信息网络安全 ›› 2022, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (1): 64-71.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2022.01.008
基于极限树特征递归消除和LightGBM的异常检测模型
何红艳1,2, 黄国言1,2( ), 张炳1,2, 贾大苗1,2
), 张炳1,2, 贾大苗1,2
- 1.燕山大学信息科学与工程学院,秦皇岛 066001
2.河北省软件工程重点实验室,秦皇岛 066001
-
收稿日期:2021-08-24出版日期:2022-01-10发布日期:2022-02-16 -
通讯作者:黄国言 E-mail:hgy@ysu.edu.cn -
作者简介:何红艳(1992—),女,河北,博士研究生,主要研究方向为入侵检测和DDoS攻击|黄国言(1969—),男,黑龙江,教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络协作技术和软件安全|张炳(1989—),男,湖北,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为软件安全和数据挖掘|贾大苗(1979—),男,黑龙江,博士研究生,主要研究方向为网络安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61772449);国家自然科学基金(61807028);国家自然科学基金(61802332);河北省自然科学基金(F2019203120);博士后科研择优资助项目(B2017003005)
Intrusion Detection Model Based on Extra Trees-recursive Feature Elimination and LightGBM
HE Hongyan1,2, HUANG Guoyan1,2( ), ZHANG Bing1,2, JIA Damiao1,2
), ZHANG Bing1,2, JIA Damiao1,2
- 1. Department of Information Science and Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao 066001, China
2. Hebei Key Laboratory of Software Engineering, Qinhuangdao 066001, China
-
Received:2021-08-24Online:2022-01-10Published:2022-02-16 -
Contact:HUANG Guoyan E-mail:hgy@ysu.edu.cn
摘要:
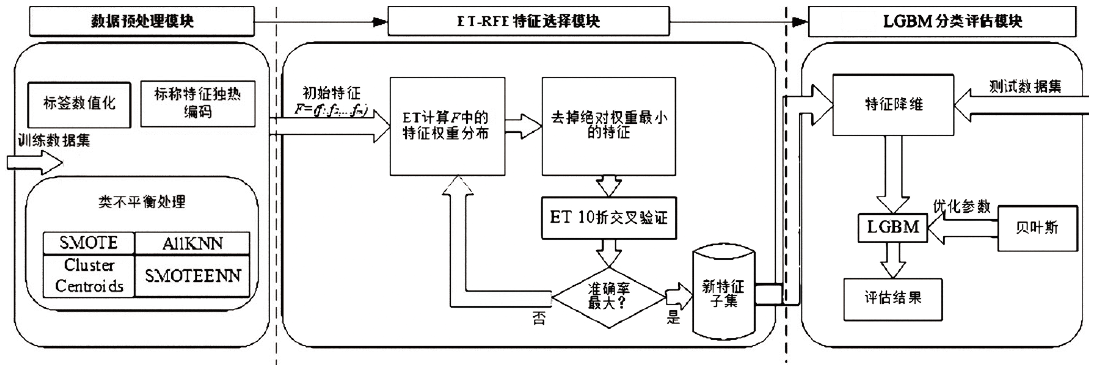
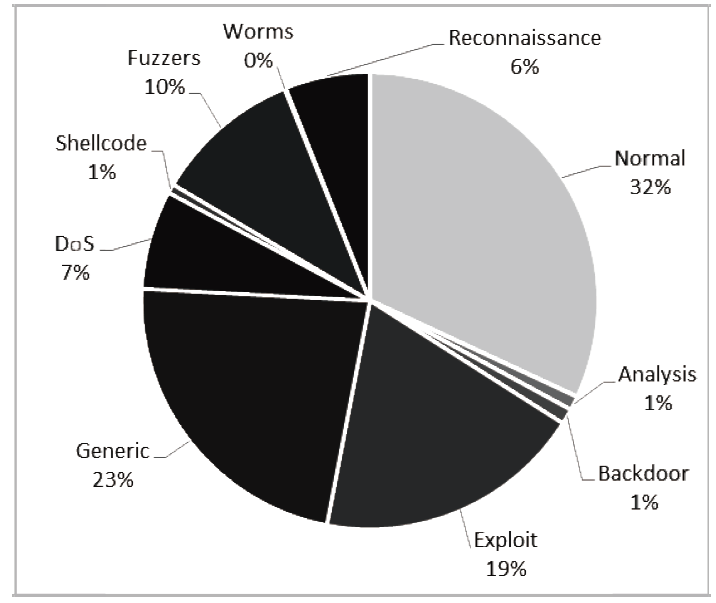
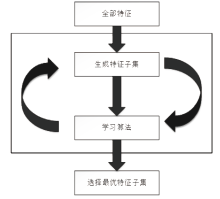
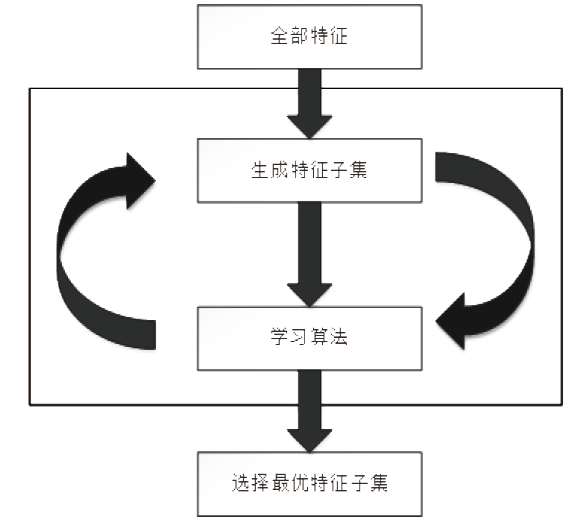
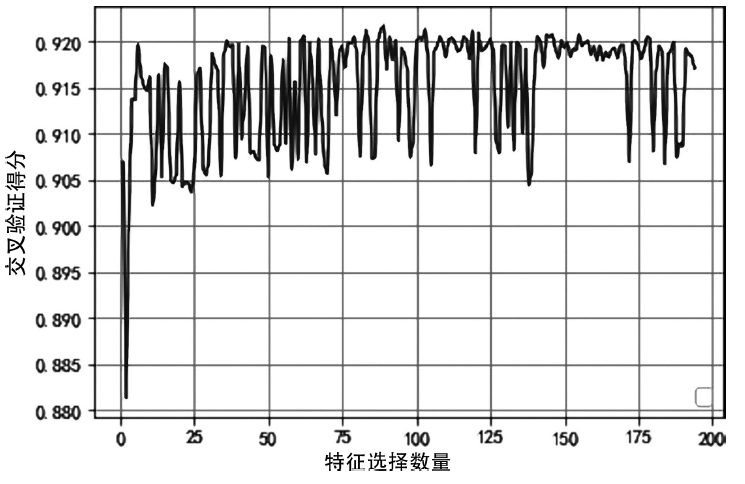
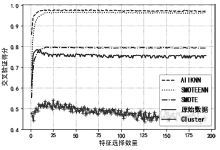
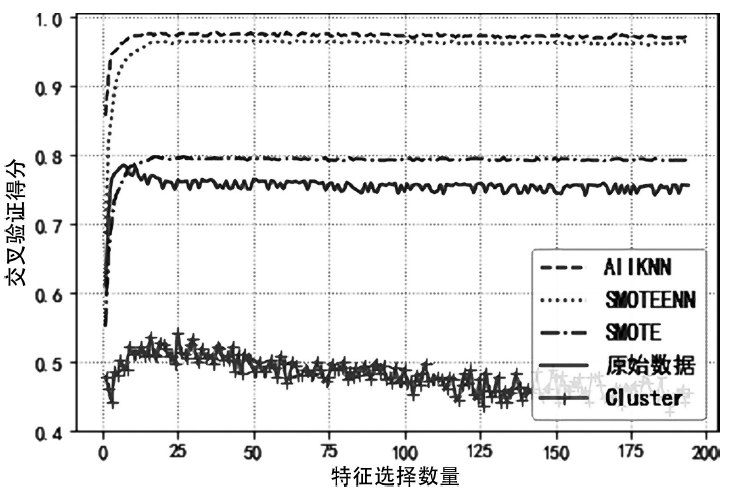
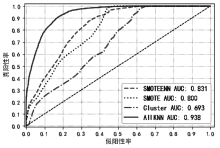
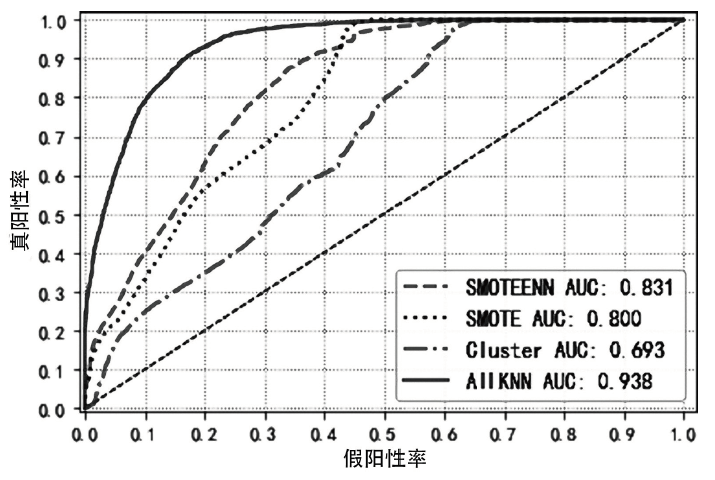
入侵检测数据维数大、数据样本不均衡、数据集分散性大的问题严重影响分类性能,为了解决该问题,文章提出基于极限随机树的特征递归消除(Extra Trees-Recursive Feature Elimination,ET-RFE)和LightGBM(LGBM)的入侵检测方法。首先对网络数据进行独热编码重构,在数据级层面均衡少量样本的攻击类别;其次,使用基于ET-RFE对流量特征进行降维处理,寻找含有信息量最大的最优特征子集;最后,将得到的最优特征子集作为LGBM输入数据集进行分类训练,并利用贝叶斯算法对LGBM参数进行优化。实验采用真实的网络流量数据集UNSW-NB15,通过与随机森林(RF)、XGboost算法和GALR-DT算法比较可得,文章所提方法能够有效提高检测率,并对小样本攻击类型实现有效的召回率。
中图分类号:
引用本文
何红艳, 黄国言, 张炳, 贾大苗. 基于极限树特征递归消除和LightGBM的异常检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 64-71.
HE Hongyan, HUANG Guoyan, ZHANG Bing, JIA Damiao. Intrusion Detection Model Based on Extra Trees-recursive Feature Elimination and LightGBM[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(1): 64-71.
表1
UNSW-NB15数据集特征描述
| 类别 | 特征名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 流特征 | Srcip、Sport、Dstip、Dsport、Proto | |
| 基本特性 | state、dur、sbytes、dbytes、sttl、dttl、sloss、dloss、service、sload、dload、spkts、dpkts | |
| 内容特征 | swin、dwin、stcpb、dtcpb、smeansz、dmeansz、trans_depth、res_bdy_len | |
| 时间特征 | sjit、djit、stime、ltime、sintpkt、dintpkt、tcprtt、synack、ackdat | |
| 附加生成的特征 | 通用特征 | is_sm_ips_ports、ct_state_ttl、ct_flw_http_mthd、 is_ftp_login、ct_ftp_cmd |
| 连接特征 | ct_srv_src、ct_srv_dst、ct_dst_ltm、ct_src_ ltm、ct_src_dport_ltm、ct_dst_sport_ltm、ct_dst_src_ltm | |
表4
平衡处理方法后的样本数量
| 类别 | 原数据 /条 | SMOTE /条 | AllKNN /条 | ClusterCentroids /条 | SMOTEENN /条 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzers | 18184 | 18184 | 14035 | 130 | 11764 |
| Analysis | 2000 | 18184 | 383 | 130 | 6705 |
| Backdoor | 1746 | 18184 | 101 | 130 | 5851 |
| DOS | 12264 | 18184 | 6161 | 130 | 4723 |
| Reconnaiss- ance | 10491 | 18184 | 6231 | 130 | 10889 |
| Shellcode | 1133 | 18184 | 258 | 130 | 17344 |
| Worms | 130 | 18184 | 130 | 130 | 18059 |
表8
本文提出算法与其他算法的检测效果对比
| 算法 | 特征选择方法 | 特征 数量 | 分类 算法 | ACC | FAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | None | 42 | EM | 78.47% | 23.79% |
| 42 | LR | 83.15% | 18.48% | ||
| 42 | ANN | 81.34% | 21.13% | ||
| 42 | NB | 82.07% | 18.56% | ||
| 42 | DT | 85.56% | 15.78% | ||
| 其他算法 | None | 42 | KNN | 78.30% | 23.53% |
| 42 | SVM | 72.30% | 25.60% | ||
| 42 | RF | 87.14% | 14.13% | ||
| ET-RFE | 89 | Xgboost | 87.58% | 13.65% | |
| 文献[ | GALR | 20 | DT | 81.42% | 6.39% |
| 本文算法 | ET-RFE | 89 | LGBM | 87.64% | 13.59% |
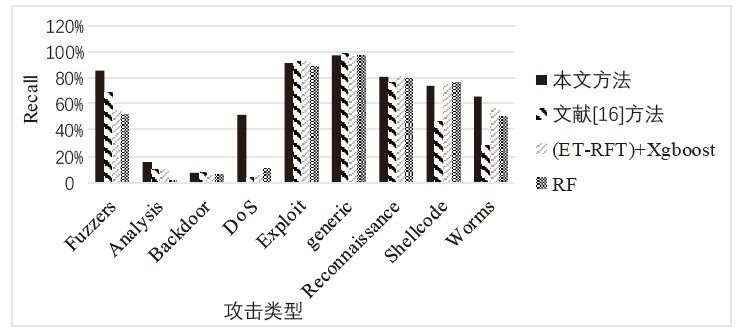
表10
本文方法的召回率与其他算法对比
| 攻击类型 | 本文方法 | 文献[ | (ET-RFE) +Xgboost | RF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzers | 85.34% | 69.112% | 54.7% | 51.32% |
| Analysis | 15.95% | 9.929% | 9.45% | 0.89% |
| Backdoor | 7.38% | 6.925% | 4.80% | 5.67% |
| DoS | 51.97% | 4.113% | 4.52% | 10.42% |
| Exploit | 91.32% | 92.317% | 92.81% | 88.99% |
| generic | 97.00% | 97.937% | 96.68% | 97.15% |
| Reconnaissance | 80.75% | 76.150% | 80.92% | 80.18% |
| Shellcode | 74.35% | 47.468% | 75.13% | 76.46% |
| Worms | 65.91% | 28.465% | 56.82% | 50.0% |
| [1] | ZHOU Yuyang, CHENG Guang, JIANG Shanqing, et al. Building an Efficient Intrusion Detection System Based on Feature Selection and Ensemble Classifier[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107247, 2020-06-19. |
| [2] | MUNA A L H, MOUSTAFA N, SITNIKOVA E. Identification of Malicious Activities in Industrial Internet of Things Based on Deep Learning Models[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2018.05.002, 2018-05-22. |
| [3] | AGARAP A F M. A Neural Network Architecture Combining Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) for Intrusion Detection in Network Traffic Data[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing (ICMLC), February 26-28, 2018, Macau, China. New York: ACM, 2018:26-30. |
| [4] |
SANGKATSANEE P N, WATTANAPONGSAKORN C, CHARNSRIPINYO C. Practical Real-time Intrusion Detection Using Machine Learning Approaches[J]. Computer Communications, 2011, 34(18):2227-2235.
doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2011.07.001 URL |
| [5] | KORONIOTIS N, MOUSTAFA N, SITNIKOVA E, et al. Towards Developing Network Forensic Mechanism for Botnet Activities in the IoT Based on Machine Learning Techniques[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90775-8_3, 2018-05-19. |
| [6] | HU Weiming, HU Wei, MAYBANK S. AdaBoost-based Algorithm for Network Intrusion Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, 2008, 38(2):577-583. |
| [7] |
MAZINI M, SHIRAZI B, MAHDAVI I. Anomaly Network-based Intrusion Detection System Using a Reliable Hybrid Artificial Bee Colony and AdaBoost Algorithms[J]. Journal of King Saud University-computer and Information Sciences, 2019, 31(4):541-553.
doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2018.03.011 URL |
| [8] | FARID D M, NOURIA H, RAHMAN M Z, et al. Combining Naive Bayes and Decision Tree for Adaptive Intrusion Detection[J]. International Journal of Network Security & Its Applications, 2010, 2(2):12-25. |
| [9] |
ABADEH M S, MOHAMADI H, HABIBI J. Design and Analysis of Genetic Fuzzy Systems for Intrusion Detection in Computer Networks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(6):7067-7075.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2010.12.006 URL |
| [10] |
KOC L, MAZZUCHI T A, SARKANI S. A Network Intrusion Detection System Based on a Hidden Naïve Bayes Multiclass Classifier[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(18):13492-13500.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.07.009 URL |
| [11] |
FOSSACECA J M, MAZZUCHI T A, SARKANI S. MARK-ELM: Application of a Novel Multiple Kernel Learning Framework for Improving the Robustness of Network Intrusion Detection[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(8):4062-4080.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.12.040 URL |
| [12] | MANZOOR I, KUMAR N. A Feature Reduced Intrusion Detection System Using ANN Classifier[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.07.005, 2017-12-01. |
| [13] | LIU Jinghao, SUN Xiaowei, JIN Jie. Intrusion Detection Model Based on Principle Component Analysis and Recurrent Neural Network[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2020, 34(10):105-112. |
| 刘敬浩, 孙晓伟, 金杰. 基于主成分分析和循环神经网络的入侵检测模型[J]. 中文信息学报, 2020, 34(10):105-112. | |
| [14] |
HAMED T, DARA R, KREMER S C. Network Intrusion Detection System Based on Recursive Feature Addition and Bigram Technique[J]. Computers & Security, 2017, 73(3):137-155.
doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2017.10.011 URL |
| [15] |
KHAMMASSI C, KRICHEN S. A GA-LR Wrapper Approach for Feature Selection in Network INTRUSION Detection[J]. Computers & Security, 2017, 70(9):255-277.
doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2017.06.005 URL |
| [16] |
ADHAO R, PACHGHARE V. Feature Selection Using Principal Component Analysis and Genetic Algorithm[J]. Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences and Cryptography, 2020, 23(2):595-602.
doi: 10.1080/09720529.2020.1729507 URL |
| [17] |
LATAH M, TOKER L. Towards an Efficient Anomaly-based Intrusion Detection for SoftWare-defined Networks[J]. IET Networks, 2018, 7(6):453-459.
doi: 10.1049/ntw2.v7.6 URL |
| [18] |
NANCY P, MUTHURAJKUMAR S, GANAPATHY S, et al. Intrusion Detection Using Dynamic Feature Selection and Fuzzy Temporal Decision Tree Classification for Wireless Sensor Network[J]. IET Communications, 2020, 14(5):888-895.
doi: 10.1049/cmu2.v14.5 URL |
| [19] | LIANG Jie, CHEN Jiahao, ZHANG Xueqin, et al. One-hot Encoding and Convolutional Neural Network Based Anomaly Detection[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2019, 59(7):523-529. |
| 梁杰, 陈嘉豪, 张雪芹, 等. 基于独热编码和卷积神经网络的异常检测[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 59(7):523-529. | |
| [20] |
CHAWLA N V, BOWYER K W, HALL L O, et al. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002, 16(1):321-357.
doi: 10.1613/jair.953 URL |
| [21] | GU Tong, XU Guoliang, LI Wanlin, et al. Intelligent House Price Evaluation Model based on Ensemble LightGBM and Bayesian Optimization Strategy[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 361(9):290-295. |
| 顾桐, 许国良, 李万林, 等. 基于集成LightGBM和贝叶斯优化策略的房价智能评估模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 361(9):290-295. | |
| [22] | WEI Zhiqiang, ZHANG Hao, CHEN Long. Web Anomaly Detection Model Using SmoteTomek and LightGBM Algorithm[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2020(3):587-592. |
| 魏志强, 张浩, 陈龙. 一种采用SmoteTomek和LightGBM算法的Web异常检测模型[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2020(3):587-592. | |
| [23] | MOUSTAFA N, SLAY J. UNSW-NB15: A Comprehensive Data Set for Network Intrusion Detection Systems[C]//IEEE. Military Communications and Information Systems Conference(MilCIS), November 10-12, 2015, Canberra, Australia. Piscataway: IEEE, 2015: 1-6. |
| [1] | 白宏鹏, 邓东旭, 许光全, 周德祥. 基于联邦学习的入侵检测机制研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 46-54. |
| [2] | 刘烁, 张兴兰. 基于双重注意力的入侵检测系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 80-86. |
| [3] | 李群, 董佳涵, 关志涛, 王超. 一种基于聚类分类的物联网恶意攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 82-90. |
| [4] | 任涛, 金若辰, 罗咏梅. 融合区块链与联邦学习的网络入侵检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(7): 27-34. |
| [5] | 杜晔, 王子萌, 黎妹红. 基于优化核极限学习机的工控入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(2): 1-9. |
| [6] | 王华忠, 程奇. 基于改进鲸鱼算法的工控系统入侵检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(2): 53-60. |
| [7] | 沈也明, 李贝贝, 刘晓洁, 欧阳远凯. 基于主动学习的工业互联网入侵检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(1): 80-87. |
| [8] | 李桥, 龙春, 魏金侠, 赵静. 一种基于LMDR和CNN的混合入侵检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 117-121. |
| [9] | 徐国天. 网络入侵检测中K近邻高速匹配算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(8): 71-80. |
| [10] | 姜楠, 崔耀辉, 王健, 吴晋超. 基于上下文特征的IDS告警日志攻击场景重建方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(7): 1-10. |
| [11] | 张晓宇, 王华忠. 基于改进Border-SMOTE的不平衡数据工业控制系统入侵检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(7): 70-76. |
| [12] | 彭中联, 万巍, 荆涛, 魏金侠. 基于改进CGANs的入侵检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(5): 47-56. |
| [13] | 王蓉, 马春光, 武朋. 基于联邦学习和卷积神经网络的入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 47-54. |
| [14] | 边玲玉, 张琳琳, 赵楷, 石飞. 基于LightGBM的以太坊恶意账户检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 73-80. |
| [15] | 罗文华, 许彩滇. 基于改进MajorClust聚类的网络入侵行为检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(2): 14-21. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||