信息网络安全 ›› 2021, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (8): 26-34.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2021.08.004
一种新的参数掩盖联邦学习隐私保护方案
- 1.中国科学院信息工程研究所,北京 100093
2.中国科学院大学网络空间安全学院,北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2021-03-19出版日期:2021-08-10发布日期:2021-09-01 -
通讯作者:王利明 E-mail:wangliming@iie.ac.cn -
作者简介:路宏琳(1995—),女,山东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为联邦学习的数据隐私保护|王利明(1978—),男,北京,正高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为云计算安全、网络安全|杨婧(1984—),女,山西,高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为网络安全、数据安全分析 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2017YFB1010004)
A New Parameter Masking Federated Learning Privacy Preserving Scheme
LU Honglin1,2, WANG Liming1( ), YANG Jing1
), YANG Jing1
- 1. Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100093, China
2. School of Cyber Security, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-03-19Online:2021-08-10Published:2021-09-01 -
Contact:WANG Liming E-mail:wangliming@iie.ac.cn
摘要:
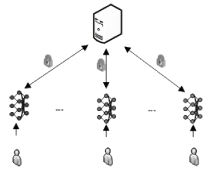
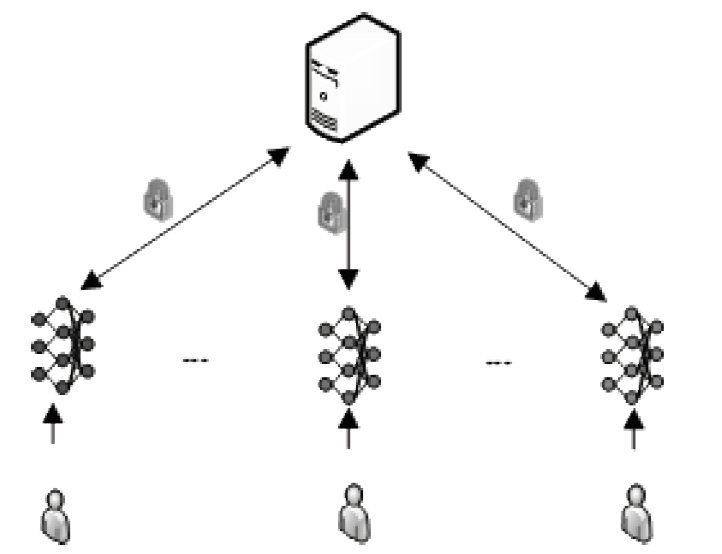
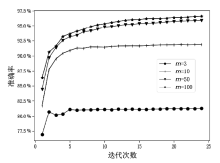
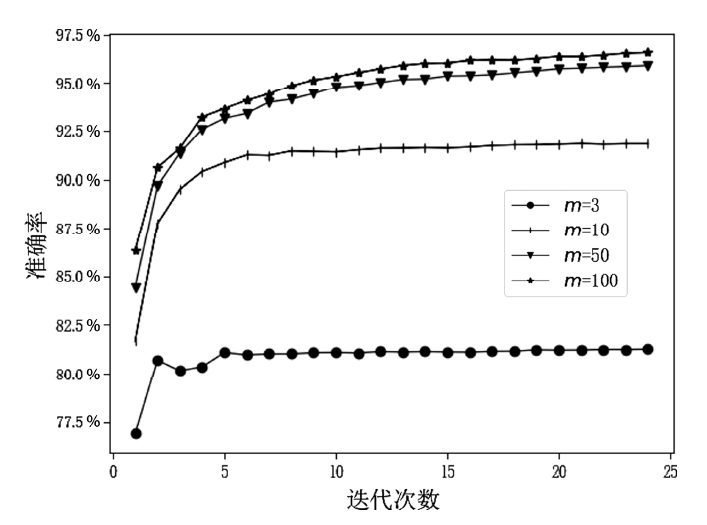
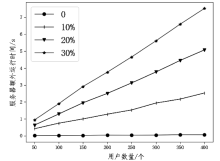
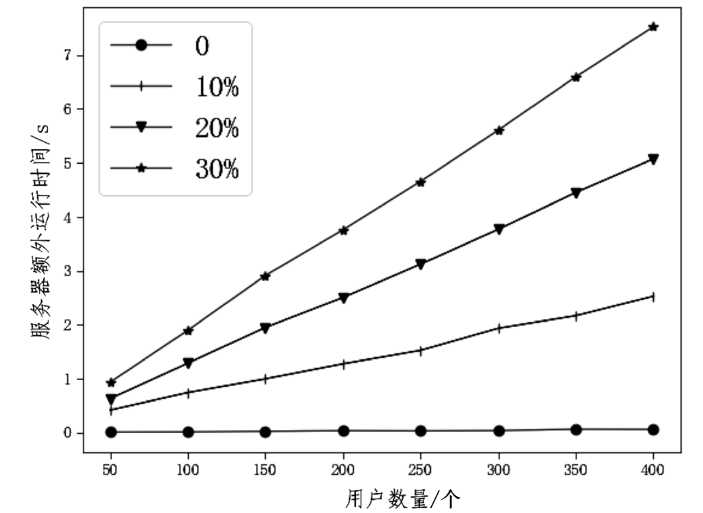
随着数据隐私保护相关的法律法规相继出台,传统集中式学习模式中的隐私数据暴露问题已经成为制约人工智能发展的重要因素。联邦学习的提出解决了这一问题,但是现有的联邦学习存在模型参数泄露敏感信息、依赖可信第三方服务器等问题。文章提出了一种新的参数掩盖联邦学习隐私保护方案,能够抵御服务器攻击、用户攻击、服务器和少于t个用户的联合攻击。该方案包含密钥交换、参数掩盖、掉线处理3个协议。用户在本地训练模型后上传掩盖的模型参数,服务器进行模型参数聚合后,只能获得掩盖后的参数聚合结果。实验表明,对于16位的输入值,27用户和220- 维向量,文章方案对比明文发送数据提供1.44×的通信扩展,相比已有研究方案具备更低的通信代价。
中图分类号:
引用本文
路宏琳, 王利明, 杨婧. 一种新的参数掩盖联邦学习隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 26-34.
LU Honglin, WANG Liming, YANG Jing. A New Parameter Masking Federated Learning Privacy Preserving Scheme[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(8): 26-34.
表1
本文符号说明
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| m | 用户个数 |
| d | 掉线用户个数 |
| P,${{P}_{d}}$、${{P}_{po}}$、${{P}_{j}}$ | 用户集合,掉线、延迟上传、普通用户 |
| g | 密钥生成元 |
| q | 密钥交换协议中的素数 |
| $\alpha $ | 额外的附加掩盖值 |
| w | 模型参数 |
| ${{\hat{w}}_{j}}$ | 本文中掩盖的模型参数 |
| ${{\dot{w}}_{j}}$ | 文献[ |
| ${{b}_{j}}$ | 文献[ |
| ${{S}_{j,i}}$ | 用户${{P}_{j}}$和${{P}_{i}}$的协商密钥 |
| t | 秘密共享门限值 |
| $P{{K}_{j}}S{{K}_{j}}$ | 用户${{P}_{j}}$的公钥、私钥 |
| R | PRG的输出最大值 |
| ${{R}_{U}}$ | 原始模型参数的输出最大值 |
| z | PRG的输出维度 |
| ${{a}_{K}}$ | 密钥交换公钥比特数 |
| ${{a}_{S}}$ | 秘密共享份额比特数 |
| [1] | CUSTERS B, SEARS A, DECHESNE F, et al. Information Technology and Law Series[M]. Netherlands: T. M. C. Asser Press, 2019. |
| [2] | The National People's Congress and its Standing Committee. The Cybersecurity Law of the People’s Republic of China[EB/OL]. http://www.npc.gov.cn/wxzl/gongbao/2017-02/20/content_2007531.htm, 2021-02-12 . |
| [3] | YANG Qiang. Federated Learning: the Last Mile of Artificial Intelligence[J]. Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2020, 15(81):189-192. |
| 杨强. 联邦学习:人工智能的最后一公里[J]. 智能系统学报, 2020, 15(81):189-192. | |
| [4] | SHOKRI R, STRONATI M, SONG Congzheng, et al. Membership Inference Attacks Against Machine Learning Models[C]//IEEE. IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, May 22-26, 2017, San Jose, CA, USA. New York: IEEE, 2017: 3-18. |
| [5] | MELIS L, SONG Congzheng, CRISTOFARO E D, et al. Exploiting Unintended Feature Leakage in Collaborative Learning[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), May 19-23, 2019, San Francisco, CA. New York: IEEE, 2019: 691-706. |
| [6] | HITAJ B, ATENIESE G, PEREZ-CRUZ F. Deep Models Under the GAN: Information Leakage from Collaborative Deep Learning[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, October 30-November 3, 2017, Dallas Texas, USA. New York: ACM, 2017: 603-618. |
| [7] | WANG Zhibo, SONG Mengkai, ZHANG Zhifei, et al. Beyond Inferring Class Representatives: User-Level Privacy Leakage From Federated Learning[C]//IEEE. IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, April 29-May 2, 2019, Paris, France. New York: IEEE, 2019: 2512-2520. |
| [8] | NASR M, SHOKRI R, HOUMANSADR A. Comprehensive Privacy Analysis of Deep Learning: Passive and Active White-box Inference Attacks against Centralized and Federated Learning[C]//IEEE. IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), May 19-23, 2019, San Francisco, CA, USA. New York: IEEE, 2019: 739-753. |
| [9] | LIM W, LUONG N, HOANG D, et al. Federated Learning in Mobile Edge Networks: A Comprehensive Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(3):2031-2063. |
| [10] | GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative Adversarial Networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 14(3):2672-2680. |
| [11] |
PHONG L, AONO Y, HAYASHI T, et al. Privacy-preserving Deep Learning via Additively Homomorphic Encryption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(5):1333-1345.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2787987 URL |
| [12] | ZHANG Qiao, WANG Cong, WU Hongyi, et al. GELU-net: A Globally Encrypted, Locally Unencrypted Deep Neural Network for Privacy-preserved Learning[C]// Morgan Kaufmann. Twenty-seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence IJCAI, July 13-19, 2018, Stockholm, Sweden. California: Morgan Kaufmann, 2018: 3933-3939. |
| [13] | MA X, ZHANG F, CHEN X, et al. Privacy Preserving Multi-party Computation Delegation for Deep Learning in Cloud Computing[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 45(9):103-116. |
| [14] | HAO Meng, LI Hongwei, XU Guowen, et al. Towards Efficient and Privacy-preserving Federated Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), May 20-24, 2019, Shanghai, China. New York: IEEE, 2019: 1-6. |
| [15] | BONAWITZ K, IVANOV V, KREUTER B, et al. Practical Secure Aggregation for Privacy-preserving Machine Learning[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, October 30-November 3, 2017, Dallas Texas, USA. New York: ACM, 2017: 1175-1191. |
| [16] | DUAN Jia, ZHOU Jiantao, LI Yuanman. Privacy-preserving Distributed Deep Learning Based on Secret Sharing[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 52(7):108-127. |
| [17] | PYRGELIS A, TRONCOSO C, CRISTOFARO E. Knock Knock. Knock Knock, Who’s There? Membership Inference on Aggregate Location Data[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323248809_Knock_Knock_Who’s_There_Membership_Inference_on_Aggregate_Location_Data , 2021-02-01. |
| [18] | KOCHER P. Timing Attacks on Implementations of Diffie-Hellman, RSA, DSS, and Other Systems[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 16th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, August 18-22, 1996, Berlin, Germany. New York: ACM, 1996: 104-113. |
| [19] |
SHAMIR A. How to Share a Secret[J]. Commun. ACM, 1979, 22(11):612-613.
doi: 10.1145/359168.359176 URL |
| [20] | LI Hongwei, LIU Dongxiao, DAI Yuanshun, et al. Engineering Searchable Encryption of Mobile Cloud Networks: When QoE Meets QoP[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2015, 22(4):74-80. |
| [21] | BELLARE M, YEE B. Forward-security in Private-key Cryptography[C]//Springer. Proceedings of the 2003 RSA Conference on The Cryptographers’ Track, April 13-17, 2003, Berlin, Germany. Berlin: Springer, 2003: 1-18. |
| [1] | 靳姝婷, 何泾沙, 朱娜斐, 潘世佳. 基于本体推理的隐私保护访问控制机制研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 52-61. |
| [2] | 任涛, 金若辰, 罗咏梅. 融合区块链与联邦学习的网络入侵检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(7): 27-34. |
| [3] | 刘子昂, 黄缘缘, 马佳利, 周睿. 基于区块链的医疗数据滥用监控平台设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(5): 58-66. |
| [4] | 王健, 赵曼莉, 陈志浩, 石波. 基于假名的智能交通条件隐私保护认证协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(4): 49-61. |
| [5] | 任航, 程相国, 张睿, 夏辉. 基于议价贝叶斯博弈模型的防欺诈策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(4): 81-88. |
| [6] | 周由胜, 王明, 刘媛妮. 支持区间查询的基于位置服务外包数据隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 26-36. |
| [7] | 路宏琳, 王利明. 面向用户的支持用户掉线的联邦学习数据隐私保护方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 64-71. |
| [8] | 刘峰, 杨杰, 齐佳音. 基于哈希证明系统的区块链两方椭圆曲线数字签名算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(1): 19-26. |
| [9] | 汪金苗, 谢永恒, 王国威, 李易庭. 基于属性基加密的区块链隐私保护与访问控制方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 47-51. |
| [10] | 李宁波, 周昊楠, 车小亮, 杨晓元. 云环境下基于多密钥全同态加密的定向解密协议设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(6): 10-16. |
| [11] | 张佳程, 彭佳, 王雷. 大数据环境下的本地差分隐私图信息收集方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(6): 44-56. |
| [12] | 王蓉, 马春光, 武朋. 基于联邦学习和卷积神经网络的入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 47-54. |
| [13] | 肖彪, 闫宏强, 罗海宁, 李炬成. 基于差分隐私的贝叶斯网络隐私保护算法的改进研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(11): 75-86. |
| [14] | 何泾沙, 杜晋晖, 朱娜斐. 基于k匿名的准标识符属性个性化实现算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(10): 19-26. |
| [15] | 黄保华, 程琪, 袁鸿, 黄丕荣. 基于距离与误差平方和的差分隐私K-means聚类算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(10): 34-40. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||