信息网络安全 ›› 2015, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (5): 41-46.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2015.05.007
基于异常特征的社交网页检测技术研究
- 1.北京航空航天大学经济管理学院,北京 100191
2.国家计算机网络应急技术处理协调中心,北京 100029
-
收稿日期:2015-04-15出版日期:2015-05-10发布日期:2018-07-16 -
作者简介:作者简介: 李旬 (1990-),男,江苏,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:网络安全;徐剑(1985-),男,湖北,工程师,博士,主要研究方向:网络安全、数据分析;焦英楠 (1983-),女,辽宁,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向:软件工程、信息安全等;严寒冰 (1975-),男,江西,教授级高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向:网络安全监测、应急响应处理、图像型垃圾邮件分析等。
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金[61171193];国家科技支撑计划[2015BAK21B01]
Research on Detection of Social Web Page Based on Abnormal Characteristics
LI Xun1,2, XU Jian2( ), JIAO Ying-nan2, YAN Han-bing2
), JIAO Ying-nan2, YAN Han-bing2
- 1. School of Economics and Management, Beihang University , Beijing 100191, China
2. National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team/Coordination Center of China, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2015-04-15Online:2015-05-10Published:2018-07-16
摘要:
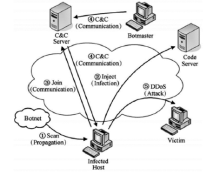
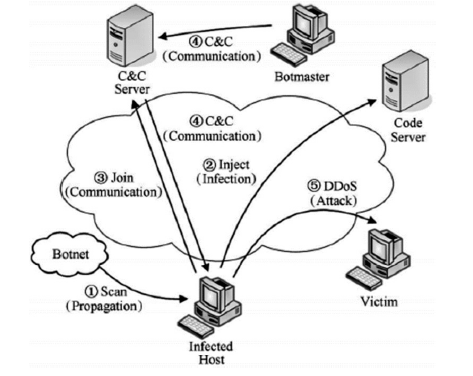
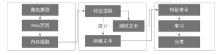
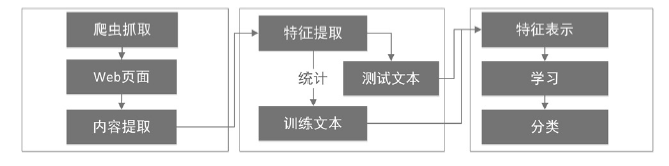
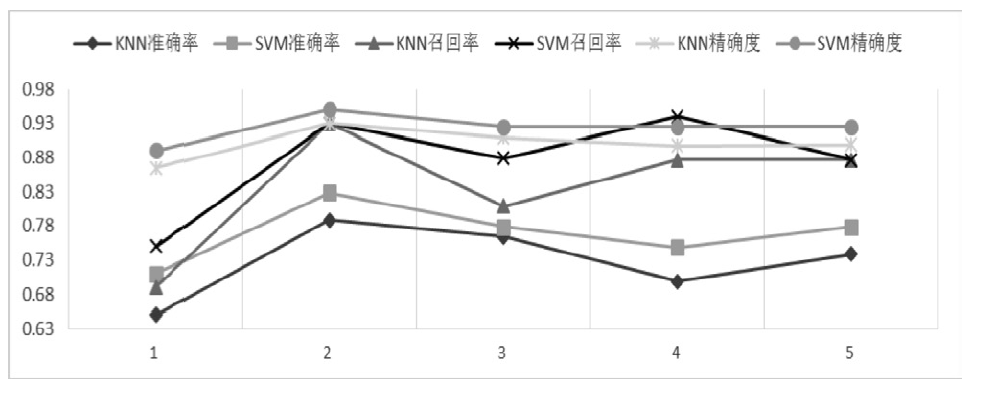
近年来,随着社交网络的快速发展,社交网络已成为僵尸网络隐匿和攻击的理想平台。僵尸网络利用社交网络作为命令与控制传播通道,通过含有控制指令或恶意程序的异常页面来传播命令和控制僵尸主机。这种攻击方式具有隐秘性高的特点,使得传统的僵尸网络检测技术的效果大打折扣。因此如何检测出含有异常文本的页面是社交僵尸网络检测面临的一个重要问题。文章将机器学习算法应用于社交网页检测中,设计并实现了一个异常页面检测系统。文章首先设计爬虫工具收集社交网络中的网页数据,然后借鉴文本分析的方法对页面进行异常特征提取,进而利用KNN和SVM分类算法对特征向量集进行判断,最后对判断结果做出评估分析。实验表明该异常页面检测系统能够有效检测异常页面,提高检测效率,为进一步发现僵尸网络提供依据。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李旬, 徐剑, 焦英楠, 严寒冰. 基于异常特征的社交网页检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(5): 41-46.
LI Xun, XU Jian, JIAO Ying-nan, YAN Han-bing. Research on Detection of Social Web Page Based on Abnormal Characteristics[J]. Netinfo Security, 2015, 15(5): 41-46.
| [1] | Abu R M, Zarfoss J, Monrose F, et al.A multifaceted approach to understanding the botnet phenomenon[C]//Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGCOMM conference on Internet measurement. ACM, 2006: 41-52. |
| [2] | 江健, 诸葛建伟, 段海新, 等. 僵尸网络机理与防御技术[J]. 软件学报, 2012, 23(1): 82-96. |
| [3] | Geer D.Malicious bots threaten network security[J]. Computer, 2005, 38(1): 18-20. |
| [4] | Han X, Guo J, Zhou Y, et al.Investigation on the botnets activities[J]. JOURNAL-CHINA INSTITUTE OF COMMUNICATIONS, 2007, 28(12): 167. |
| [5] | 诸葛建伟, 韩心慧, 周勇林, 等. 僵尸网络研究[J] .软件学报, 2008, 19(3): 702-715. |
| [6] | Athanasopoulos E, Makridakis A, Antonatos S, et al.Antisocial networks: Turning a social network into a botnet[M].Heidelberg: Springer Berlin, 2008. |
| [7] | Govil J, Govil J .Criminology of botnets and their detection and defense methods[C] //Proc of 2007 IEEE Int Conf on Electro/Information Technology (EIT 2007).Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2007: 215-220. |
| [8] | Govil J.Examining the criminology of bot zoo[C]//Information, Communications & Signal Processing, 2007 6th International Conference on. IEEE, 2007: 1-6. |
| [9] | Gu G, Perdisci R, Zhang J, et al.BotMiner: Clustering Analysis of Network Traffic for Protocol-and Structure-Independent Botnet Detection[C]//USENIX Security Symposium. 2008, 5(2): 139-154. |
| [10] | Holz T, Steiner M, Dahl F, et al.Measurements and Mitigation of Peer-to-Peer-based Botnets: A Case Study on Storm Worm[J]. LEET, 2008, 8(1): 1-9. |
| [11] | Arce I, Levy E.An analysis of the slapper worm[J]. Security & Privacy, IEEE, 2003, 1(1): 82-87. |
| [12] | Barford P, Yegneswaran V.An inside look at botnets[M].New York: Malware Detection. Springer US, 2007. |
| [13] | 方滨兴, 崔翔, 王威. 僵尸网络综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2011, 48(8):1315-1331. |
| [14] | Stover S, Dittrich D, Hernandez J, et al.Analysis of the Storm and Nugache Trojans: P2P is here[J]. USENIX; login, 2007, 32(6): 18-27. |
| [15] | Holz T, Steiner M, Dahl F, et al.Measurements and Mitigation of Peer-to-Peer-based Botnets: A Case Study on Storm Worm[J]. LEET, 2008, 8(1): 1-9. |
| [16] | Kanich C, Kreibich C, Levchenko K, et al.Spamalytics: An empirical analysis of spam marketing conversion[C]//Proceedings of the 15th ACM conference on Computer and communications security. ACM, 2008: 3-14. |
| [17] | Turner D, Fossi M, Johnson E, et al. Symantec global internet security threat report-trends for 2008[EB/OL].. |
| [18] | Cooke E, Jahanian F, McPherson D. The zombie roundup: Understanding, detecting, and disrupting botnets[C]//Proceedings of the USENIX SRUTI Workshop. 2005, (39): 44. |
| [19] | Chiang K, Lloyd L.A case study of the rustock rootkit and spam bot[C]//The First Workshop in Understanding Botnets. 2007. |
| [20] | Daswani N, Stoppelman M.The anatomy of Clickbot. A[C]//Proceedings of the first conference on First Workshop on Hot Topics in Understanding Botnets. USENIX Association, 2007: 11. |
| [21] | Kartaltepe E J, Morales J A, Xu S, et al.Social network-based botnet command-and-control: emerging threats and countermeasures[C]//Applied Cryptography and Network Security. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2010: 511-528. |
| [22] | 王海龙, 龚正虎, 侯婕.僵尸网络检测技术研究进展[J].计算机研究与发展, 2010, 47(12) : 2037-2048. |
| [23] | Binkley J R, Singh S.An algorithm for anomaly-based botnet detection[C]//Proceedings of USENIX Steps to Reducing Unwanted Traffic on the Internet Workshop (SRUTI), 2006: 43-48. |
| [24] | Strayer W T, Walsh R, Livadas C, et al.Detecting botnets with tight command and control[C]// Proceedings 2006 31st IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2006: 195-202. |
| [25] | Livadas C, Walsh R, Lapsley D, et al.Usilng machine learning technliques to identify botnet traffic[C]// Proceedings 2006 31st IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2006: 967-974. |
| [26] | Goebel J, Holz T.Rishi: Identify bot contaminated hosts by IRC nickname evaluation[C]// Proceedings of the first conference on First Workshop on Hot Topics in Understanding Botnets. 2007: 8. |
| [27] | Gu G, Porras P A, Yegneswaran V, et al.BotHunter: Detecting Malware Infection Through IDS-Driven Dialog Correlation[C]//Usenix Security. 2007,(7): 1-16. |
| [28] | Lee J S, Jeong H C, Park J H, et al.The activity analysis of malicious http-based botnets using degree of periodic repeatability[C]// International Conference on. IEEE, 2008: 83-86. |
| [29] | Gu G, Zhang J, Lee W.BotSniffer: Detecting botnet command and control channels in network traffic[C]//Proc of the 15th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symp. Berkeley, CA: USENIX,2008:269-286. |
| [30] | 张昊,陶然,李志勇,等. 判断矩阵法在网页恶意脚本检测中的应用[J].兵工学报,2008, 29(4): 469-473. |
| [31] | 王松. 基于学习的恶意网页智能检测系统[D].南京:南京理工大学, 2011. |
| [32] | Salton G, Wong A, Yang C S.On the specification of term values in automatic indexing[J].Journal of Documentation,1973,29(4): 351-372. |
| [33] | Soucy P, Mineau G W.A simple KNN algorithm for text categorization[C]//Proceedings IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2001: 647-648. |
| [34] | Chang C C, Lin C J.LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines[J]. ACM Transcations on Intelligent Systems and Technology(TIST), 2011, 2(3): 27. |
| [1] | 李志华, 陈亮, 卢徐霖, 方朝晖, 钱军浩. 面向物联网Mirai僵尸网络的轻量级检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 667-681. |
| [2] | 屠晓涵, 张传浩, 刘孟然. 恶意流量检测模型设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 520-533. |
| [3] | 戚晗, 王敬童, 拱长青. 基于随机量子层的变分量子卷积神经网络鲁棒性研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 363-373. |
| [4] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [5] | 宋玉涵, 祝跃飞, 魏福山. 一种基于AdaBoost模型的区块链异常交易检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 24-35. |
| [6] | 张玉臣, 张雅雯, 吴越, 李程. 基于时频图与改进E-GraphSAGE的网络流量特征提取方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 12-24. |
| [7] | 薛羽, 张逸轩. 深层神经网络架构搜索综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 58-74. |
| [8] | 武伟, 徐莎莎, 郭森森, 李晓宇. 基于位置社交网络的兴趣点组合推荐算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 75-84. |
| [9] | 王鹃, 张冲, 龚家新, 李俊娥. 基于机器学习的模糊测试研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 1-16. |
| [10] | 许春根, 薛少康, 徐磊, 张盼. 基于安全两方计算的高效神经网络推理协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 22-30. |
| [11] | 赵小林, 王琪瑶, 赵斌, 薛静锋. 基于机器学习的匿名流量分类方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(5): 1-10. |
| [12] | 胡智杰, 陈兴蜀, 袁道华, 郑涛. 基于改进随机森林的Android广告应用静态检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 85-95. |
| [13] | 孙永奇, 宋泽文, 朱卫国, 赵思聪. 基于安全多方计算的图像分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 27-37. |
| [14] | 秦一方, 张健, 梁晨. 基于神经网络的电子病历数据特征提取技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 70-76. |
| [15] | 赵欣荷, 谢永恒, 万月亮, 汪金苗. 基于多模态数据的博彩网站检测识别模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 77-82. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||