信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 85-95.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.02.010
基于改进随机森林的Android广告应用静态检测方法
- 1.四川大学计算机学院,成都 610065
2.四川大学网络空间安全学院,成都 610207
-
收稿日期:2022-10-19出版日期:2023-02-10发布日期:2023-02-28 -
通讯作者:陈兴蜀 E-mail:chenxsh@scu.edu.cn -
作者简介:胡智杰(1992—),男,贵州,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为移动安全|陈兴蜀(1968—),女,贵州,教授,博士,主要研究方向为可信计算、云计算和大数据安全|袁道华(1963—),男,四川,教授,硕士,主要研究方向为分布式并行处理和网络计算|郑涛(1994—)男,四川,博士研究生,主要研究方向为移动安全和软件安全分析 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(U19A2081);国家自然科学基金(61802270);国家自然科学基金(61802271);教育部-中国移动科研基金(CM20200409);四川大学工科特色团队项目(2020SCUNG129)
Static Detection Method of Android Adware Based on Improved Random Forest Algorithm
HU Zhijie1, CHEN Xingshu2( ), YUAN Daohua1, ZHENG Tao2
), YUAN Daohua1, ZHENG Tao2
- 1. School of Computer Science, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China
2. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610207, China
-
Received:2022-10-19Online:2023-02-10Published:2023-02-28 -
Contact:CHEN Xingshu E-mail:chenxsh@scu.edu.cn
摘要:
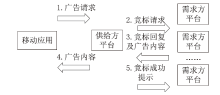
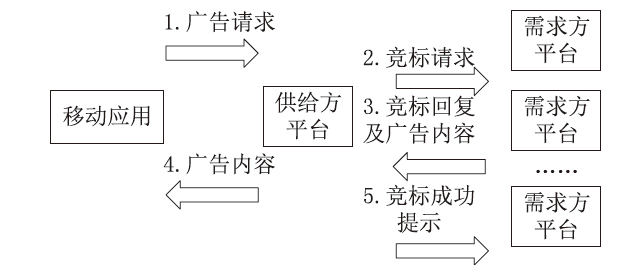
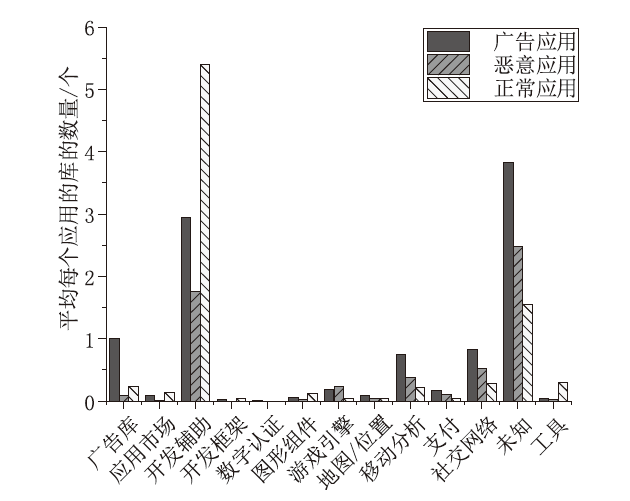
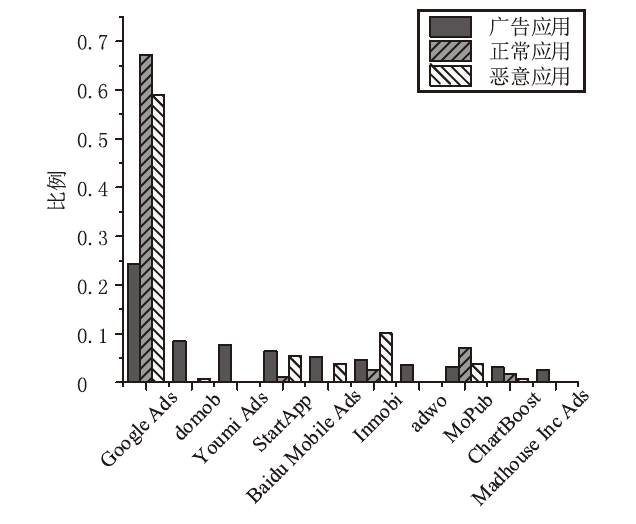
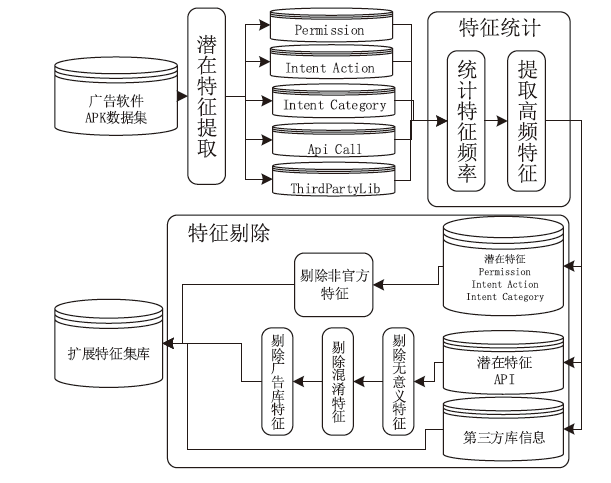
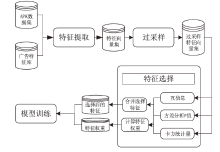
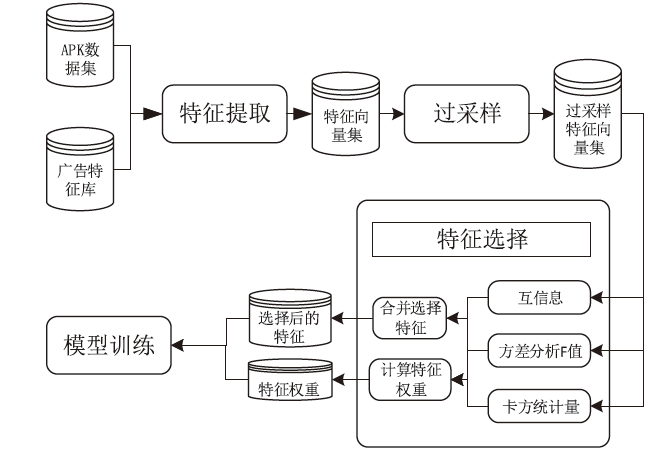
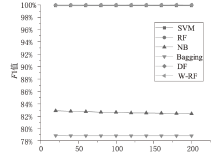
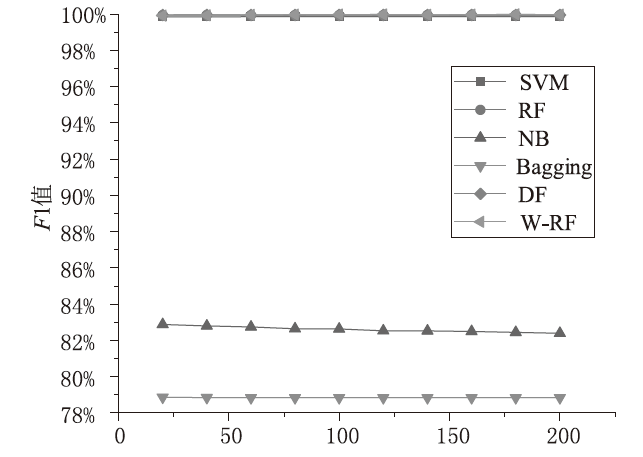
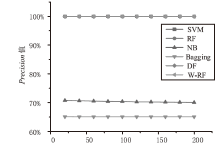
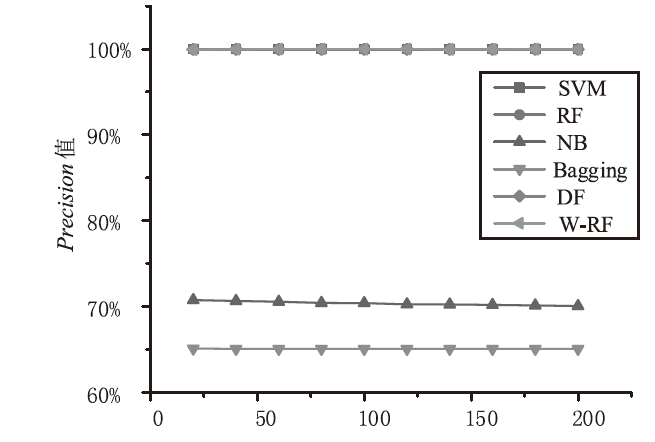
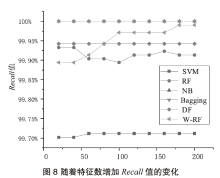
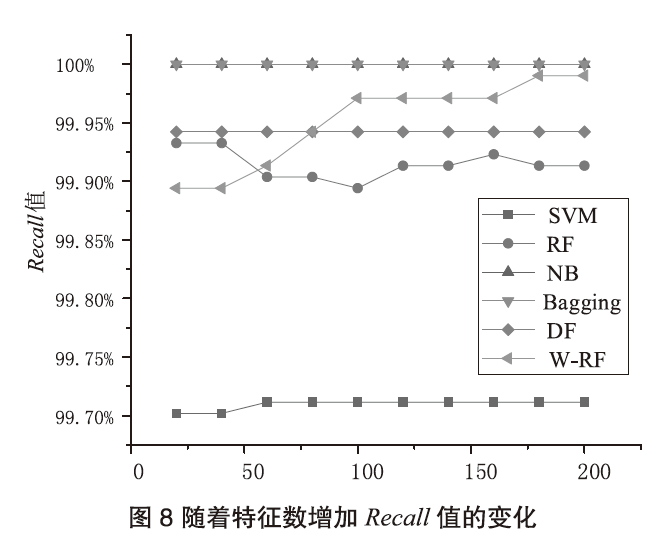
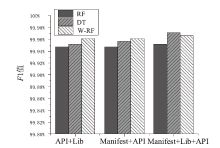
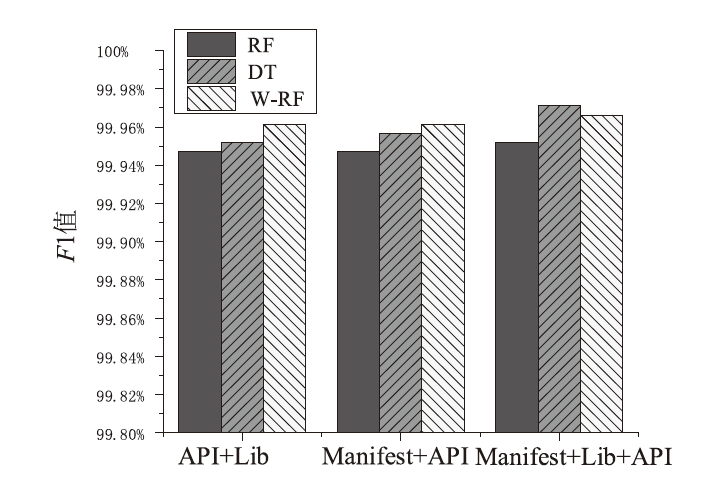
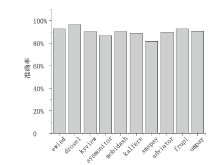
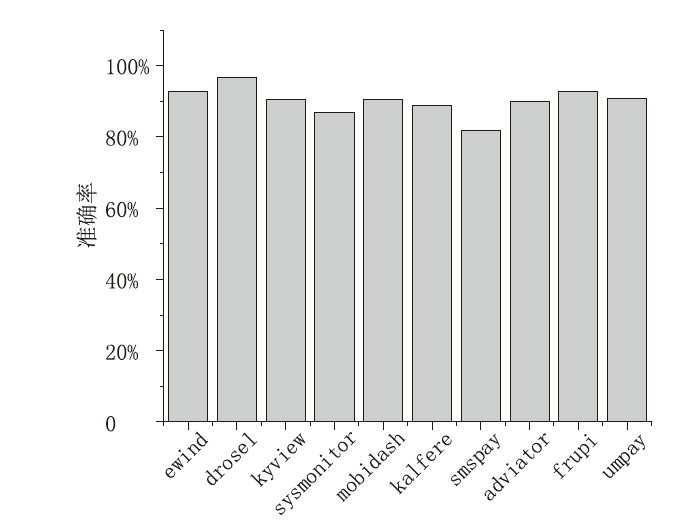
Android广告应用对用户正常使用Android手机构成了威胁,传统的广告应用检测方法时间成本高且受限于动态特征,难以满足大规模、高精度的检测需求。为解决此问题,文章提出一种基于改进随机森林的Android广告应用静态检测方法。首先,基于广告应用的特点,文章在传统的应用程序编程接口、权限、意图的基础上,将第三方库纳入特征选择的范围;对数据集中的广告软件的APK提取静态信息进行统计学分析,筛选后确定基准特征集合,将APK特征向量化;然后基于集成思想,利用多种特征选择算法共同选择用于模型训练的特征并赋予特征权重;最后使用基于特征权重的改进随机森林算法提高分类器的性能。实验选取了5751个广告应用和3465个非广告应用进行分类检测,实验结果表明,该方法能在保证准确率的情况下,具有较快的检测速度。
中图分类号:
引用本文
胡智杰, 陈兴蜀, 袁道华, 郑涛. 基于改进随机森林的Android广告应用静态检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 85-95.
HU Zhijie, CHEN Xingshu, YUAN Daohua, ZHENG Tao. Static Detection Method of Android Adware Based on Improved Random Forest Algorithm[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(2): 85-95.
| [1] | STATCOUNTER. Mobile Operating System Market Share Worldwide[EB/OL]. (2021-09-01)[2022-09-01]. https://gs.statcounter.com/os-market-share/mobile/worldwide. |
| [2] | CHEBYSHEV V. Mobile Malware Evolution 2020[EB/OL]. (2020-03-01)[2022-09-01]. https://securelist.com/mobile-malware-evolution-2020/101029/. |
| [3] | DARTMOUTH. A Course on Android Malware Analysis[EB/OL]. (2020-12-14)[2022-09-01]. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CwCOGf4Uunk. |
| [4] | NDAGI J Y, ALHASSAN J K. Machine Learning Classification Algorithms for Adware in Android Devices: A Comparative Evaluation and Analysis[C]// IEEE. 2019 15th International Conference on Electronics, Computer and Computation. New York: IEEE, 2019: 1-6. |
| [5] | IDESES I, NEUBERGER A. Adware Detection and Privacy Control in Mobile Devices[C]// IEEE. Electrical & Electronics Engineers in Israel. New York: IEEE, 2014: 1-5. |
| [6] | LEE K, PARK H. Malicious Adware Detection on Android Platform Using Dynamic Random Forest[C]// Springer. 13th International Conference on Innovative Mobile and Internet Services in Ubiquitous Computing. Berlin:Springer, 2019: 609-617. |
| [7] |
SURESH S, DI T F, POTIKA K, et al. An Analysis of Android Adware[J]. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, 2019, 15(3): 147-160.
doi: 10.1007/s11416-018-0328-8 URL |
| [8] | BAGUI S, BENSON D. Android Adware Detection Using Machine Learning[J]. International Journal of Cyber Research and Education, 2021, 3(2): 1-19 |
| [9] | LIU Bin, NATH S, GOVINDAN R, et al. DECAF: Detecting and Characterizing Ad Fraud in Mobile Apps[C]// USENIX. 11th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation. Berkeley: USENIX, 2014: 57-70. |
| [10] | DONG Feng, WANG Haoyu, LI Li, et al. FraudDroid: Automated Ad Fraud Detection for Android Apps[C]// ACM. 26th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference/ Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2018: 257-268. |
| [11] | LIU Tianming, WANG Haoyu, LI Li, et al. MadDroid: Characterising and Detecting Devious Ad Content for Android Apps[C]// ACM. 29th World Wide Web Conference. New York: ACM, 2020: 1715-1726. |
| [12] | DOGTIEV A. Top Mobile Advertising Companies (2021)[EB/OL]. (2021-12-23)[2022-09-27]. https://www.businessofapps.com/ads. |
| [13] | DOGTIEV A. Real Time Bidding Advertising Networks[EB/OL]. (2021-12-23)[2022-08-26]. https://www.businessofapps.com/ads/real-time-bidding-rtb/. |
| [14] | TREND MICRO. Mobile Ad Fraud Schemes: How They Work, and How to Defend Against Them[EB/OL]. (2019-04-26)[2022-07-17]. https://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/us/security/news/mobile-safety/mobile-ad-fraud-schemes-how-they-work-and-how-to-defend-against-them. |
| [15] | WANG Haoyu, GUO Yao, MA Ziang, et al. WuKong: a Scalable and Accurate Two-Phase Approach to Android App Clone Detection[C]// ACM. 2015 International Symposium on Software Testing & Analysis. New York: ACM, 2015: 71-82. |
| [16] | GOLOVIN I, KIVVA A. Aggressive in-App Advertising in Android[EB/OL]. (2020-05-25)[2022-09-01]. https://securelist.com/in-app-advertising-in-android/97065/. |
| [17] | GOLOVIN I, KIVVA A. An Advertising Dropper in Google Play[EB/OL]. (2019-08-27)[2022-09-16]. https://securelist.com/dropper-in-google-play/92496/. |
| [18] | MA Ziang, WANG Haoyu, GUO Yao, et al. LibRadar: Fast and Accurate Detection of Third-Party Libraries in Android Apps[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE/ACM 38th International Conference on Software Engineering Companion. New York: IEEE, 2017: 653-656. |
| [19] | LI Li, BISSYANDE T F, KLEIN J, et al. An Investigation into the Use of Common Libraries in Android Apps[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution, and Reengineering. New York: IEEE, 2016: 403-414. |
| [20] | HAN Hui, WANGWenyuan, MAOBinghuan. Borderline-SMOTE: A New Over-Sampling Method in Imbalanced Data Sets Learning[C]// Springer. 2005 International Conference on Intelligent Computing. Berlin:Springer, 2005: 878-887. |
| [21] | HE Haibo, BAI Yang, GARCIA E A, et al. ADASYN: Adaptive Synthetic Sampling Approach for Imbalanced Learning[C]// IEEE. 2008 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. New York: IEEE, 2008: 1322-1328. |
| [22] | SEBASTI’AN S, CABALLERO J. AVclass2: Massive Malware Tag Extraction from AV Labels[C]// ACM. Annual Computer Security Applications Conference. New York: ACM, 2020: 42-53. |
| [1] | 刘翔宇, 芦天亮, 杜彦辉, 王靖翔. 基于特征选择的物联网轻量级入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(1): 66-72. |
| [2] | 张梦杰, 王剑, 黄恺杰, 杨刚. 一种基于字节波动特征的ROP流量静态检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 64-72. |
| [3] | 秦宝东, 余沛航, 郑东. 基于双陷门同态加密的决策树分类模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 9-17. |
| [4] | 王鹃, 王蕴茹, 翁斌, 龚家新. 机器学习在x86二进制反汇编中的应用研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(6): 9-25. |
| [5] | 唐明, 黎聪, 李永波, 岳天羽. RISC-V架构上的时间侧信道静态检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(4): 7-19. |
| [6] | 牛艺诺, 张逸飞, 高能, 马存庆. 融合时序和逻辑关系的日志异常检测系统设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11): 1-6. |
| [7] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王靖亚, 杨莹. 一种面向Android恶意软件的多视角多任务学习检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 1-7. |
| [8] | 段晓毅, 李邮, 令狐韫行, 胡荣磊. 基于RF算法的侧信道攻击方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 19-26. |
| [9] | 郭春, 蔡文艳, 申国伟, 周雪梅. 基于关键载荷截取的SQL注入攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(7): 43-53. |
| [10] | 马骁, 蔡满春, 芦天亮. 基于CNN改进模型的恶意域名训练数据生成技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 69-75. |
| [11] | 徐瑜, 周游, 林璐, 张聪. 无监督机器学习在游戏反欺诈领域的应用研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 32-36. |
| [12] | 袁晓筱, 罗森林, 杨鹏. Android系统应用程序DEX文件保护方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(7): 60-69. |
| [13] | 郑东, 赵月. 基于SM3与多特征值的Android恶意软件检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(6): 17-25. |
| [14] | 郭春, 陈长青, 申国伟, 蒋朝惠. 一种基于可视化的勒索软件分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 31-39. |
| [15] | 杜义峰, 郭渊博. 一种基于信任值的雾计算动态访问控制方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 65-72. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||