信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 73-83.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.03.008
一种面向微服务的多维度根因定位算法
- 1.中国科学院信息工程研究所,北京 100093
2.中国科学院大学网络安全学院,北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2022-11-13出版日期:2023-03-10发布日期:2023-03-14 -
通讯作者:李杨 E-mail:liyang@iie.ac.cn -
作者简介:施园(1996—),男,四川,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为智能运维|李杨(1980—),女,北京,副研究员,博士,主要研究方向为5G安全、大数据处理与分析、智能运维|詹孟奇(1996—),男,四川,博士研究生,主要研究方向为网络协议异常检测 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFB1005200);国家重点研发计划(2019YFB1005201)
A Multi-Dimensional Root Cause Localization Algorithm for Microservices
SHI Yuan1,2, LI Yang1,2( ), ZHAN Mengqi1,2
), ZHAN Mengqi1,2
- 1. Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100093, China
2. School of Cyber Security, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2022-11-13Online:2023-03-10Published:2023-03-14 -
Contact:LI Yang E-mail:liyang@iie.ac.cn
摘要:
伴随着Docker等虚拟化容器技术的逐渐成熟,因其可扩展性、灵活性等特点与微服务架构完美契合,工业界逐渐将微服务架构应用部署在基于容器的云环境下,并用Kubernetes等容器编排工具来管理应用的全生命周期。在这样复杂的微服务架构下,如何使用人工智能技术高效发现异常并且定位根因成为重中之重。首先,文章总结了在微服务系统环境下进行异常检测和根因定位所面临的主要挑战和现有的关键技术;然后,针对现有技术异常检测覆盖范围不全面的问题,文章提出了一种基于无监督学习的多维度的异常检测方法,在调用链Trace数据的基础上结合服务和机器资源利用数据进行综合分析,确保能够检测出服务响应时间异常的同时,也能够识别服务资源利用异常和环境异常;最后,在异常已知的情况下,为了减少根因定位时间,拓展定位范围和缩小粒度,文章提出了一种轻量的基于异常传播子图的方法,将服务接口和机器节点两种维度的数据统一到异常传播子图中进行根因定位。实验表明,文章所提方法与已有方法相比,定位时间更短,不仅拓宽了根因定位场景,而且准确率也有明显提升。
中图分类号:
引用本文
施园, 李杨, 詹孟奇. 一种面向微服务的多维度根因定位算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 73-83.
SHI Yuan, LI Yang, ZHAN Mengqi. A Multi-Dimensional Root Cause Localization Algorithm for Microservices[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(3): 73-83.
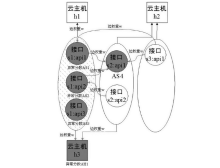
表2
STMV真实示例
| 向量状态 | STMV ID | a的响应时间/ms | b的响应时间/ms | a的cpu使用量/core | b的cpu使用量/core | a的内存使用量/byte | b内存使用量/byte | a的 摘要 | b的 摘要 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 | 1 | 222 | 209 | 0.207 | 0.219 | 2765402112 | 3866624 | 0.8279 | 1.7778 |
| 正常 | 2 | 198 | 203 | 0.244 | 0.239 | 2768973824 | 3903488 | 0.8465 | 1.8079 |
| 正常 | 3 | 212 | 204 | 0.232 | 0.219 | 2780045312 | 4788224 | 0.8562 | 1.7898 |
| 异常 | 4 | 1302 | 1138 | 0.209 | 0.282 | 2680045312 | 4687824 | 0.8892 | 1.7989 |
| 异常 | 5 | 1102 | 1305 | 0.392 | 0.246 | 2700045312 | 4695824 | 0.8578 | 1.7789 |
| 异常 | 6 | 232 | 198 | 2.827 | 0.267 | 2710045435 | 4995912 | 1.012 | 1.8789 |
| 异常 | 7 | 221 | 178 | 0.401 | 0.298 | 2980045345 | 3803483 | 1000.2 | 28.2 |
表3
算法对比结果
| 算法名称 | 响应时间 异常 | 调用路径 异常 | 微服务负载 异常 | 微服务系统 环境异常 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 准确率 | 召回率 | 准确率 | 召回率 | 准确率 | 召回率 | 准确率 | 召回率 | |
| Hard-coded Rule算法 | 0.89 | 0.79 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Multimodal LSTM 算法 | 0.62 | 0.95 | N/A | 0.93 | 0.53 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.89 |
| Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes算法 | 0.16 | 0.52 | 0.17 | 0.98 | 0.64 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.84 |
| Omni- Anomaly 算法 | 0.45 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.94 | 0.6 | 0.94 | 0.65 | 0.91 |
| Trace- Anomaly 算法 | 0.98 | 0.97 | N/A | 0.89 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 本文算法 | 0.97 | 0.98 | N/A | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.99 |
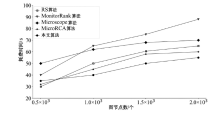
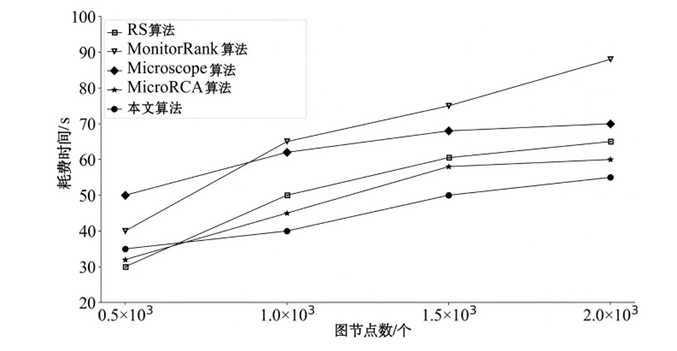
表4
本文算法和其他根因定位算法比较
| Metric | RS 算法 | MonitorRank 算法 | Microscope 算法 | MicroRCA 算法 | 本文所提 算法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 服务接口响应超时根因 | |||||
| PR@1 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.71 | 0.87 | 0.89 |
| PR@3 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| MAP | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| 服务资源利用异常根因 | |||||
| PR@1 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.45 | 0.76 | 0.89 |
| PR@3 | 0.46 | 0.33 | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.91 |
| MAP | 0.42 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.7 | 0.92 |
| 云主机资源利用异常根因 | |||||
| PR@1 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.52 | 0.78 | 0.91 |
| PR@3 | 0.26 | 0.65 | 0.56 | 0.83 | 0.93 |
| MAP | 0.41 | 0.61 | 0.6 | 0.81 | 0.94 |
| [1] | LI Zhenhao. Development and Impact Analysis of Microservice Architecture[J]. China CIO News, 2017, 1: 154-155. |
| 李贞昊. 微服务架构的发展与影响分析[J]. 信息系统工程, 2017, 1: 154-155. | |
| [2] |
BOETTIGER C. An Introduction to Docker for Reproducible Research, with Examples from the R Environment[J]. ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review, 2015, 49(1): 71-79.
doi: 10.1145/2723872.2723882 URL |
| [3] |
BERNSTEIN D. Containers and Cloud: From LXC to Docker to Kubernetes[J]. IEEE Cloud Computing, 2014, 1(3): 81-84.
doi: 10.1109/MCC.2014.51 URL |
| [4] | ZHANG Xuejian, ZHANG Yu, CHUAN Tao, et al. Construction Method of It Operation and Maintenance Data Management System Based on Big Data Technology[J]. Electronic Science and Technology, 2018, 31(4): 84-86. |
| 张雪坚, 张榆, 钏涛, 等. 基于大数据技术的IT运维数据管理系统构建方法[J]. 电子科技, 2018, 31(4): 84-86. | |
| [5] | WANG Wei, SHEN Xudong. Research on Anomaly Detection Al- Gorithm of Migration Time Series Based on Instance[J]. Netinfo Security, 2019, 19(3): 11-18. |
| 王伟, 沈旭东. 基于实例的迁移时间序列异常检测算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(3): 11-18. | |
| [6] | LAN Qing. Application Analysis of Intelligent Operation and Maintenance in Enterprise Mmanagement[J]. Electronic World, 2020(5): 89-90. |
| 兰清. 智能运维在企业IT管理中的应用分析[J]. 电子世界, 2020(5): 89-90. | |
| [7] | GUO Hongcheng, LIN Xingyu, YANG Jian, et al. TransLog: A Unified Transformer-Based Framework for Log Anomaly Detection[EB/OL]. (2022-01-17)[2022-11-10]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2201.00016. |
| [8] | HE Shilin, ZHU Jieming, HE Pinjia, et al. Loghub: A Large Collection of System Log Datasets Towards Automated Log Analytics[EB/OL]. (2020-09-14)[2022-11-10]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2008.06448. |
| [9] | JACOB D, CHANG Mingwei, KENTON L, et al. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding[EB/OL]. (2019-05-24)[2022-11-10]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1810.04805. |
| [10] | HALL S. Encoding/Decoding[M]. New York: Culture, Media, Language, 1980. |
| [11] | TIMCENKO V, GALIN S. Ensemble Classifiers for Supervised Anomaly Based Network Intrusion Detection[C]// IEEE. 2017 13th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing (ICCP). New York: IEEE, 2017: 13-19. |
| [12] |
WANG W, KANNEG D. An Integrated Classifier for Gear System Monitoring[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2009, 23(4): 1298-1312.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2008.10.006 URL |
| [13] | XU Yong, ZHU Yaokang, QIAO Bo, et al. Tracelingo: Trace Representation and Learning for Performance Issue Diagnosis in Cloud Services[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/ACM International Workshop on Cloud Intelligence (Cloudintelligence). New York: IEEE, 2021: 37-40. |
| [14] | ZHANG Shenglin, LIN Xiaofei, SUN Yongqian, et al. Research on Unsupervised KPI Anomaly Detection Based on Deep Learning[J]. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2020, 2(3): 87-100. |
| [15] | LIU Ping, XU Haowen, OUYANG Qianyu, et al. Unsupervised Detection of Microservice Ttrace Anomalies Through Service-Level Deep Bayesian Networks[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE 31st International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering(ISSRE). New York: IEEE, 2020: 48-58. |
| [16] | CHANDOLA V, BANERJEE A, KUMAR V. Anomaly Detection: A Survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2009, 41(3): 1-58. |
| [17] | AHMED T. Online Anomaly Detection Using KDE[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 28th IEEE conference Global Telecommunications. New York: IEEE, 2009: 1009-1016. |
| [18] |
AHMED F, ERMAN J, GE Zihui, et al. Detecting and Localizing End-to-End Performance Degradation for Cellular Data Services Based on TCP Loss Ratio and Round Trip Time[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2017, 25(6): 3709-3722.
doi: 10.1109/TNET.2017.2761758 URL |
| [19] | LIN F, MUZUMDAR K, LAPTEV N P, et al. Fast Dimensional Analysis for Root Cause Investigation in a Large-Scale Service Environment[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Measurement and Analysis of Computing Systems, 2020, 4(2): 1-23. |
| [20] |
SUN Yongqian, ZHAO Youjian, SU Ya, et al. Hotspot: Anomaly Localization for Additive KPIs with Multi-Dimensional Attributes[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 10909-10923.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2804764 URL |
| [21] | GU Jiazhen, LUO Chuan, QIN Si, et al. Efficient Incident Identification from Multi-Dimensional Issue Rports via Meta-Heuristic Search[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 28th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2020: 292-303. |
| [22] | XING Wenpu, GHORBANI A. Weighted PageRank Algorithm[C]// IEEE. Proceedings Of the Second Annual Conference on Communication Networks and Services Research,. New York: IEEE, 2004: 305-314. |
| [23] |
FOUSS F, PIROTTE A, RENDERS J M, et al. Random-Walk Computation of Similarities Between Nodes of a Graph with Application to Collaborative Recommendation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2007, 19(3): 355-369.
doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2007.46 URL |
| [24] |
KIM M, SUMBALY R. Root Cause Detection in a Service-Oriented Architecture[J]. ACM SIGMETRICS Performance Evaluation Review, 2013, 41(1): 93-104.
doi: 10.1145/2494232.2465753 URL |
| [25] |
BRIN S, PAGE L. The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine[J]. Computer Networks and ISDN Systems, 1998, 30(1): 107-117.
doi: 10.1016/S0169-7552(98)00110-X URL |
| [26] |
TAI Liyuan, TIAN Chunqi, WANG Wei. Anomaly Detection of Large Scale Microservice Architecture Software System Based on Log Parsing[J]. Computer Science and Application, 2019, 9(12): 2266-2276.
doi: 10.12677/CSA.2019.912252 URL |
| [27] | JIA Tong, YANG Lin, CHEN Pengfei, et al. LogSed: Anomaly Diagnosis Through Mining Time-Weighted Control Flow Graph in Logs[C]// IEEE. IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing. New York: IEEE, 2017: 447-455. |
| [28] | GULEMKO A, SCHMIDT F, ACKER A, et al. Ddetecting Anomalous Behavior of Black-Box Services Modeled with Distance-Based Online Clustering[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing. New York: IEEE, 2018: 912-915. |
| [29] | SAMIR A, PAHL C. DLA: Detecting and Localizing Anomalies in Containerized Microservice Architectures Using Markov Models[C]// IEEE. 2019 7th International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud (FiCloud). New York: IEEE, 2019: 205-213. |
| [30] | NEDELKOSKI S, CARDOSO J, KAO O. Anomaly Detection and Classification Using Distributed Tracing and Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. 2019 19th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing (CCGRID). New York: IEEE, 2019: 241-250. |
| [31] | MA Meng, XU Jingmin, WANG Yuan, et al. AutoMAP: Diagnose Your Microservice-Based Web Applications Automatically[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Web Conference 2020. New York: ACM, 2020: 246-258. |
| [32] | AN J, CHO S. Variational Autoencoder Based Anomaly Detection Using Reconstruction Probability[J]. Special Lecture on IE, 2015, 2(1): 1-18. |
| [33] | SHLENS J. A Tutorial on Principal Component Analysis[EB/OL]. (2014-04-03)[2022-11-10]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1404.1100. |
| [34] | KINGMA D P, WELLING M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes[EB/OL]. (2014-05-01)[2022-11-10]. https://max.book118.com/html/2021/0321/5314343041003201.shtm. |
| [35] | WU Li, TORDSSON J, ELMROTH E, et al. MicroRCA: Root Cause Localization of Performance Issues in Microservices[C]// IEEE. NOMS 2020-2020 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-9. |
| [36] | JEF G, WIDOM J. Scaling Personalized Web Search[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on World Wide Web. New York: ACM, 2003: 271-279. |
| [1] | 夏懿航, 张志龙, 王木子, 陈力波. 基于依赖关系的容器供应链脆弱性检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 76-84. |
| [2] | 文伟平, 刘成杰, 时林. 基于数据流追溯的空指针引用挖掘系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(9): 40-45. |
| [3] | 顾兆军, 刘婷婷, 高冰, 隋翯. 基于GAN-Cross的工控系统类不平衡数据异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 81-89. |
| [4] | 周婧怡, 李红娇. 针对PMU测量的虚假数据注入攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 75-83. |
| [5] | 陈彬杰, 魏福山, 顾纯祥. 基于KNN的具有隐私保护功能的区块链异常交易检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 78-84. |
| [6] | 徐茹枝, 吕畅冉, 龙燕, 刘远彬. 工业控制系统高隐蔽性数据攻击防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(12): 34-46. |
| [7] | 郭森森, 王同力, 慕德俊. 基于生成对抗网络与自编码器的网络流量异常检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(12): 7-15. |
| [8] | 牛艺诺, 张逸飞, 高能, 马存庆. 融合时序和逻辑关系的日志异常检测系统设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11): 1-6. |
| [9] | 黄子龙, 詹东阳, 叶麟, 张宏莉. 一种基于虚拟机自省的安全容器管理方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11): 55-61. |
| [10] | 秦中元, 胡宁, 方兰婷. 基于免疫仿生机理和图神经网络的网络异常检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 10-16. |
| [11] | 徐洪平, 马泽文, 易航, 张龙飞. 基于卷积循环神经网络的网络流量异常检测技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(7): 54-62. |
| [12] | 郑军, 聂榕, 王守信, 谭毓安. 基于Docker容器故障恢复的属性权重快照选择策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(5): 12-18. |
| [13] | 吴驰, 帅俊岚, 龙涛, 于俊清. 基于Linux Shell命令的用户异常操作检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(5): 31-38. |
| [14] | 李佳玮, 吴克河, 张波. 基于高斯混合聚类的电力工控系统异常检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 53-63. |
| [15] | 吴佳洁, 吴绍岭, 王伟. 基于TCN和注意力机制的异常检测和定位算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(11): 85-94. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||