Netinfo Security ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 1027-1037.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.07.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
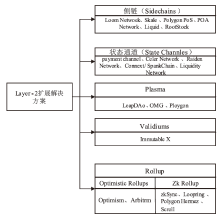
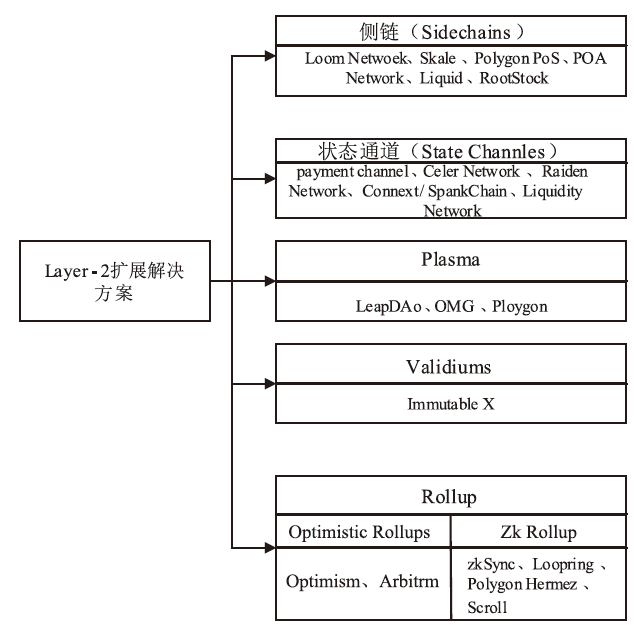
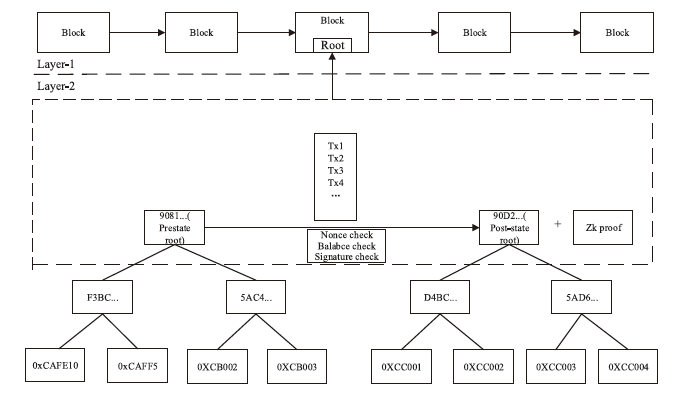
Blockchain Scaling Solutions: ZK-Rollup Review
ZHANG Jiwei1, WANG Wenjun1( ), NIU Shaozhang1, GUO Xiangkuo2
), NIU Shaozhang1, GUO Xiangkuo2
- 1. School of Computer Science, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2. National Security College, National Defense University, Beijing 100091, China
-
Received:2024-02-02Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-08-02
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Jiwei, WANG Wenjun, NIU Shaozhang, GUO Xiangkuo. Blockchain Scaling Solutions: ZK-Rollup Review[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(7): 1027-1037.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.07.005
| 可信 设置 | 证明者算法复杂度 | 验证者时间复杂度 | 证明 大小 /B | 生成证明时间 /s | 验证证明时间/ms | 参考 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK-SNARKs | 需要 | O(nlogn) | O(1) | 288 | 2.3 | 10 | [ |
| Bulletproofs | 不需要 | O(nlogn) | O(n) | 1000 | 30 | 1100 | [ |
| Sonic | 需要 | O(nlogn) | O(logn) | 2000 | 5 | 100 | [ |
| ZK-STARKs | 不需要 | O(npoly-logn) | O(poly-logn) | 45000 | 1.6 | 16 | [ |
| Plonk | 需要 | O(nlogn) | O(1) | 1000 | 4 | 50 | [ |
| 编程 语言 | 兼容性 | 交易费类型 | 零知识 证明算法 | 支付 费用 /美元 | 交换费用 /美元 | 支付费用节 省率 | 交换费用节 省率 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polygon ZKEVM | Solidity | 完全兼容EVM | 仅限ETH | ZK-STARKS/ZK-SNARKS | 0.12 | 1.68 | 88% | 32% |
| Loopring | Solidity | 不兼容EVM | 任何ERC-20代币 | ZK-SNARKS | 0.03 | 0.62 | 97% | 88% |
| Scroll | Solidity | 完全兼容EVM | 仅限ETH | ZK-SNARKS | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| ZKSync Era | Yul | 仅语言兼容 | 任何ERC-20代币 | ZK-SNARKS | 0.05 | N/A | 95% | N/A |
| StarkNet | Cairo | 仅语言兼容 | STRK或者ETH | ZK-STARKS | 0.11 | 0.36 | 89% | 93% |
| 优化类型 | 优点 | 缺点 | 方案举例 | 方案所用算法 |
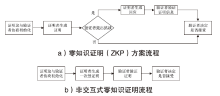
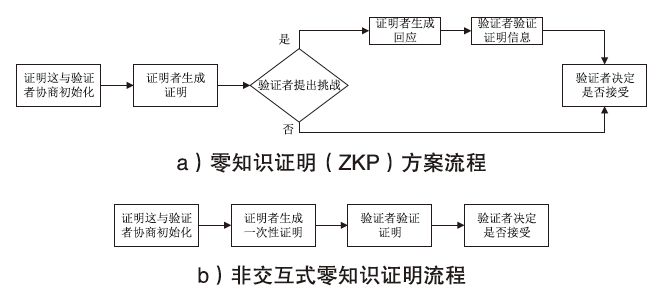
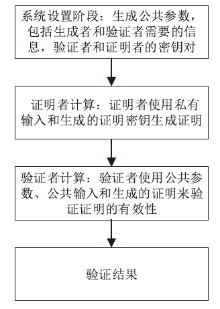
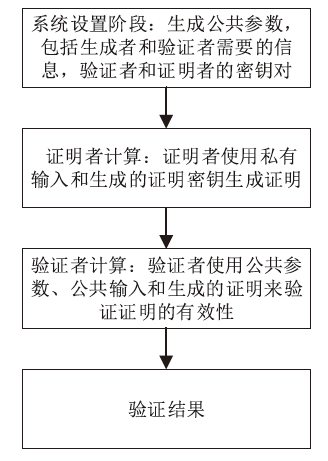
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优化加密 算法 | 提高零知识证明生成的速度 | 需要更复杂的技术和 资源 | Polygon Zero[ | Plonky2[ |
| 混合Optimistic Rollup和ZK Rollup | 实现更高的吞吐量和更低的费用 | 需要更复杂的协议和 协调 | Polygon Nightfall[ | Nightfall[ |
| 开发专门的ZK-evm | 扩展Ethereum的功能和 兼容性 | 技术复杂 | AppliedZKp[ | KZG[ Halo2[ BN-254[ |
| Polygon Hermez[ | Groth16[ plonk[ KZG[ | |||
| Polygon Miden[ | STARK Based ZK VM[ | |||
| 硬件优化 | 提高效率和 性能 | 需要更高的硬件成本和维护成本 | DIZK[ | Distributed ZKSNARK[ |
| HardAcc- Groth16[ | Groth16[ | |||
| CPU/GPUAcc - Bulletproof[ | Bulletproof [ | |||
| PipeMSM[ | PipeMSM[ |
| [1] | NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[EB/OL]. (2008-11-01)[2023-11-15]. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf. |
| [2] | WANG Huaimin, ZHENG Zibin, XIE Shaoan, et al. Blockchain Challenges and Opportunities: A Survey[J]. International Journal of Web and Grid Services, 2018, 14(4): 352-375. |
| [3] | SANKA A I, CHEUNG R C C. A Systematic Review of Blockchain Scalability: Issues, Solutions, Analysis and Future Research[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2021, 1959(12): 1-25. |
| [4] | KAUR M, KHAN M Z, GUPTA S, et al. MBCP: Performance Analysis of Large Scale Mainstream Blockchain Consensus Protocols[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 80931-80944. |
| [5] | GURU A, MOHANTA B K, MOHAPATRA H, et al. A Survey on Consensus Protocols and Attacks on Blockchain Technology[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(4): 1-21. |
| [6] | HAN Runchao, YU Jiangshan, LIN Haoyu, et al. On the Security and Performance of Blockchain Sharding[J]. IACR Cryptol EPrint Arch, 2021, 1276(9): 1-15. |
| [7] | GUDGEON L, MORENO-SANCHEZ P, ROOS S, et al. SoK: Layer-Two Blockchain Protocols[C]// Springer. Financial Cryptography and Data Security:24th International Conference, FC 2020. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 201-226. |
| [8] | GANGWAL A, GANGAVALLI H R, THIRUPATHI A. A Survey of Layer-Two Blockchain Protocols[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2023, 209(1): 1-17. |
| [9] | LI Yang, MEN Jinbao, YU Han, et al. Overview of Blockchain Capacity Expansion Technology[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2020, 18(6): 1-9. |
| 李洋, 门进宝, 余晗, 等. 区块链扩容技术研究综述[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2020, 18(6): 1-9. | |
| [10] | XU Jie, WANG Cong, JIA Xiaohua. A Survey of Blockchain Consensus Protocols[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(13s): 1-35. |
| [11] | HONG Zicong, GUO Song, LI Peng. Scaling Blockchain via Layered Sharding[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(12): 3575-3588. |
| [12] | BACK A, CORALLO M, DASHJR L, et al. Enabling Blockchain Innovations with Pegged Sidechains[EB/OL]. (2014-09-12)[2023-11-25]. http://www.opensciencereview.com/papers/123/enablingblockchain-innovations-with-pegged-sidechains. |
| [13] | ETHEREUM Org. Sidechains[EB/OL]. [2024-01-31]. https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/scaling/sidechains/. |
| [14] | HEWA T, YLIANTTILA M, LIYANAGE M. Survey on Blockchain Based Smart Contracts: Applications, Opportunities and Challenges[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2021, 177(3): 1-39. |
| [15] | COLEMAN J. State Channels[EB/OL]. (2015-11-06)[2024-01-09]. https://www.jeffcoleman.ca/state-channels/ |
| [16] | GRAU P. Lessons Learned From Making a Chess Game for Ethereum[EB/OL]. (2016-09-03)[2024-01-02]. https://medium.com/@graycoding/lessons-learned-from-making-a-chess-game-for-ethereum-6917c01178b6. |
| [17] | ZHAO Sijia, O’MAHONY D. Applying Blockchain Layer2 Technology to Mass E-Commerce[J]. IACR Cryptol EPrint Arch, 2020, 502(4): 1-30. |
| [18] | NEGKA L D, SPATHOULAS G P. Blockchain State Channels: A State of the Art[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 160277-160298. |
| [19] | POON J, BUTERIN V. Plasma: Scalable Autonomous Smart Contracts[J]. White Paper, 2017: 1-47. |
| [20] | THIBAULT L T, SARRY T, HAFID A S. Blockchain Scaling Using Rollups: A Comprehensive Survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10(8): 93039-93054. |
| [21] | NEIHEISER R, INÁCIO G, RECH L, et al. Practical Limitations of Ethereum’s Layer-2[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11(1): 8651-8662. |
| [22] | OPTIMISM FOUNDATION. Optimism[EB/OL]. (2023-11-15)[2024-01-02]. https://www.optimism.io/. |
| [23] | ARBITRUM FOUNDATION. Arbitrum[EB/OL]. (2023-11-15)[2024-01-31]. https://arbitrum.io/. |
| [24] | LAVAUR T, DETCHART J, LACAN J, et al. Modular ZK-Rollup On-Demand[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2023, 217(8): 1-9. |
| [25] | BUTERIN V. The Dawn of Hybrid Layer 2 Protocols[EB/OL]. (2019-08-28)[2024-01-01]. https://alidevjimmy.github.io/general/2019/08/28/hybrid-layer-2.html. |
| [26] | BUTERIN V, CONNER E, DUDLEY R, et al. EIP-1559: Fee Market Change for ETH 1.0 Chain[EB/OL]. (2019-04-13)[2023-11-29]. https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-1559. |
| [27] | YCHARTS FOUNDATION. Ycharts[EB/OL]. (2023-03-19)[2023-11-29]. https://get.ycharts.com/platform/data/. |
| [28] | BUTERIN V. EIP-4844: Shard Blob Transactions[EB/OL]. (2022-02-25)[2024-01-02]. https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-4844. |
| [29] | HUANG Chengpeng, SONG Rui, GAO Shang, et al. Data Availability and Decentralization: New Techniques for Zk-Rollups in Layer 2 Blockchain Networks[J]. ArXiv Preprint, 2024, 10828(3): 1-14. |
| [30] | GOLDWASSER S MIT, MICALI S, et al. The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof-Systems[C]//ACM. Providing Sound Foundations for Cryptography:On the Work of Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali. New York: ACM, 2019, 203-225. |
| [31] | GROTH J. Short Pairing-Based Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments[C]// Springer. Advances in Cryptology-ASIACRYPT 2010. Heidelberg: Springer, 2010: 321-340. |
| [32] | BEN-SASSON E, BENTOV I, HORESH Y, et al. Scalable, Transparent, and Post-Quantum Secure Computational Integrity[EB/OL]. (2018-03-06)[2024-01-19]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/046.pdf. |
| [33] | BÜNZ B, BOOTLE J, BONEH D, et al. Bulletproofs: Short Proofs for Confidential Transactions and More[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2018: 315-334. |
| [34] | MALLER M, BOWE S, KOHLWEISS M, et al. Sonic: Zero-Knowledge SNARKs from Linear-Size Universal and Updatable Structured Reference Strings[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 2111- 2128. |
| [35] | GABIZON A, WILLIAMSON Z J, CIOBOTARU O. Plonk: Permutations over Lagrange-Bases for Oecumenical Noninteractive Arguments of Knowledge[EB/OL]. (2019-08-21)[2024-01-10]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2019/953.pdf. |
| [36] | SEFRANEK M. How to Simulate PLONK: A Formal Security Analysis of a ZK-SNARK[D]. Wienna: Technical University of Wienna, 2023. |
| [37] | MATTER LABS. Zero-Knowledge-Proofs[EB/OL]. (2023-03-19)[2023-12-16]. https://github.com/matter-labs/awesome-zero-knowledge-proofs. |
| [38] | BEN-SASSON E, BENTOV I, HORESH Y, et al. Scalable, Transparent, and Post-Quantum Secure Computational Integrity[J]. IACR Cryptol EPrint Arch, 2018, 46(3): 1-83. |
| [39] | BITANSKY N, CANETTI R, CHIESA A, et al. Recursive Composition and Bootstrapping for SNARKS and Proof-Carrying Data[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Forty-Fifth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 2013: 111-120. |
| [40] | MATTER LABS. Zkporter: A Breakthrough in L2 Scaling[EB/OL]. (2021-04-13)[2023-11-15]. https://blog.matter-labs.io/zkporter-a-breakthrough-inl2-scaling-ed5e48842fbf. |
| [41] | WANG D, ZHOU J, WANG A, et al. Loopring: A Decentralized Token Exchange Protocol[EB/OL]. (2018-05-11)[2023-11-15]. https://github.com/Loopring/whitepaper/blob/master/en_whitepaper.pdf. |
| [42] | LOOPRING FOUNDATION. Loopring_v3[EB/OL]. (2021-06-26)[2023-11-15]. https://github.com/Loopring/protocols/blob/master/packages/loopring_v3/. |
| [43] | POLYGON-HERMEZ. Polygon-Hermez-Whitepaper[EB/OL]. (2018-04-06)[2023-11-15]. https://hermez.io/polygon-hermez-whitepaper.pdf. |
| [44] | STARKEX FOUNDATION. StarkEX[EB/OL]. (2013-06-15)[2023-11-15]. https://docs.starkware.co/starkex/transaction_throughput.html. |
| [45] | DAVID Mihal. l2fees[EB/OL]. (2023-12-05)[2024-01-31]. https://l2fees.info/. |
| [46] | POLYGON ZERO. Plonky2[EB/OL]. (2023-11-30)[2023-12-05]. https://github.com/mirprotocol/plonky2. |
| [47] | POLYGON FOUNDATION. Polygon Nightfall[EB/OL]. (2023-11-05)[2024-01-29]. https://blog.polygon.technology/zk-proofs-protocol-polygonnightfall-launches-on-testnet-to-provide-low-cost-private-ethereumtransaction/. |
| [48] | APPLIED ZKP FOUNDATION. Applied ZKP[EB/OL]. (2021-11-05)[2023-12-05]. https://github.com/appliedzkp. |
| [49] | SYN7Y. Exploring Popular zkEVM Solutions: AppliedZKP, Matter Labs, Hermez, and Sin7Y[EB/OL]. (2021-08-24)[2023-12-05]. https://hackernoon.com/exploring-popular-zkevm-solutions-appliedzkp-matter-labs-hermez-and-sin7y-quick-publication-ltq37ah. |
| [50] | POLYGON MIDEN. Miden[EB/OL]. (2023-08-24)[2023-12-05]. https://github.com/maticnetwork/miden. |
| [51] | WU Howard, ZHENG Wenting, CHIESA A, et al. DIZK: A Distributed Zero Knowledge Proof System[C]// USENIX.27th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 18). New York: USENIX, 2018: 675-692. |
| [52] | KATE A, ZAVERUCHA G M, GOLDBERG I. Constant-Size Commitments to Polynomials and Their Applications[C]// Springer. Advances in Cryptology-ASIACRYPT 2010: 16th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2010: 177-194. |
| [53] | HOPWOOD D, BOWE S, GRIGG J, et al. The Halo2 Book[EB/OL]. (2021-11-05)[2023-12-05]. https://zcash.github.io/halo2/. |
| [54] | BARRETO P S L M, NAEHRIG M. Pairing-Friendly Elliptic Curves of Prime Order[C]// Springer. Selected Areas in Cryptography. Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 319-331. |
| [55] | GROTH J. On the Size of Pairing-Based Non-Interactive Arguments[C]// Springer. Advances in Cryptology-EUROCRYPT 2016: 35th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 305-326. |
| [56] | BEB-SASSON E, BENTOV I, HORESH Y, et al. Scalable, Transparent, and Post-Quantum Secure Computational Integrity[EB/OL]. (2018-03-22)[2023-12-05]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2794982701. |
| [57] | XAVIER C F. Pipemsm: Hardware aCeleration for Multi-Scalar Multiplication[EB/OL]. (2022-08-03)[2024-01-19]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2022/999. |
| [58] | PENG B O, ZHU Yongxin, JING Naifeng, et al. Design of a Hardware Accelerator for Zero-Knowledge Proof in Blockchains[C]// Springer. Smart Computing and Communication:5th International Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 136-145. |
| [59] | ZHANG Ye, WANG Shuo, ZHANG Xian, et al. PipeZK: Accelerating Zero-Knowledge Proof with a Pipelined Architecture[C]// IEEE. 2021 ACM/IEEE 48th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA). New York: IEEE, 2021: 416-428. |
| [1] | GUO Rui, YANG Xin, WANG Junming. Verifiable and Revocable Attribute Encryption Scheme Based on Blockchain [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(6): 863-878. |
| [2] | LING Zhi, YANG Ming, YU Jiangyin. Research on Power Security Trading Platform Based on IPFS and Blockchain Technology [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(6): 968-976. |
| [3] | TIAN Zhao, NIU Yajie, SHE Wei, LIU Wei. A Reputation Evaluation Method for Vehicle Nodes in V2X [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [4] | SHI Runhua, YANG Jingyi, WANG Pengbo, LIU Huawei. Online/Off line Cross-Domain Identity Authentication Scheme Based on Blockchain in Vehicle to Grid [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 587-601. |
| [5] | HU Haiyang, LIU Chang, WANG Dong, WEI Xu. Clean Energy Data Traceability Mechanism Based on Blockchain [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 626-639. |
| [6] | XUE Mingzhu, HU Liang, WANG Ming, WANG Feng. TAP Rule Processing System Based on Federated Learning and Blockchain Technology [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 473-485. |
| [7] | ZHAI Peng, HE Jingsha, ZHANG Yu. An Identity Authentication Method Based on SM9 and Blockchain in the IoT Environment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 179-187. |
| [8] | HE Yefeng, QUAN Jiahui, LIU Yan. A Location Privacy Protection Scheme Based on Hybrid Blockchain [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 229-238. |
| [9] | WU Haotian, LI Yifan, CUI Hongyan, DONG Lin. Federated Learning Incentive Scheme Based on Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Blockchain [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 1-13. |
| [10] | ZHU Guocheng, HE Debiao, AN Haoyang, PENG Cong. The Proxy Voting Scheme Based on the Blockchain and SM9 Digital Signature [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 36-47. |
| [11] | GONG Pengfei, XIE Sijiang, CHENG Andong. The Multi-Leader Consensus Algorithm Based on Improvements to HotStuff [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(9): 108-117. |
| [12] | ZHOU Quan, CHEN Minhui, WEI Kaijun, ZHENG Yulong. Blockchain Access Control Scheme with SM9-Based Attribute Encryption [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(9): 37-46. |
| [13] | ZHAO Jiahao, JIANG Jiajia, ZHANG Yushu. Cross-Chain Data Consistency Verification Model Based on Dynamic Merkle Hash Tree [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(9): 95-107. |
| [14] | SHAO Zhenzhe, JIANG Jiajia, ZHAO Jiahao, ZHANG Yushu. An Improved Weighted Byzantine Fault Tolerance Algorithm for Cross-Chain System [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 109-120. |
| [15] | QIN Sihang, DAI Weiqi, ZENG Haiyan, GU Xianjun. Secure Sharing of Power Application Data Based on Blockchain [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 52-65. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||