信息网络安全 ›› 2020, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (5): 47-56.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2020.05.006
基于改进CGANs的入侵检测方法研究
- 1. 中国科学院计算机网络信息中心,北京 100190
2. 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3. 中国科学院办公厅,北京 100864
-
收稿日期:2020-02-20出版日期:2020-05-10发布日期:2020-06-05 -
通讯作者:万巍 E-mail:anquanip@cnic.cn -
作者简介:彭中联(1996—),男,湖南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络空间安全|万巍(1982—),男,湖北,高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为网络空间安全;|荆涛(1979—),男,吉林,高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为网络与信息安全、流量协议分析|魏金侠(1979—),女,河北,高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为网络信息安全、机器学习 -
基金资助:中国科学院信息化专项(XXH13507)
Research on Intrusion Detection Method Based on Modified CGANs
PENG Zhonglian1,2, WAN Wei1,*( ), JING Tao3, WEI Jinxia1
), JING Tao3, WEI Jinxia1
- 1. Computer Network Information Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Office of General Affairs, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2020-02-20Online:2020-05-10Published:2020-06-05 -
Contact:Wei WAN E-mail:anquanip@cnic.cn
摘要:
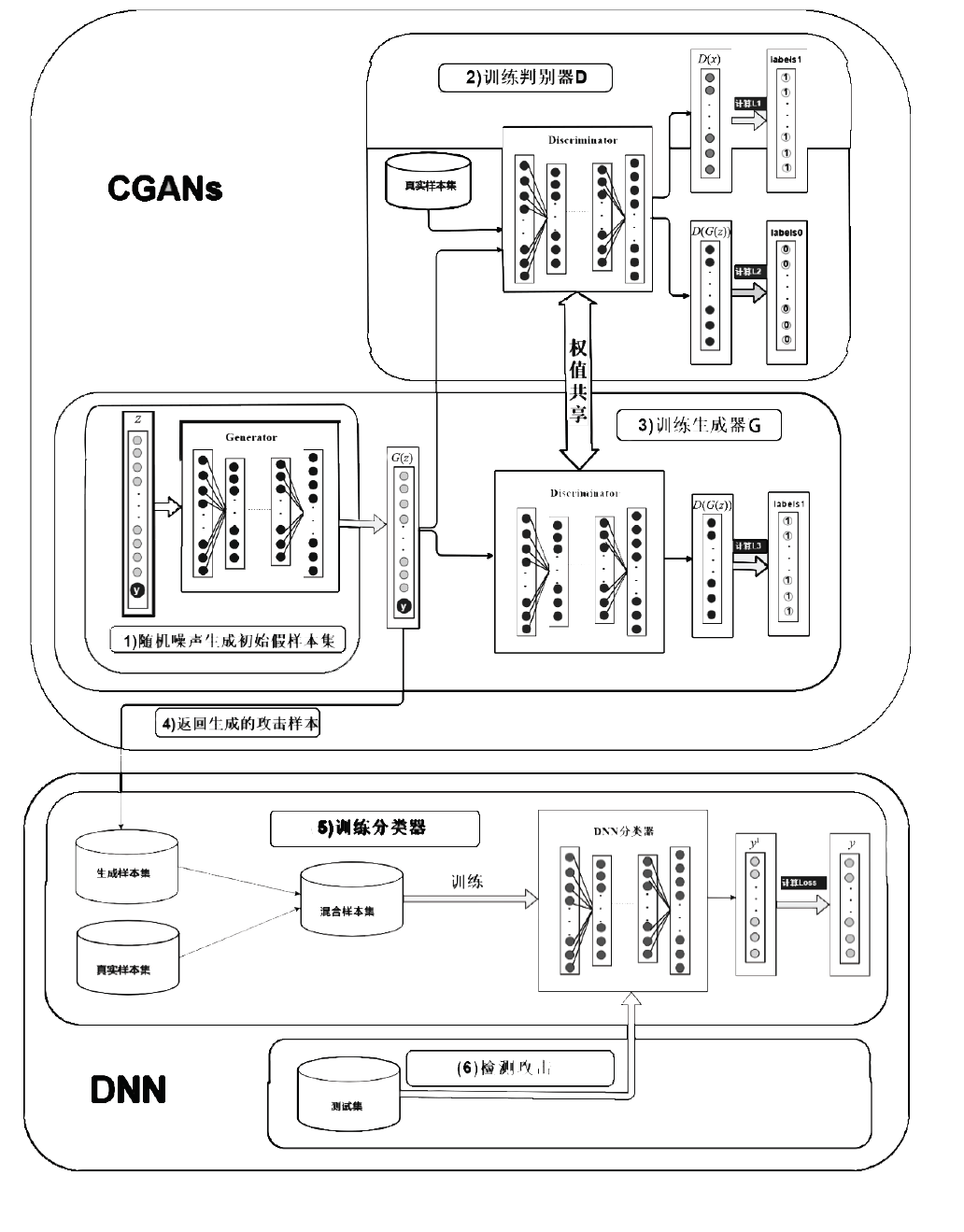
近年来,机器学习算法在入侵检测系统(IDS)中的应用获得越来越多的关注。然而,传统的机器学习算法更多的依赖于已知样本,因此需要尽可能多的数据样本来对模型进行训练。遗憾地是,随着越来越多未知攻击的出现,且用于训练的攻击样本具有不平衡性,传统的机器学习模型会遇到瓶颈。文章提出一种将改进后的条件生成对抗网络(CGANs)与深度神经网络(DNN)相结合的入侵检测模型(CGANs-DNN),通过解决样本不平衡性问题来提高检测模型对未知攻击类型或只有少数攻击样本类型的检测率。深度神经网络(DNN)具有表征数据潜在特征的能力,而经过改进后的条件CGANs,能够通过学习已知攻击样本潜在数据特征分布,来根据指定类型生成新的攻击样本。此外,与生成对抗网络(GANs)和变分自编码器(VAE)等无监督生成模型相比,CGANs-DNN经过改进后加入梯度惩罚项,在训练的稳定性上有了很大地提升。通过NSL-KDD数据集对模型进行评估,与传统算法相比CGANs-DNN不仅在整体准确率、召回率和误报率等方面有更好的性能,而且对未知攻击和只有少数样本的攻击类型具有较高的检测率。
中图分类号:
引用本文
彭中联, 万巍, 荆涛, 魏金侠. 基于改进CGANs的入侵检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(5): 47-56.
PENG Zhonglian, WAN Wei, JING Tao, WEI Jinxia. Research on Intrusion Detection Method Based on Modified CGANs[J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(5): 47-56.
表3
4种攻击类型分类
| 攻击类型 | 分类 | 总计 |
|---|---|---|
| DoS | back, land, neptune, pod, smurf, teardrop, mailbomb, processtable, udpstorm,apache2, worm | 11 |
| Probe | Satan, ipsweep, nmap, portsweep, mscan, saint | 6 |
| R2L | guess_passwd, ftp_write, imap, phf, multihop, warezmaster, xlock, xsnoop, snmpguess, snmpgetattack, httptunnel, sendmail, named, warezclient, spy | 15 |
| U2R | buffer_overflow, loadmodule, rootkit, perl, slotbacks, xterm, ps | 7 |
| 总计 | 39 |
表4
测试集数据分布
| 类别 | KDDTrain+_20Percent | KDDTest+ | KDDTest-21 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 攻击类型 | 数量 | 攻击类型 | 数量 | 攻击类型 | 数量 | |
| Normal | normal | 13449 | normal | 9711 | normal | 2152 |
| 合计 | 13449 | 9711 | 2152 | |||
| Probe | ipsweep satan portsweep nmap | 710 691 587 301 | ipsweep satan portsweep nmap saint mscan | 141 735 157 73 319 996 | ipsweep satan portsweep nmap saint mscan | 141 727 156 73 309 996 |
| 合计 | 2289 | 2421 | 2402 | |||
| DoS | neptune smurf back teardrop pod land | 8282 529 196 188 38 1 | neptune smurf back teardrop pod land apache2 mailbomb processtable udpstorm | 4657 665 359 12 41 7 737 293 685 2 | neptune smurf back teardrop pod land apache2 mailbomb processtable udpstorm | 1579 627 359 12 41 7 737 293 685 2 |
| 合计 | 9234 | 7458 | 4342 | |||
| U2R | buffer_over?ow rootkit loadmodule | 6 4 1 | buffer_over?ow rootkit loadmodule perl httptunnel ps sqlattack xterm | 20 13 2 2 133 15 2 13 | buffer_over?ow rootkit loadmodule perl httptunnel ps sqlattack xterm | 20 13 2 2 133 15 2 13 |
| 合计 | 11 | 200 | 200 | |||
| R2L | guess_passwd warezmaster imap multihop phf ftp_write spy warezclient | 10 7 5 2 2 1 1 181 | guess_passwd warezmaster imap multihop phf ftp_write named sendmail xlock xsnoop worm snmpgetattack snmpguess | 1231 944 1 18 2 3 17 14 9 4 2 178 331 | guess_passwd warezmaster imap multihop phf ftp_write named sendmail xlock xsnoop worm snmpgetattack snmpguess | 1231 944 1 18 2 3 17 14 9 4 2 178 331 |
| 合计 | 209 | 2754 | 2754 | |||
| 总计 | 25192 | 22544 | 11850 | |||
表9
NSL-KDD (KDDTest+)数据集上不同的过采样方法的检测性能比较(%)
| 模型 | Normal | Probe | DoS | U2R | R2L | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1- measure | FPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROS-DNN | 92.61 | 56.26 | 80.32 | 6.00 | 12.75 | 78.26 | 67.41 | 92.34 | 77.93 | 7.39 |
| SMOTE-DNN | 96.59 | 56.75 | 82.19 | 11.00 | 10.93 | 81.16 | 69.48 | 96.42 | 80.76 | 3.41 |
| ADASYN-DNN | 96.43 | 59.81 | 83.28 | 8.00 | 9.84 | 80.10 | 67.74 | 96.16 | 79.49 | 3.57 |
| CGANs-DNN | 96.76 | 78.88 | 88.67 | 11.00 | 46.71 | 87.98 | 79.46 | 96.98 | 88.27 | 2.33 |
表10
NSL-KDD (KDDTest-21)数据集上不同的过采样方法的检测性能比较(%)
| 模型 | Normal | Probe | DoS | U2R | R2L | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1- measure | FPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROS-DNN | 85.83 | 65.36 | 74.14 | 5.50 | 10.02 | 63.43 | 58.46 | 94.89 | 72.35 | 14.17 |
| SMOTE-DNN | 86.76 | 60.99 | 66.86 | 12.00 | 14.45 | 65.34 | 60.59 | 95.37 | 74.10 | 13.24 |
| ADASYN-DNN | 67.98 | 54.29 | 67.94 | 8.00 | 11.58 | 57.76 | 55.50 | 88.65 | 68.26 | 32.02 |
| CGANs-DNN | 89.04 | 80.19 | 78.27 | 11.33 | 25.17 | 78.43 | 75.84 | 96.63 | 84.12 | 11.22 |
表11
NSL-KDD (KDDTest+)数据集上不同分类方法的检测性能比较(%)
| 模型 | Normal | Probe | DoS | U2R | R2L | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1- measure | FPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 91.68 | 60.4 | 81.25 | 3.52 | 3.71 | 75.11 | 65.29 | 93.36 | 74.18 | 7.13 |
| SVM | 92.12 | 60.71 | 74.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 72.68 | 57.13 | 90.36 | 70.97 | 7.21 |
| RF | 97.37 | 58.53 | 80.64 | 0.54 | 7.25 | 75.61 | 60.19 | 96.14 | 72.32 | 2.54 |
| DNN | 96.12 | 67.30 | 84.40 | 2.61 | 14.26 | 80.44 | 68.47 | 95.65 | 76.10 | 3.79 |
| CGANs-DNN | 97.16 | 76.97 | 87.25 | 11.00 | 46.42 | 86.98 | 78.43 | 97.79 | 88.27 | 2.68 |
表12
NSL-KDD (KDDTest-21)数据集上不同分类方法的检测性能比较(%)
| 模型 | Normal | Probe | DoS | U2R | R2L | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1- measure | FPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 67.49 | 60.08 | 69.31 | 3.51 | 3.16 | 56.01 | 52.69 | 88.41 | 65.13 | 30.91 |
| SVM | 68.36 | 60.44 | 57.89 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 46.88 | 41.64 | 84.15 | 58.17 | 32.14 |
| RF | 88.44 | 60.48 | 65.88 | 0.54 | 10.82 | 56.94 | 50.84 | 94.98 | 64.89 | 11.44 |
| DNN | 85.99 | 67.26 | 64.17 | 4.60 | 14.02 | 61.16 | 54.24 | 94.19 | 70.88 | 13.79 |
| CGANs-DNN | 88.14 | 80.89 | 78.82 | 12.50 | 26.17 | 73.43 | 76.86 | 97.20 | 84.92 | 12.66 |
| [1] | ZHANG Huanguo, MU Yi . Cyberspace Security[J]. China Communications, 2016,11(2):68-69. |
| [2] | ALI MH, MOHAMMED B A D A, ISMAIL M A B , et al. A New Intrusion Detection System Based on Fast Learning Network and Particle Swarm Optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2018,18(6):20255-20261. |
| [3] | TIAN Yingjie, MIRZABAGHERI M, BAMAKAN S M H , et al. Ramp Loss One-Class Support Vector Machine; A Robust and Effective Approach to Anomaly Detection Problems[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018,310(3):223-235. |
| [4] | GANESHAN R, PAUL R S . I-AHSDT: Intrusion Detection Using Adaptive Dynamic Directive Operative Fractional Lion Clustering and Hyperbolic Secant-Based Decision Tree Classifier[J]. Journal of Experimental & Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, 2018,6(30):887-910. |
| [5] | SERPEN G , AGHAEIE. Host-Based Misuse Intrusion Detection Using PCA Feature Extraction and KNN Classification Algorithms[J]. Intelligent Data Analysis, 2018,22(5):1101-1114. |
| [6] | LI Deng, DONG Yu . Deep Learning: Methods and Applications[J]. Foundations and Trends in Signal Processing, 2014,7(3-4):197-387. |
| [7] | WONGSUPHASAWAT K, SMILKOV D, WEXLER J , et al. Visualizing Dataflow Graphs of Deep Learning Models in Tensor Flow[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2018,24(1):1-24. |
| [8] | MALAIYA R K, KWON D, KIM J , et al. An Empirical Evaluation of Deep Learning for Network Anomaly Detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018,18(7):140806-140817. |
| [9] | LI Chaopeng, WANG Jinlin, YE Xiaozhou . Using a Recurrent Neural Network and Restricted Boltzmann Machines for Malicious Traffic Detection[J]. Neuro Quantology, 2018,16(5):823-831. |
| [10] | ZHENG Wang . Deep Learning Based Intrusion Detection with Adversaries[J]. IEEE Access, 2018,18(6):38367-38384. |
| [11] | XIN Yang, KONG Lingshuang, LIU Zhi , et al. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods for Cybersecurity[J]. IEEE Access, 2018,18(6):35365-35381. |
| [12] | SEO E, SONG H M, KIM H K . GIDS: GAN based Intrusion Detection System for In-Vehicle Network [C]//IEEE. 16th Annual Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust (PST), August 28-30, 2018, Belfast, UK. New York: IEEE, 2018: 1-6. |
| [13] | GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M et al. Generative Adversarial Nets[EB/OL]. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.747.1316&rep=rep1&type=pdf, 2014-10-15. |
| [14] | GULRAJANI I, AHMED F, ARJOVSKY M , et al. Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.00028.pdf, 2017-10-15. |
| [15] | DHANABAL L, SHAN THARAJAH . A Study on NSL-KDD Dataset for Intrusion Detection System Based on Classification Algorithms[EB/OL]. https://ijarcce.com/upload/2015/june-15/IJARCCE%2096.pdf, 2015-10-15. |
| [16] | WANG Xiaosen, HE Kun, SONG Chuanbiao , et al. AT-GAN: A Generative Attack Model for Adversarial Transferring on Generative Adversarial Nets[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.07793.pdf, 2020-1-15. |
| [17] | HU Weiwei, TAN Ying . Generating Adversarial Malware Examples for Black-Box Attacks Based on GAN[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.05983.pdf, 2017-10-15. |
| [18] | MUHAMMAD U, MUHAMMAD A, SIDDIQUE L , et al. Generative Adversarial Networks For Launching and Thwarting Adversarial Attacks on Network Intrusion Detection Systems [C]//IEEE. 15th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), June 24-28, 2019, Tangier, Morocco. New York: IEEE, 2019: 78-83. |
| [19] | MA Tao, WANG Fen, CHENG Jianjun , et al. A Hybrid Spectral Clustering and Deep Neural Network Ensemble Algorithm for Intrusion Detection in Sensor Networks[J]. Sensors, 2016,16(10):1701-1723. |
| [20] | TANG T A, MHAMDI L, MCLERNON D , et al. Deep Recurrent Neural Network for Intrusion Detection in SDN-based Networks [C]//IEEE. 4th IEEE Conference on Network Softwarization and Workshops (NetSoft), June 25-29, 2018, Montreal, QC, Canada. New York: IEEE, 2018: 202-206. |
| [21] | MUNA A H, MOUSTAFA N, SITNIKOVA E , et al. Identification of Malicious Activities in Industrial Internet of Thingsbased on Deep Learning Models[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2018,41:1-11. |
| [22] | GUILLAUME L, FERNANDO N, CHRISTOS A . Imbalanced-Learn: A Python Toolbox to Tackle the Curse of Imbalanced Datasets in Machine learning[EB/OL]. https://hal.inria.fr/hal-01516244/document, 2017-10-15. |
| [23] | CHAWLA N V, BOWYER K W, HALL L O , et al. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002,16(1):321-357. |
| [24] | HE Haibo, BAI Yang, GARCIA E A , et al. ADASYN: Adaptive Synthetic Sampling Approach for Imbalanced Learning [C]//IEEE. 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), June 1-8, 2008, Hong Kong, China. New York: IEEE, 2018: 1322-1328. |
| [1] | 李桥, 龙春, 魏金侠, 赵静. 一种基于LMDR和CNN的混合入侵检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 117-121. |
| [2] | 姜楠, 崔耀辉, 王健, 吴晋超. 基于上下文特征的IDS告警日志攻击场景重建方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(7): 1-10. |
| [3] | 张晓宇, 王华忠. 基于改进Border-SMOTE的不平衡数据工业控制系统入侵检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(7): 70-76. |
| [4] | 王蓉, 马春光, 武朋. 基于联邦学习和卷积神经网络的入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 47-54. |
| [5] | 罗文华, 许彩滇. 基于改进MajorClust聚类的网络入侵行为检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(2): 14-21. |
| [6] | 康健, 王杰, 李正旭, 张光妲. 物联网中一种基于多种特征提取策略的入侵检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 21-25. |
| [7] | 冯文英, 郭晓博, 何原野, 薛聪. 基于前馈神经网络的入侵检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 101-105. |
| [8] | 饶绪黎, 徐彭娜, 陈志德, 许力. 基于不完全信息的深度学习网络入侵检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(6): 53-60. |
| [9] | 刘敬浩, 毛思平, 付晓梅. 基于ICA算法与深度神经网络的入侵检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(3): 1-10. |
| [10] | 陈虹, 肖越, 肖成龙, 陈建虎. 融合最大相异系数密度的SMOTE算法的入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(3): 61-71. |
| [11] | 田峥, 李树, 孙毅臻, 黎曦. 一种面向S7协议的工控系统入侵检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(11): 8-13. |
| [12] | 张阳, 姚原岗. 基于Xgboost算法的网络入侵检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(9): 102-105. |
| [13] | 张戈琳, 李勇. 非负矩阵分解算法优化及其在入侵检测中的应用[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(8): 73-78. |
| [14] | 魏书宁, 陈幸如, 焦永, 王进. AR-OSELM算法在网络入侵检测中的应用研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(6): 1-6. |
| [15] | 和湘, 刘晟, 姜吉国. 基于机器学习的入侵检测方法对比研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(5): 1-11. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||