信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (12): 1896-1910.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.12.008
基于控制流变换的恶意程序检测GNN模型对抗样本生成方法
- 1.四川大学网络空间安全学院,成都 610065
2.中国电子科技网络信息安全有限公司,北京 100048
-
收稿日期:2024-07-09出版日期:2024-12-10发布日期:2025-01-10 -
通讯作者:贾鹏pengjia@scu.edu.cn -
作者简介:李奕轩(1999—),男,河北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为恶意软件检测|贾鹏(1988—),男,四川,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为软件漏洞挖掘|范希明(1993—),男,四川,博士研究生,主要研究方向为软件漏洞挖掘、人工智能安全|陈尘(1984—),男,四川,高级工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为网络安全 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFB3101803)
Control Flow Transformation Based Adversarial Example Generation for Attacking Malware Detection GNN Model
LI Yixuan1, JIA Peng1( ), FAN Ximing1, CHEN Chen2
), FAN Ximing1, CHEN Chen2
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Sichuan University, ChengDu 610065, China
2. China Electronics Technology Cyber Security Co., Ltd., Beijing 100048, China
-
Received:2024-07-09Online:2024-12-10Published:2025-01-10
摘要:
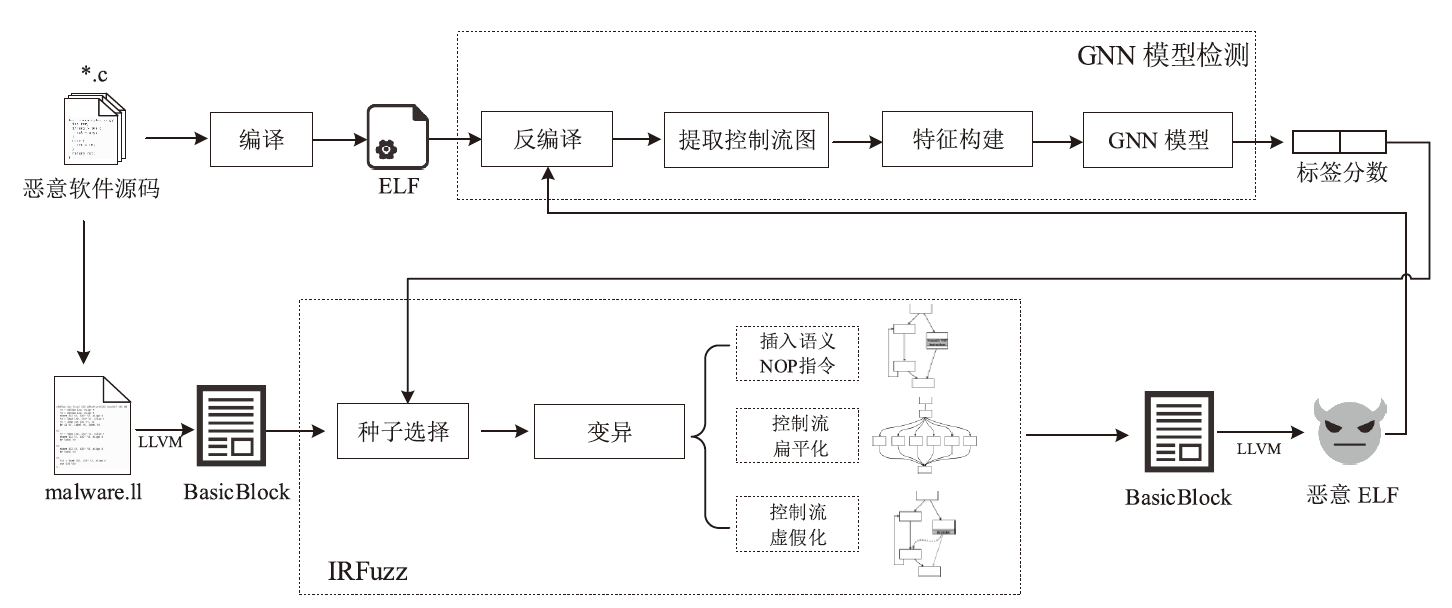
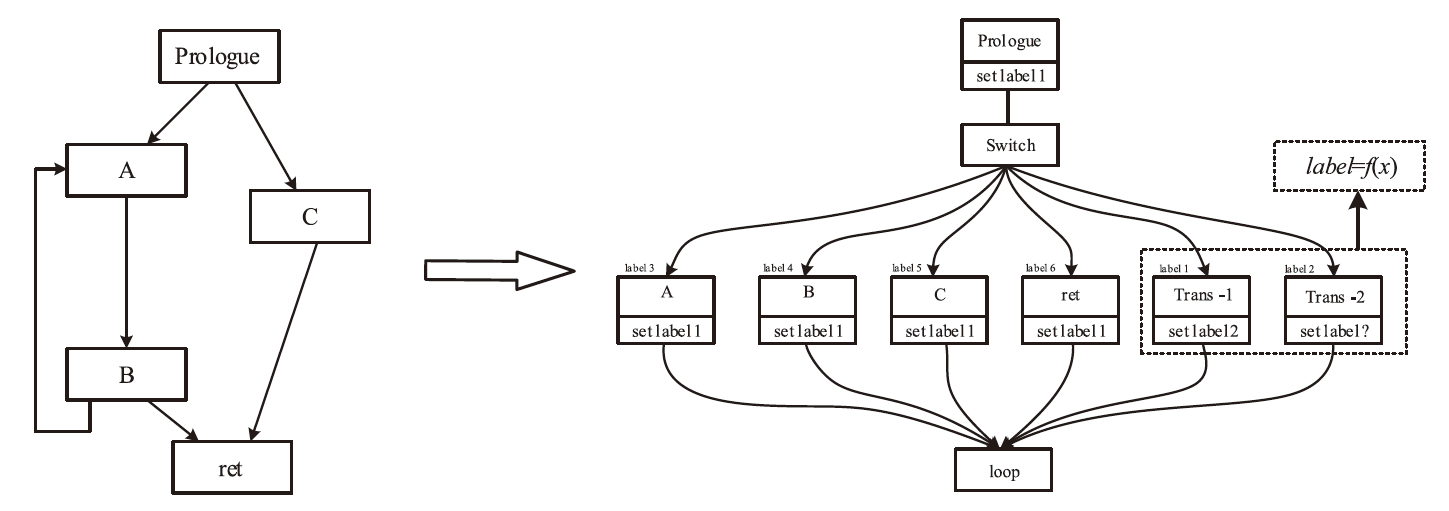
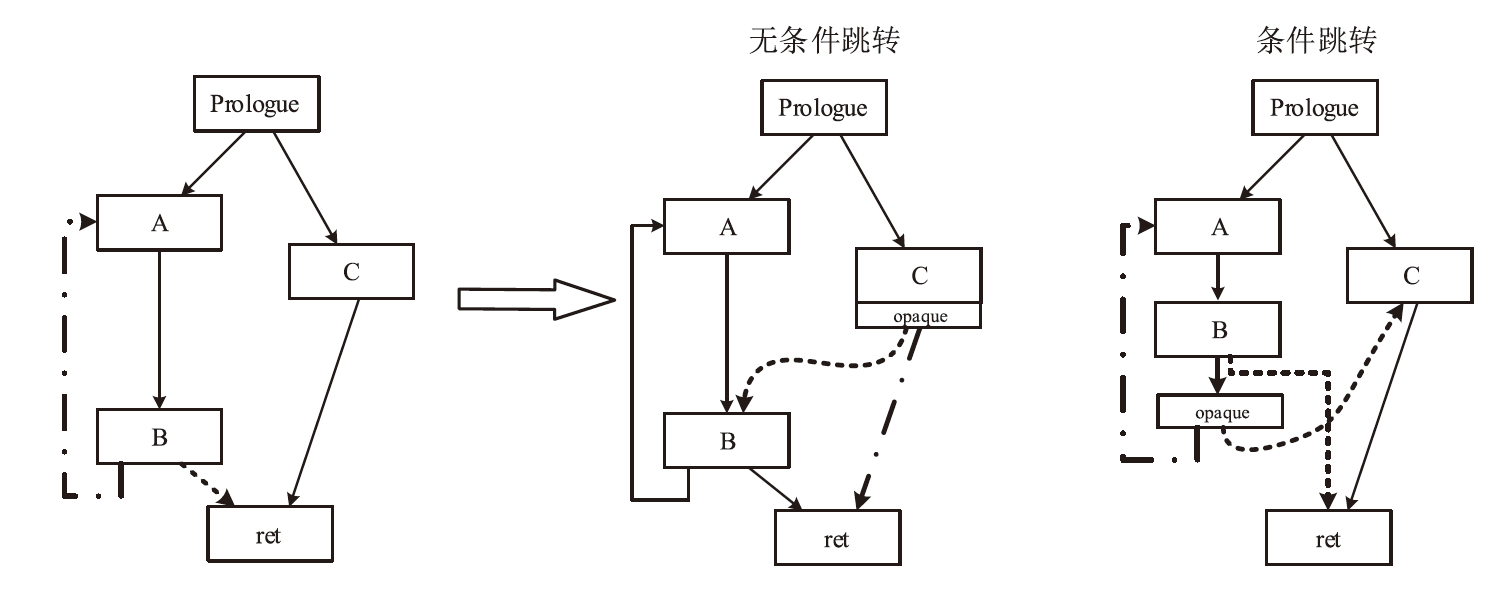
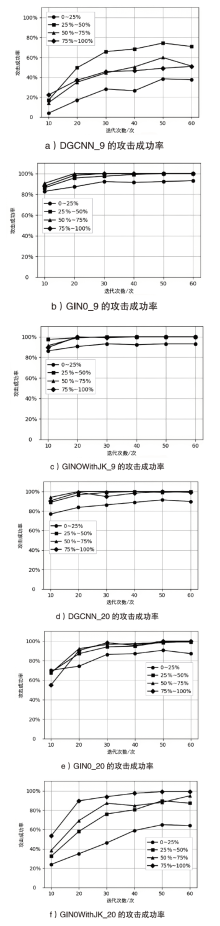
基于控制流图的图神经网络检测器在恶意程序检测领域取得了显著的成果,是目前的主流也是最先进的方法。现有的针对恶意程序图神经网络检测模型的对抗样本生成方法,主要通过修改控制流图的基本块或边特征实现,而不是修改输入到模型的原始二进制程序。其做法在真实场景下受限,即攻击方难以直接接触到控制流图的特征提取过程,也难以获得模型中间层的特征形式。文章提出通过变换中间语言改变二进制程序控制流图的对抗攻击框架IRAttack,该框架能够针对基于控制流图的图神经网络检测模型高效地产生对抗样本。文章通过插入语义NOP指令、控制流扁平化、控制流虚假化3种修改中间语言的操作,改变对二进制程序进行特征提取后产生的控制流图的节点特征和结构特征。同时,结合模糊测试思想选择需要修改的位置和添加的内容,从而更高效地产生可以误导检测模型的样本。文章在5472个良性样本和5230个恶意样本上,使用两种不同的特征提取方式和3种模型架构进行两两组合,训练了6种模型作为攻击目标。实验结果显示,相较于同背景下的SRLAttack与IMalerAttack,IRAttack的平均攻击成功率分别提升了46.39%和62.69%。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李奕轩, 贾鹏, 范希明, 陈尘. 基于控制流变换的恶意程序检测GNN模型对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(12): 1896-1910.
LI Yixuan, JIA Peng, FAN Ximing, CHEN Chen. Control Flow Transformation Based Adversarial Example Generation for Attacking Malware Detection GNN Model[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(12): 1896-1910.
表1
语义NOP指令集
| 序号 | 指令内容 |
|---|---|
| 1 | nop |
| 2 | subq |
| 3 | addq |
| 4 | leaq (%rax),%rax |
| 5 | movq %rax,%rax |
| 6 | xchgq %rax,%rax |
| 7 | pushfq pushq %rax xorl %eax,%eax cmovol %ecx,%eax popq %rax popfq |
| 8 | pushfq pushq %rax xorl %eax,%eax cmovpl %eax,%eax popq %rax popfq |
| 9 | pushfq cmpq %rax,%rax cmovb %eax,%eax popfq |
| 10 | pushfq cmpq %rax,%rax cmovg %ecx,%eax popfq |
| 11 | pushfq cmpq %rax,%rax cmovs %ecx,%eax popfq |
| 12 | pushfq cmpq %rax,%rax cmovl %ecx,%eax popfq |
| 13 | pushfq cmpq %rax,%rax cmovns %eax,%eax popfq |
| 14 | pushfq pushq %rax xorl %eax,%eax cmovnp %ecx,%eax popq %rax popfq |
| 15 | pushfq cmpq %rax,%rax cmovno %ecx,%eax popfq |
| 16 | addq |
| 17 | subq |
| 18 | pushq %rax negq %rax negq %rax popq %rax |
| 19 | notq %rax notq %rax |
| 20 | pushq %rax popq %rax |
| 21 | pushfq popfq |
| 22 | xchgq %rax,%rcx xchgq %rcx,%rax |
| 23 | pushq %rax notq %rax popq %rax |
| 24 | xorq %rbx,%rax xorq %rax,%rbx xorq %rax,%rbx xorq %rbx,%rax |
| 25 | pushq %rbx movq %rax,%rbx addq |
| 26 | pushq %rax incq %rax decq %rax decq %rax popq %rax |
| 27 | pushq %rbx movq %rax,%rbx cmpq %rax,%rax setg %al movzbq %al,%rax movq %rbx,%rax popq %rbx |
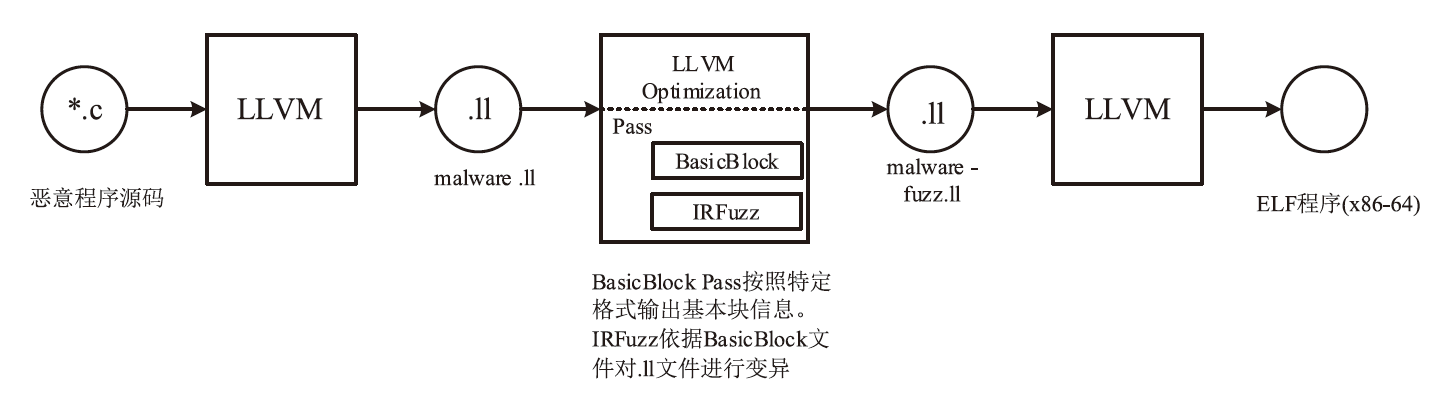
表2
BasicBlock文件
| 行号 | 文件内容 |
|---|---|
| 1 | [FunctionName-1@1,0] |
| 2 | FunctionName-1#BasicBlock-1&8: +1+3 |
| 3 | FunctionName-1#BasicBlock-2&7: +1 |
| 4 | FunctionName-1#BasicBlock-3&1: +12+4 |
| 5 | FunctionName-1#BasicBlock-4&10: +1 |
| 6 | FunctionName-1#BasicBlock-5&4: +1 |
| 7 | [FunctionName-2@0,30] |
| 8 | FunctionName-2#BasicBlock-1&3: +1 |
| 9 | FunctionName-2#BasicBlock-2&9: +1 |
| 10 | FunctionName-2#BasicBlock-3&3: +1+15 |
| 11 | FunctionName-2#BasicBlock-4&6: +1 |
| 12 | FunctionName-2#BasicBlock-5&2: +1 |
表4
模型准确率
| Model | Train | ACC Val | Test | FPR | FNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGCNN_9 | 95.47% | 96.35% | 95.57% | 3.27% | 4.85% |
| DGCNN_20 | 96.69% | 97.25% | 96.54% | 1.84% | 4.43% |
| GIN0_9 | 96.62% | 97.42% | 96.89% | 1.40% | 4.53% |
| GIN0_20 | 96.93% | 98.57% | 96.38% | 2.58% | 1.78% |
| GIN0WithJK_9 | 97.27% | 98.58% | 96.84% | 2.29% | 2.57% |
| GIN0WithJK_20 | 96.88% | 98.04% | 96.44% | 1.34% | 3.35% |
表5
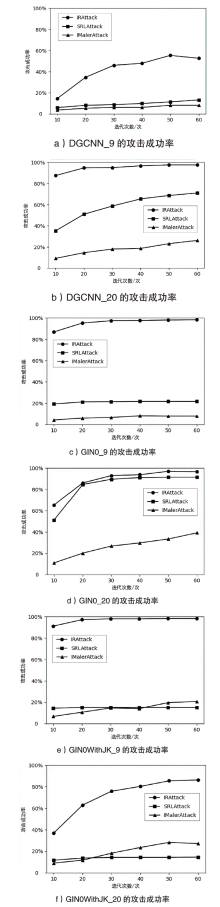
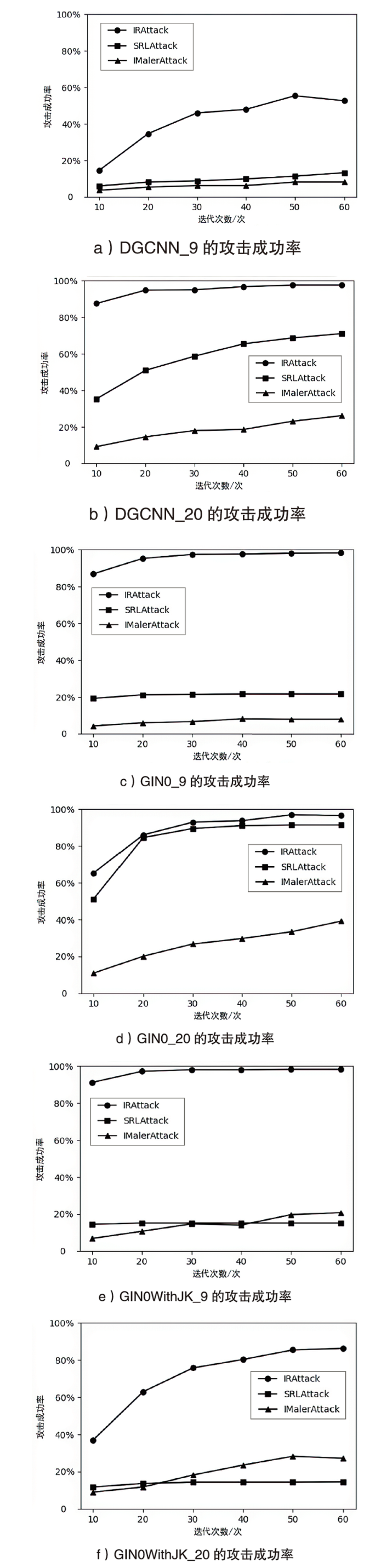
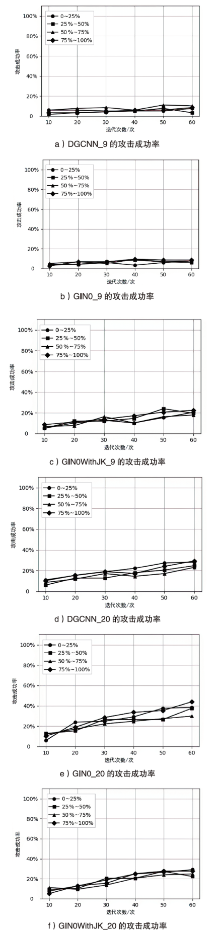
不同迭代次数下IRAttack与SRLAttack攻击成功率(%)
| Iteration | DGCNN_9 | DGCNN_20 | GIN0_9 | GIN0_20 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRAttack | SRLAttack | IRAttack | SRLAttack | IRAttack | SRLAttack | IRAttack | SRLAttack | ||||
| 10 | 14.56 (+8.56) | 6.00 | 87.58 (+52.25) | 35.33 | 86.94 (+67.67) | 19.27 | 65.31 (+14.13) | 51.18 | |||
| 20 | 34.69 (+26.55) | 8.14 | 94.86 (+43.9) | 50.96 | 95.29 (+74.09) | 21.20 | 86.08 (+1.5) | 84.58 | |||
| 30 | 46.04 (+37.26) | 8.78 | 95.07 (+36.4) | 58.67 | 97.43 (+76.02) | 21.41 | 92.93 (+3.42) | 89.51 | |||
| 40 | 47.97 (+38.12) | 9.85 | 96.79 (+31.27) | 65.52 | 97.64 (+76.01) | 21.63 | 93.79 (+2.72) | 91.07 | |||
| 50 | 55.46 (+44.11) | 11.35 | 97.64 (+28.90) | 68.74 | 98.07 (+76.44) | 21.63 | 97.00 (+5.57) | 91.43 | |||
| 60 | 52.68 (+39.4) | 13.28 | 97.64 (+26.55) | 71.09 | 98.29 (+76.66) | 21.63 | 96.57 (+5.14) | 91.43 | |||
| Iteration | GIN0WithJK_9 | GIN0WithJK_20 | Average | ||||||||
| IRAttack | SRLAttack | IRAttack | SRLAttack | IRAttack | SRLAttack | ||||||
| 10 | 91.22 (+76.66) | 14.56 | 37.04 (+25.26) | 11.78 | 56.09 (+33.07) | 23.02 | |||||
| 20 | 97.22 (+82.02) | 15.20 | 62.96 (+49.26) | 13.70 | 70.16 (+37.86) | 32.30 | |||||
| 30 | 98.07 (+82.87) | 15.20 | 75.80 (+61.45) | 14.35 | 76.48 (+41.82) | 34.65 | |||||
| 40 | 98.07 (+82.87) | 15.20 | 80.30 (+65.95) | 14.35 | 79.22 (+42.95) | 36.27 | |||||
| 50 | 98.29 (+83.09) | 15.20 | 85.44 (+71.09) | 14.35 | 83.13 (+46.01) | 37.12 | |||||
| 60 | 98.29 (+83.09) | 15.20 | 86.30 (+71.74) | 14.56 | 84.25 (+46.39) | 37.87 | |||||
表6
不同迭代次数下IRAttack与IMalerAttack攻击成功率(%)
| Iteration | DGCNN_9 | DGCNN_20 | GIN0_9 | GIN0_20 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRAttack | IMalerAttack | IRAttack | IMalerAttack | IRAttack | IMalerAttack | IRAttack | IMalerAttack | |
| 10 | 14.56 (+10.92) | 3.64 | 87.58 (+78.37) | 9.21 | 86.94 (+82.66) | 4.28 | 65.31 (+54.39) | 10.92 |
| 20 | 34.69 (+29.34) | 5.35 | 94.86 (+80.3) | 14.56 | 95.29 (+89.29) | 6.00 | 86.08 (+65.95) | 20.13 |
| 30 | 46.04 (+39.83) | 6.21 | 95.07 (+77.08) | 17.99 | 97.43 (+90.79) | 6.64 | 92.93 (+66.16) | 26.77 |
| 40 | 47.97 (+41.76) | 6.21 | 96.79 (+78.16) | 18.63 | 97.64 (+89.5) | 8.14 | 93.79 (+64.03) | 29.76 |
| 50 | 55.46 (+47.32) | 8.14 | 97.64 (+74.51) | 23.13 | 98.07 (+90.15) | 7.92 | 97.00 (+63.6) | 33.40 |
| 60 | 52.68 (+44.54) | 8.14 | 97.64 (+71.47) | 26.17 | 98.29 (+90.37) | 7.92 | 96.57 (+57.38) | 39.19 |
| Iteration | GIN0WithJK_9 | GIN0WithJK_20 | Average | |||||
| IRAttack | IMalerAttack | IRAttack | IMalerAttack | IRAttack | IMalerAttack | |||
| 10 | 91.22 (+84.37) | 6.85 | 37.04 (+28.05) | 8.99 | 56.09 (+48.78) | 7.32 | ||
| 20 | 97.22 (+86.51) | 10.71 | 62.96 (+51.18) | 11.78 | 70.16 (+58.74) | 11.42 | ||
| 30 | 98.07 (+83.29) | 14.78 | 75.80 (+57.6) | 18.20 | 76.48 (+61.38) | 15.10 | ||
| 40 | 98.07 (+83.94) | 14.13 | 80.30 (+56.75) | 23.55 | 79.22 (+62.49) | 16.74 | ||
| 50 | 98.29 (+78.59) | 19.70 | 85.44 (+57.17) | 28.27 | 83.13 (+63.04) | 20.09 | ||
| 60 | 98.29 (+77.52) | 20.77 | 86.30 (+59.11) | 27.19 | 84.25 (+62.69) | 21.56 | ||
表9
不同迭代次数下IRAttack产生对抗样本所需时间的中位数/s
| Iteration | DGCNN_9 | DGCNN_20 | GIN0_9 | GIN0_20 | GIN0-WithJK_9 | GIN0-WithJK_20 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 66.99 | 56.43 | 68.40 | 92.58 | 54.45 | 82.36 | 70.20 |
| 20 | 122.86 | 68.18 | 81.21 | 120.88 | 67.14 | 122.52 | 97.13 |
| 30 | 172.17 | 64.86 | 93.25 | 132.45 | 67.44 | 180.04 | 118.37 |
| 40 | 258.97 | 60.48 | 80.76 | 122.92 | 59.41 | 171.79 | 125.72 |
| 50 | 272.23 | 66.11 | 82.44 | 109.14 | 60.31 | 206.63 | 132.81 |
| 60 | 207.17 | 57.21 | 73.37 | 107.26 | 57.42 | 223.84 | 121.05 |
| [1] | PEI Xinjun, YU Long, TIAN Shengwei. AMalNet: A Deep Learning Framework Based on Graph Convolutional Networks for Malware Detection[EB/OL]. (2020-07-01)[2024-05-09]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167404820300778. |
| [2] | YAN Jiaqi, YAN Guanhua, JIN Dong. Classifying Malware Represented as Control Flow Graphs Using Deep Graph Convolutional Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 49th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN). New York: IEEE, 2019: 52-63. |
| [3] | KARGARNOVIN O, SADEGHZADEH A M, JALILI R. Mal2GCN: A Robust Malware Detection Approach Using Deep Graph Convolutional Networks with Non-Negative Weights[J]. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, 2024, 20(1): 95-111. |
| [4] | LING Xiang, WU Lingfei, DENG Wei, et al. Malgraph: Hierarchical Graph Neural Networks for Robust Windows Malware Detection[C]// IEEE. INFOCOM 2022-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. New York: IEEE, 2022: 1998-2007. |
| [5] | WU Bolun, XU Yuanhang, ZOU Futai. Malware Classification by Learning Semantic and Structural Features of Control Flow Graphs[C]// IEEE. 20th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom). New York: IEEE, 2021: 540-547. |
| [6] | CHEN Yihsien, LIN Sichen, HUANG Suchun, et al. Guided Malware Sample Analysis Based on Graph Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18: 4128-4143. |
| [7] | DING Yuxin, ZHOU Zihan, QIAN Wen. A Malware Family Classification Method Based on the Point Cloud Model DGCNN[C]// Springer. Network and System Security:15th International Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 210-221. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zikai, LI Yidong, WANG Wei, et al. Malware Detection with Dynamic Evolving Graph Convolutional Networks[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2022, 37(10): 7261-7280. |
| [9] | ZHANG Lan, LIU Peng, CHOI Y H, et al. Semantics-Preserving Reinforcement Learning Attack against Graph Neural Networks for Malware Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 20(2): 1390-1402. |
| [10] | CHEN Yanhui, FENG Yun, WANG Zhi, et al. IMaler: an Adversarial Attack Framework to Obfuscate Malware Structure against DGCNN-Based Classifier via Reinforcement Learning[C]// IEEE. ICC 2023-IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2023: 790-796. |
| [11] | JUNOD P, RINALDINI J, WEHRLI J, et al. Obfuscator-LLVM: Software Protection for the Masses[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE/ACM 1st International Workshop on Software Protection. New York: IEEE, 2015: 3-9. |
| [12] | FEY M, LENSSEN J E. Fast Graph Representation Learning with PyTorch Geometric[EB/OL]. (2019-03-06)[2024-06-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.02428. |
| [13] | BIlOT T, EL M N, AL AK, et al. A Survey on Malware Detection with Graph Representation Learning[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2024, 56(11): 1-36. |
| [14] | XU Zhiwu, REN Kerong, QIN Shengchao, et al. CDGDroid: Android Malware Detection Based on Deep Learning Using CFG and DFG[C]// Springer. Formal Methods and Software Engineering:20th International Conference on Formal Engineering Methods. Heidelberg: Springer, 2018: 177-193. |
| [15] | ANDERSON H S, KHARKAR A, FILAR B, et al. Learning to Evade Static PE Machine Learning Malware Models via Reinforcement Learning[EB/OL]. (2018-01-26)[2024-05-12]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.08917. |
| [16] | LIU Yuying, YANG Pin, JIA Peng, et al. MalFuzz: Coverage-Guided Fuzzing on Deep Learning-Based Malware Classification Model[EB/OL]. (2022-09-15)[2024-05-09]. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0273804. |
| [17] | ZHAN Dazhi, DUAN Yexin, HU Yue, et al. MalPatch: Evading DNN-Based Malware Detection With Adversarial Patches[C]// IEEE. Transactions on Information Forensics and Security. New York: IEEE, 2023: 1183-1198. |
| [18] | LUCAS K, SHARIF M, BAUER L, et al. Malware Makeover: Breaking ML-Based Static Analysis by Modifying Executable Bytes[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2021: 744-758. |
| [19] | ZUGNER D, BORCHERT O, AKBARNEJAD A, et al. Adversarial Attacks on Graph Neural Networks: Perturbations and Their Patterns[J]. Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2020, 14(5): 1-31. |
| [20] | PAPPAS V, POLYCHRONAKIS M, KEROMYTIS A D. Smashing the Gadgets: Hindering Return-Oriented Programming Using In-place Code Randomization[C]// IEEE. 2012 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2012: 601-615. |
| [21] | CHEN Yue, WANG Zhi, WHALLEY D, et al. Remix: On-Demand Live Randomization[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Sixth ACM Conference on Data and Application Security and Privacy. New York: ACM, 2016: 50-61. |
| [22] | GIBERT D, FREDRIKSON M, MATEU C, et al. Enhancing the Insertion of NOP Instructions to Obfuscate Malware via Deep Reinforcement Learning[EB/OL]. (2022-01-01)[2024-05-09]. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102543. |
| [23] | BALACHANDRAN V, KEONG N W, EMMANUEL S. Function Level Control Flow Obfuscation for Software Security[C]// IEEE. 2014 the Eighth International Conference on Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems. New York: IEEE, 2014: 133-140. |
| [24] | BERNAT A R, MILLER B P. Structured Binary Editing with A CFG Transformation Algebra[C]// IEEE. 2012 the 19th Working Conference on Reverse Engineering. New York: IEEE, 2012: 9-18. |
| [25] | DUCK G J, GAO X, ROYCHOUDHURY A. Binary Rewriting without Control Flow Recovery[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 41st ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation. New York: ACM, 2020: 151-163. |
| [26] | GIUFFRIDA C, KUIJSTEN A, TANENBAUM A S. Enhanced Operating System Security Through Efficient and Fine-Grained Address Space Randomization[C]// USENIX. 21st USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 12). New York: USENIX, 2012: 475-490. |
| [27] | SRNDIC N, LASKOV P. Practical Evasion of a Learning-Based Classifier: A Case Study[C]// IEEE. 2014 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2014: 197-211. |
| [28] | KREUK F, BARAK A, AVIV-REUVEN S, et al. Deceiving End-to-End Deep Learning Malware Detectors using Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2018-02-13)[2024-05-09]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1802.04528. |
| [29] | CRANE S, LIEBCHEN C, HOMESCU A, et al. Readactor: Practical Code Randomization Resilient to Memory Disclosure[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2015: 763-780. |
| [30] | WILLIAMS-KING D, GOBIESKI G, WILLIAMS-KING K, et al. Shuffler: Fast and Deployable Continuous Code Re-Randomization[C]// USENIX. 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 16). New York: USENIX, 2016: 367-382. |
| [31] | KOO H, POLYCHRONAKIS M. Juggling the Gadgets: Binary-Level Code Randomization Using Instruction Displacement[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 11th ACM on Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 23-34. |
| [32] | CARLINI N, ATHALYE A, PAPERNOT N, et al. On Evaluating Adversarial Robustness[EB/OL]. (2019-02-18)[2024-05-09]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.06705. |
| [33] | GITHUB. Toy LLVM Obfuscator Pass[EB/OL]. (2021-11-25)[2024-05-09]. https://github.com/veritas501/ToyObfuscator/tree/master. |
| [34] | TSINGHUA. Index of Tsinghua Open Source Mirror[EB/OL]. (2015-01-01)[2024-04-13]. https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/gnu/coreutils. |
| [35] | ROKON M, ISLAM R, DARKI A, et al. SourceFinder: Finding Malware Source-Code from Publicly Available Repositories in GitHub[C]// USENIX. 23rd International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and Defenses (RAID 2020). New York: USENIX, 2020: 149-163. |
| [36] | GITHUB. MalwareSamples/Linux-Malware-Samples: Linux Malware Sample Archive Including Various Types of Malicious ELF Binaries and Viruses[EB/OL]. (2021-01-01)[2024-05-09]. https://github.com/MalwareSamples/Linux-Malware-Samples. |
| [37] | GITHUB. A Collection of Well Labeled ELF Binaries Compiled from Benign and Malicious Code in Various Ways[EB/OL]. (2021-03-26)[2024-05-11]. https://github.com/nimrodpar/Labeled-Elfs. |
| [38] | XU Keyulu, HU Weihua, LESKOVEC J, et al. How Powerful are Graph Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2018-10-01)[2024-05-09]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.00826. |
| [39] | XU Keyulu, LI Chengtao, TIAN Yonglong, et al. Representation Learning on Graphs with Jumping Knowledge Networks[EB/OL]. (2018-07-09)[2024-05-09]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1806.03536. |
| [40] | DOCKER. Docker Image | Docker Hub[EB/OL]. (2022-11-25)[2024-05-30]. https://hub.docker.com/r/hacrot3000/docker-wine-ida. |
| [1] | 王健, 陈琳, 王凯崙, 刘吉强. 基于时空图神经网络的应用层DDoS攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 509-519. |
| [2] | 张新有, 孙峰, 冯力, 邢焕来. 基于多视图表征的虚假新闻检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 438-448. |
| [3] | 余尚戎, 肖景博, 殷琪林, 卢伟. 关注社交异配性的社交机器人检测框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 319-327. |
| [4] | 张选, 万良, 罗恒, 杨阳. 基于两阶段图学习的僵尸网络自动化检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(12): 1933-1947. |
| [5] | 李鹏超, 张全涛, 胡源. 基于双注意力机制图神经网络的智能合约漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1624-1631. |
| [6] | 芦效峰, 程天泽, 龙承念. 基于随机游走的图神经网络黑盒对抗攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1570-1577. |
| [7] | 秦中元, 马楠, 余亚聪, 陈立全. 基于双重图神经网络和自编码器的网络异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 1-11. |
| [8] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王靖亚, 杨莹. 一种面向Android恶意软件的多视角多任务学习检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 1-7. |
| [9] | 朱丽娜, 马铭芮, 朱东昭. 基于图神经网络和通用漏洞分析框架的C类语言漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 59-68. |
| [10] | 秦中元, 胡宁, 方兰婷. 基于免疫仿生机理和图神经网络的网络异常检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 10-16. |
| [11] | 于克辰, 郭莉, 姚萌萌. 基于空间及能量维度的黑盒对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 72-78. |
| [12] | 张文;严寒冰;文伟平. 一种Android恶意程序检测工具的实现[J]. , 2013, 13(1): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||