信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 1265-1276.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.08.012
面向多维属性融合的加权网络结构洞节点发现算法
- 1.重庆理工大学电气与电子工程学院,重庆 400054
2.天津大学智能与计算学部,天津 300072
3.重庆警察学院信息安全系,重庆 401331
-
收稿日期:2024-05-23出版日期:2024-08-10发布日期:2024-08-22 -
通讯作者:刘彦飞cqlyf@tju.edu.cn -
作者简介:王文涛(1998—),男,重庆,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为复杂网络建模与分析、数据挖掘、机器学习|刘彦飞(1985—),男,重庆,研究员,博士,主要研究方向为复杂网络建模与分析、数据挖掘、机器学习、知识图谱|毛博文(1980—),男,天津,正高级工程师,博士,主要研究方向为网络空间治理、公共安全知识工程|余成波(1965—),男,重庆,教授,博士,主要研究方向为信息传输与通信、自动化处理 -
基金资助:重庆市自然科学基金创新发展联合基金(CSTB2023NSCQ-LMX0014);重庆市教育委员会科学技术研究项目(KJZD-K202201701)
Weighted Network Structural Hole Node Discovery Algorithm for Multi-Dimensional Attribute Fusion
WANG Wentao1, LIU Yanfei1,2,3( ), MAO Bowen2, YU Chengbo1
), MAO Bowen2, YU Chengbo1
- 1. School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Technology, Chongqing 400054, China
2. College of Intelligence and Computing, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
3. Department of Information Security, Chongqing Police College, Chongqing 401331, China
-
Received:2024-05-23Online:2024-08-10Published:2024-08-22
摘要:
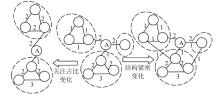
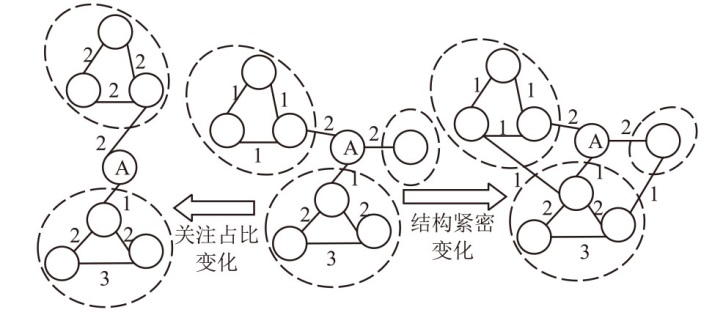
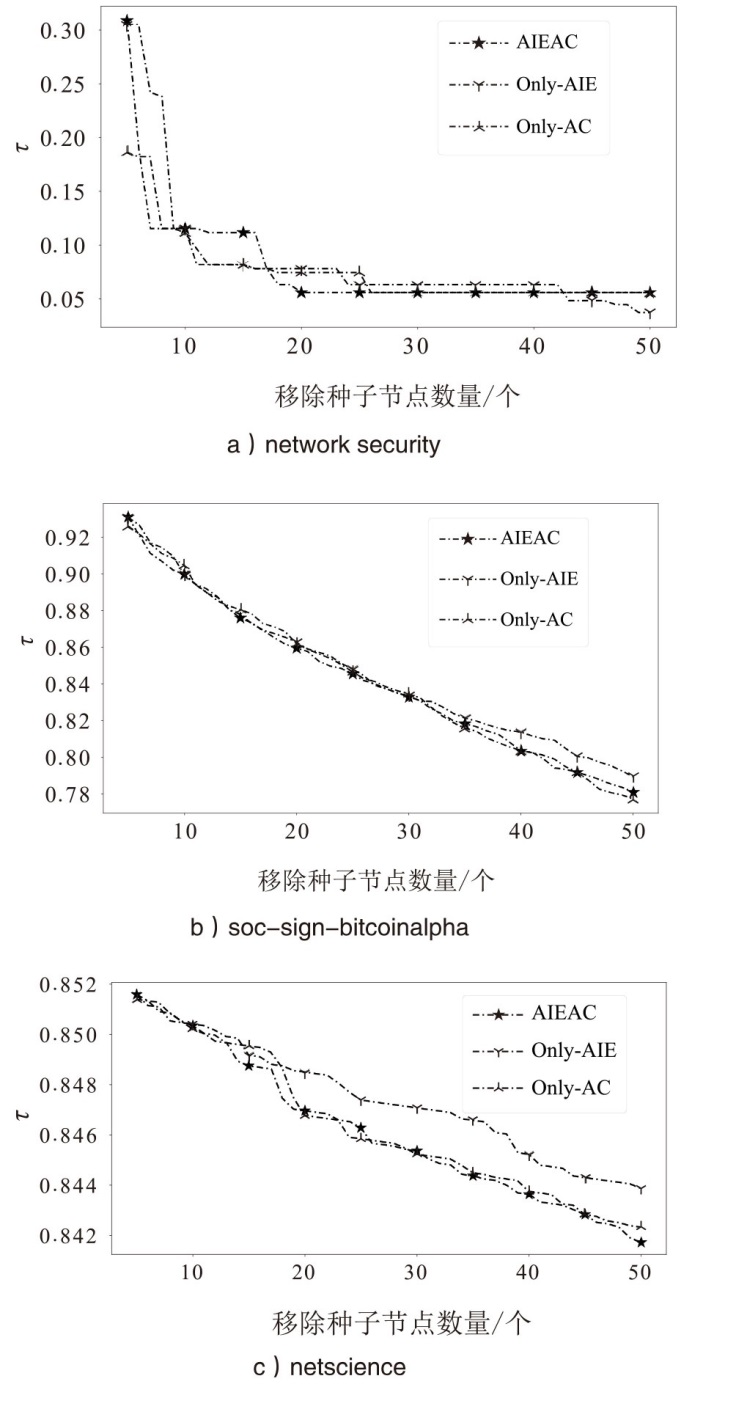
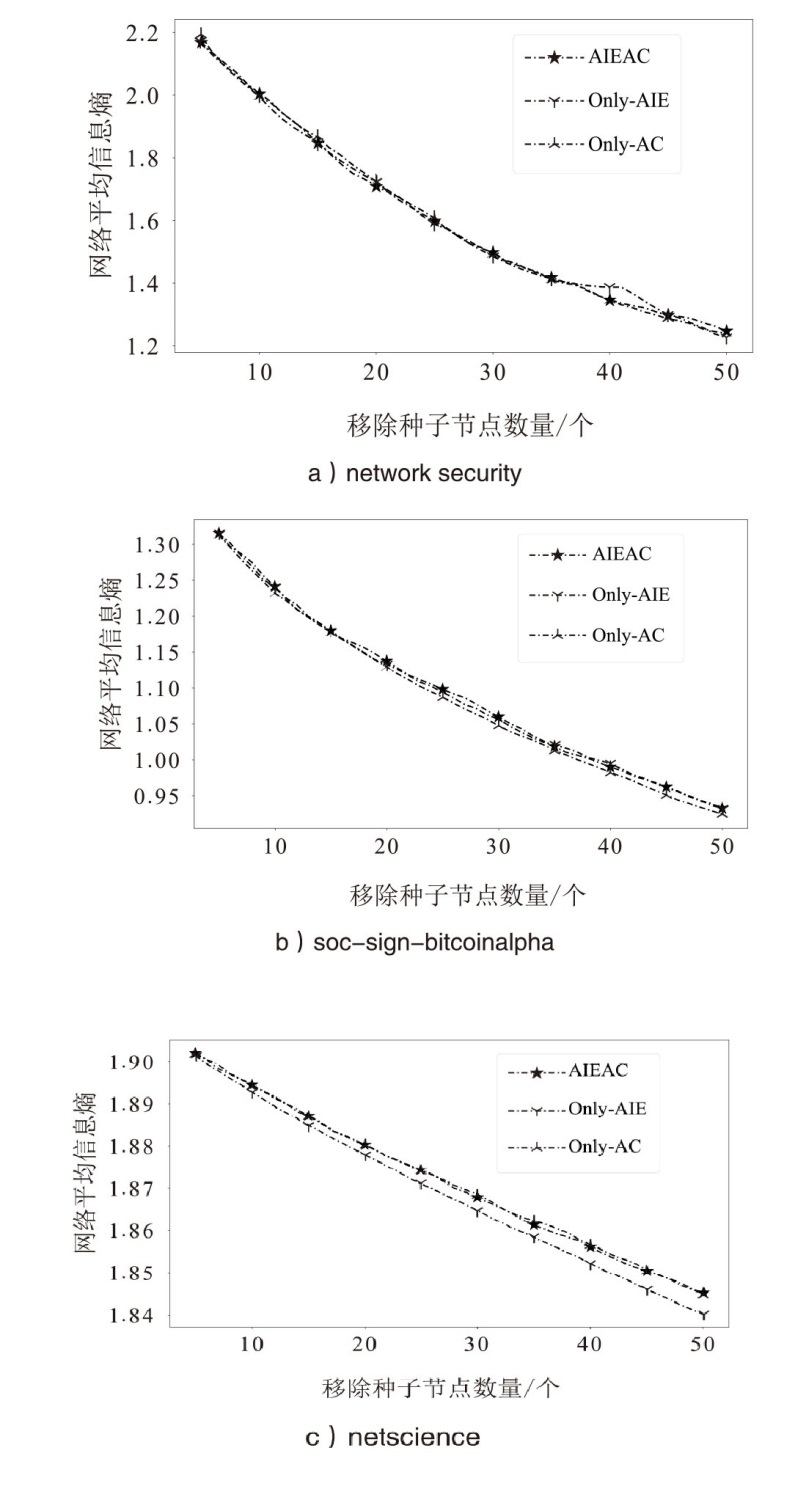
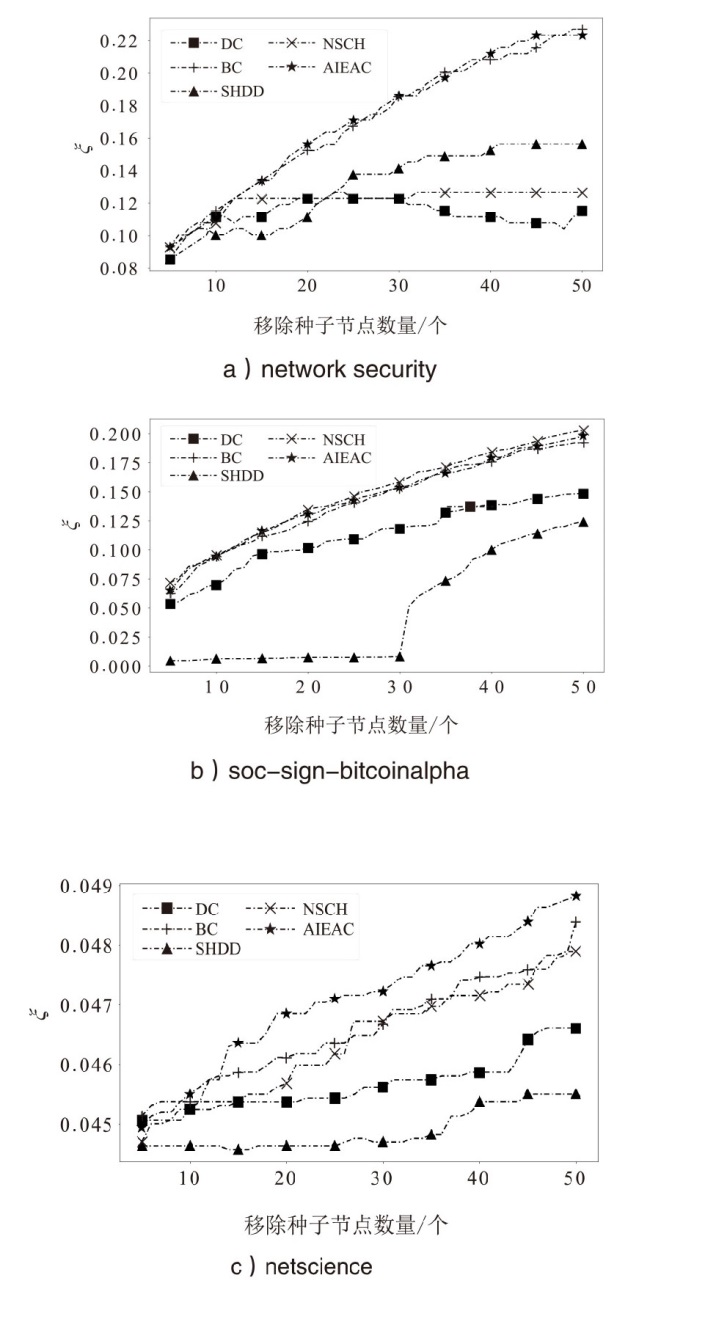
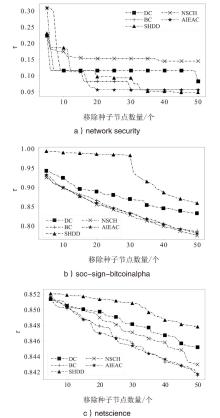
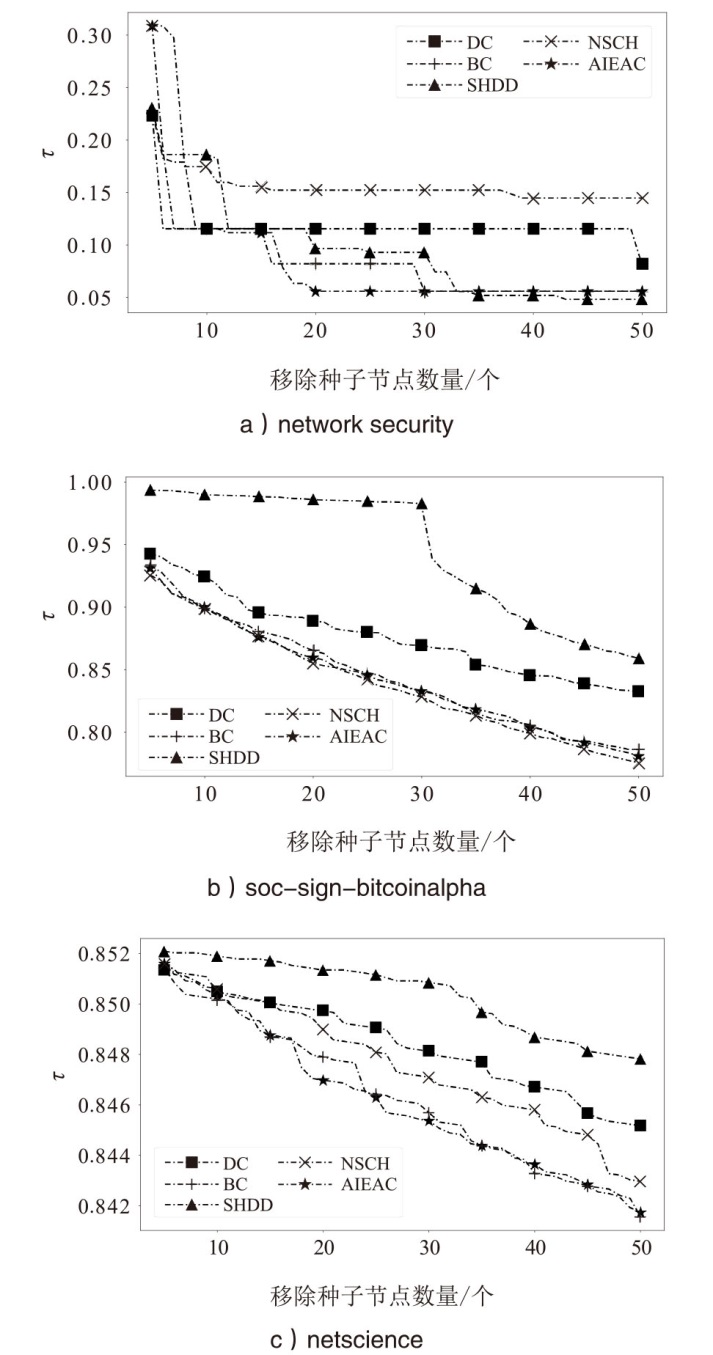
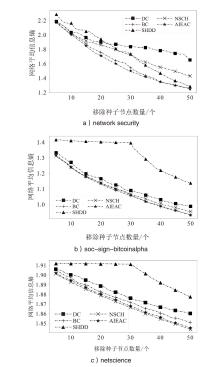
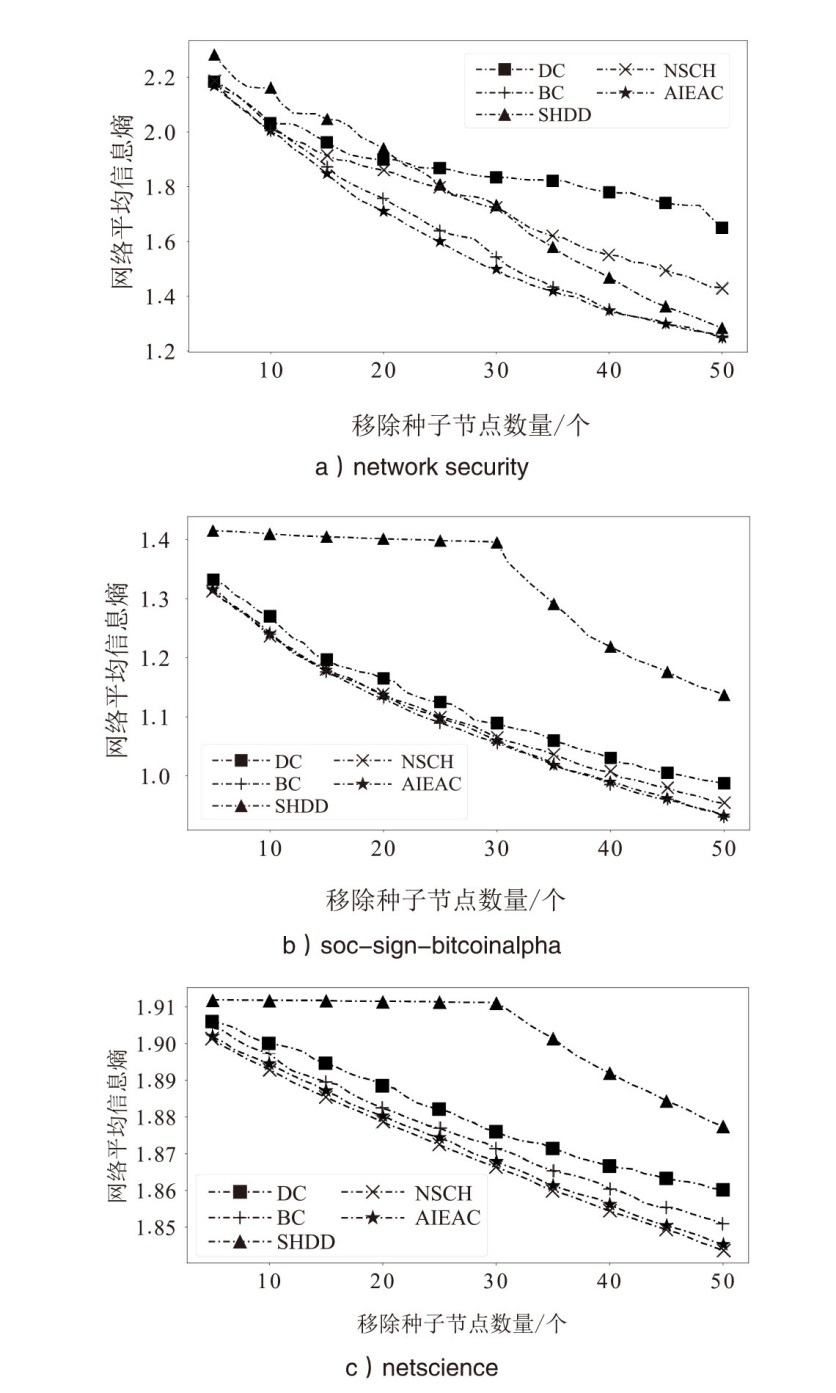
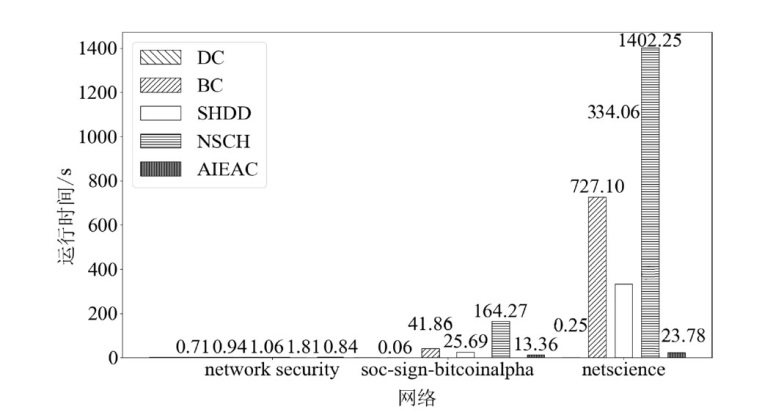
在大规模复杂网络空间中,快速识别结构洞节点对于病毒和舆情的传播控制具有重要意义。针对现有识别结构洞节点的方法在网络结构发生变化时,识别精度不高的问题,文章基于多维属性映射与融合,提出一种结合邻接信息熵与邻接中心性的结构洞节点识别算法。该算法将加权的邻接信息熵作为邻居节点的信息量,使用邻接中心性度量节点传播这些邻居节点信息量的重要性,通过将结构洞节点的局部属性表示为节点传播信息的能力,识别网络中的关键结构洞节点。实验结果表明,在不同网络规模和网络结构的数据集下,该算法的ξ、τ和网络平均信息熵3个评估指标的总得分分别为0.470、1.679和4.027,优于现有算法,具有更优越和稳定的性能,且将该算法应用于大规模网络中仍然具有较低的时间成本。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王文涛, 刘彦飞, 毛博文, 余成波. 面向多维属性融合的加权网络结构洞节点发现算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1265-1276.
WANG Wentao, LIU Yanfei, MAO Bowen, YU Chengbo. Weighted Network Structural Hole Node Discovery Algorithm for Multi-Dimensional Attribute Fusion[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1265-1276.
表2
不同算法性能对比
| 算法 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| network security | soc-sign-bitcoinalpha | netscience | |
| DC | 0.115 | 0.148 | 0.047 |
| BC | 0.226 | 0.192 | 0.048 |
| SHDD | 0.156 | 0.124 | 0.045 |
| NSCH | 0.126 | 0.203 | 0.048 |
| AIEAC | 0.223 | 0.198 | 0.049 |
| 算法 | |||
| network security | soc-sign-bitcoinalpha | netscience | |
| DC | 0.082 | 0.832 | 0.845 |
| BC | 0.056 | 0.786 | 0.842 |
| SHDD | 0.048 | 0.859 | 0.848 |
| NSCH | 0.144 | 0.776 | 0.843 |
| AIEAC | 0.056 | 0.781 | 0.842 |
| 算法 | 网络平均剩余信息熵 | ||
| network security | soc-sign-bitcoinalpha | netscience | |
| DC | 1.65 | 0.987 | 1.860 |
| BC | 1.25 | 0.933 | 1.851 |
| SHDD | 1.28 | 1.138 | 1.877 |
| NSCH | 1.43 | 0.954 | 1.844 |
| AIEAC | 1.25 | 0.932 | 1.845 |
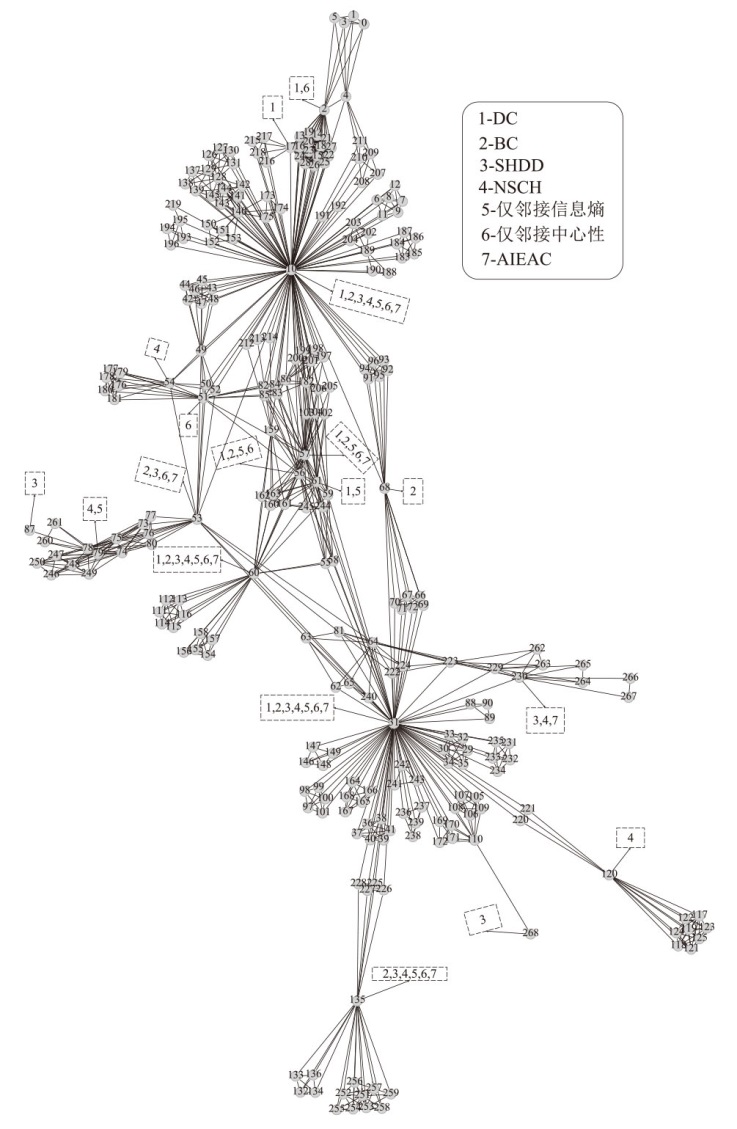
表3
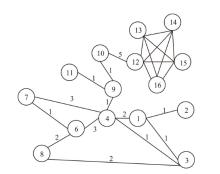
不同算法下top-8节点对比
| DC | BC | SHDD | NSCH | 仅邻接 信息熵 | 仅邻接 中心性 | AIEAC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | 值 | ID | 值 | ID | 值 | ID | 值 | ID | 值 | ID | 值 | ID | 值 |
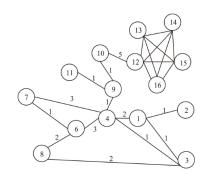
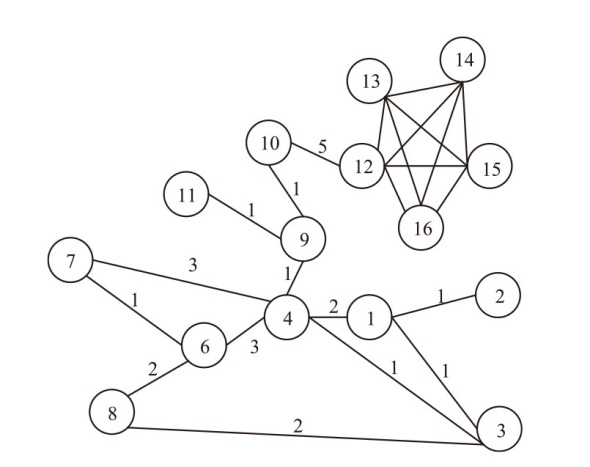
| 10 | 0.44 | 31 | 0.58 | 268 | 1 | 10 | 117 | 10 | 121.5 | 10 | 106.5 | 10 | 104.9 |
| 31 | 0.32 | 10 | 0.55 | 87 | 1 | 31 | 79 | 31 | 87.6 | 31 | 81.5 | 31 | 77.6 |
| 57 | 0.12 | 53 | 0.19 | 31 | 0.95 | 60 | 15 | 57 | 26.0 | 60 | 17.5 | 60 | 13.1 |
| 56 | 0.09 | 57 | 0.1 | 10 | 0.94 | 79 | 12 | 56 | 20.1 | 135 | 14.2 | 57 | 12.1 |
| 60 | 0.09 | 135 | 0.09 | 53 | 0.77 | 135 | 11 | 60 | 16.1 | 53 | 13 | 135 | 6.4 |
| 2 | 0.08 | 60 | 0.08 | 60 | 0.76 | 120 | 5 | 135 | 15.9 | 57 | 10.9 | 53 | 4.7 |
| 17 | 0.08 | 56 | 0.08 | 135 | 0.73 | 54 | 2 | 61 | 13.2 | 2 | 8.0 | 230 | 4.6 |
| 61 | 0.08 | 68 | 0.07 | 230 | 0.72 | 230 | 0 | 79 | 11.8 | 51 | 6.2 | 56 | 4.4 |
| [1] | ZHOU Jianlin, ZENG An, FAN Ying, et al. Identifying Important Scholars via Directed Scientific Collaboration Networks[J]. Scientometrics, 2018, 114: 1327-1343. |
| [2] | TIAN Zhao, JIA Limin, DONG Honghui, et al. Analysis of Urban Road Traffic Network Based on Complex Network[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 137: 537-546. |
| [3] | AL-TARAWNEH A, AL-SARAIREH J. Efficient Detection of Hacker Community Based on Twitter Data Using Complex Networks and Machine Learning Algorithm[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 40(6): 12321-12337. |
| [4] | TIAN Jiyang. Research on Detection of Suspicious Money Laundering Based on Complex Transaction Network[D]. Heifei: Heifei University of Technology, 2022. |
| 田继阳. 基于复杂交易网络的可疑洗钱行为识别方法研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2022. | |
| [5] | DUAN Pinsheng, ZHOU Jianliang, GOH Y M. Spatial-Temporal Analysis of Safety Risks in Trajectories of Construction Workers Based on Complex Network Theory[EB/OL]. [2024-02-10]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1474034623001180?via%3Dihub. |
| [6] | LI Ning, HUANG Qian, GE Xiaoyu, et al. A Review of the Research Progress of Social Network Structure[J]. Complexity, 2021(1): 1-14. |
| [7] | BURT R S. Structural Holes: The Social Structure of Competition[M]. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2009. |
| [8] |
ZHU Jiang, BAO Chongming, WANG Chongyun, et al. Discovery Algorithm for Top-k Structure Holes Based on Graph Structure Feature Analysis[J]. Computer Engineering, 2020, 46(5): 94-101, 108.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0054340 |
|
朱江, 包崇明, 王崇云, 等. 基于图结构特征分析的Top-k结构洞发现算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2020, 46(5): 94-101,108.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0054340 |
|
| [9] |
LI Minjia, XU Guoyan, ZHU Shuai, et al. Influence Maximization Algorithm Based on Structure Hole and Degree Discount[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2018, 38(12): 3419-3424.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018040920 |
|
李敏佳, 许国艳, 朱帅, 等. 基于结构洞和度折扣的影响力最大化算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2018, 38(12): 3419-3424.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018040920 |
|
| [10] | PENG Sancheng, ZHOU Yongmei, CAO Lihong, et al. Influence Analysis in Social Networks: A Survey[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2018, 106: 17-32. |
| [11] | SUN Xijing, SI Shoukui. Complex Network Algorithms and Applications[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2015. |
| 孙玺菁, 司守奎. 复杂网络算法与应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2015. | |
| [12] | LI Gang, WANG Yuda, CUI Rong. KIC: An Extended K-Shell Decomposition Based on Improved Network Constraint Cofficient[J]. Journal of Modern Information, 2020, 40(12): 27-35. |
|
李钢, 王聿达, 崔蓉. KiC:一种结合“结构洞”约束值与K壳分解的社交网络关键节点识别算法[J]. 现代情报, 2020, 40(12): 27-35.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0821.2020.12.003 |
|
| [13] | ZHAO Zhili, LI Ding, SUN Yue, et al. Ranking Influential Spreaders Based on Both Node K-Shell and Structural Hole[EB/OL]. (2023-01-25)[2024-02-10]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S095070512201259X?via%3Dihub. |
| [14] | WANG Hao, WANG Jian, LIU Qian, et al. Identifying Key Spreaders in Complex Networks Based on Local Clustering Coefficient and Structural Hole Information[EB/OL]. [2024-02-10]. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1367-2630/ad0e89. |
| [15] | BERAHMAND K, BOUYER A, SAMADI N. A New Centrality Measure Based on The Negative and Positive Effects of Clustering Coefficient for Identifying Influential Spreaders in Complex Networks[J]. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals: The Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, and Nonequilibrium and Complex Phenomena, 2018, 110: 41-54. |
| [16] |
YANG Jie, ZHANG Mingyang, RUI Xiaobin, el al. Influence Maximization Algorithm Based on Node Coverage and Structural Hole[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(4): 1155-1161.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021071256 |
|
杨杰, 张名扬, 芮晓彬, 等. 融合节点覆盖范围和结构洞的影响力最大化算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(4): 1155-1161.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021071256 |
|
| [17] | GAO Juyuan, WANG Zhixiao, RUI Xiaobin, el al. Node Coverage Based on Algorithm for Influence Maximization[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2019, 40(8): 2211-2215, 2246. |
| 高菊远, 王志晓, 芮晓彬, 等. 基于节点覆盖范围的影响力最大化算法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2019, 40(8): 2211-2215,2246. | |
| [18] | ZHAO Linhai, LI Yingjie, WU Y J. An Identification Algorithm of Systemically Important Financial Institutions Based on Adjacency Information Entropy[J]. Computational Economics, 2022, 59(4): 1735-1753. |
| [19] | HUANG Wencheng, LI Haoran, YIN Yanhui, et al. Node Importance Identification of Unweighted Urban Rail Transit Network: An Adjacency Information Entropy Based Approach[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2024(2): 1-16. |
| [20] | XU Xiang, ZHU Cheng, WANG Qingyong, et al. Identifying Vital Nodes in Complex Networks by Adjacency Information Entropy[EB/OL]. (2020-02-14)[2024-03-10]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32060330/. |
| [21] | KUMAR S, SPEZZANO F, SUBRAHMANIAN V S, et al. Edge Weight Prediction in Weighted Signed Networks[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining(ICDM). New York: IEEE, 2016: 221-230. |
| [22] | KUMAR S, HOOI B, MAKHIJA D, et al. Rev2: Fraudulent User Prediction in Rating Platforms[C]// ACM. The Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2018: 333-341. |
| [23] | NEWMAN M E. Finding Community Structure in Networks Using The Eigenvectors of Matrices[J]. Physical Review E-Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2006, 74(3): 6104-6126. |
| [24] | LI Peng, WANG Shilin, CHEN Guangwu, et al. Identifying Key Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Local Structural Entropy and Clustering Coefficient[EB/OL]. (2022-08-30)[2024-02-10]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2022/8928765. |
| [25] | LU Mengke. Node Importance Evaluation Based on Neighborhood Structure Hole and Improved TOPSIS[EB/OL]. (2020-05-30)[2024-02-10]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S138912861931031X. |
| [1] | 秦元庆, 董泽阳, 韩汶君. 一种基于任务和可信等级的数控网络跨域互操作方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1143-1151. |
| [2] | 杜晔, 田晓清, 李昂, 黎妹红. 基于改进鲸鱼算法优化SVM的软件缺陷检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1152-1162. |
| [3] | 夏辉, 钱祥运. 基于特征空间相似的隐形后门攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1163-1172. |
| [4] | 许楷文, 周翊超, 谷文权, 陈晨, 胡晰远. 基于多尺度特征融合重建学习的深度伪造人脸检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1173-1183. |
| [5] | 徐茹枝, 张凝, 李敏, 李梓轩. 针对恶意软件的高鲁棒性检测模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [6] | 郭倩, 赵津, 过弋. 基于分层聚类的个性化联邦学习隐私保护框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1196-1209. |
| [7] | 张兴兰, 李登祥. 基于Grover量子搜索算法的MD5碰撞攻击模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1210-1219. |
| [8] | 孙中岫, 彭诚, 范伟. 基于无证书签名的5G系统广播消息身份认证协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1220-1230. |
| [9] | 陈昊然, 刘宇, 陈平. 基于大语言模型的内生安全异构体生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1231-1240. |
| [10] | 郭钰铮, 郭春, 崔允贺, 李显超. 基于随机博弈网的窃密木马诱导式博弈模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1241-1251. |
| [11] | 赵伟, 任潇宁, 薛吟兴. 基于集成学习的成员推理攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1252-1264. |
| [12] | 邢长友, 王梓澎, 张国敏, 丁科. 基于预训练Transformers的物联网设备识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1277-1290. |
| [13] | 吕秋云, 周凌飞, 任一支, 周士飞, 盛春杰. 一种全生命周期可控的公共数据共享方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1291-1305. |
| [14] | 黄旺旺, 周骅, 王代强, 赵麒. 基于国密SM9的物联网可重构密钥安全认证协议设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1006-1014. |
| [15] | 张晓均, 张楠, 郝云溥, 王周阳, 薛婧婷. 工业物联网系统基于混沌映射三因素认证与密钥协商协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1015-1026. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||