信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (2): 319-327.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.02.015
关注社交异配性的社交机器人检测框架
余尚戎1,2,3, 肖景博1,2,3, 殷琪林1,2,3, 卢伟1,2,3( )
)
- 1.中山大学计算机学院,广州 510006
2.中山大学信息技术教育部重点实验室,广州 510006
3.广东省信息安全技术重点实验室,广州 510006
-
收稿日期:2023-10-31出版日期:2024-02-10发布日期:2024-03-06 -
通讯作者:卢伟 E-mail:luwei3@mail.sysu.edu.cn -
作者简介:余尚戎(1999—),男,湖北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为多媒体内容安全|肖景博(2001—),男,河南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为多媒体内容安全|殷琪林(1995—),男,江苏,博士研究生,主要研究方向为数字多媒体取证|卢伟(1979—),男,河南,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为人工智能安全与对抗、信息取证与安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(U2001202);国家自然科学基金(62072480)
A Social Heterophily Focused Framework for Social Bot Detection
YU Shangrong1,2,3, XIAO Jingbo1,2,3, YIN Qilin1,2,3, LU Wei1,2,3( )
)
- 1. School of Computer Science and Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China
2. Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Information Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China
3. Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Information Security Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
-
Received:2023-10-31Online:2024-02-10Published:2024-03-06 -
Contact:LU Wei E-mail:luwei3@mail.sysu.edu.cn
摘要:
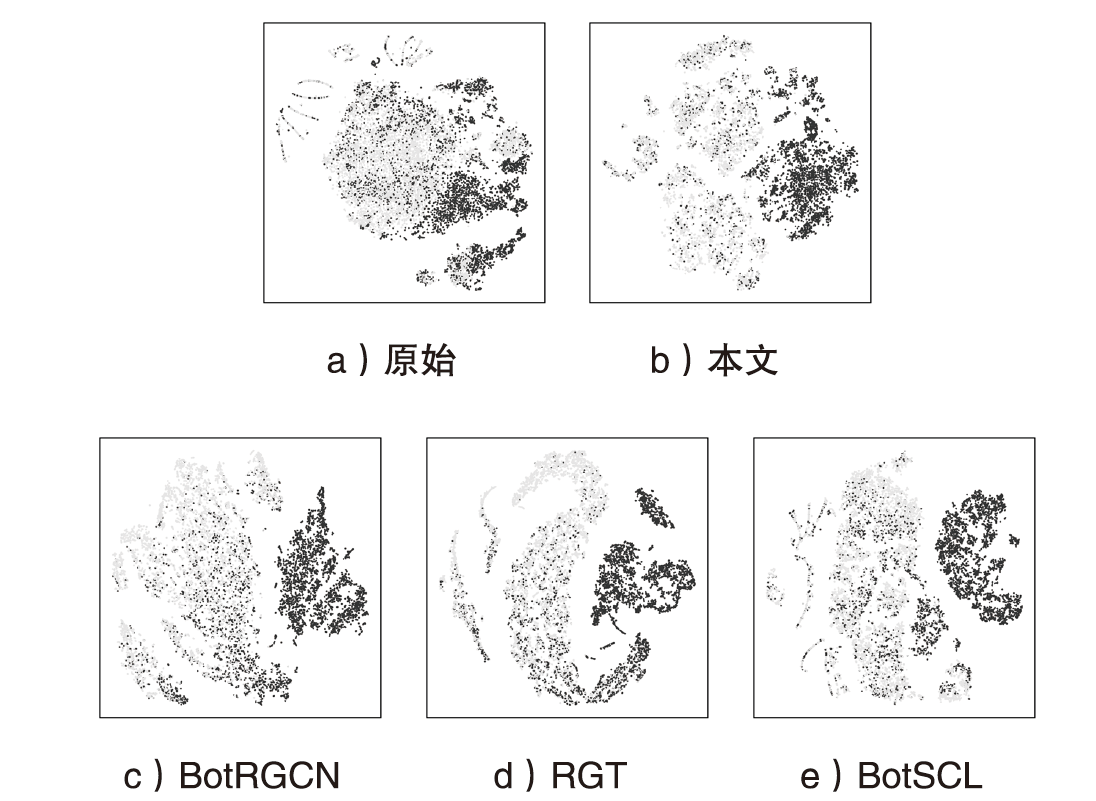
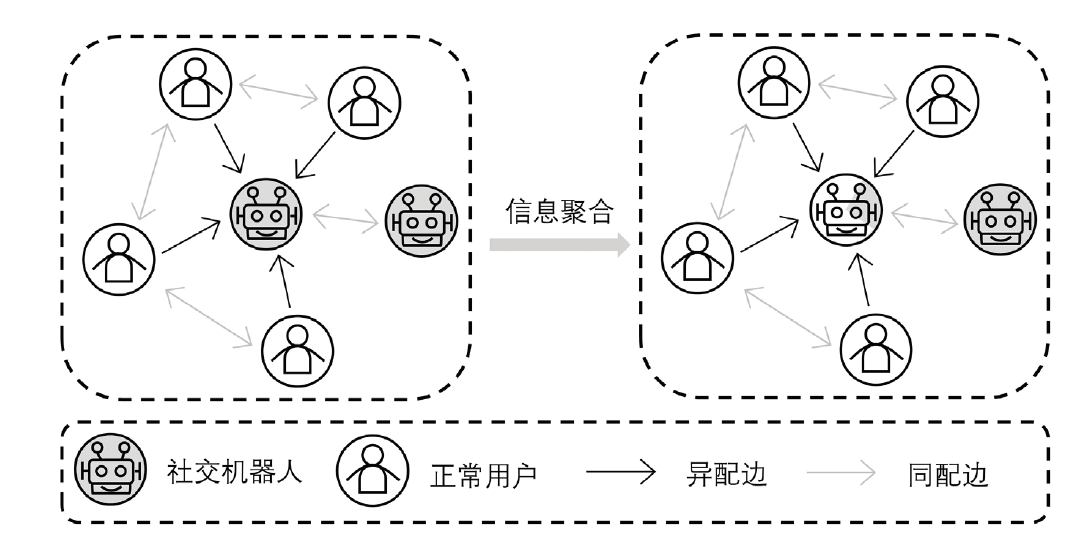
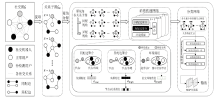
随着社交机器人的迭代,其倾向于与正常用户进行更多交互,对其检测变得更具挑战性。现有检测方法大多基于同配性假设,由于忽视了不同类用户间存在的联系,难以保持良好的检测性能。针对这一问题文章提出一种关注社交异配性的社交机器人检测框架,以社交网络用户间的联系为依据,通过充分挖掘用户社交信息来应对异配影响,并实现更精准的检测。文章分别在同配视角和异配视角下看待用户之间的联系,将社交网络构建为图,通过消息传递机制实现同配边和异配边聚合,以提取节点的频率特征,同时利用图中各节点特征聚合得到社交环境特征,将以上特征混合后用于检测。实验结果表明,文章所提方法在开源数据集上的检测效果优于基线方法,证明了该方法的有效性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
余尚戎, 肖景博, 殷琪林, 卢伟. 关注社交异配性的社交机器人检测框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 319-327.
YU Shangrong, XIAO Jingbo, YIN Qilin, LU Wei. A Social Heterophily Focused Framework for Social Bot Detection[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 319-327.
表2
对比实验结果
| 数据集 | 模型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TwiBot-20 | BotRGCN | 83.41 %±0.41 % | 85.94 %±0.36 % |
| RGT | 83.92 %±0.27 % | 86.57 %±0.17 % | |
| BotSCL | 83.81 %±0.42 % | 86.47 %±0.26 % | |
| 本文方法 | 84.76 %±0.27 % | 87.15 %±0.21 % | |
| TwiBot-22 | BotRGCN | 85.02 %±0.29 % | 64.46 %±1.7 % |
| RGT | 85.11 %±0.06 % | 64.61 %±0.21 % | |
| BotSCL | 84.82 %±0.15 % | 62.58 %±2.78 % | |
| 本文方法 | 85.02 %±0.08 % | 65.97 %±1.57 % |
| [1] | BESSI A, FERRARA E. Social Bots Distort the 2016 Us Presidential Election Online Discussion[J]. First Monday, 2016, 16(21): 7-11. |
| [2] | WENG Zixuan, LIN Aijun. Public Opinion Manipulation on Social Media: Social Network Analysis of Twitter Bots During the Covid-19 Pandemic[EB/OL]. (2022-12-07)[2023-10-20]. https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/24/16376. |
| [3] | WANG Gang, MOHANLAL M, WILSON C, et al. Social Turing Tests: Crowdsourcing Sybil Detection[EB/OL]. (2012-12-07)[2023-10-20]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1205.3856.pdf. |
| [4] | DAVIS C A, VAROL O, FERRARA E, et al. Botornot: A System to Evaluate Social Bots[C]// ACM. 25th International Conference Companion on World Wide Web. New York: ACM, 2016: 273-274. |
| [5] | DEWANGAN M, KAUSHAL R. Socialbot: Behavioral Analysis and Detection[C]// Springer. 4th International Symposium on Security in Computing and Communications (SSCC). Heidelberg:Springer, 2016: 450-460. |
| [6] |
KUDUGUNTA S, FERRARA E. Deep Neural Networks for Bot Detection[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 467: 312-322.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.08.019 URL |
| [7] | PING Heng, QIN Sujuan. A Social Bots Detection Model Based on Deep Learning Algorithm[C]// IEEE. 18th IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT). New York:IEEE, 2018: 1435-1439. |
| [8] | ALI A S, BIN T R, NAJAFI P, et al. Detect Me If You Can: SPAM Bot Detection Using Inductive Representation Learning[C]// ACM. Companion Proceedings of the 2019 World Wide Web Conference. New York: ACM, 2019: 148-153. |
| [9] | FENG Shangbin, WAN Herun, WANG Ningnan, et al. BotRGCN: Twitter Bot Detection with Relational Graph Convolutional Networks[C]// ACM. 2021 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining. New York: ACM, 2021: 236-239. |
| [10] | FENG Shangbin, WAN Herun, WANG Ningnan, et al. Satar: A Self-Supervised Approach to Twitter Account Representation Learning and Its Application in Bot Detection[C]// ACM. 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Managemen. New York: ACM, 2021: 3808-3817. |
| [11] | FENG Shangbin, TAN Zhaoxuan, LI Rui, et al. Heterogeneity-Aware Twitter Bot Detection with Relational Graph Transformers[C]// AAAI. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2022, 36(4): 3977-3985. |
| [12] | LE T, TRAN-THANH L, LEE D. Socialbots on Fire: Modeling Adversarial Behaviors of Socialbots via Multi-Agent Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning[C]// ACM. 31st ACM Web Conference (WWW). New York:ACM, 2022: 545-554. |
| [13] |
DES M N G, HUNTER D S, EL H Z, et al. Detecting Bots and Assessing Their Impact in Social Networks[J]. Operations Research, 2022, 70(1): 1-22.
doi: 10.1287/opre.2021.2118 URL |
| [14] |
MCPHERSON M, SMITH-LOVIN L, COOK J M. Birds of a Feather: Homophily in Social Networks[J]. Annual Review of Sociology, 2001, 27(1): 415-444.
doi: 10.1146/soc.2001.27.issue-1 URL |
| [15] | SHEN Xiao, SUN Dewang, PAN Shirui, et al. Neighbor Contrastive Learning on Learnable Graph Augmentation[C]// AAAI. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2023, 37(8): 9782-9791. |
| [16] | YANG Peipei, ZHENG Zhuoyuan. Fake Account Detection with Attention-Based Graph Convolution Networks[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Automation, Electronics and Electrical Engineering (AUTEEE). New York:IEEE, 2020: 106-110. |
| [17] | FENG Shangbin, WAN Herun, WANG Ningnan, et al. Twibot-20: A Comprehensive Twitter Bot Detection Benchmark[C]// ACM. 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management. New York: ACM, 2021: 4485-4494. |
| [18] | FENG Shangbin, TAN Zhaoxuan, WAN Herun, et al. TwiBot-22: Towards Graph-Based Twitter Bot Detection[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2022(35): 35254-35269. |
| [19] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, (30): 6000-6010. |
| [20] | WU Qi, YANG Yingguan, HE Buyun, et al. Heterophily-Aware Social Bot Detection with Supervised Contrastive Learning[EB/OL]. (2023-06-15)[2023-10-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.07478. |
| [21] | GILANI Z, FARAHBAKHSH R, TYSON G, et al. Of Bots and Humans (on Twitter)[C]// IEEE. The 2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining. New York: IEEE, 2017: 349-354. |
| [22] | LUAN Sitao, HUA Chenqing, LU Qincheng, et al. Is Heterophily a Real Nightmare for Graph Neural Networks to Do Node Classification?[EB/OL]. (2021-09-12)[2023-10-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2109.05641. |
| [23] | BO Deyu, WANG Xiao, SHI Chuan, et al. Beyond Low-Frequency Information in Graph Convolutional Networks[C]// AAAI. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2021, 35(5): 3950-3957. |
| [24] | LIU Nian, WANG Xiao, BO Deyu, et al. Revisiting Graph Contrastive Learning from The Perspective of Graph Spectrum[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2022, (35): 2972-2983. |
| [25] | EKAMBARAM V N. Graph-Structured Data Viewed through a Fourier Lens[M]. Berkeley: University of California, 2014. |
| [26] | VAN D M L, HINTON G. Visualizing Data Using T-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(11): 2579-2605. |
| [1] | 秦中元, 马楠, 余亚聪, 陈立全. 基于双重图神经网络和自编码器的网络异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 1-11. |
| [2] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王靖亚, 杨莹. 一种面向Android恶意软件的多视角多任务学习检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 1-7. |
| [3] | 朱丽娜, 马铭芮, 朱东昭. 基于图神经网络和通用漏洞分析框架的C类语言漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 59-68. |
| [4] | 秦中元, 胡宁, 方兰婷. 基于免疫仿生机理和图神经网络的网络异常检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 10-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||