信息网络安全 ›› 2018, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (9): 1-9.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2018.09.001
• • 下一篇
恶意流量特征提取综述
鲁刚, 郭荣华, 周颖, 王军
- 中国洛阳电子装备试验中心,河南洛阳 471003
-
收稿日期:2018-07-17出版日期:2018-09-30发布日期:2020-05-11 -
作者简介:作者简介:鲁刚(1982—),男,辽宁,工程师,博士,主要研究方向为网络行为分析;郭荣华(1972—),男,湖北,副研究员,博士,主要研究方向为软件测试;周颖(1975—),男,湖南,研究员,博士,主要研究方向为网络测量;王军(1985—),男,江苏,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为模式识别。
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金[61402485]
Review of Malicious Traffic Feature Extraction
Gang LU, Ronghua GUO, Ying ZHOU, Jun WANG
- Chinese Luoyang Electronic Equipment Test Center, Luoyang Henan 471003, China
-
Received:2018-07-17Online:2018-09-30Published:2020-05-11
摘要:
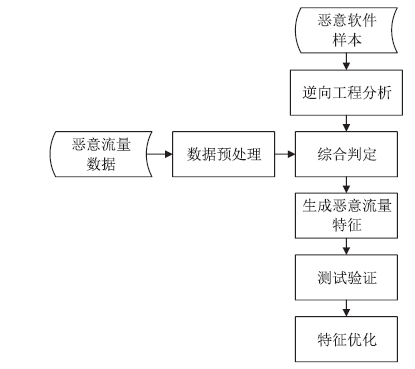
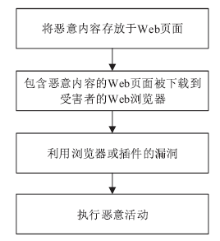
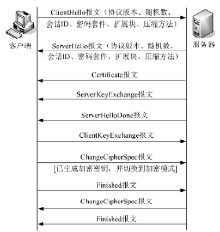
新型恶意软件的频繁出现给网络安全带来严峻挑战。恶意流量特征提取是解决该问题的重要手段。文章主要对近年恶意流量特征提取方法进行研究:首先给出恶意流量的类别;然后以恶意流量特征提取过程为主线,重点从流量采集、逆向分析、特征生成、特征评估与优化4个方面总结恶意流量特征提取研究工作;接着详细阐述手机和物联网设备的恶意流量特征提取方法;最后总结全文并给出未来研究方向。
中图分类号:
引用本文
鲁刚, 郭荣华, 周颖, 王军. 恶意流量特征提取综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(9): 1-9.
Gang LU, Ronghua GUO, Ying ZHOU, Jun WANG. Review of Malicious Traffic Feature Extraction[J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(9): 1-9.
| [1] | CNCERT. 2016 China Internet Network Security Report. [EB/OL]. , 2017-5-31. |
| 国家计算机网络应急技术处理协调中心. 《2016年中国互联网网络安全报告》[EB/OL]. . | |
| [2] | Symantec.2017 Internet Security Threat Report[EB/OL]. , 2017-10-11. |
| [3] | Topsec. TopSentry Product White Paper of Topsec[EB/OL]. , 201. |
| 天融信.天融信入侵检测系统TopSentry产品白皮书[EB/OL]. ,2017. | |
| [4] | Snort. Snort-network Intrusion Detection & Prevention System[EB/OL]., 2017-10-11. |
| [5] | Antiy.Depth Analysis Report for WannaCry[EB/OL]. . |
| 安天实验室.安天针对勒索蠕虫“魔窟”(WannaCry)的深度分析报告[EB/OL]. , 2017-6-6. | |
| [6] | TOMLIN C.PXE Windows Image Using Linux[EB/OL]. , 2018-4-11. |
| [7] | MOUSTAFA N, LAY J.UNSW-NB15: A Comprehensive Data set for Network Intrusion Detection systems[C]//IEEE. 2015 Military Communications and Information Systems Conference, November 10-12, 2015, Canberra, ACT, Australia. New Jersey: IEEE, 2015: 1-6. |
| [8] | IXIA Company.IXIA PerfectStorm[EB/OL]., 2018-4-11. |
| [9] | WU Di, CUI Xiang, LIU Qixu, et al.Research on Ubiquitous Botnet[J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(7): 16-28. |
| 吴迪,崔翔,刘奇旭,等. 泛在僵尸网络发展研究[J]. 信息网络安全,2017,17(7):16-28. | |
| [10] | BILGE L, SEN S, BALZAROTTI D, et al.Exposure: a Passive DNS Analysis Service to Detect and Report Malicious Domains[J]. ACM Transactions on Information & System Security, 2014, 16(4): 1-28. |
| [11] | WEI Shuning, CHEN Xingru, JIAO Yong, et al.Research on the Application of AR-OSELM Algorithm in Network Intrusion Detection[J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(6): 1-6. |
| 魏书宁,陈幸如,焦永,等. AR-OSELM算法在网络入侵检测中的应用研究[J]. 信息网络安全,2017,17(6):1-6. | |
| [12] | LIU Zhen, WANG Ruoyu, TANG Deyu, et al.A System for Linking Ground Truth to Mobile Network Traffic[C]//ACM. International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services, November 28-December 1, 2016, Hiroshima, Japan. New York: ACM, 2016: 292-293. |
| [13] | CABALLERO J, POOSANKAM P, KREIBICH C, et al.Dispatcher: Enabling Active Botnet Infiltration Using Automatic Protocol Reverse-engineering[C]//ACM. 16th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, November 9-13, 2009, Chicago, Illinois, USA. New York: ACM, 2009: 621-634. |
| [14] | KRUEGER T,KRÄMER N,RIECK K. ASAP: Automatic Semantics-aware Analysis Of Network Payloads[C]//Springer. International ECML/PKDD Workshop on Privacy and Security Issues in Data Mining and Machine Learning, September 24, 2011, Barcelona, Spain. Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 50-63. |
| [15] | LU Gang, DU Jing, GUO Ronghua, et al.Application Feature Extraction Using Both Dynamic Binary Tracking and Statistical Learning[C]//IEEE. 17th International Conference on Communication Technology, October 27-30, 2017, Chengdu, China. New Jersey: IEEE, 2017: 2018-2025. |
| [16] | WONG M Y,LIE D.IntelliDroid: a Targeted Input Generator for the Dynamic Analysis of Android Malware[EB/OL] , 2017-10-11. |
| [17] | JULIEN D, COLAS L G, ERIC A, et al.State of the Art of Network Protocol Reverse Engineering Tools[J]. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, 2018, 14(1): 53-68. |
| [18] | SAROIU S, GIRBBLE S D, LEVY H M.Measurement and Analysis of Spyware in a University Environment[C]//ACM. 1st Conference on Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, March 29-31, 2004, San Francisco, CA, USA. New York: ACM, 2004: 11. |
| [19] | LE V L, WELCH I, GAO X, et al.Anatomy of Driven-by Download Attack[C]//ACM. 11th Australasian Information Security Conference, January 29- February 1, 2013, Adelaide, Australia. New York: ACM, 2013: 49-58. |
| [20] | NEWSOME J, KARP B, SONG D.Polygraph: Automatically Generating Signatures for Polymorphic Worms[C]//IEEE. 2005 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, May 8-11, 2005, Oakland, CA, USA. New Jersey: IEEE, 2005: 226-241. |
| [21] | LI Zhichun, SANGHI M, YAN Chen, et al.Hamsa: Fast Signature Generation for Zero-day Polymorphic Worms with Provable Attack Resilience[C]//IEEE. 2006 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, May 21-24, 2006, Berkeley/Oakland, CA, USA. New Jersey: IEEE, 2006: 15-47. |
| [22] | CAVALLARO L, LANZI A, MAYER L, et al.LISABETH: Automated Content-based Signature Generator for Zero-day Polymorphic Worms[C]//ACM. 4th International Workshop on Software Engineering for Secure Systems , May 17-18, 2008, Leipzig, Germany. New York: ACM, 2008: 41-48. |
| [23] | LEE S, KIM S, LEE S, et al. LARGen: Automatic Signature Generation for Malwares Using Latent Dirichlet Allocation[EB/OL]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7569096, 2016-9-15 . |
| [24] | PARKOUR M.Blog Sobre Compartici´on de Malware, Recursoen l´ınea Disponible[EB/OL]. , 2018-4-12. |
| [25] | ZHAO Guodong, XU Kai, XU Lei, et al. Detecting APT Malware Infections Based on Malicious DNS and Traffic Analysis[EB/OL]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7569096, 2016-9-15 |
| [26] | CELIK Z B, WALLS R J, MCDANIEL P, et al.Malware Traffic Detection Using Tamper Resistant Features[C]//IEEE. 2015 IEEE Military Communications Conference, October 26-28, 2015, Tampa, FL,USA. New Jersey: IEEE, 2015: 330-335. |
| [27] | ANDERSON B, MCGREW D.Identifying Encrypted Malware Traffic with Contextual Flow Data[C]//ACM. ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, October 28, 2016, New York, USA. New York: ACM, 2016: 35-46. |
| [28] | ANDERSON B, MCGREW D.Machine Learning for Encrypted Malware Traffic Classification: Accounting for Noisy Labels and Non-stationarity[C]//ACM. 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, August 13-17, 2017, Halifax, NS, Canada. New York: ACM, 2017: 1723-1732. |
| [29] | HE Xiang, LIU Sheng, JIANG Jiguo.Comparative Study of Intrusion Detection Methods Based on Machine Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(5): 1-11. |
| 和湘,刘晟,姜吉国. 基于机器学习的入侵检测方法对比研究[J]. 信息网络安全,2018,18(5):1-11. | |
| [30] | BARTOS K, SOFKA M, FRANC V.Optimized Invariant Representation of Network Traffic for Detecting Unseen Malware Variants[C]//USENIX. 25th USENIX Security Symposium, August 10-12, 2016, AUSTIN, TX, USA. Berkeley: USENIX, 2016: 807-822. |
| [31] | BOCCHI E, GRIMAUDO L, MELLIA M, et al.MAGMA Network Behavior Classifier for Malware Traffic[EB/OL]. 2017-10-11. |
| [32] | RAHBARINIA B, PERDISCI R, ANTONAKAKIS M.Efficient and Accurate Behavior-based Tracking of Malware-control Domains in Large ISP Networks[J]. ACM Transactions on Privacy and Security, 2016, 19(2): 1-4. |
| [33] | NARI S, GHORBANI A A.Automated Malware Classification Based on Network Behavior[C]//IEEE. 2013 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications, January 28-31, 2013, San Diego, CA, USA. New Jersey: IEEE, 2013: 642-647. |
| [34] | ZHAO D, TRAORE I, SAYED B, et al.Botnet Detection Based on Traffic Behavior Analysis and Flow Intervals[J]. Computers & Security, 2013, 39(4): 2-16. |
| [35] | TANAKA Y, GOTO A.Analysis of Malware Download Sites by Focusing on Time Series Variation of Malware[C]//IEEE. 2016 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communication, June 27-30, 2016, Messina, Italy. New Jersey: IEEE, 2016: 301-313. |
| [36] | XIE Yinglian, YU Fang, ACHAN K, et al. Automatic Botnet SPAM Signature Generation[P]. USA: United States Patent Application 20090265786, 2009-10-22. |
| [37] | LUO Bin, XIA Jingbo.A Novel Intrusion Detection System Based on Feature Generation with Visualization Strategy[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, 41(9): 4139-4147. |
| [38] | MUANDET K, BALDUZZI D,SCHÖLKOPF B.Domain Generalization via Invariant Feature Representation[EB/OL]. , 2017-10-12. |
| [39] | Statista. Number of Smartphone Users Worldwide from 2014 to 2020 (in billions)[EB/OL]. , 2018-4-12. |
| [40] | Rising.Chinese Network Security Report in the First Half of 2017[EB/OL]. . |
| 瑞星. 2017年上半年中国网络安全报告[EB/OL]. . | |
| [41] | PanGu Team. Pegasus - Analysis on APT Attack against iOS Devices[EB/OL]. . |
| [42] | Mobile Threat Response Team.ZNIU: First Android Malware to Exploit Dirty COW Vulnerability[EB/OL]. 2018-4-12. |
| [43] | SU Xin, LIU Xuchong, LIN Jiuchuang, et al.De-cloaking Malicious Activities in Smartphones Using HTTP Flow Mining[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and information systems, 2017, 11(6): 3230-3253. |
| [44] | Egham. Gartner Says 8.4 Billion Connected “Things” will be in Use in 2017,Up 31 Percent From 2016[EB/OL]. , 2018-4-12. |
| [45] | BERTINO E, ISLAM N.Botnets and Internet of Things Security[J]. Computer, 2017, 50(2): 76-79. |
| [46] | KASINATHAN P, PASTRONE C, SPIRITO M A, et al.Denial-of-service Detection in 6LoWPAN Based Internet of Things[C]//IEEE. 9th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications, October 7-9, 2013, Lyon, France. 2013. New Jersey: IEEE, 2013: 600-607. |
| [47] | CHO E J, KIM J H, HONG C S.Attack Model and Detection Scheme for Botnet on 6LoWPAN[C]//ACM. 12th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Conference on Management Enabling the Future Internet for Changing Business and New Computing Services, September 23-25, 2009, Jeju Island, Korea. New York: ACM, 2009: 515-518. |
| [48] | KOLIAS C, KAMBOURAKIS G, STAVROU A, et al.DDoS in the IoT: Mirai and Other Botnets[J]. Computer, 2017, 50(7): 80-84. |
| [49] | ELZEN I, HEUGTEN J.Techniques for Detecting Compromised IoT Devices[EB/OL]. . |
| [50] | SINANOVIC H, MRDOVIC S. Analysis of Mirai Malicious Software[EB/OL]. 2017-11-12. |
| [51] | SHALEV S S, BEN S B.Understanding Machine Learning from Theory to Algorithms[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2016. |
| [1] | 刘建伟, 韩祎然, 刘斌, 余北缘. 5G网络切片安全模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 1-11. |
| [2] | 赵志岩, 纪小默. 智能化网络安全威胁感知融合模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 87-93. |
| [3] | 黎水林, 祝国邦, 范春玲, 陈广勇. 一种新的等级测评综合得分算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(2): 1-6. |
| [4] | 荆涛, 万巍. 面向属性迁移状态的P2P网络行为分析方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(1): 16-25. |
| [5] | 康健, 王杰, 李正旭, 张光妲. 物联网中一种基于多种特征提取策略的入侵检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 21-25. |
| [6] | 裘玥. 大型体育赛事网络安全风险分析与评估[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 61-65. |
| [7] | 高孟茹, 谢方军, 董红琴, 林祥. 面向关键信息基础设施的网络安全评价体系研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 111-114. |
| [8] | 陈良臣, 刘宝旭, 高曙. 网络攻击检测中流量数据抽样技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(8): 22-28. |
| [9] | 尚文利, 尹隆, 刘贤达, 赵剑明. 工业控制系统安全可信环境构建技术及应用[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(6): 1-10. |
| [10] | 张可, 汪有杰, 程绍银, 王理冬. DDoS攻击中的IP源地址伪造协同处置方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(5): 22-29. |
| [11] | 李辉, 倪时策, 肖佳, 赵天忠. 面向互联网在线视频评论的情感分类技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(5): 61-68. |
| [12] | 倪一涛, 陈咏佳, 林柏钢. 基于自动解混淆的恶意网页检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(4): 37-46. |
| [13] | 陈良臣, 高曙, 刘宝旭, 卢志刚. 网络加密流量识别研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(3): 19-25. |
| [14] | 傅建明, 黎琳, 郑锐, 苏日古嘎. 基于GAN的网络攻击检测研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(2): 1-9. |
| [15] | 韦力, 段沁, 刘志伟. 互联网时代医院网络安全管理综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(12): 88-92. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||