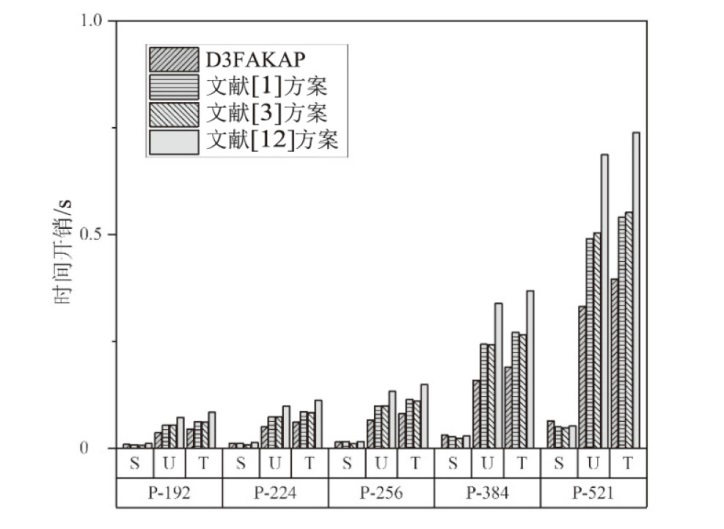
信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1407-1417.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.09.009
面向物联网场景的动态三因素认证密钥协商协议
- 太原理工大学计算机科学与技术学院(大数据学院),太原 030024
-
收稿日期:2025-03-25出版日期:2025-09-10发布日期:2025-09-18 -
通讯作者:黄鑫huangxin@tyut.edu.cn -
作者简介:杨昱坤(2000—),男,山西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全|肖为恩(1997—),男,山西,博士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全|梁博轩(2004—),男,山西,本科,主要研究方向为信息安全|黄鑫(1982—),男,山西,教授,博士,主要研究方向为信息安全、区块链、物联网 -
基金资助:山西省回国留学人员科研资助项目(2021-038)
Dynamic Three-Factor Authentication Key Agreement Protocol for IoT Scenarios
YANG Yukun, XIAO Weien, LIANG Boxuan, HUANG Xin( )
)
- Department of Computer Science and Technology (College of Data Science), Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
-
Received:2025-03-25Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-09-18
摘要:
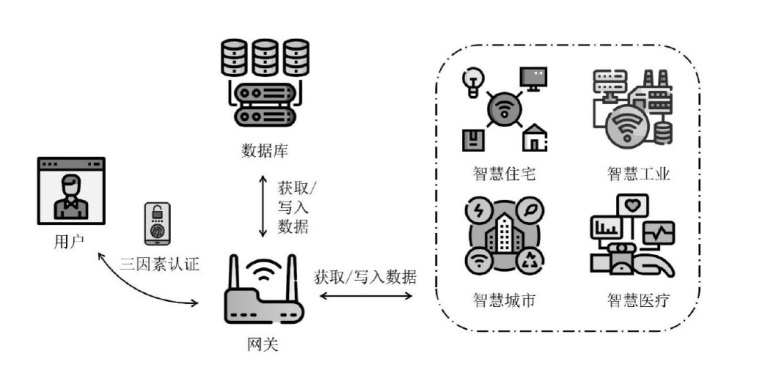
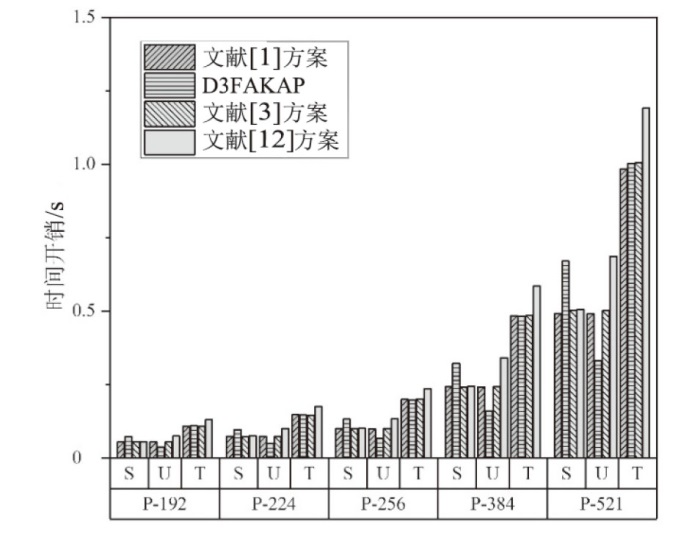
近年来,物联网设备的广泛应用,显著提升了人们的生活质量和工作效率。然而,物联网设备之间的数据共享通过网络进行,这使得数据容易受到网络攻击和泄露的威胁。文章旨在提高物联网设备数据交换的安全性,研究重点是多因素认证密钥协商(MFAKA)协议。文章围绕物联网设备间数据共享的安全性展开研究,采用了生物哈希技术(BioHash)和椭圆曲线密码学(ECC),并基于可证明安全中的真实或随机(ROR)模型进行理论分析,设计了一种结合了生物哈希技术和椭圆曲线密码学的新型动态三因素认证密钥协商协议D3FAKAP,确保了用户在登录过程中的匿名性和不可链接性。此外,文章所提方案在真实或随机模型下被证明具有语义安全性。性能分析表明,该方案在安全性和资源占用方面适合物联网环境。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨昱坤, 肖为恩, 梁博轩, 黄鑫. 面向物联网场景的动态三因素认证密钥协商协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1407-1417.
YANG Yukun, XIAO Weien, LIANG Boxuan, HUANG Xin. Dynamic Three-Factor Authentication Key Agreement Protocol for IoT Scenarios[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1407-1417.
表1
符号说明
| 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 定义在有限素数域 | |
| 用户的身份标识和密码 | |
| 拥有一定存储和计算能力的智能卡 | |
| 用户输入的生物特征 | |
| 用户注册时录入的生物特征模板 | |
| 无碰撞哈希函数 | |
| 生物哈希函数 | |
| 异或操作 | |
| 连接操作 | |
| 会话密钥 |
| [1] | XIE Qi, WONG D S, WANG Guilin, et al. Provably Secure Dynamic ID-Based Anonymous Two-Factor Authenticated Key Exchange Protocol with Extended Security Model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics & Security, 2017, 12(6): 1382-1392. |
| [2] | GOPE P. PMAKE: Privacy-Aware Multi-Factor Authenticated Key Establishment Scheme for Advance Metering Infrastructure in Smart Grid[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 152: 338-344. |
| [3] | ZHOU Lu, GE Chunpeng, SU Chunhua. A Privacy Preserving Two-Factor Authentication Protocol for the Bitcoin SPV Nodes[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(3): 34-48. |
| [4] | HAQ I U, WANG Jian. Secure Two-Factor Lightweight Authentication Protocol Using Self-Certified Public Key Cryptography for Multi-Server 5G Networks[EB/OL]. (2020-07-01)[2025-03-21]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S108480452030134X. |
| [5] | BADAR H M S, QADRI S, SHAMSHAD S, et al. An Identity Based Authentication Protocol for Smart Grid Environment Using Physical Uncloneable Function[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12(5): 4426-4434. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xin, HUANG Xin, YIN Haotian, et al. LLAKEP: A Low-Latency Authentication and Key Exchange Protocol for Energy Internet of Things in the Metaverse Era[EB/OL]. (2022-07-21)[2025-03-21]. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7390/10/14/2545. |
| [7] | QI Mingping. An Improved Three-Factor Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol for Smart Grid[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2023, 14(12): 16465-16476. |
| [8] | MEHTA P J, PARNE B L, PATEL S J. MAKA: Multi-Factor Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for LoRa-Based Smart Grid Communication Services[J]. IETE Journal of Research, 2023, 70(5): 4989-5005. |
| [9] | SHUKLA S, PATEL S J. A Novel ECC-Based Provably Secure and Privacy-Preserving Multi-Factor Authentication Protocol for Cloud Computing[J]. Computing, 2022, 104(5): 1173-1202. |
| [10] | SHUKLA S, PATEL S J. A Design of Provably Secure Multi-Factor ECC-Based Authentication Protocol in Multi-Server Cloud Architecture[J]. Cluster Computing, 2024, 27(2): 1559-1580. |
| [11] | BRAEKEN A. Highly Efficient Bidirectional Multifactor Authentication and Key Agreement for Real-Time Access to Sensor Data[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(23): 21089-21099. |
| [12] | ZHANG Shiwen, YAN Ziwei, LIANG Wei, et al. BAKA: Biometric Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme Based on Fuzzy Extractor for Wireless Body Area Networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 11(3): 5118-5128. |
| [13] | MALL P, AMIN R, DAS A K, et al. PUF-Based Authentication and Key Agreement Protocols for IoT, WSNs, and Smart Grids: A Comprehensive Survey[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(11): 8205-8228. |
| [14] | DEVANAPALLI S, PHANEENDRA K. Security Analysis of Three-Factor Authentication Protocol Based on Extended Chaotic-Maps[C]// IEEE. 2022 OPJU International Technology Conference on Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Development (OTCON). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-6. |
| [15] | QIU Shuming, WANG Ding, XU Guoai, et al. Practical and Provably Secure Three-Factor Authentication Protocol Based on Extended ChaoticMmaps for Mobile Lightweight Devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2020, 19(2): 1338-1351. |
| [16] | LEE J, YU S, KIM M, et al. On the Design of Secure and Efficient Three-Factor Authentication Protocol Using Honey List for Wireless Sensor Networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 107046-107062. |
| [17] | CHAKRABORTY N, LI Jiangqiang, LEUNG V C M, et al. Honeyword-Based Authentication Techniques for Protecting Passwords: A Survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 55(8): 1-37. |
| [18] | HUANG Zonghao, BAUER L, REITER M K. The Impact of Exposed Passwords on Honeyword Efficacy[C]// USENIX. 33th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley:USENIX,2024: 559-576. |
| [19] | FAN C, LIN Yihui. Provably Secure Remote Truly Three-Factor Authentication Scheme with Privacy Protection on Biometrics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2009, 4(4): 933-945. |
| [20] | ZHANG Liping, ZHANG Yixin, TANG Shanyu, et al. Privacy Protection for E-Health Systems by Means of Dynamic Authentication and Three-Factor Key Agreement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 65(3): 2795-2805. |
| [21] | KOBLITZ N. Elliptic Curve Cryptosystems[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1987, 48(177): 203-209. |
| [22] | MILLER V S. Use of Elliptic Curves in Cryptography[C]// Springer. Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 1985: 417-426. |
| [23] | JIN A T B, LING D N C, GOH A. Biohashing: Two Factor Authentication Featuring Fingerprint Data and Tokenised Random Number[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2004, 37(11): 2245-2255. |
| [24] | RATHA N, CONNELL J, BOLLE R M, et al. Cancelable Biometrics: A Case Study in Fingerprints[C]// IEEE.18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06). New York: IEEE, 2006: 370-373. |
| [25] | LUMINI A, NANNI L. An Improved Biohashing for Human Authentication[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2007, 40(3): 1057-1065. |
| [26] | TEOH A B J, KUAN Y W, LEE S. Cancellable Biometrics and Annotations on Biohash[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(6): 2034-2044. |
| [27] | HANKERSON D, MENEZES A. NIST Elliptic Curves[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2025. |
| [1] | 王梅, 杨潇然, 李增鹏. 简洁低交互的物联网设备认证协议研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1032-1043. |
| [2] | 张光华, 常继友, 陈放, 毛伯敏, 王鹤, 张建燕. 基于库函数动态替换的物联网设备固件仿真方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1053-1062. |
| [3] | 邓东上, 王伟业, 张卫东, 吴宣够. 基于模型特征方向的分层个性化联邦学习框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(6): 889-897. |
| [4] | 李强, 沈援海, 王锦泽, 黄晏瑜, 孙建国. 一种面向工业物联网环境的离线—在线签名方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 392-402. |
| [5] | 袁征, 张跃飞, 冯笑, 乔雅馨. 基于PUF的电力物联网智能终端认证协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(1): 13-26. |
| [6] | 张学旺, 陈思宇, 罗欣悦, 雷志滔, 谢昊飞. 面向云辅助工业物联网的高效可搜索属性基加密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1352-1363. |
| [7] | 邢长友, 王梓澎, 张国敏, 丁科. 基于预训练Transformers的物联网设备识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1277-1290. |
| [8] | 张晓均, 张楠, 郝云溥, 王周阳, 薛婧婷. 工业物联网系统基于混沌映射三因素认证与密钥协商协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1015-1026. |
| [9] | 李志华, 陈亮, 卢徐霖, 方朝晖, 钱军浩. 面向物联网Mirai僵尸网络的轻量级检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 667-681. |
| [10] | 杨杰超, 胡汉平, 帅燕, 邓宇昕. 基于时变互耦合双混沌系统的轻量级序列密码[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 385-397. |
| [11] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [12] | 翟鹏, 何泾沙, 张昱. 物联网环境下基于SM9算法和区块链技术的身份认证方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 179-187. |
| [13] | 印杰, 陈浦, 杨桂年, 谢文伟, 梁广俊. 基于人工智能的物联网DDoS攻击检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1615-1623. |
| [14] | 王君艳, 伊鹏, 贾洪勇, 张建辉. 基于改进CAE的物联网终端风险评估模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 150-159. |
| [15] | 张伟, 李子轩, 徐晓瑀, 黄海平. SDP-CoAP:基于软件定义边界的安全增强CoAP通信框架设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 17-31. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||