信息网络安全 ›› 2021, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (1): 27-40.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2021.01.004
一种基于多阶段攻击响应的SDN动态蜜罐
- 1.武汉大学国家网络安全学院,武汉 430072
2.空天信息安全与可信计算教育部重点实验室,武汉 430072
-
收稿日期:2020-11-10出版日期:2021-01-10发布日期:2021-02-23 -
通讯作者:王鹃 E-mail:jwang@whu.edu.cn -
作者简介:王鹃(1976—),女,湖北,教授,博士,主要研究方向为系统和网络安全、可信计算、云计算、物联网安全|杨泓远(1995—),男,广东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为软件测试、网络安全|樊成阳(1994—),男,湖北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为可信计算、云计算、网络安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61872430)
A SDN Dynamic Honeypot with Multi-phase Attack Response
WANG Juan1,2( ), YANG Hongyuan1,2, FAN Chengyang1,2
), YANG Hongyuan1,2, FAN Chengyang1,2
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
2. Key Laboratory of Aerospace Information Security and Trusted Computing, Ministry of Education, Wuhan 430072, China
-
Received:2020-11-10Online:2021-01-10Published:2021-02-23 -
Contact:WANG Juan E-mail:jwang@whu.edu.cn
摘要:
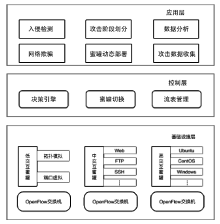
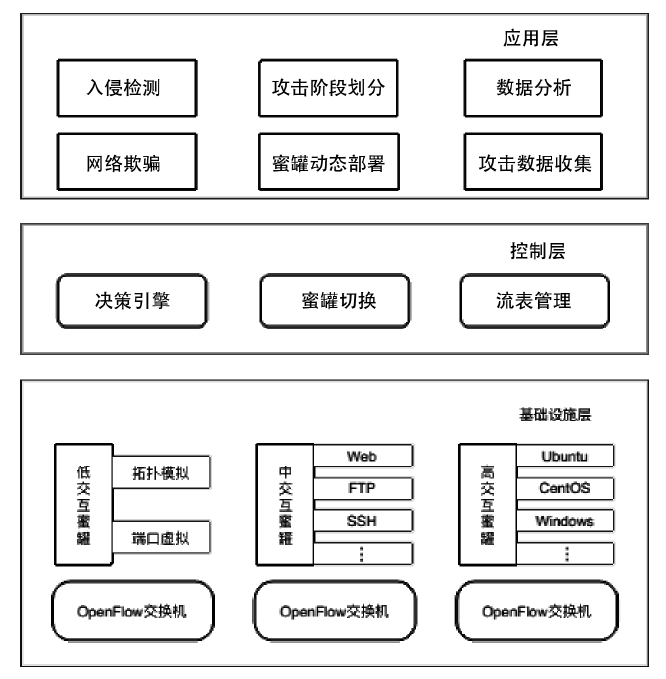
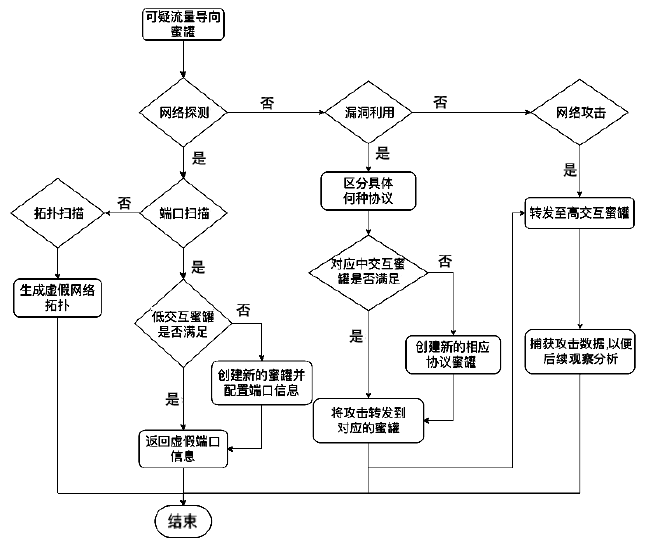
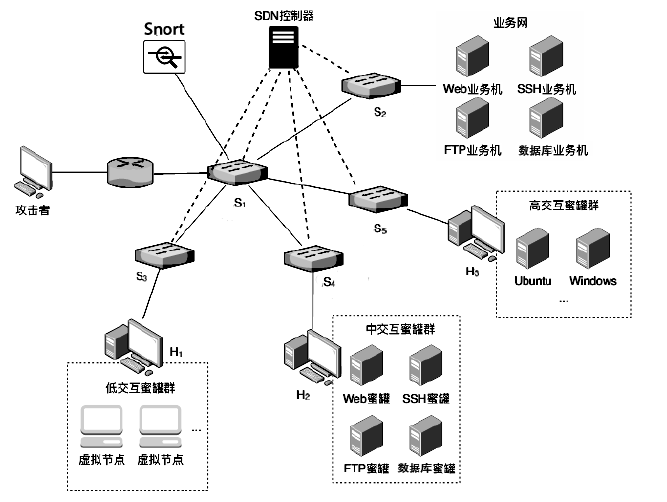
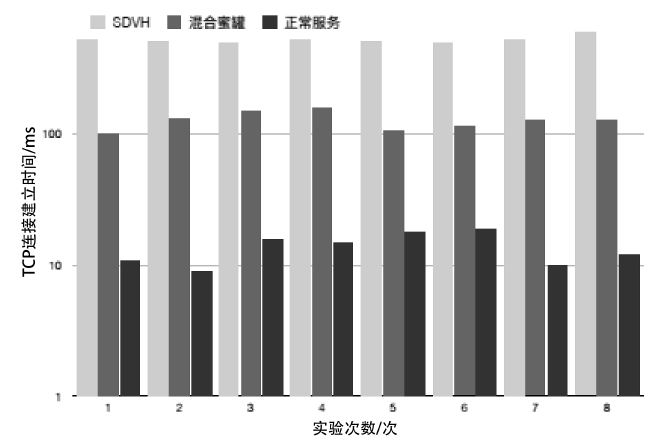
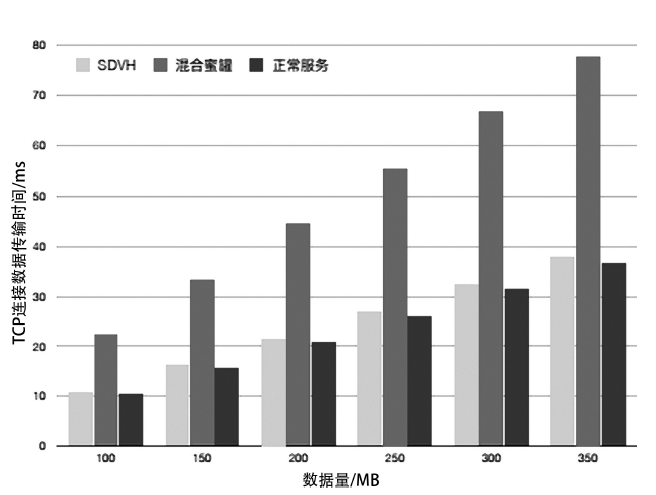
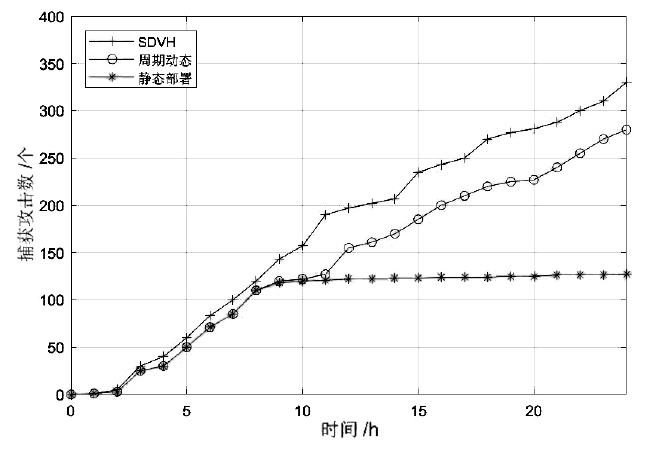
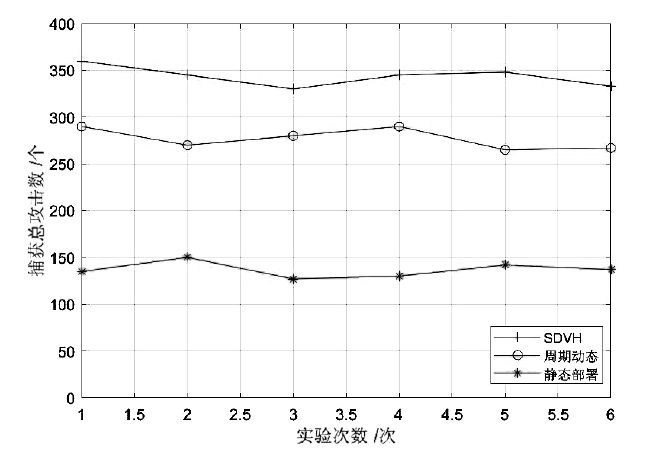
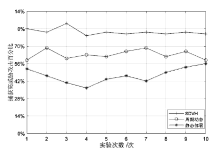
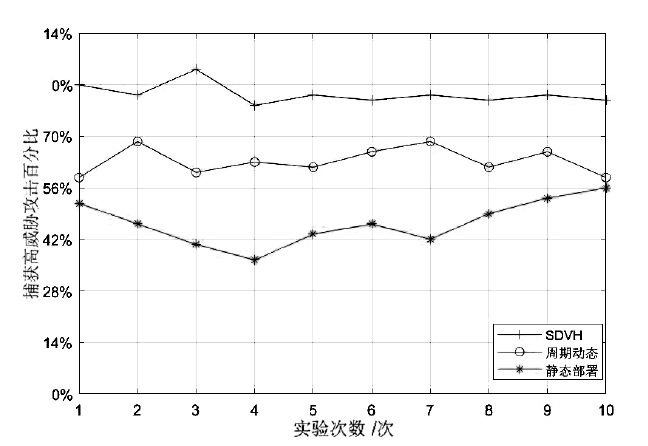
蜜罐作为一种主动防御机制,可以通过部署诱饵目标,主动吸引攻击者与虚假资源进行交互,从而在防止有价值的真实资源受到破坏的同时,也能根据收集到的数据分析攻击行为并主动应对。然而,现有蜜罐方案存在无法针对复杂攻击手段部署特定蜜罐防御;蜜罐攻防博弈中动态性考虑不够充分,无法根据收益与成本有效选择蜜罐最佳防御策略;以及性能开销较大等缺陷。文章提出基于多阶段攻击响应和动态博弈相结合的SDN动态蜜罐架构以及基于Docker的SDN动态蜜罐部署策略和方法,设计和实现了一种可根据攻击阶段动态调整的SDN动态蜜罐系统。实验证明,该系统能够根据网络情况,面向攻击者行为,快速动态生成针对性蜜罐进行响应,有效提升了蜜罐的动态性和诱骗能力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王鹃, 杨泓远, 樊成阳. 一种基于多阶段攻击响应的SDN动态蜜罐[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(1): 27-40.
WANG Juan, YANG Hongyuan, FAN Chengyang. A SDN Dynamic Honeypot with Multi-phase Attack Response[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(1): 27-40.
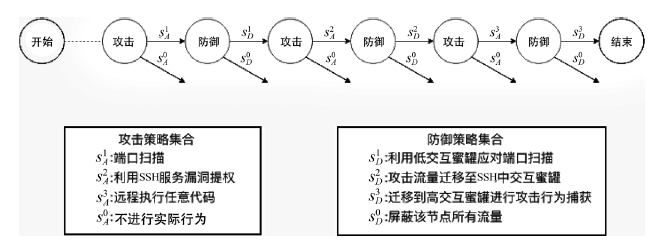
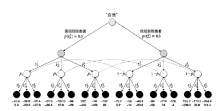
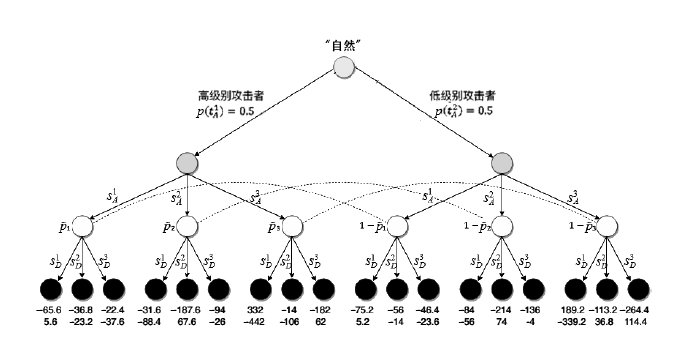
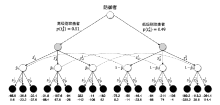
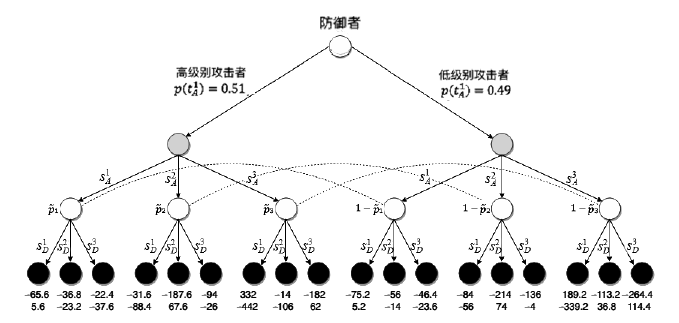
表5
攻防双方效用
| 防御策略 攻击策略 | $s_{D}^{1}$ | $s_{D}^{2}$ | $s_{D}^{3}$ |
|---|---|---|---|
| $s_{A}^{1}$ | (-65.6, 5.6) (-75.2, 5.2) | (-36.8,-23.2) (-56,-14) | (-22.4,-37.6) (-46.4,-23.6) |
| $s_{A}^{2}$ | (-31.6,-88.4) (-84, -56) | (-187.6,67.6) (-214,74) | (-94,-26) (-136, -4) |
| $s_{A}^{3}$ | (332, -442) (189.2,-339.2) | (-14, -106) (-113.2, 36.8) | (-182,62) (-264.4, 114.4) |
| [1] | HAYATLE O, OTROK H, YOUSSEF A. A Game Theoretic Investigation for High Interaction Honeypots[C] //IEEE. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), June 10-15, 2012, Ottawa, ON, Canada. NJ: IEEE, 2012: 6662-6667. |
| [2] |
LA Q D, QUEK T Q S, LEE J, et al. Deceptive Attack and Defense Game in Honeypot-enabled Networks for the Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016,3(6):1025-1035.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2547994 URL |
| [3] | GARG N, GROSU D. Deception in Honeynets: A Game-theoretic Analysis[C] //IEEE. 2007 IEEE SMC Information Assurance and Security Workshop, June 20-22, 2007, West Point, NY, USA. NJ: IEEE, 2007: 107-113. |
| [4] | PANJWANI S, TAN S, JARRIN K M, et al. An Experimental Evaluation to Determine If Port Scans are Precursors to an Attack[C] //IEEE. 2005 International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN'05), June 28- July 1, 2005, Yokohama, Japan. NJ: IEEE, 2005: 602-611. |
| [5] |
WANG Kun, DU Miao, MAHARJAN S, et al. Strategic Honeypot Game Model for Distributed Denial of Service Attacks in the Smart Grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017,8(5):2474-2482.
doi: 10.1109/TSG.2017.2670144 URL |
| [6] | MCKEOWN N. Software-defined Networking[J]. INFOCOM Keynote Talk, 2009,2009(17):30-32. |
| [7] |
DU Miao, WANG Kun. An SDN-enabled Pseudo-honeypot Strategy for Distributed Denial of Service Attacks in Industrial Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019,16(1):648-657.
doi: 10.1109/TII.9424 URL |
| [8] |
WANG Juan, WEN Ru, LI Jiangqi, et al. Detecting and Mitigating Target Link-flooding Attacks Using SDN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019,16(6):944-956.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.8858 URL |
| [9] | SHI Yuan, ZHANG Huanguo, WANG Juan, et al. Chaos: An SDN-based Moving Target Defense System[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2017,2017(4):11-23. |
| [10] | HAN W, ZHAO Ziming, DOUPÉ A, et al. Honeymix: Toward SDN-based Intelligent Honeynet[C] //ACM. The 2016 ACM International Workshop on Security in Software Defined Networks & Network Function Virtualization, March 9-11, 2016, New Orleans Louisiana USA. New York: ACM, 2016: 1-6. |
| [11] | KYUNG S, HAN W, TIWARI N, et al. Honeyproxy: Design and Implementation of Next-generation Honeynet via SDN[C] //IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), October 9-11, 2017, Las Vegas, NV, USA. NJ: IEEE, 2017: 1-9. |
| [12] |
FAN Wenjun, DU Zhihui, SMITH-CREASEY M, et al. HoneyDOC: An Efficient Honeypot Architecture Enabling All-round Design[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019,37(3):683-697.
doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2894307 URL |
| [13] | DODIA P, ZHAUNIAROVICH Y. Poster: SDN-based System to Filter Out DRDoS Amplification Traffic in ISP Networks[C] //ACM. The 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, November 11-15, 2019, London, United Kingdom. New York: ACM, 2019: 2645-2647. |
| [14] |
LIANG Xiannuan, XIAO Yang. Game Theory for Network Security[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2012,15(1):472-486.
doi: 10.1109/SURV.2012.062612.00056 URL |
| [15] | The Honenet Project. The Honenet Project[EB/OL]. http://www.honeynet.org, 2020-03-18. |
| [16] | The Honeynet Project. Know Your Enemy: Honeynets[EB/OL]. http://old.honeynet.org/papers/honeynet/, 2009-03-30. |
| [17] | The Honeynet Project. Know Your Enemy GenII Honeynets[EB/OL]. http://project.honeynet.org/papers/gen2/index.html, 2020-03-25. |
| [18] | CHAMALES G. The Honeywall CD-ROM[J]. Security & Privacy IEEE, 2005,2(2):77-79. |
| [19] | YAN L K. Virtual Honeynets Revisited[C] //IEEE. The Sixth Annual IEEE SMC Information Assurance Workshop, June 15-17, 2005, West Point, NY, USA. NJ: IEEE, 2005: 232-239. |
| [20] | STUMPF F, GÖRLACH A, HOMANN F, et al. Nose-building Virtual Honeynets Made Easy[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228978549_NoSE-building_virtual_honeynets_made_easy, 2020-03-20. |
| [21] | ABBASI F H, HARRIS R J. Experiences with a Generation III Virtual Honeynet[C] //IEEE. 2009 Australasian Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ATNAC), November 10-12, 2009, Canberra, ACT, Australia. NJ: IEEE, 2009: 1-6. |
| [22] | ARTAIL H, SAFA H, SRAJ M, et al. A Hybrid Honeypot Framework for Improving Intrusion Detection Systems in Protecting Organizational Networks[J]. Computers & Security, 2006,25(4):274-288. |
| [23] | PROVOS N. A Virtual Honeypot Framework[C] //USENIX. The 13th USENIX Security Symposium, August 9-13, 2004, San Diego, California, USA. Berkeley: USENIX Association, 2004: 1-14. |
| [24] |
PORTOKALIDIS G, BOS H. Sweetbait: Zero-hour Worm Detection and Containment Using Low-and High-interaction Honeypots[J]. Computer Networks, 2007,51(5):1256-1274.
doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2006.09.005 URL |
| [25] | BAILEY M, COOKE E, WATSON D, et al. A Hybrid Honeypot Architecture for Scalable Network Monitoring[EB/OL]. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.84.7009&rep=rep1&type=pdf, 2014-10-27. |
| [26] | JIANG Xuxian, XU Dongyan. Collapsar: A VM-based Architecture for Network Attack Detention Center[C] // USENIX. The 13th USENIX Security Symposium, August 9-13, 2004, San Diego, California, USA. Berkeley: USENIX Association, 2004: 15-28. |
| [27] | ANTONIOU J. Game Theory and Networking[M] //Springer. Game Theory, the Internet of Things and 5G Networks. Cham: Springer, 2020: 1-20. |
| [28] | LALLIE H S, DEBATTISTA K, BAL J. A Review of Attack Graph and Attack Tree Visual Syntax in Cyber Security[EB/OL]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1574013719300772, 2020-03-20. |
| [29] | JIANG Wei. Research on Key Technologies of Active Defense Based on Attack Defense Game Model[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010. |
| 姜伟. 基于攻防博弈模型的主动防御关键技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学, 2010. | |
| [30] | NEUMANN J V, MORGENSTERN O. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1944. |
| [31] | MYERSON R B. Game Theory: Analysis of Conflict[M]. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1997. |
| [32] | ÇEKER H, ZHUANG Jun, UPADHYAYA S, et al. Deception-based Game Theoretical Approach to Mitigate DoS Attacks[M] //Springer. Decision and Game Theory for Security. Cham: Springer, 2016: 18-38. |
| [33] |
NASH J F. Equilibrium Points in n-person Games[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1950,36(1):48-49.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.36.1.48 URL pmid: 16588946 |
| [34] | GIBBONS R S. Game Theory for Applied Economists[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1992. |
| [35] |
HARSANYI J C. Games with Incomplete Information Played by Bayesian Players: Part I[J]. Management Science, 1967,14(3):159-182.
doi: 10.1287/mnsc.14.3.159 URL |
| [36] | MIT Lincoln Laboratory. 2000 DARPA Intrusion Detection Scenario SpecificDatasets[EB/OL]. https://www.ll.mit.edu/r-d/datasets/2000-darpa-intrusion-detection-scenario-specific-datasets, 2020-03-20. |
| [1] | 金志刚, 王新建, 李根, 岳顺民. 融合攻击图和博弈模型的网络防御策略生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(1): 1-9. |
| [2] | 张涛, 芦斌, 李玎, 何康. 一种基于软件定义网络的主机指纹抗探测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(7): 42-52. |
| [3] | 边曼琳, 王利明. 云环境下Docker容器隔离脆弱性分析与研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(7): 85-95. |
| [4] | 冉金鹏, 王翔, 赵尚弘, 高航航. 基于果蝇优化的虚拟SDN网络映射算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(6): 65-74. |
| [5] | 王健, 王语杰, 韩磊. 基于突变模型的SDN环境中DDoS攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(5): 11-20. |
| [6] | 白嘉萌, 寇英帅, 刘泽艺, 查达仁. 云计算平台基于角色的权限管理系统设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(1): 75-82. |
| [7] | 周亚球, 任勇毛, 李琢, 周旭. 基于SDN的科学DMZ研究与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 134-138. |
| [8] | 田春岐, 李静, 王伟, 张礼庆. 一种基于机器学习的Spark容器集群性能提升方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(4): 11-19. |
| [9] | 郭亚军, 蒲东齐. 基于蜜罐加密算法的个人隐私数据保护[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(12): 38-46. |
| [10] | 赖成喆, 王文娟. 面向车队的安全且具备隐私保护的移动性管理框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(7): 36-46. |
| [11] | 陈瑞滢, 陈泽茂, 王浩. 基于攻击图的工控网络威胁建模研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(10): 70-77. |
| [12] | 石悦, 李相龙, 戴方芳. 一种基于属性基加密的增强型软件定义网络安全框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(1): 15-22. |
| [13] | 李剑锋, 刘渊, 张浩, 王晓锋. 面向IaaS云平台的路由转发优化研究与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(9): 10-15. |
| [14] | 徐洋, 陈燚, 何锐, 谢晓尧. SDN中DDoS检测及多层防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(12): 22-28. |
| [15] | 齐宇. SDN安全研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(9): 69-72. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||