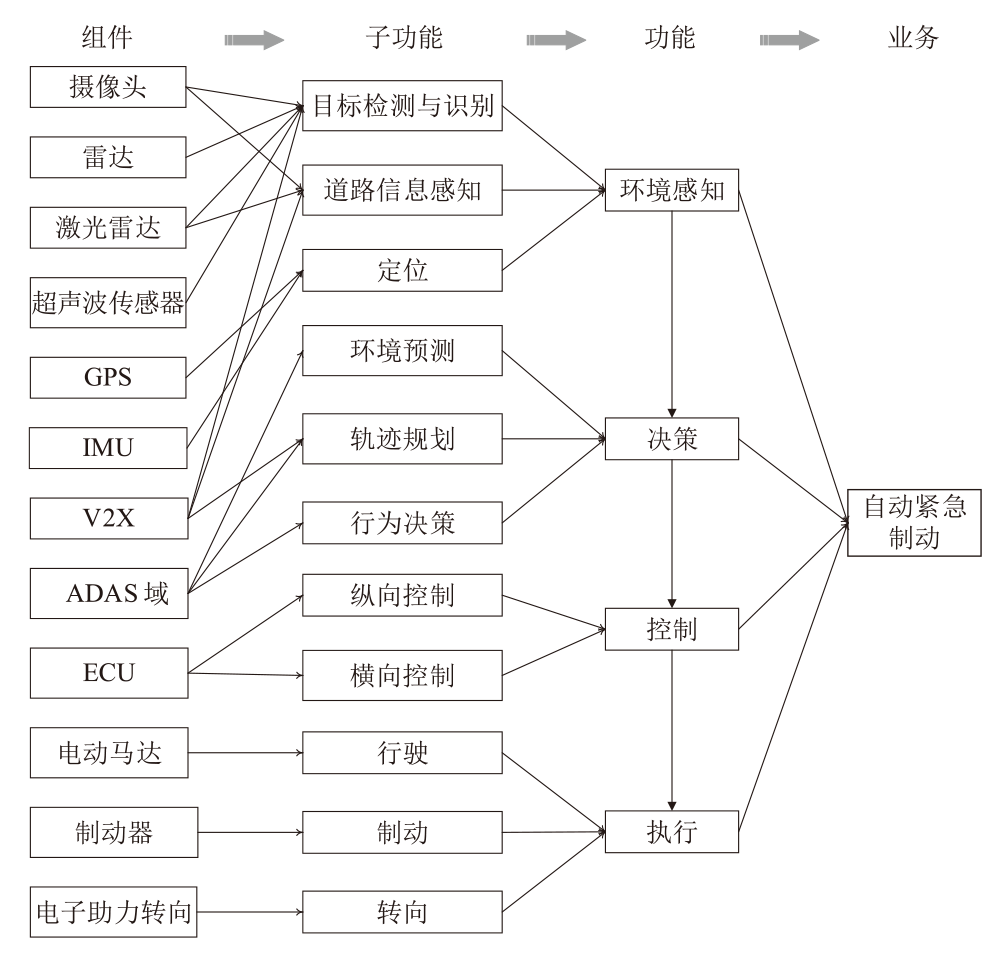
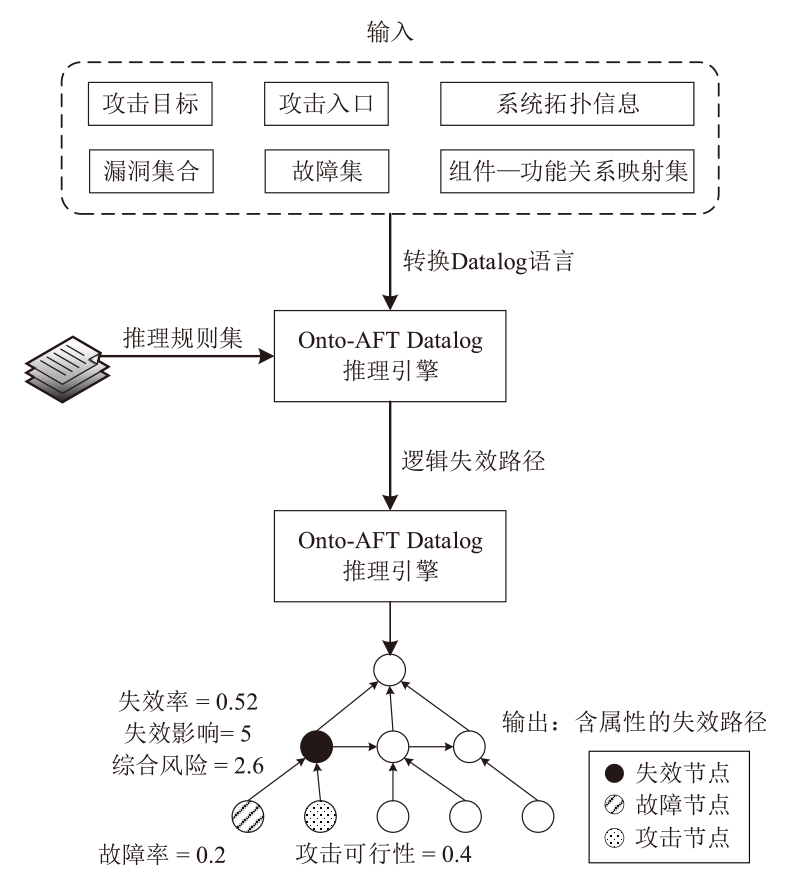
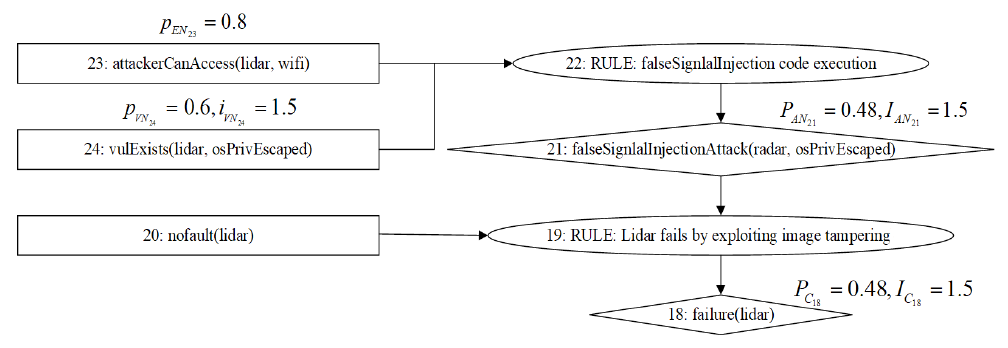
Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 598-609.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.04.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
A Safety and Security Co-Analysis and Assessment Method for Intelligent Connected Vehicles Based on Ontology and Attack-Fault Tree
- Department of Cyberspace Security, University of Information Engineering, Zhengzhou 450001, China
-
Received:2025-02-04Online:2025-04-10Published:2025-04-25
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Shun, QIU Han, HE Ying. A Safety and Security Co-Analysis and Assessment Method for Intelligent Connected Vehicles Based on Ontology and Attack-Fault Tree[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(4): 598-609.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.04.008
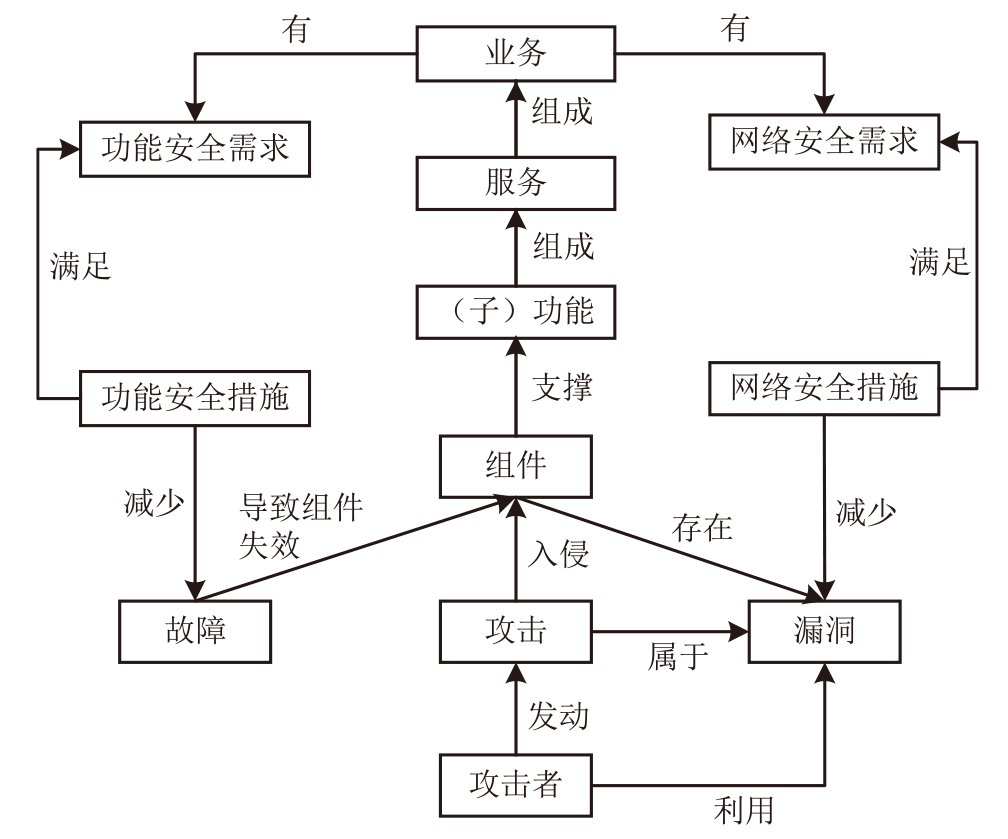
| S&S 视角 | 本体—本体 | 关系 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 宏观 | 功能安全需求—网络安全需求、功能安全措施—网络安全措施 | 独立 | 无交互 |
| 相互强化 | 功能安全需求(措施)有助于满足网络安全需求(措施),反之亦然 | ||
| 条件依赖 | 网络安全是满足功能安全的条件,反之亦然 | ||
| 对立 | 同时考虑功能安全需求(措施)和网络安全需求(措施)存在矛盾 | ||
| 微观 | 组件—组件 | 独立 | 组件之间无功能或资源交互 |
| 冗余(相互强化) | 组件冗余设计提升整体可靠性 | ||
| 组件—功能 | 依赖(条件依赖) | 功能依赖组件可用性 | |
| 攻击—失效、 故障—失效 | 因果(条件依赖) | 攻击或故障直接引起组件失效 | |
| 攻击—故障 | 独立 | 无交互 | |
| 触发(条件依赖) | 一方导致另一方发生(例如,攻击导致故障发生) | ||
| 抑制(对立) | 一方阻断另一方发生(例如,故障阻断攻击传播) |
| 编号 | 组件 | 漏洞/故障原因 | 威胁模式/失效模式 | 威胁影响 /失效 影响 | 系统 状态 | 系统 影响 | 严重度 | 系统易感性 | 威胁属性 | 攻击/失效可能性 | 风险值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
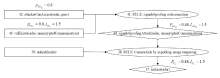
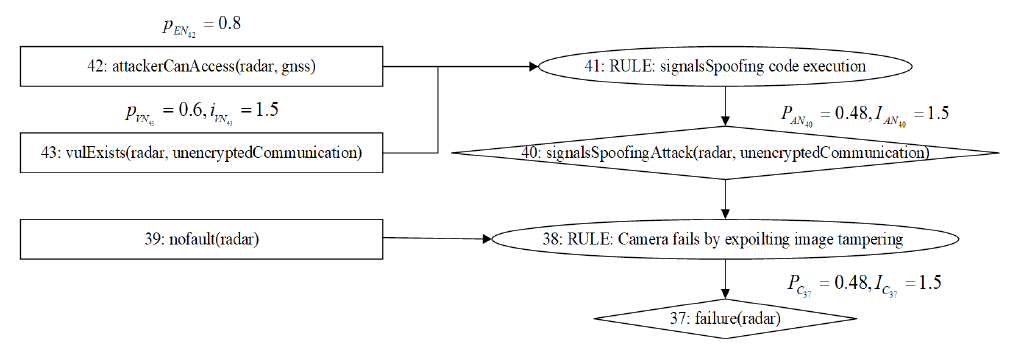
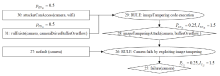
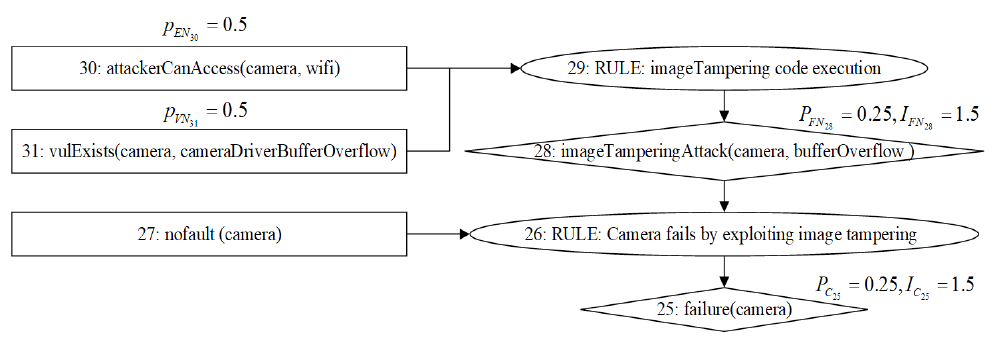
| 1 | 摄像头 | 被攻击者干扰的图像被摄像头观察到后产生不正确的 视觉预测 | 攻击者对摄像头注入对抗性图像 | 摄像头输出错误的判断信息 | 安全关键,系统需要紧急 制动 | 系统失去可靠的视觉预测 服务 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 28 |
| 2 | 摄像头 | 攻击者用额外的光线使摄像头失灵 | 摄像头 致盲 | 摄像头拒绝服务 | 安全关键,系统需要紧急 制动 | 系统失去摄像头功能 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 21 |
| 3 | T-box | 攻击者通过蓝牙技术实现缓冲区溢出 | 攻击者使用已连接的设备并提升其 权限 | 攻击者能在关键ECU上执行代码 | 连接到受感染的设备 | 安全关键,攻击者可以控制车辆 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 42 |
| 4 | T-box | 无线连接协议缺乏强身份验证方法 | 攻击者通过V2I通信发送伪造信息 | 窃取合法身份并传播伪造 信息 | 连接到受感染的设备 | 安全关键,运行环境和信息完整性遭受 破坏 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 30 |
| 5 | T-box | 无线连接易受干扰 | 攻击者终端OTA或车载 诊断 | OTA更新中断或车载诊断 终止 | OTA升级中或远程车载诊断运行中 | 无 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 10 | 10 |
| 6 | OBD 端口 | 攻击者从OBD端口观察到CAN消息 | 攻击者通过OBD端口传输伪造 信息 | 攻击者能在关键ECU上执行代码 | 连接到受感染的设备 | 安全关键,攻击者可以控制车辆 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 42 |
| 7 | OBD 端口 | CAN总线被大量优先级高的消息占用 | 攻击者通过OBD端口发送大量优先级消息,使CAN拒绝服务 | CAN无法处理总线上的其他消息 | 连接到受感染的设备 | 安全关键,车内通信网络 瘫痪 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 24 |
| 维度 | FMVEA | Six-Step Model | Improved-STPA-SafeSec-BN | Onto-AFT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 风险识别的全面性 | S&S需求/措施关系 | 独立 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 依赖 | × | √ | × | √ | ||
| 强化 | × | √ | × | √ | ||
| 对立 | × | √ | × | √ | ||
| 组件—组件 | 独立 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 冗余 | × | √ | × | √ | ||
| 组件—功能 | 依赖 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 攻击/故障—失效 | 因果 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 攻击—故障 | 独立 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 触发 | × | × | × | √ | ||
| 抑制 | × | × | × | √ | ||
| 风险量化的准确性 | 定性/定量分析 | 定量 | 定性 | 定量 | 定量 | |
| 数据来源 | 公共知识,专家评分 | 公共知识 | 公共知识, 统计概率 | 公共知识,统计概率,CVSS评分 | ||
| 方法适应性 | 符合标准 | ISO 26262 | 无特定 标准 | ISO 26262+ISO/SAE 21434 | ISO 26262+ISO/SAE 21434+本体扩展 | |
| 工具支持 | 表格 (人工) | 关系矩阵(人工) | 贝叶斯网络工具(如GeNIe) | 开源推理引擎(如XSB) | ||
| 动态系统适配性 | 低 | 低 | 中(重构CPT) | 高(规则动态更新) | ||
| [1] | KRIAA S, PIETRE-CAMBACEDES L, BOUISSOU M, et al. A Survey of Approaches Combining Safety and Security for Industrial Control Systems[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2015, 139: 156-178. |
| [2] | SABALIAUSKAITE G, BRYANS J, JADIDBONAB H, et al. TOMSAC-Methodology for Trade-Off Management between Automotive Safety and Cyber Security[EB/OL]. (2024-05-01)[2025-01-07]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2024.103798. |
| [3] | NICOLETTI S M, PEPPELMAN M, KOLB C, et al. Model-Based Joint Analysis of Safety and Security: Survey and Identification of Gaps[EB/OL]. (2023-11-01)[2025-01-07]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2106.06272. |
| [4] | KUMAR R, STOELINGA M. Quantitative Security and Safety Analysis with Attack-Fault Trees[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE 18th International Symposium on High Assurance Systems Engineering (HASE). New York: IEEE, 2017: 25-32. |
| [5] | KRIAA S, BOUISSOU M, COLIN F, et al. Safety and Security Interactions Modeling Using the BDMP Formalism: Case Study of a Pipeline[C]// Springer. Computer Safety, Reliability, and Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 326-341. |
| [6] | KORNECKI A J, SUBRAMANIAN N, ZALEWSKI J. Studying Interrelationships of Safety and Security for Software Assurance in Cyber-Physical Systems: Approach Based on Bayesian Belief Networks[C]// IEEE. 2013 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems. New York: IEEE, 2013: 1393-1399. |
| [7] | JACKSON D. Alloy: A Lightweight Object Modelling Notation[J]. ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology (TOSEM), 2002, 11(2): 256-290. |
| [8] | VISTBAKKA I, TROUBITSYNA E, KUISMIN T, et al. Co-Engineering Safety and Security in Industrial Control Systems: A Formal Outlook[C]// Springer. Software Engineering for Resilient Systems (SERENE 2017). Heidelberg: Springer, 2017: 96-114. |
| [9] | LIEDTKE T. Risk Assessment According to the ISO/SAE 21434: 2021-Rxperiences, Help and Pitfalls[EB/OL]. (2021-09-29)[2025-01-07]. https://hss-opus.ub.ruhr-uni-bochum.de/opus4/frontdoor/index/index/docId/8356. |
| [10] | STAAB S, STUDER R. Handbook on Ontologies[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2013. |
| [11] | AZIZ A, AHMED S, KHAN F I. An Ontology-Based Methodology for Hazard Identification and Causation Analysis[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 123: 87-98. |
| [12] | RAAD J, CRUZ C. A Survey on Ontology Evaluation Methods[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2015). New York: ACM, 2015: 179-186. |
| [13] | BHOSALE P, KASTNER W, SAUTER T. Integrated Safety-Security Risk Assessment for Industrial Control System: An Ontology-Based Approach[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE 28th International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-8. |
| [14] | HUANG Ning. Network Reliability and Its Evaluation Technology[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2020. |
| 黄宁. 网络可靠性及评估技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2020. | |
| [15] | LUO Feng, JIANG Yifan, WANG Jiajia, et al. A Framework for Cybersecurity Requirements Management in the Automotive Domain[EB/OL]. (2023-05-22)[2025-01-07]. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104979. |
| [16] | International Electrotechnical Commission. Industrial Communication Networks-Network and System Security-Part 1-1: Terminology, Concepts and Models[EB/OL]. (2009-07-30)[2025-01-07]. https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/7029. |
| [17] | JING Pengfei, CAI Zhiqiang, CAO Yingjie, et al. Revisiting Automotive Attack Surfaces: A Practitioners’ Perspective[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2024: 2348-2365. |
| [18] | RICHTER A, WALZ T P, DHANANI M, et al. Components and Their Failure Rates in Autonomous Driving[C]// Wiley. Proceeding of the 33rd European Safety and Reliability Conference. New York: Wiley, 2023: 233-240. |
| [19] | SCHMITTNER C, MA Zhendong, SMITH P. FMVEA for Safety and Security Analysis of Intelligent and Cooperative Vehicles[C]// Springer. Computer Safety, Reliability, and Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 282-288. |
| [20] | SABALIAUSKAITE G, ADEPU S, MATHUR A. A Six-Step Model for Safety and Security Analysis of Cyber-Physical Systems[C]// Springer. Critical Information Infrastructures Security (CRITIS 2016). Heidelberg: Springer, 2017: 189-200. |
| [21] | LIU Qi, SUN Ke, LIU Wenqi, et al. Quantitative Risk Assessment for Connected Automated Vehicles: Integrating Improved STPA-SafeSec and Bayesian Network[EB/OL]. (2025-01-01)[2025-01-07]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2024.110528. |
| [22] | SABALIAUSKAITE G, LIEW L S, CUI J. Integrating Autonomous Vehicle Safety and Security Analysis Using STPA Method and the Six-Step Model[J]. International Journal on Advances in Security, 2018, 11(1): 160-169. |
| [1] | XU Zhishuang, ZHANG Kun, FAN Junchao, CHANG Xiaolin. Construction Method of Cybersecurity Knowledge Graph Based on Ontology [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 451-466. |
| [2] | YUAN Yulin, YUAN Shuguang, YU Jing, CHEN Chi. Anonymization General Process and Risk Assessment Method for Data Compliance [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(12): 1855-1870. |
| [3] | ZHAO Ge, ZHENG Yang, TAO Zelin. Systematic Risk Assessment Analysis for Smart Wearable Devices [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(10): 1595-1603. |
| [4] | WANG Junyan, YI Peng, JIA Hongyong, ZHANG Jianhui. IoT Terminal Risk Assessment Model Based on Improved CAE [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 150-159. |
| [5] | HUANG Bo, QIN Yuhai, LIU Yang, JI Duo. Research of Vulnerability Assessment and Risk Probability Base on General Attack Tree [J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(10): 39-44. |
| [6] | JIN Shuting, HE Jingsha, ZHU Nafei, PAN Shijia. Research on Privacy Protection Access Control Mechanism Based on Ontology Reasoning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(8): 52-61. |
| [7] | ZHU Rongchen, LI Xin, LIN Xiaonuan. The Security Risk Analysis Method for Video Private Network Based on Bayesian Network [J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(12): 91-101. |
| [8] | ZHAO Xiaolin, ZHAO Bin, ZHAO Jingjing, XUE Jingfeng. Research on Network Security Measurement Method Based on Attack Identification [J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(11): 17-27. |
| [9] | LIU Hong, XIE Yongheng, WANG Guowei, JIANG Shuai. Ontology-based Cross-domain Security Analysis [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(9): 82-86. |
| [10] | LIU Yonglei, JIN Zhigang, HAO KUN, ZHANG Weilong. Risk Assessment of Mobile Payment System Based on STRIDE and Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(2): 49-56. |
| [11] | Yi LI, Jian GU, Tiejun GU. Knowledge Modeling and Application of Quality Evaluation System for Complex Network Security Product [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(9): 55-59. |
| [12] | Qing WANG, Chenyang TU, shenjiahui@iie.ac.cn. Design and Application of General Framework for Side Channel Attack [J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(5): 57-62. |
| [13] | Xiaoning DONG, Huarong ZHAO, Dianwei LI, Jiasheng WANG. Research on Information Systems Security Risk Assessment Based on Fuzzy Theory of Evidence [J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(5): 69-73. |
| [14] | Zhong LIANG, Jiakun ZHOU, Han ZHU, Bo CHEN. Research on Aggregation Technology for Information Security Knowledge Based on Security Ontology [J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(4): 78-85. |
| [15] | Zhiqiang LIANG, Dansheng LIN. Information Security Risk Assessment Mechanism Research Based on Power System [J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(4): 86-90. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||