信息网络安全 ›› 2018, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (9): 10-18.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2018.09.002
机器学习系统面临的安全攻击及其防御技术研究
于颖超1, 丁琳1, 陈左宁2
- 1.江南计算技术研究所,江苏无锡 214083
2. 数学工程与先进计算国家重点实验室,江苏无锡 214083
-
收稿日期:2018-07-17出版日期:2018-09-30发布日期:2020-05-11 -
作者简介:作者简介:于颖超(1983—),女,河南,工程师,博士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全、安全操作系统、机器学习安全等; 丁琳(1982—),女,江苏,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为国产安全平台、信息安全等;陈左宁(1957—),女,北京,研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为信息安全、计算机体系结构等。
-
基金资助:国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)[2018YFB1003600]
Research on Attacks and Defenses towards Machine Learning Systems
Yingchao YU1, Lin DING1, Zuoning CHEN2
- 1. Jiangnan Institute of Computing Technology, Wuxi Jiangsu 214083, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Mathematical Engineering and Advanced Computing, Wuxi Jiangsu 214083, China
-
Received:2018-07-17Online:2018-09-30Published:2020-05-11
摘要:
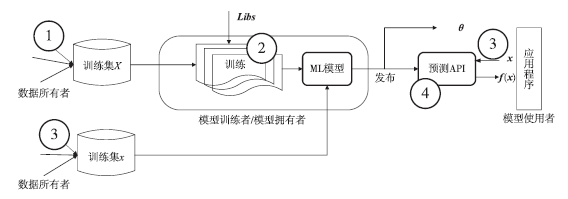
研究表明,几乎机器学习系统管道的各个阶段都有可能遭遇数据污染攻击、对学习算法及依赖库的攻击、逃逸攻击、模型窃取及模型推理攻击等。这些攻击不仅会影响机器学习系统的学习过程,而且还可能影响模型的性能或使系统在特定输入下出现攻击者想要模型出现的错误,从而影响模型的精度。因此,理解机器学习算法和系统的安全性,并探索它们的安全改进方法越来越成为计算机安全和机器学习交叉领域的一个研究方向。文章首先定义了机器学习系统管道,然后对管道上各点可能遭受的攻击及潜在的解决方案进行了研究,最后对全文进行了总结并对下一步的研究方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
于颖超, 丁琳, 陈左宁. 机器学习系统面临的安全攻击及其防御技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(9): 10-18.
Yingchao YU, Lin DING, Zuoning CHEN. Research on Attacks and Defenses towards Machine Learning Systems[J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(9): 10-18.
| [1] | BIGGIO B, NELSON B, LASKOV P.Poisoning Attacks against Support Vector Machines[C]//ACM. The 29th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, June 26-July 1, 2012, Edinburgh, Scotland.New York:ACM,2012:1467-1474. |
| [2] | KEARNS M, LI Ming.Learning in the Presence of Malicious Errors[C]//ACM. the Twentieth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, May 2 - 4, 1988, Chicago, Illinois, USA.New York:ACM,1988:267-280. |
| [3] | The Guardian. Microsoft 'deeply sorry' for Racist and Sexist Tweets by AI Chatbot[EB/OL] . ,2018-6-30. |
| [4] | CHEN Xinyun, LIU Chang, LI Bo, et al.Targeted Backdoor Attacks on Deep Learning Systems Using Data Poisoning[EB/OL]. 2018-6-30. |
| [5] | HUANG Ling, JOSEPH A D, NELSON B, et al.Adversarial Machine Learning[C]//ACM. The 4th ACM Workshop on Security and Artificial Intelligence, October 21, 2011,Chicago, USA.New York: ACM, 2011: 43-58. |
| [6] | RUBINSTEIN B I P, NELSON B, HUANG Ling, et al. ANTIDOTE: Understanding and Defending against Poisoning of Anomaly Detectors[C]//ACM. The 9th ACM Sigcomm Internet Measurement Conference, November 4-6, 2009,Chicago,USA. New York: ACM, 2009: 1-14. |
| [7] | BARRENO M, NELSON B, SEARS R, et al.Can Machine Learning Be Secure[C]//ACM. The 2006 ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security, March 21 - 24, 2006, Taipei,China. New York: ACM, 2006: 16-25. |
| [8] | BIGGIO B, FUMERA G, ROLI F.Multiple Classifier Systems for Robust Classifier Design in Adversarial Environments[J]. Inter- national Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2010, 1(1-4): 27-41. |
| [9] | BIGGIO B, CORONA I, FUMERA G, et al.Bagging Classifiers for Fighting Poisoning Attacks in Adversarial Classification Tasks[C]//LNCS. The 10th International Conference on Multiple Classifier Systems, June 15-17, 2011, Naples, Italy. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag Berlin, 2011: 350-359. |
| [10] | Google Cloud Platform.CLOUD AI[EB/OL]. ,2018-6-30. |
| [11] | aws.Amazon machine learning[EB/OL].,2018-6-30. |
| [12] | BigML[EB/OL]., 2018-6-30. |
| [13] | SONG Congzheng, RISTENPART T,SHMATIKOV V.Machine Learning Models that RememberToo Much[C]//ACM. The 2017 ACM Sigsac Conference on Computer and Communications Security, October 30 - November 3, 2017, Dallas, Texas, USA. New York:ACM,2017:587-601. |
| [14] | HUNT T, SONG Congzheng, SHOKRI R, et al.Chiron: Privacy-preserving Machine Learning as a Service[J]. Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2018(3):123-142. |
| [15] | OHRIMENKO O, SCHUSTER F, FOURNET C, et al.Oblivious Multi-party Machine Learning on Trusted Processors[EB/OL].,2016-7-13. |
| [16] | SZEGEDY C,ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, J.et al.Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL].. |
| [17] | SHARIF M, BHAGAVATULA S, BAUER L, et al.Accessorize to a Crime: Real and Stealthy Attacks on State-of-the-Art Face Recognition[C]//ACM. The 2016 ACM Sigsac Conference on Computer and Communications Security, October 24 - 28, 2016, Vienna, Austria. New York: ACM, 2016:1528-1540. |
| [18] | GROSSE K, PAPERNOT N, MANOHARAN P, et al.Adversarial Perturbations Against Deep Neural Networks for Malware Classification[EB/OL]. , 2018-6-30. |
| [19] | PAPERNOT N, ABADI M, Erlingsson Ú, et al. Semi-supervised Knowledge Transfer for Deep Learning from Private Training Data[EB/OL].,2018-6-30. |
| [20] | PRANAV R, ZHANG Jian, KONSTANTIN L, et al.Squad: 100,000+ Questions for Machine Comprehension of Text[EB/OL]. , 2016-6-16. |
| [21] | EYKHOLT K, EVTIMOV I, FERNANDES E,et al. Robust Physical-world Attacks on Deep Learning Models[EB/OL]. . |
| [22] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I,et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. . |
| [23] | GOODFELLOW I J,SHLENS J,SZEGEDY C.Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. . |
| [24] | LU Jiajun, ISSARANON T, Forsyth D.Safetynet: Detecting and Rejecting |
| Adversarial Examples Robustly[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, October 22-29, 2017, Venice, Italy .NJ:IEEE,2017:446-454. | |
| [25] | METZEN J H, GENEWEIN T, FISCHER V, et al.On Detecting Adversarial Perturbations[EB/OL]. ,2017-2-21. |
| [26] | PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, WU Xi, et al.Distillation as a Defense to Adversarial Perturbations against Deep Neural Networks[C]//IEEE. 2016 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), May 22-26, 2016, San Jose, CA, USA.NJ:IEEE,2016: 582-597. |
| [27] | HUANG Ruitong, XU Bing, SCHUURMANS Dale, et al. Learning with a Strong Adversary[EB/OL]. 2016-1-16. |
| [28] | TRAMÈR F, KURAKIN A, PAPERNOT N, et al. Ensemble Adversarial Training: Attacks and Defenses[EB/OL].,2017-5-19. |
| [29] | TRAMER F,ZHANG Fan, JUELS A, et al.Stealing Machine Learing Models via Prediction APIs[EB/OL]. . |
| [30] | DANG H,HUANG Y,Chang E C.Evading Classifiers by Morphing in the Dark[EB/OL]. . |
| [31] | PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, GOODFELLOW I, et al.Practical Black-box Attacks against Machine Learning[C]// ACM. The 2017 ACM on Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, April 2 - 6, 2017, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. New York:ACM,2017:506-519. |
| [32] | SHOKRI R, STRONATI M, SONG Congzheng, et al.Membership Inference Attacks against Machine Learning Models[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), May 22-26, 2017, San Jose, CA, USA.NJ: IEEE, 2017: 3-18. |
| [33] | ABADI M, CHU A, GOODFELLOW I, et al.Deep Learning with Differential Privac[C]//ACM. the2016 ACM Sigsac Conference on Computer and Communications Security,October 24-28, 2016 Vienna,Austria.New York: ACM, 2016:308-318. |
| [34] | PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The Limitations of Deep Learning in Adversarial Settings [C]//IEEE.2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy(EuroS&P), March 21-24,2016, Saarbrucken,Germany.March 21-24, 2016, Saarbrucken, Germany.NJ:IEEE, 2016:372-387. |
| [35] | FREDRIKSON M,JHA S,RISTENPART T.Model Inversion Attacks that Exploit Confidence Information and Basic Countermeasures[C]//ACM. The 22nd ACM Sigsac Conference on Computer and Communications Security, October 12 - 16, 2015, Denver, Colorado, USA. New York:ACM,2015:1322-1333. |
| [36] | ERKIN Z, VEUGEN T, TOFT T, et al.Generating Private Recommendations Efficiently Using Homomorphic Encryption and Data Packing[J].IEEE. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2012,7(3): 1053-1066. |
| [37] | DOWLIN N, GILAD-BACHRACH R, LAINE K, et al.CryptoNets: Applying Neural Networks to Encrypted Data with High Throughput and Accuracy[EB/OL].,2018-6-30. |
| [38] | XIE Pengtao, BILENKO M, FINLEY T, et al. Crypto-nets: Neural Networks over Encrypted Data[EB/OL]. , 2014-11-24. |
| [39] | ERLINGSSON Ú, PIHUR V, KOROLOVA A.RAPPOR: Randomized Aggregatable Privacy- preserving Ordinal Response[C]//ACM. The 2014 ACM Sigsac Conference on Computer and Communications Security, November 3-7, 2014, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA. New York: ACM, 2014: 1054-1067. |
| [40] | anquanke.2017 AI White Paper on Security Risks[EB/OL]. |
| 安全客. 2017年AI安全风险白皮书[EB/OL]. | |
| [41] | GU Tianyu, DOLAN-GAVITT B, GARG S. Badnets: Identifying Vulnerabilities in the Machine Learning Model Supply Chain[EB/OL]. . |
| [42] | CARLINI N, WAGNER D.Adversarial Examples Are Not Easily Detected: Bypassing Ten Detection Methods[C]//ACM. The 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, November 3 , 2017, Dallas, Texas, USA. New York:ACM,2017:3-14. |
| [1] | 郭春, 陈长青, 申国伟, 蒋朝惠. 一种基于可视化的勒索软件分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 31-39. |
| [2] | 杜义峰, 郭渊博. 一种基于信任值的雾计算动态访问控制方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 65-72. |
| [3] | 马泽文, 刘洋, 徐洪平, 易航. 基于集成学习的DoS攻击流量检测技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 115-119. |
| [4] | 陈冠衡, 苏金树. 基于深度神经网络的异常流量检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(6): 68-75. |
| [5] | 田春岐, 李静, 王伟, 张礼庆. 一种基于机器学习的Spark容器集群性能提升方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(4): 11-19. |
| [6] | 胡建伟, 赵伟, 闫峥, 章芮. 基于机器学习的SQL注入漏洞挖掘技术的分析与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(11): 36-42. |
| [7] | 张健, 陈博翰, 宫良一, 顾兆军. 基于图像分析的恶意软件检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(10): 24-31. |
| [8] | 文伟平, 李经纬, 焦英楠, 李海林. 一种基于随机探测算法和信息聚合的漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(1): 1-7. |
| [9] | 张阳, 姚原岗. 基于Xgboost算法的网络入侵检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(9): 102-105. |
| [10] | 文伟平, 吴勃志, 焦英楠, 何永强. 基于机器学习的恶意文档识别工具设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(8): 1-7. |
| [11] | 和湘, 刘晟, 姜吉国. 基于机器学习的入侵检测方法对比研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 0(5): 1-11. |
| [12] | 陈红松, 王钢, 宋建林. 基于云计算入侵检测数据集的内网用户异常行为分类算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 0(3): 1-7. |
| [13] | 段桂华, 申卓祥, 申东杰, 李智. 一种基于特征提取的有效下载链接识别方案研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(10): 31-36. |
| [14] | 孙靖超. 一种基于机器学习的网页分类技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(9): 45-48. |
| [15] | 陈旭, 黎宇坤, 袁华平, 刘文印. 基于分类置信度和网站特征的钓鱼检测系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(9): 111-114. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||