信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 1277-1290.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.08.013
基于预训练Transformers的物联网设备识别方法
- 陆军工程大学指挥控制工程学院,南京 210007
-
收稿日期:2024-03-27出版日期:2024-08-10发布日期:2024-08-22 -
通讯作者:王梓澎17641235907@163.com -
作者简介:邢长友(1982—),男,河南,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为软件定义网络、网络安全和网络功能虚拟化|王梓澎(2000—),男,辽宁,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络安全|张国敏(1979—),男,山东,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为软件定义网络、网络安全、网络测量和分布式系统|丁科(1978—),男,江苏,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为网络虚拟化技术和网络安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62172432)
IoT Device Identification Method Based on Pre-Trained Transformers
XING Changyou, WANG Zipeng( ), ZHANG Guomin, DING Ke
), ZHANG Guomin, DING Ke
- Command and Control Engineering College, Army Engineering University, Nanjing 210007, China
-
Received:2024-03-27Online:2024-08-10Published:2024-08-22
摘要:
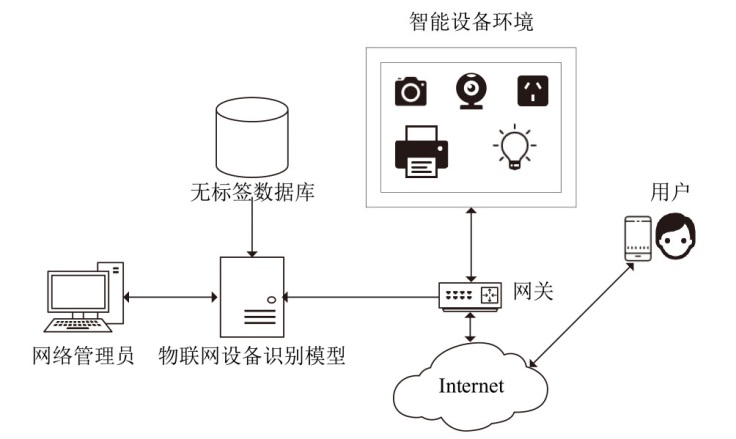
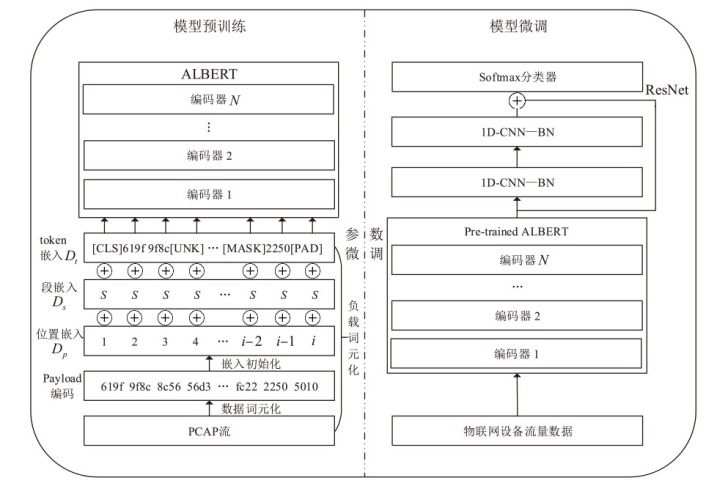
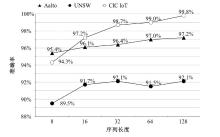
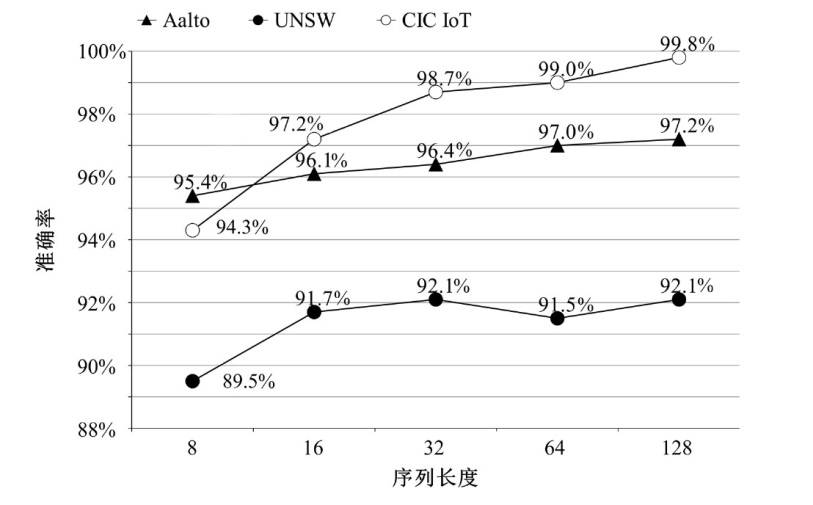
为帮助网络管理员迅速隔离局域网内的异常、易受攻击的物联网设备,以防攻击者利用设备漏洞侵入内部网络进行潜伏和后续深度攻击,高效的物联网设备识别方法显得尤为重要。然而,现有基于机器学习的识别方法普遍存在特征选择过程复杂、获取的数据流特征不稳定等问题,从而影响了识别准确性。为此,文章提出了一种基于预训练Transformers的物联网设备识别方法,该方法主要通过IoTBERT模型对设备流量进行处理,以实现物联网设备识别目标。IoTBERT包括预训练单元和设备识别单元等核心组件,预训练单元通过使用无标记物联网设备流量数据训练ALBERT模型,将数据特征编码嵌入高维特征向量中,从而获取流量特征表示模型。设备识别单元则利用标记数据微调预训练模型的参数权重,并结合残差网络在分组级别上完成物联网设备识别。该方法自动学习流量特征表示并执行分类识别决策,无需人工设计特征工程和手动构建多阶段处理流程,直接将原始数据分组编码映射到相应的类别标签,从而实现端到端的物联网设备识别。在公开数据集Aalto、UNSW和CIC IoT上的实验结果表明,文章所提方法能够基于数据分组有效识别物联网设备,并且该方法的平均识别准确率分别达到97.2%、92.1%和99.8%。
中图分类号:
引用本文
邢长友, 王梓澎, 张国敏, 丁科. 基于预训练Transformers的物联网设备识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1277-1290.
XING Changyou, WANG Zipeng, ZHANG Guomin, DING Ke. IoT Device Identification Method Based on Pre-Trained Transformers[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1277-1290.
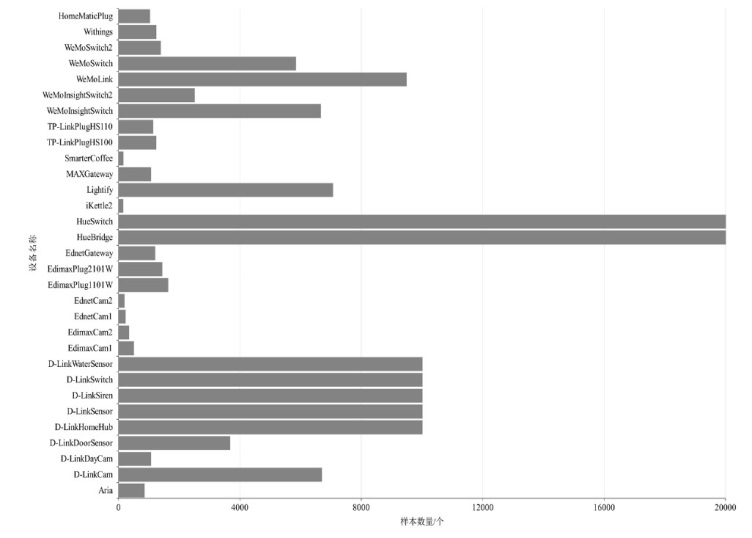
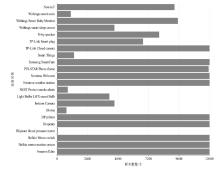
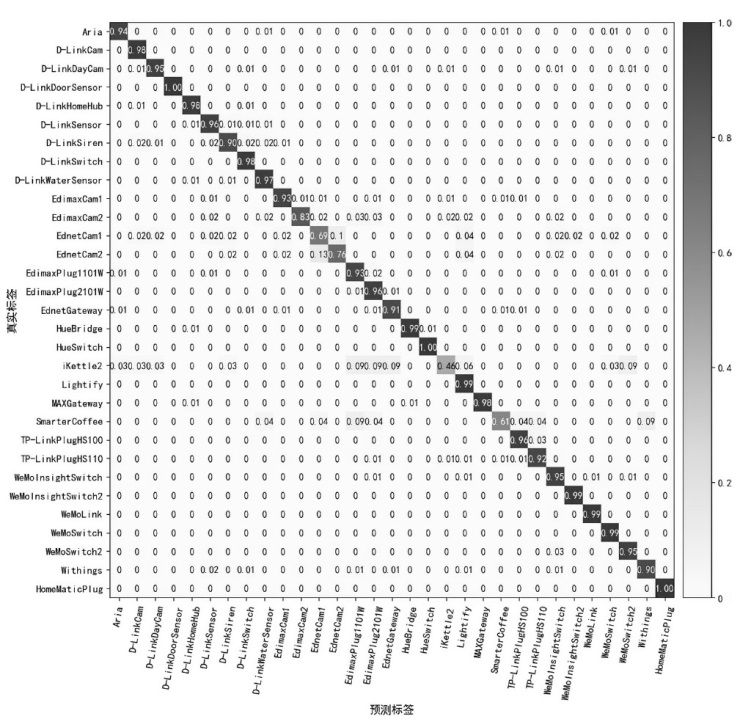
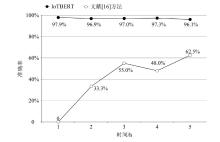
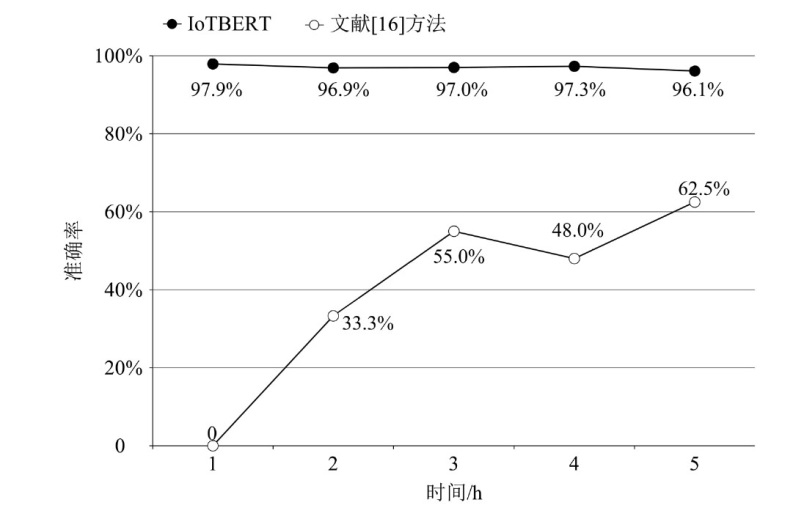
表2
Aalto和UNSW中设备识别结果
| Aalto | 设备名称 | Precision | Recall | F1-score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aria | 94.1% | 94.1% | 0.941 | |
| D-LinkCam | 98.5% | 95.0% | 0.967 | |
| D-LinkDayCam | 95.4% | 81.9% | 0.881 | |
| D-LinkDoorSensor | 99.9% | 99.7% | 0.998 | |
| D-LinkHomeHub | 97.9% | 96.1% | 0.970 | |
| D-LinkSensor | 96.1% | 96.1% | 0.961 | |
| D-LinkSiren | 90.0% | 97.1% | 0.934 | |
| D-LinkSwitch | 98.2% | 94.9% | 0.965 | |
| D-LinkWaterSensor | 97.2% | 95.7% | 0.965 | |
| EdimaxCam1 | 93.3% | 85.2% | 0.891 | |
| EdimaxCam2 | 83.3% | 86.2% | 0.847 | |
| EdnetCam1 | 68.7% | 82.5% | 0.750 | |
| EdnetCam2 | 75.6% | 87.2% | 0.810 | |
| EdimaxPlug1101W | 92.9% | 92.6% | 0.928 | |
| EdimaxPlug2101W | 95.8% | 87.2% | 0.913 | |
| EdnetGateway | 90.8% | 94.4% | 0.926 | |
| HueBridge | 98.9% | 99.9% | 0.994 | |
| HueSwitch | 99.9% | 99.5% | 0.997 | |
| iKettle2 | 45.7% | 50.0% | 0.478 | |
| Lightify | 99.1% | 98.3% | 0.987 | |
| MAXGateway | 98.1% | 100% | 0.991 | |
| SmarterCoffee | 60.9% | 53.8% | 0.571 | |
| TP-LinkPlugHS100 | 95.5% | 95.9% | 0.957 | |
| TP-LinkPlugHS110 | 92.4% | 93.6% | 0.930 | |
| WeMoInsightSwitch | 94.6% | 98.0% | 0.962 | |
| WeMoInsightSwitch2 | 99.2% | 98.6% | 0.989 | |
| WeMoLink | 99.2% | 99.0% | 0.991 | |
| WeMoSwitch | 99.3% | 98.5% | 0.989 | |
| WeMoSwitch2 | 95.3% | 93.5% | 0.944 | |
| Witdings | 90.3% | 99.1% | 0.945 | |
| Home Matic Plug | 100% | 100% | 1 | |
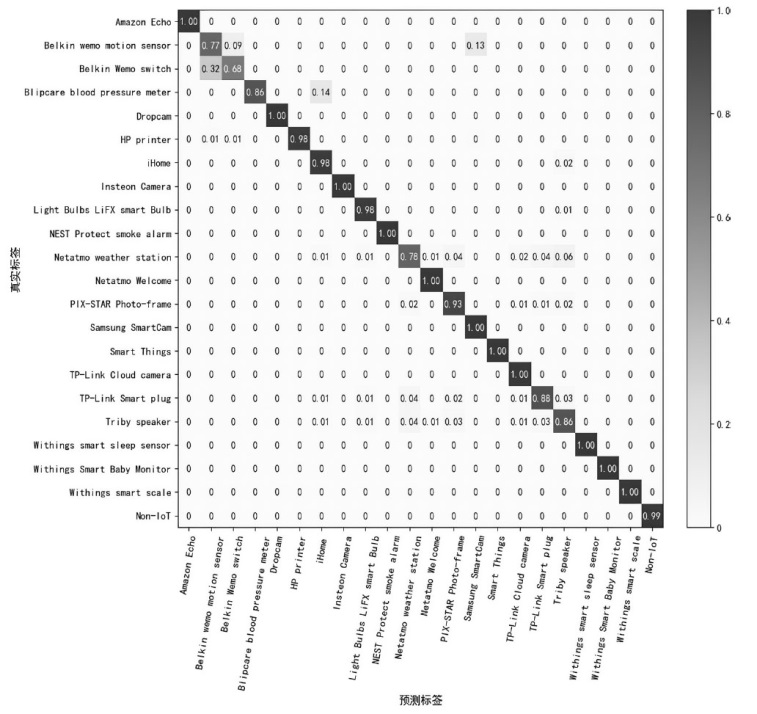
| UNSW | Amazon Echo | 99.8% | 99.1% | 0.995 |
| Belkin Wemo Motion Sensor | 77.3% | 57.3% | 0.658 | |
| Belkin Wemo Switch | 67.5% | 91.7% | 0.778 | |
| Blipcare Blood Pressure Meter | 85.7% | 54.5% | 0.667 | |
| Dropcam | 100% | 100% | 1 | |
| HP Printer | 97.9% | 100% | 0.989 | |
| iHome | 98.4% | 47.7% | 0.642 | |
| Insteon Camera | 99.8% | 99.9% | 0.998 | |
| Light Bulbs LiFX Smart Bulb | 97.8% | 91.9% | 0.947 | |
| NEST Protect Smoke Alarm | 100% | 93.2% | 0.965 | |
| Netatmo Weather Station | 78.4% | 92.8% | 0.850 | |
| Netatmo Welcome | 99.9% | 97.6% | 0.988 | |
| PIX-STAR Photo-Frame | 92.6% | 92.4% | 0.925 | |
| Samsung SmartCam | 99.7% | 89.5% | 0.943 | |
| Smart Things | 99.7% | 99.7% | 0.997 | |
| TP-Link Cloud Camera | 99.5% | 95.4% | 0.974 | |
| TP-Link Smart Plug | 87.7% | 86.1% | 0.869 | |
| Triby Speaker | 85.7% | 82.8% | 0.842 | |
| Withings Smart Sleep Sensor | 99.7% | 98.8% | 0.992 | |
| Withings Smart Baby Monitor | 99.8% | 99.9% | 0.999 | |
| Withings Smart Scale | 100% | 97.6% | 0.988 | |
| Non-IoT | 99.4% | 97.6% | 0.985 |
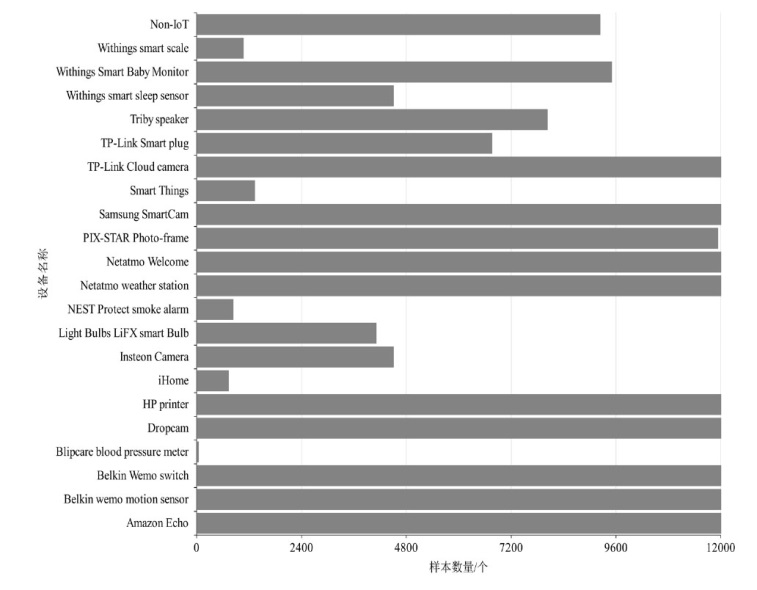
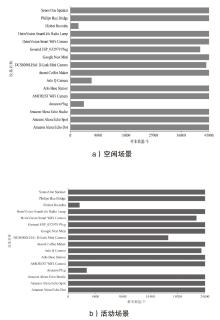
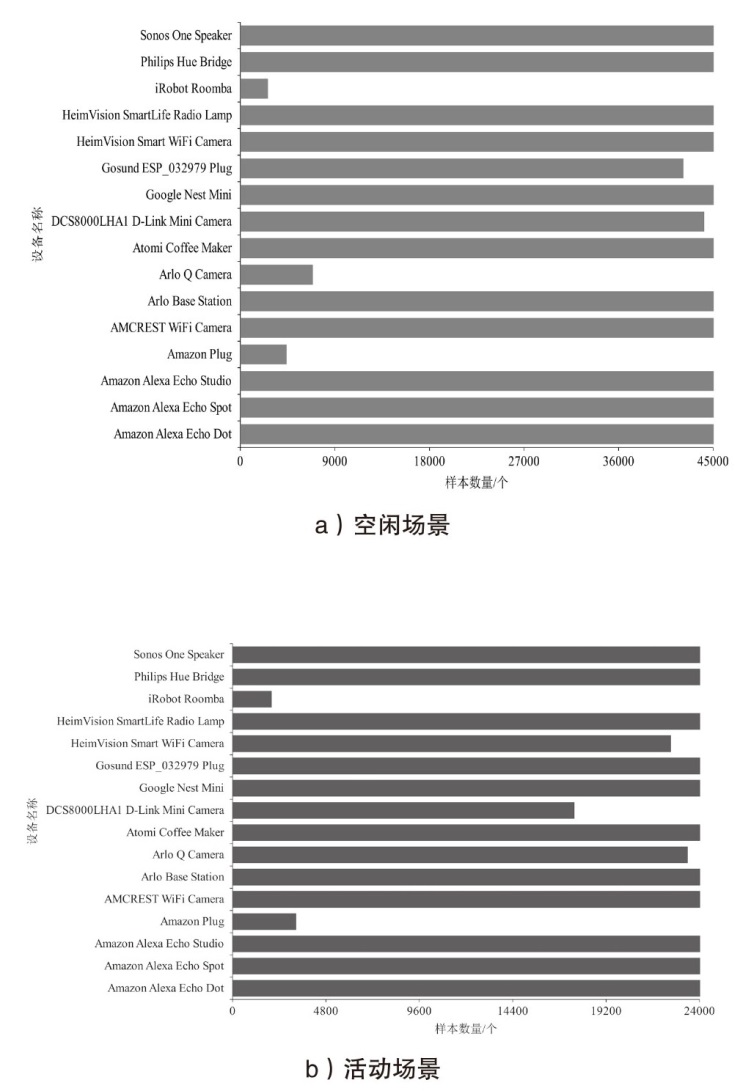
表3
CIC IoT中设备识别结果评估
| 设备名称 | CIC IoT Dataset(空闲场景) | CIC IoT Dataset(活动场景) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1-score | Precision | Recall | F1-score | |
| Amazon Alexa Echo Dot | 99.9% | 99.8% | 0.998 | 99.7% | 99.7% | 0.997 |
| Amazon Alexa Echo Spot | 99.5% | 99.8% | 0.996 | 99.5% | 99.5% | 0.995 |
| Amazon Alexa Echo Studio | 99.8% | 99.7% | 0.997 | 99.7% | 99.4% | 0.996 |
| Amazon Plug | 100% | 99.7% | 0.998 | 99.8% | 99.8% | 0.998 |
| AMCREST Wi-Fi Camera | 100% | 100% | 1 | 100% | 99.9% | 1 |
| Arlo Base Station | 99.9% | 100% | 1 | 99.8% | 99.9% | 0.999 |
| Arlo Q Camera | 99.9% | 99.6% | 0.997 | 99.9% | 99.9% | 0.999 |
| Atomi Coffee Maker | 100% | 100% | 1 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| DCS8000LHA1 D-Link Mini Camera | 100% | 100% | 1 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| Google Nest Mini | 100% | 100% | 1 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| Gosund ESP_032979 Plug | 100% | 100% | 1 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| HeimVision Smart Wi-Fi Camera | 100% | 99.9% | 1 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| HeimVision SmartLife Radio Lamp | 100% | 100% | 1 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| iRobot Roomba | 100% | 98.7% | 0.994 | 100% | 99.5% | 0.997 |
| Philips Hue Bridge | 100% | 100% | 0.1 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| Sonos One Speaker | 99.9% | 99.9% | 0.999 | 99.8% | 100% | 0.999 |
表4
物联网设备识别技术对比
| 识别方法 | 特征类型 | 数据集 | 评估指标 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoTSentinel | 数据分组头部字段 | Aalto | Accuracy | 81.5% |
| 文献[ | 流统计特征 | Aalto | F1-score | 0.903 |
| IoTDevID | 数据分组头部字段和有效载荷 | Aalto | Accuracy | 83.3% |
| UNSW | 94.3% | |||
| 文献[ | 流统计特征和协议字段 | UNSW | Accuracy | 98.4% |
| 文献[ | 流统计特征和流间特征 | CIC IoT(空闲场景) | Accuracy | 98.5% |
| CIC IoT(活动场景) | 98.9% | |||
| IoTBERT | 数据分组十六进制编码 | Aalto | Accuracy | 97.2% |
| F1-score | 0.915 | |||
| UNSW | Accuracy | 92.1% | ||
| CIC IoT(空闲场景) | Accuracy | 99.9% | ||
| CIC IoT(活动场景) | 99.8% |
| [1] | ROSEN M. Driving the Digital Agenda Requires Strategic Architec-ture[EB/OL]. (2015-04-22)[2024-02-11]. https://idc-cema.com/dwn/SF_177701. |
| [2] | Fortune Business Insights. IoT Market Size, Growth IoT Industry Report 2026[EB/OL]. (2019-01-01)[2024-02-11]. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/internet-of-things-iot-market-100307. |
| [3] | FENG Guangsheng, JIANG Shunpeng, HU Xianlang, et al. New Research Progress on Intrusion Detection Techniques for the Internet of Things[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 等. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. | |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiaolu, UPTON O, BEEBE N L, et al. IoT Botnet Forensics: A Comprehensive Digital Forensic Case Study on Mirai Botnet Servers[EB/OL]. (2020-04-12)[2024-02-11]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666281720300214. |
| [5] | LIU Yongxin, WANG Jian, LI Jianqiang, et al. Machine Learning for the Detection and Identification of Internet of Things Devices: A Survey[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(1): 298-320. |
| [6] | WU Hua, WU Qiuyan, CHENG Guang, et al. SFIM: Identify User Behavior Based on Stable Features[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2021, 14(6): 3674-3687. |
| [7] | ZHANG Haozhen, YU Le, XIAO Xi, et al. TFE-GNN: A Temporal Fusion Encoder Using Graph Neural Networks for Fine-Grained Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023. New York: ACM, 2023: 2066-2075. |
| [8] | ZENG Jun, WANG Ziwei, YU Yang, et al. Word Embedding Methods in Natural Language Processing: A Review[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2024, 18(1): 24-43. |
|
曾骏, 王子威, 于扬, 等. 自然语言处理领域中的词嵌入方法综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2024, 18(1): 24-43.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2303056 |
|
| [9] | DEVLIN J, CHANG Mingwei, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding[EB/OL]. (2018-10-12)[2024-02-11]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805v2. |
| [10] | LAN Zhenzhong, CHEN Mingda, GOODMAN S, et al. ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-Supervised Learning of Language Representations[EB/OL]. (2019-09-26)[2024-02-11]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942v6. |
| [11] | SENGUPTA S, GANGULY N, DE P, et al. Exploiting Diversity in Android TLS Implementations for Mobile App Traffic Classification[C]// ACM. The World Wide Web Conference. New York: ACM, 2019: 1657-1668. |
| [12] | HE Hongye, YANG Zhiguo, CHEN Xiangning. PERT: Payload Encoding Representation from Transformer for Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// IEEE. 2020 ITU Kaleidoscope:Industry-Driven Digital Transformation (ITU K). New York: IEEE, 2020: 111-118. |
| [13] | LIN Xinjie, XIONG Gang, GOU Gaopeng, et al. ET-BERT: A Contextualized Datagram Representation with Pre-Training Transformers for Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022. New York: ACM, 2022: 633-642. |
| [14] | MIETTINEN M, MARCHAL S, HAFEEZ I, et al. IoT SENTINEL: Automated Device-Type Identification for Security Enforcement in IoT[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS). New York: IEEE, 2017: 2177-2184. |
| [15] | HAMAD S A, ZHANG W E, SHENG Q Z, et al. IoT Device Identification via Network-Flow Based Fingerprinting and Learning[C]// IEEE. 2019 18th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications/13th IEEE International Conference on Big Data Science and Engineering (TrustCom/BigDataSE). New York: IEEE, 2019: 103-111. |
| [16] | SIVANATHAN A, GHARAKHEILI H H, LOI F, et al. Classifying IoT Devices in Smart Environments Using Network Traffic Characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 18(8): 1745-1759. |
| [17] | YIN Feihong, YANG Li, WANG Yuchen, et al. IoT ETEI: End-to-End IoT Device Identification Method[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE Conference on Dependable and Secure Computing (DSC). New York: IEEE, 2021: 1-8. |
| [18] | KOSTAS K, JUST M, LONES M A. IoTDevID: A Behavior-Based Device Identification Method for the IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(23): 23741-23749. |
| [19] | LI Zhihua, WANG Zhihao. IoT Device Identification Method Based on LCNN and LSTM Hybrid Structure[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(6): 43-54. |
| 李志华, 王志豪. 基于LCNN和LSTM混合结构的物联网设备识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 43-54. | |
| [20] | LUO Yantian, CHEN Xu, GE Ning, et al. Transformer-Based Device-Type Identification in Heterogeneous IoT Traffic[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(6): 5050-5062. |
| [21] | WANG Juan, ZHONG Jing, LI Jiangqi. IoT-Portrait: Automatically Identifying IoT Devices via Transformer with Incremental Learning[J]. Future Internet, 2023, 15(3): 102-115. |
| [22] | PENG Chuang, TAN Xiaobin, XIE Peng, et al. IoT Device Identification Base on Inter-Flow Correlation Analysis Using Graph Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2023 9th International Conference on Big Data Computing and Communications (BigCom). New York: IEEE, 2023: 24-31. |
| [23] |
REZAEI S, LIU Xin. Deep Learning for Encrypted Traffic Classification: An Overview[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(5): 76-81.
doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2019.1800819 |
| [24] | SENNRICH R, HADDOW B, BIRCH A. Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units[EB/OL]. (2015-08-31)[2024-02-11]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.07909v5. |
| [25] | HWANG R H, PENG Mingchun, NGUYEN V L, et al. An LSTM Based Deep Learning Approach for Classifying Malicious Traffic at the Packet Level[EB/OL]. (2019-08-19)[2024-02-11]. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163414. |
| [26] | HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| [27] | DADKHAH S, MAHDIKHANI H, DANSO P K, et al. Towards the Development of a Realistic Multidimensional IoT Profiling Dataset[C]// IEEE. 2022 19th Annual International Conference on Privacy, Security & Trust (PST). New York: IEEE, 2022: 1-11. |
| [28] | LOSHCHILOV I, HUTTER F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization[EB/OL]. (2017-11-14)[2024-02-11]. 1711.05101. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101v3. |
| [1] | 张晓均, 张楠, 郝云溥, 王周阳, 薛婧婷. 工业物联网系统基于混沌映射三因素认证与密钥协商协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1015-1026. |
| [2] | 任昌禹, 张玲, 姬航远, 杨立群. 基于预训练模型和中英文威胁情报的TTP识别方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1076-1087. |
| [3] | 李志华, 陈亮, 卢徐霖, 方朝晖, 钱军浩. 面向物联网Mirai僵尸网络的轻量级检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 667-681. |
| [4] | 杨杰超, 胡汉平, 帅燕, 邓宇昕. 基于时变互耦合双混沌系统的轻量级序列密码[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 385-397. |
| [5] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [6] | 翟鹏, 何泾沙, 张昱. 物联网环境下基于SM9算法和区块链技术的身份认证方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 179-187. |
| [7] | 王君艳, 伊鹏, 贾洪勇, 张建辉. 基于改进CAE的物联网终端风险评估模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 150-159. |
| [8] | 张伟, 李子轩, 徐晓瑀, 黄海平. SDP-CoAP:基于软件定义边界的安全增强CoAP通信框架设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 17-31. |
| [9] | 李志华, 王志豪. 基于LCNN和LSTM混合结构的物联网设备识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 43-54. |
| [10] | 郭瑞, 魏鑫, 陈丽. 工业物联网环境下可外包的策略隐藏属性基加密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 1-12. |
| [11] | 郇鑫焘, 缪凯焘, 陈稳, 吴畅帆. 基于自主舍弃与校准的鲁棒物联网设备无线密钥生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 17-26. |
| [12] | 宋丽华, 张津威, 张少勇. 基于博弈论对手建模的物联网SSH自适应蜜罐策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 38-47. |
| [13] | 廖丽云, 张伯雷, 吴礼发. 基于代价敏感学习的物联网异常检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 94-103. |
| [14] | 陈星任, 熊焰, 黄文超, 付贵禄. 一种基于静态分析的多视图硬件木马检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 48-57. |
| [15] | 刘翔宇, 芦天亮, 杜彦辉, 王靖翔. 基于特征选择的物联网轻量级入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(1): 66-72. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||