更新差异的安全聚合的研究方法
| 研究 | 特征依据 | 具体方案 |
|---|---|---|
| BLANCHARD[ | 欧氏距离 | Krum、Multi-Krum |
| MHAMDI[ | Bulyan | |
| CHEN[ | 中位数 | 取分组后均值的中位数 |
| XIE[ | 每个维度都取中位数 | |
| YIN[ | ||
| KHAZBAK[ 等人 | 余弦相似度 | “用户梯度更新”与“其他所有参与方的梯度” |
| MU?OZ-GONZáLEZ[ | “用户梯度更新”与“所有梯度更新的加权平均值” | |
| FUNG[ | “用户的历史聚合更新”与“其他所有参与方的梯度更新” | |
| YU[ | 聚类算法 | K-means |
| SINGH[ | 按照公开属性(如地区、偏好、性别等)聚类分组 |
表2
| [1] | POUYANFAR S, SADIQ S, YAN Yilin, et al. A Survey on Deep Learning: Algorithms, Techniques, and Applications[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2019, 51(5): 1-36. |
| [2] | HATCHER W G, YU Wei. A Survey of Deep Learning: Platforms, Applications and Emerging Research Trends[J]. IEEE Access, 2018(6), 24411-24432. |
| [3] | GOODFELLOW I, COURVILLE A, BENGIOB Y. Deep Learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2016. |
| [4] | TRASK A W. Grokking Deep Learning[M]. Greenwich: Manning Publications, 2019. |
| [5] | YANG Qiang, LIU Yang, CHEN Tianjian, et al. Federated Machine Learning: Concept and Applications[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2019, 10(2): 1-19. |
| [6] | MCMAHAN H B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data[EB/OL]. (2023-01-26)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.05629. |
| [7] | MCMAHAN H B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Federated Learning of Deep Networks Using Model Averaging[EB/OL]. (2017-02-28)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.05629v3. |
| [8] | LIU Yang, YANG Qiang, CHEN Tianjian, et al. Federated Learning and Transfer Learning for Privacy, Security and Confidentiality[EB/OL]. (2019-02-21)[2023-10-10]. https://aisp-1251170195.cos.ap-hongkong.myqcloud.com/fedweb/1552916850679.pdf. |
| [9] | YANG T, ANDREW G, EICHNER H, et al. Applied Federated Learning: Improving Google Keyboard Query Suggestions[EB/OL]. (2018-12-07)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.02903. |
| [10] | HARD A, RAO K, MATHEWS R, et al. Federated Learning for Mobile Keyboard Prediction[EB/OL]. (2019-02-28)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.03604. |
| [11] | CRAMER R, DAMGARD I, NIELSEN J B. Multiparty Computation from Threshold Homomorphic Encryption[C]// IACR. Proceedings of the International Conference on the Theoryand Application of Cryptographic Techniques: Advances in Cryptology. Berlin:Springer, 2001: 280-299. |
| [12] | DAMGARD I, NIELSEN J B. Universally Composable Efficient Multiparty Computation from Threshold Homomorphic Encryption[C]// IACR.Proceedings of Advances in Cryptology. Berlin:Springer, 2003: 247-264. |
| [13] | KAIROUZ P, MCMAHAN H B, AVENT B, et al. Adances and Open Problems in Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2019-12-10)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.04977. |
| [14] | SHOKRI R, STRONATI M, SONG Congzheng, et al. Membership Inference Attacks against Machine Learning Models[EB/OL]. (2017-03-31)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.05820. |
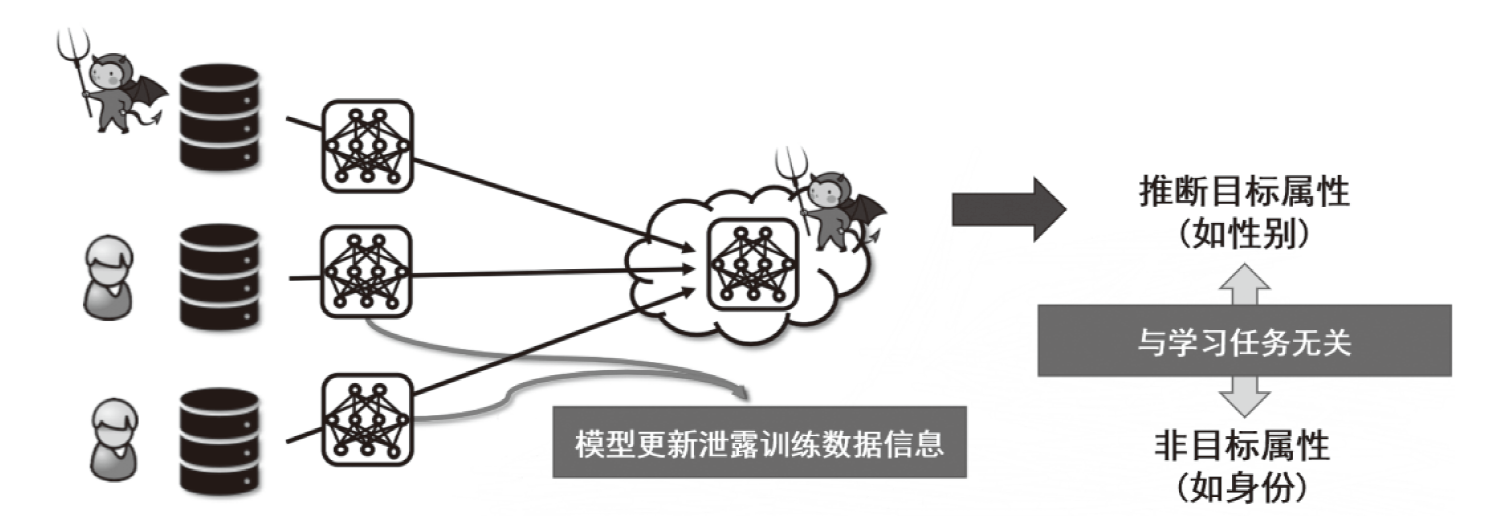
| [15] | MELIS L, SONG Congzheng, DE C E, et al. Exploiting Unintended Feature Leakage in Collaborative Learning[C]// IEEE.Proceedings of 40th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. Berlin:IEEE, 2019: 691-706. |
| [16] | NASR M, SHOKRI R, HOUMANSADR A. Comprehensive Privacy Analysis of Deep Learning: Passive and Active White-Box Inference Attacks against Centralized and Federated Learning[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. Berlin:IEEE, 2019: 739-753. |
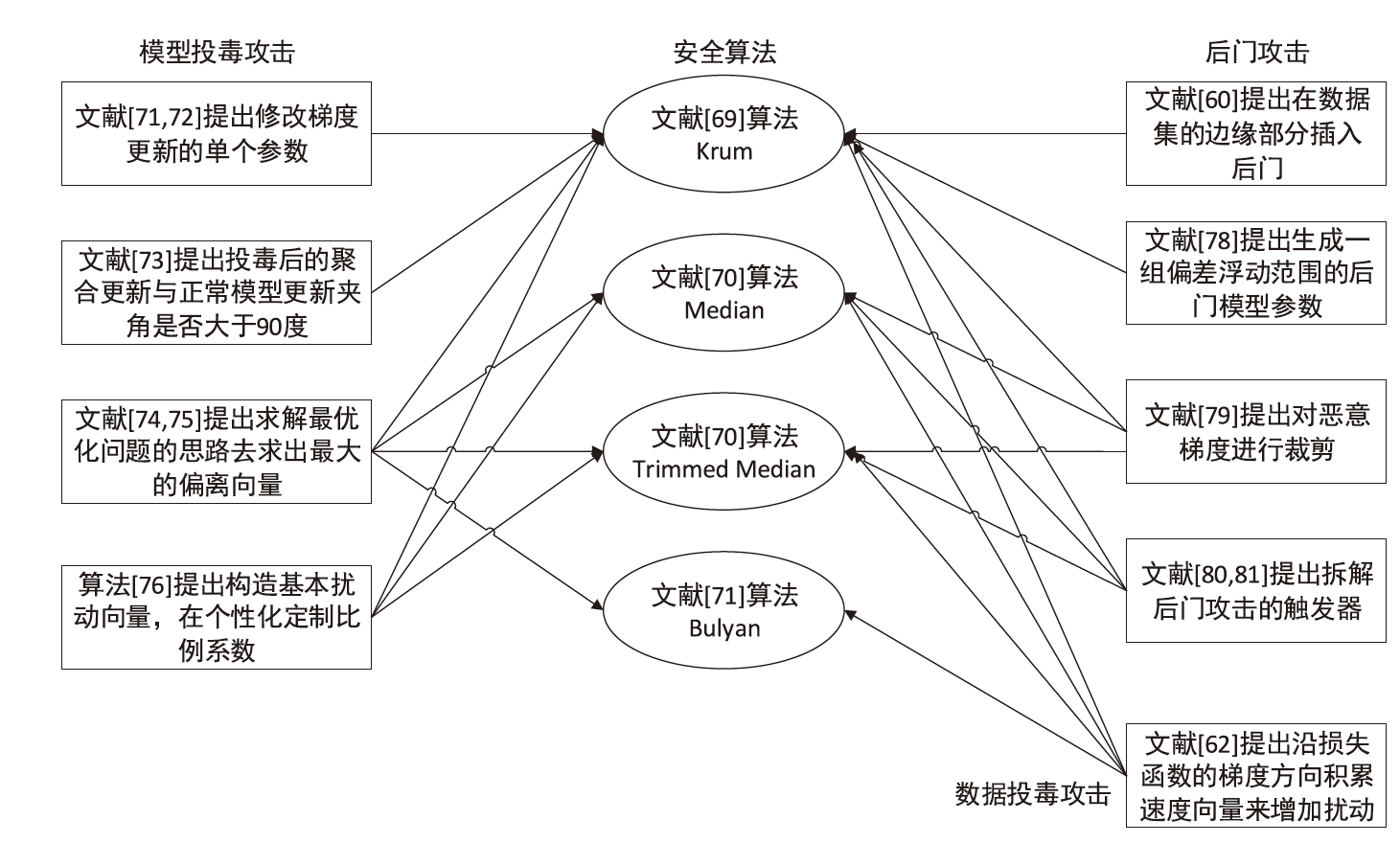
| [17] | CHEN Jiale, ZHANG Jiale, ZHAO Yanchao, et al. Beyond Model-Level Membership Privacy Leakage: An Adversarial Approach in Federated Learning[C]// IEEE. International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-9. |
| [18] | ZHANG Jingwen, ZHANG Jiale, CHEN Junjun, et al. GAN Enhanced Membership Inference: A Passive Local Attack in Federated Learning[C]// IEEE.ICC 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-6. |
| [19] | HITAJ B, ATENIESE G, PEREZ-CRUZ F. Deep Models Under the GAN: Information Leakage from Collaborative Deep Learning[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. Dallas: Association for Computing Machinery, 2017: 603-618. |
| [20] | WANG Zhibo, SONG Mengkai, ZHANG Zhifei, et al. Beyond Inferring Class Representatives: User-Level Privacy Leakage from Federated Learning.[C]// IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. New York: IEEE, 2019: 2512-2520. |
| [21] |
SONG Mengkai, WANG Zhibo, ZHANG Zhifei, et al. Analyzing User-Level Privacy Attack against Federated Learning[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(10): 2430-2444.
doi: 10.1109/JSAC.49 URL |
| [22] |
LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324.
doi: 10.1109/5.726791 URL |
| [23] | ZHU Ligeng, LIU Zhijian, HAN Song. Deep Leakage from Gradients[C]// NIPS. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver: NIPS, 2019: 14747-14756. |
| [24] | GEIPING J, BAUERMEISTER H, DRÖGE H, et al. Inverting Gradients-How Easy is It to Break Privacy in Federated Learning?[C]// NIPS. Proceedings of the 34rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver: ACM, 2020: 16937-16947. |
| [25] | KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization[EB/OL]. (2017-01-30)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980. |
| [26] | ZHAO Bo, MOPURI K R, BILEN H. IDLG: Improved Deep Leakage from Gradients[EB/OL]. (2020-01-08)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.02610. |
| [27] | WEI Wenqi, LIU Ling, LOPER M, et al. A Framework for Evaluating Client Privacy Leakages in Federated Learning[C]// Springer. Computer Security-ESORICS 2020. Berlin:Springer, 2020: 545-566. |
| [28] | DARIO P, DANILO F, GIUSEPPE A. Eluding Secure Aggregation in Federated Learning via Model Inconsistency[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2022 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2022: 2429-2443. |
| [29] |
SHEN Meng, WANG Huan, ZHANG Bin, et al. Exploiting Unintended Property Leakage in Blockchain-Assisted Federated Learning for Intelligent Edge Computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(4): 2265-2275.
doi: 10.1109/JIoT.6488907 URL |
| [30] | ZHOU Chunyi, GAO Yansong, FU Anmin, et al. PPA: Preference Profiling Attack against Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2022-08-09)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.04856. |
| [31] | YAO A C. Protocols for Secure Computations[EB/OL]. (2008-07-18)[2023-10-10]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4568388. |
| [32] | XU Runhua, BARACALDO N, ZHOU Yi, et al. HybridAlpha: An Efficient Approach for Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning[C]// ACM.Proceedings of the 12th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 13-23. |
| [33] | BONEH D, SAHAI A, WATERS B. Functional Encryption: Definitions and Challenges[C]// Springer. Proceedings of the 8th Theory of Cryptography Conference IACR, Berlin:Springer. 2011: 253-273. |
| [34] | KHAZBAK Y, TANTianxiang, CAOGuohong. MLGuard: Mitigating Poisoning Attacks in Privacy Preserving Distributed Collaborative Learning[C]// IEEE.Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-9. |
| [35] |
LI Yong, ZHOU Yipeng, JOLFAEI A, et al. Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Framework Based on Chained Secure Multiparty Computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(8): 6178-6186.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3022911 URL |
| [36] | DWORK C. Differential Privacy[EB/OL]. (2006-07-10)[2023-10-10]. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-5906-5_752. |
| [37] | GEYER R C, KLEIN T, NABI M. Differentially Private Federated Learning: A Client Level Perspective[EB/OL]. (2018-03-01)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.07557. |
| [38] | JAYARAMAN B, WANG Lingxiao, EVANS D, et al. Distributed Learning without Distress: Privacy-Preserving Empirical Risk Minimization[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 32nd Internationall Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2018: 6346-6357. |
| [39] | BHOWMICK A, DUCHI J, FREUDIGER J, et al. Protection against Reconstruction and Its Applications in Private Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2019-06-03)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.00984. |
| [40] | TRIASTCYN A, FALTINGS B. Federated Learning with Bayesian Differential Privacy[C]// IEEE.Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data. New York: IEEE, 2019: 2587-2596. |
| [41] |
HUANG Xixi, DING Ye, JIANG Z L, et al. DP-Fl: A Novel Differentially Private Federated Learning Framework for the Unbalanced Data[J]. World Wide Web, 2020, 23(4): 2529-2545.
doi: 10.1007/s11280-020-00780-4 |
| [42] |
WU Maoqiang, YE Dongdong, DING Jiahao, et al. Incentivizing Differentially Private Federated Learning: A Multidimensional Contract Approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(13): 10639-10651.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3050163 URL |
| [43] | RIVEST R L, ADLEMAN L, DERTOUZOS M L, et al. On Data Banks and Privacy Homomorphisms[J]. Foundations of Secure Computation, 1978, 4 (11): 169-180. |
| [44] | PAILLIER P. Public-Key Cryptosystems Based on Composite Degree Residuosity Classe[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. New York: IEEE, 1999: 223-238. |
| [45] | PHONG L T, AONO Y, HAYASHI T, et al. Privacy-Preserving Deep Learning: Revisited and Enhanced[C]// ATIS.Proceedings of the 8th Internaitonal Conference on Applications and Techniques in Information Security. Berlin:Springer, 2017: 100-110. |
| [46] | HAO Meng, LI Hongwei, XU Guowen, et al. Towards Efficient and Privacy-Preserving Federated Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2019: 1-6. |
| [47] |
CHAI Di, WANG Leye, CHEN Kai, et al. Secure Federated Matrix Factorization[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2021, 36(5): 11-20.
doi: 10.1109/MIS.2020.3014880 URL |
| [48] | FANG Chen, GUO Yuanbo, WANG Na, et al. Highly Efficient Federated Learning with Strong Privacy Preservation in Cloud Computing[EB/OL]. (2020-09-01)[2023-10-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2020.101889. |
| [49] |
HAO Meng, LI Hongwei, LUO Xizhao, et al. Efficient and Privacy-Enhanced Federated Learning for Industrial Artificial Intelligence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(10): 6532-6542.
doi: 10.1109/TII.9424 URL |
| [50] | FANG Chen, GUO Yuanbo, HU Yongjin, et al. Privacy-Preserving and Communication-Efficient Federated Learning in Internet of Things[EB/OL]. (2021-04-01)[2023-10-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102199. |
| [51] |
FROELICHER D, TRONCOSO-PASTORIZA J R, PYRGELIS A, et al. Scalable Privacy-Preserving Distributed Learning[J]. Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2021, 2021(2): 323-347.
doi: 10.2478/popets-2021-0030 URL |
| [52] | SAV S, PYRGELIS A, TRONCOSO-PASTORIZA J R, et al. POSEIDON: Privacy-Preserving Federated Neural Network Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-01-08)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.00349. |
| [53] | BONAWITZ K, IVANOV V, KREUTER B, et al. Practical Secure Aggregation for Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning[C]// ACM.Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 1175-1191. |
| [54] | SO J, ALI R E, GULER B, et al. Securing Secure Aggregation: Mitigating Multi-Round Privacy Leakage in Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2023-07-27)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.03328. |
| [55] | LI Wenqi, MILLETARÌ F, XU Daguang, et al. Privacy-Preserving Federated Brain Tumour Segmentation[EB/OL]. (2023-10-10)[2023-10-10]. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-32692-0_16. |
| [56] |
ZHAO Bin, FAN Kai, YANG Kan, et al. Anonymous and Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning with Industrial Big Data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17: 6314-6323.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3052183 URL |
| [57] | IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift[C]// ACM.Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2015: 448-456. |
| [58] | ANDREUX M, DU T J O, BEGUIER C, et al. Siloed Federated Learning for Multi-Centric Histopathology Datasets[EB/OL]. (2022-08-17)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.07424. |
| [59] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2013-12-21)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6199. |
| [60] | WANG Hongyi, SREENIVASAN K, RAJPUT S, et al. Attack of the Tails: Yes, You Really Can Backdoor Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2020-07-09)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.05084. |
| [61] | PANG Qi, YUAN Yuanyuan, WANG Shuai. Attacking Vertical Collaborative Learning System Using Adversarial Dominating Inputs[EB/OL]. (2023-04-11)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.02775v1. |
| [62] | SHI Lei, CHEN Zhen, SHI Yucheng, et al. Data Poisoning Attacks on Federated Learning by Using Adversarial Samples[EB/OL]. (2022-07-01)[2023-10-10]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9853326. |
| [63] | BIGGIO B, NELSON B, LASKOV P. Poisoning Attacks against Support Vector Machines[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 29th International Coference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2012: 1467-1474. |
| [64] | TOLPEGIN V, TRUEX S, GURSOY M E, et al. Data Poisoning Attacks against Federated Learning Systems[EB/OL]. (2020-08-11)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.08432. |
| [65] | ZHANG Jiale, CHEN Junjun, WU Di, et al. Poisoning Attack in Federated Learning Using Generative Adversarial Nets[EB/OL]. (2019-10-31)[2023-10-10]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8887357. |
| [66] | GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative Adversarial Nets[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2014: 2672-2680. |
| [67] |
ZHANG Jiale, CHEN Bing, CHENG Xiang, et al. PoisonGAN: Generative Poisoning Attacks against Federated Learning in Edge Computing Systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(5): 3310-3322.
doi: 10.1109/JIoT.6488907 URL |
| [68] | LI Tian, SAHU A K, ZAHEER M, et al. Federated Optimization in Heterogeneous Networks[EB/OL]. (2020-04-21)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.06127. |
| [69] | BLANCHARD P, EL M E M, GUERRAOUI R, et al. Machine Learning with Adversaries: Byzantine Tolerant Gradient Descent[C]// ACM.Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2017: 118-128. |
| [70] | YIN Dong, CHEN Yudong, RAMCHANDRAN K, et al. Byzantine-Robust Distributed Learning: Towards Optimal Statistical Rates[EB/OL]. (2021-02-25)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.01498. |
| [71] | MHAMDI EL M E, GUERRAOUI R, ROUAULT S. The Hidden Vulnerability of Distributed Learning in Byzantium[EB/OL]. (2018-07-17)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.07927. |
| [72] | BARUCH M, BARUCH G, GOLDBERG Y. A Little is Enough: Circumventing Defenses for Distributed Learning[EB/OL]. (2019-02-16)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.06156. |
| [73] | XIE Cong, KOYEJO O, GUPTA I. Fall of Empires: Breaking Byzantine-Tolerant SGD by Inner Product Manipulation[EB/OL](2019-03-10)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.03936. |
| [74] | BHAGOJI A N, CHAKRABORTY S, MITTAL P, et al. Analyzing Federated Learning through Anadversarial Lens[C]// IMLS. Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ICML, 2019: 1012-1021. |
| [75] | FANG Minghong, CAO Xiaoyu, JIA Jinyuan, et al. Local Model Poisoning Attacks to Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning[C]// USENIX.Proceedingsof the 29th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX Association, 2020: 1623-1640. |
| [76] | SHEJWALKAR V, HOUMANSADR A. Manipulating the Byzantine: Optimizing Model Poisoning Attacks and Defenses for Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-01-01)[2023-10-10]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350050756_Manipulating_the_Byzantine_Optimizing_Model_Poisoning_Attacks_and_Defenses_for_Federated_Learning. |
| [77] | BAGDASARYAN E, VEIT A, HUA Yiqing, et al. How to Backdoor Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2019-08-06)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.00459. |
| [78] | BARUCH M, BARUCH G, GOLDBERG Y. A Little is Enough: Circumventing Defenses for Distributed Learning[EB/OL]. (2019-02-16)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.06156. |
| [79] | SUN Ziteng, KAIROUZ P, SURESH A T, et al. Can You Really Backdoor Federated Learning?[EB/OL]. (2019-12-02)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.07963. |
| [80] | XIE Chulin, HUANG Keli, CHEN Pinyu, et al. DBA: Distributed Backdoor Attacks against Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2023-05-06)[2023-10-10]. https://openreview.net/forum?id=rkgyS0VFvr. |
| [81] | GONG Xueluan, CHEN Yanjiao, HUANG Huayang, et al. Coordinated Backdoor Attacks against Federated Learning with Model-Dependent Triggers[J]. IEEE Network, 2022, 36: 84-90. |
| [82] | CHEN Yudong, SU Lili, XU Jiaming. Distributed Statistical Machine Learning in Adversarial Settings: Byzantine Gradient Descent[EB/OL]. (2017-12-19)[2023-10-10]. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3154503. |
| [83] | XIE Cong, KOYEJO O, GUPTA I. Generalized Byzantine-Tolerant SGD[EB/OL]. (2018-05-23)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.10116. |
| [84] | MUÑOZ-GONZÁLEZ L, CO K T, LUPU E C. Byzantine-Robust Federated Machine Learning through Adaptive Model Averaging[EB/OL]. (2019-09-11)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05125. |
| [85] | FUNG C, YOON C J M, BESCHASTNIKH I. The Limitations of Federated Learning in Sybil Settings[C]// USENIX. Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and Defenses. San Sebastian: USENIX Association, 2020: 301-316. |
| [86] | YU Lei, WU Lingfei. Towards Byzantine-Resilient Federated Learning via Group-Wise Robust Aggregation[EB/OL]. (2020-11-26)[2023-10-10]. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63076-8_6. |
| [87] |
JAIN A K. Data Clustering: 50 Years Beyond K-Means[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2010, 31 (8): 651-666.
doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2009.09.011 URL |
| [88] | SINGH A K, BLANCO-JUSTICIA A, DOMINGO-FERRER J, et al. Fair Detection of Poisoning Attacks in Federated Learning[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence. New York: IEEE, 2020: 224-229. |
| [89] | WANG Yuao, ZHU Tianqing, CHANG Wenhan, et al. Model Poisoning Defense on Federated Learning: A Validation Based Approach[C]// Springer. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Network and System Security. Berlin:Springer, 2020: 207-223. |
| [90] |
CHEN Zheyi, TIAN Pu, LIAO Weixian, et al. Zero Knowledge Clustering Based Adversarial Mitigationin Heterogeneous Federated Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(2): 1070-1083.
doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.3002796 URL |
| [91] | XIE Cong, KOYEJO S, GUPTA I. Zeno: Distributed Stochastic Gradient Descent with Suspicion-Based Fault-Tolerance[EB/OL]. (2019-05-18)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.10032. |
| [92] | BAO Xianglin, SU Cheng, XIONG Yan, et al. FLChain: A Blockchain for Auditable Federated Learning with Trust and Incentive[C]// IEEE.Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Big Data Computing and Communications. New York: IEEE, 2019: 151-159. |
| [93] | LI Yuzheng, CHEN Chuan, LIU Nan, et al. A Blockchain-Based Decentralized Federated Learning Framework with Committee Consensus[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(1): 234-241. |
| [94] |
PENG Zhe, XU Jianliang, CHU Xiaowen, et al. VFChain: Enabling Verifiable and Auditable Federated Learning via Blockchain Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(1): 173-186.
doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3050781 URL |
| [95] |
SHAYAN M, FUNG C, YOON C J M, et al. Biscotti: A Blockchain System for Private and Secure Federated Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 32(7): 1513-1525.
doi: 10.1109/TPDS.71 URL |
| [96] |
QU Youyang, POKHREL S R, GARG S, et al. A Blockchained Federated Learning Framework for Cognitive Computing in Industry 4.0 Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(4): 2964-2973.
doi: 10.1109/TII.9424 URL |
| [97] | LIU Yi, PENG Jialiang, KANG Jiawen, et al. A Secure Federated Learning Framework for 5G Networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(4): 24-31. |
| [98] |
BENTOV I, LEE C, MIZRAHI A, et al. Proof of Activity: Extending Bitcoin’s Proof of Work via Proof of Stake[J]. ACM SIGMETRICS Performance Evaluation Review, 2014, 42(3): 34-37.
doi: 10.1145/2695533.2695545 URL |
| [99] | MCKEEN F, ALEXANDROVICH I, BERENZON A, et al. Innovative Instructions and Software Model for Isolated Execution[EB/OL]. (2013-06-23)[2023-10-10]. https://doi.org/10.1145/2487726.2488368. |
| [100] |
CHEN Yu, LUO Fang, LI Tong, et al. A Training-Integrity Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Scheme with Trusted Execution Environment[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 522: 69-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.02.037 URL |
| [101] | ZHANG Xiaoli, LI Fengting, ZHANG Zeyu, et al. Enabling Execution Assuranceof Federated Learning at Untrusted Participants[C]// IEEE.Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1877-1886. |
| [102] | ZHAO Yi, XU Ke, WANG Haiyang, et al. Stability-Based Analysis and Defense against Backdoor Attacks on Edge Computing Services[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(1): 163-169. |
| [103] | ZHANG Jiale, WU Di, LIU Chengyong, et al. Defending Poisoning Attacks in Federated Learning via Adversarial Training Method[C]// Springer. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Frontiers in Cyber Security. Berlin:Springer, 2020: 83-94. |
| [104] | IBITOYE O, SHAFIQ M O, MATRAWY A. DiPSeN: Differentially Private Self-Normalizing Neural Networks For Adversarial Robustness in Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-01-08)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.03218v1. |
| [105] | GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2015-03-20)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572. |
| [106] | SHEJWALKAR V, HOUMANSADR A, KAIROUZ P, et al. Back to the Drawing Board: A Critical Evaluation of Poisoning Attacks on Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-12-13)[2023-10-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.10241. |
| [1] | 彭翰中, 张珠君, 闫理跃, 胡成林. 联盟链下基于联邦学习聚合算法的入侵检测机制优化研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 76-85. |
| [2] | 陈晶, 彭长根, 谭伟杰, 许德权. 基于差分隐私和秘密共享的多服务器联邦学习方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 98-110. |
| [3] | 刘长杰, 石润华. 基于安全高效联邦学习的智能电网入侵检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 90-101. |
| [4] | 秦中元, 戈臻伟, 潘经纬, 陈立全. 基于虚拟可信平台模块的完整性度量方案研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 11-18. |
| [5] | 刘吉强, 王雪微, 梁梦晴, 王健. 基于共享数据集和梯度补偿的分层联邦学习框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12): 10-20. |
| [6] | 刘忻, 李韵宜, 王淼. 一种基于机密计算的联邦学习节点轻量级身份认证协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 37-45. |
| [7] | 吕国华, 胡学先, 杨明, 徐敏. 基于联邦随机森林的船舶AIS轨迹分类算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(4): 67-76. |
| [8] | 易铮阁, 袁文勇, 李瑞峰, 杨晓元. 一种支持动态操作的身份基云存储方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 86-95. |
| [9] | 李桐, 任帅, 王刚, 孟庆宇. 基于变色龙认证树的云边端协同流式数据完整性验证模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 37-45. |
| [10] | 白宏鹏, 邓东旭, 许光全, 周德祥. 基于联邦学习的入侵检测机制研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 46-54. |
| [11] | 徐硕, 张睿, 夏辉. 基于数据属性修改的联邦学习隐私保护策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 55-63. |
| [12] | 路宏琳, 王利明, 杨婧. 一种新的参数掩盖联邦学习隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 26-34. |
| [13] | 任涛, 金若辰, 罗咏梅. 融合区块链与联邦学习的网络入侵检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(7): 27-34. |
| [14] | 沈卓炜, 高鹏, 许心宇. 基于安全协商的DDS安全通信中间件设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(6): 19-25. |
| [15] | 路宏琳, 王利明. 面向用户的支持用户掉线的联邦学习数据隐私保护方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 64-71. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||