信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 667-681.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.05.002
面向物联网Mirai僵尸网络的轻量级检测方法
- 1.江南大学人工智能与计算机学院,无锡 214122
2.湖南博匠信息科技有限公司,长沙 410073
3.江南大学物联网工程学院,无锡 214122
-
收稿日期:2024-03-05出版日期:2024-05-10发布日期:2024-06-24 -
通讯作者:李志华 E-mail:jswxzhli@aliyun.com -
作者简介:李志华(1969—),男,湖南,教授,博士,主要研究方向为云、边、端关键技术及信息安全|陈亮(1994—),男,江苏,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为深度学习、信息安全|卢徐霖(1999—),男,江苏,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全|方朝晖(1968—),男,湖南,高级工程师,主要研究方向为高性能通信指挥系统、国产操作系统、信息设备自主可控技术及安全|钱军浩(1969—),男,江苏,副教授,主要研究方向为农业物联网、智能水环境治理与监控、智能标识技术与应用和大数据分析与深度学习 -
基金资助:工业和信息化部智能制造项目(ZH-XZ-180004);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(JUSRP211A41);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(JUSRP42003)
Lightweight Detection Method for IoT Mirai Botnet
LI Zhihua1( ), CHEN Liang1, LU Xulin1, FANG Zhaohui2, QIAN Junhao3
), CHEN Liang1, LU Xulin1, FANG Zhaohui2, QIAN Junhao3
- 1. School of Artificial Intelligence and Computer, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China
2. Hunan Bojiang Information Technology Co., Ltd., Changsha 410073, China
3. School of Internet of Things Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China
-
Received:2024-03-05Online:2024-05-10Published:2024-06-24 -
Contact:LI Zhihua E-mail:jswxzhli@aliyun.com
摘要:
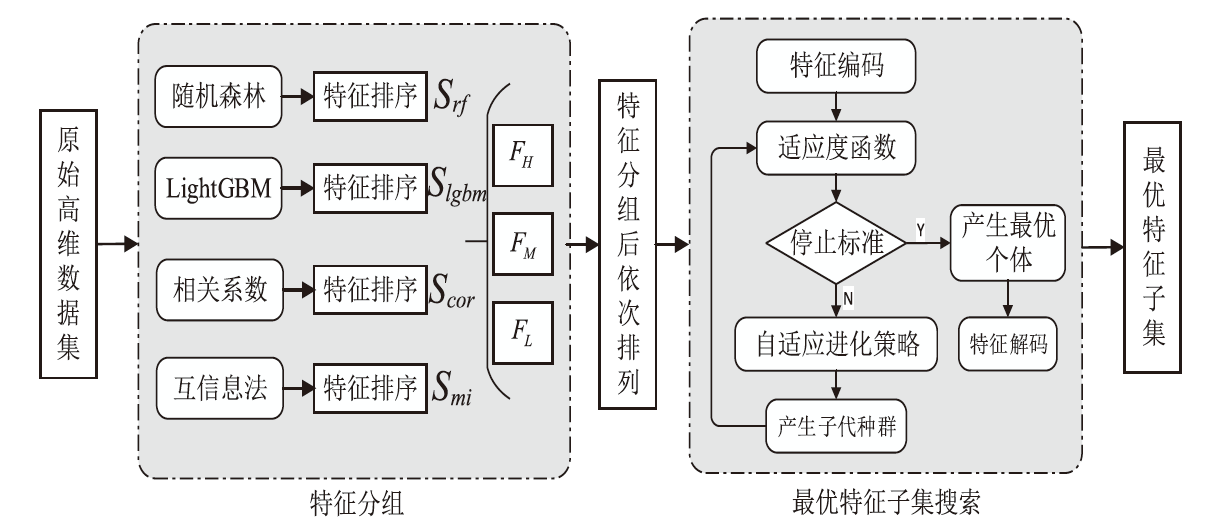
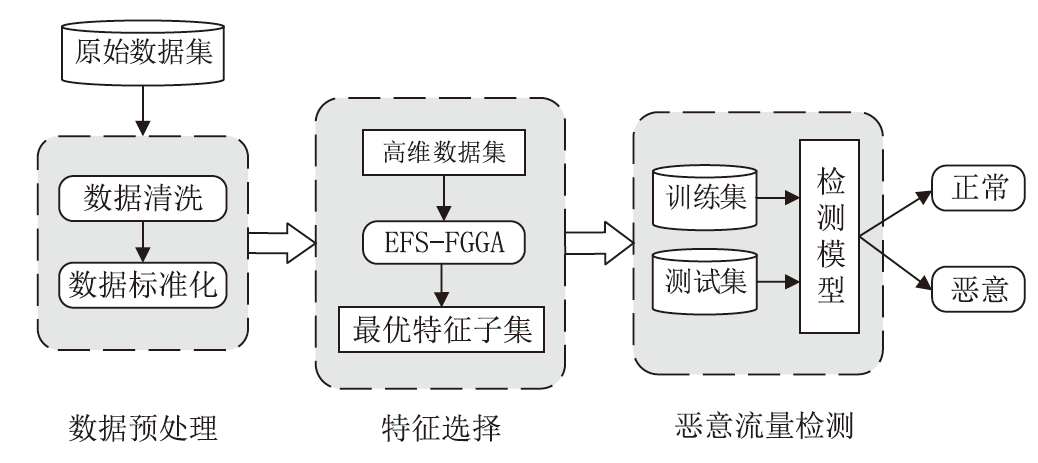
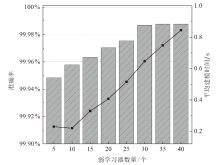
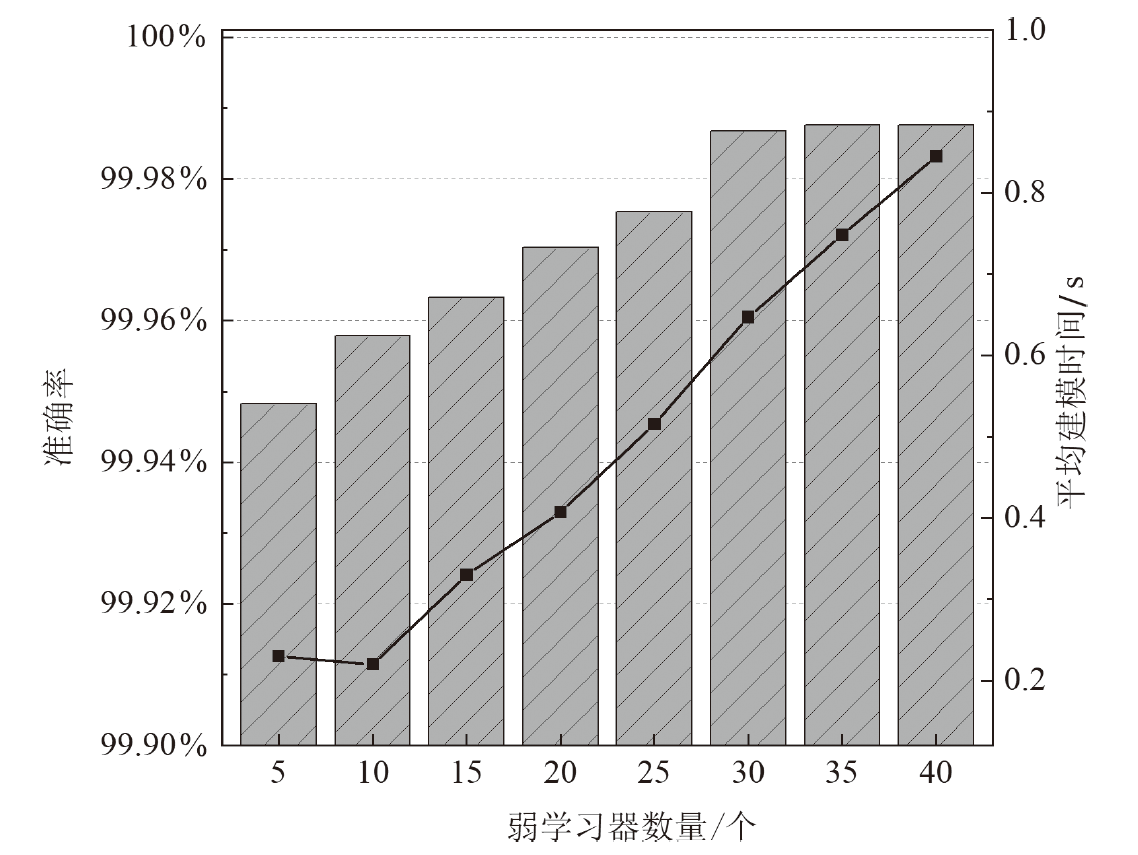
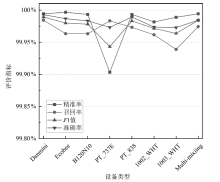
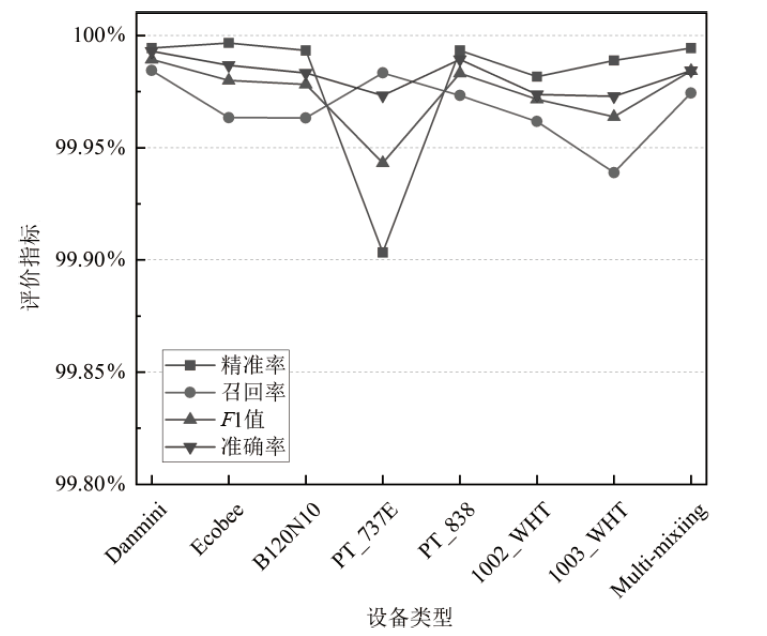
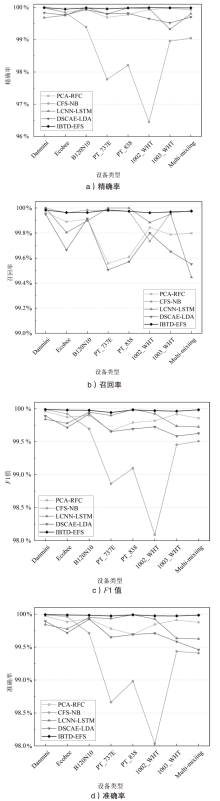
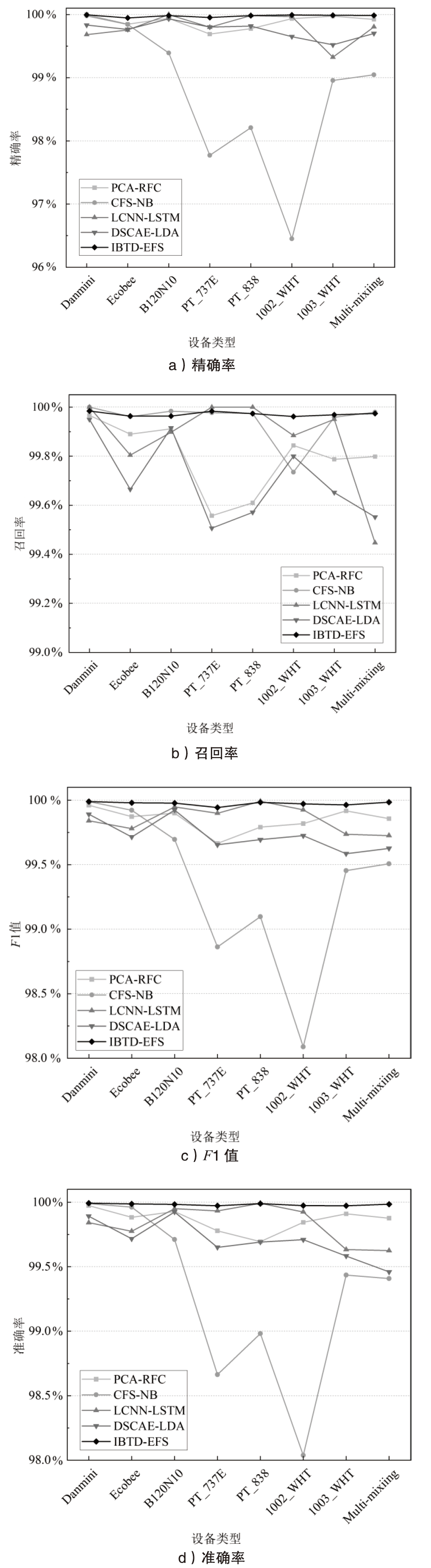
针对物联网Mirai僵尸网络流量数据的高维度和大规模数据导致传统检测方法存在检测时间长、资源消耗大和准确性欠佳的不足,文章提出了一种基于集成特征选择的物联网僵尸网络流量检测(IoT Botnet Traffic Detection Based on Ensemble Feature Selection,IBTD-EFS)方法。首先,为了降低网络流量数据样本的特征维度以便获取最优特征子集,文章提出了一种基于特征分组和遗传算法相结合的集成特征选择(Ensemble Feature Selection Based on Feature Group and Genetic Algorithm,EFS-FGGA)算法;然后,为了高效地检测Mirai僵尸网络流量,提出了基于极限梯度提升的物联网僵尸网络流量分类(IoT Botnet Traffic Classification Based on eXtreme Gradient Boosting,IBTC-XGB)算法;最后,联合上述算法,进一步提出了物联网僵尸网络流量检测IBTD-EFS方法。实验结果表明,IBTD-EFS方法能屏蔽物联网设备的异构性,对Mirai僵尸网络流量检测达到99.95%的准确率,而且保持了较低的时间开销。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李志华, 陈亮, 卢徐霖, 方朝晖, 钱军浩. 面向物联网Mirai僵尸网络的轻量级检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 667-681.
LI Zhihua, CHEN Liang, LU Xulin, FANG Zhaohui, QIAN Junhao. Lightweight Detection Method for IoT Mirai Botnet[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(5): 667-681.
| [1] | STATISTA R D. Internet of Things-Number of Connected Devices Worldwide 2012-2025[EB/OL]. (2016-11-27)[2024-02-02]. https://www.statista.com/statistics/471264/iot-number-of-connected-devices-worldwide/. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Ye, LI Zhihua, WANG Changjie. Kernel Density Estimation-Based Lightweight IoT Anomaly Traffic Detection Method[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(9): 337-344.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.200600108 |
|
张叶, 李志华, 王长杰. 基于核密度估计的轻量级物联网异常流量检测方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(9): 337-344.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.200600108 |
|
| [3] | ANTONAKAKIS M, APRIL T, BAILEY M, et al. UnderStanding the Mirai Botnet[C]// USENIX. 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17). Berkeley: USENIX, 2017: 1093-1110. |
| [4] | SHOBANA M, RATHI S. IoT Malware: An Analysis of IoT Device Hijacking[J]. International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 5: 2456-3307. |
| [5] | KHAN A, SHARMA I. Tackling Okiru Attacks in IoT with AI-Driven Detection and Mitigation Strategies[C]// IEEE. 2023 International Conference on Power Energy, Environment & Intelligent Control (PEEIC). New York: IEEE, 2023: 336-341. |
| [6] | ABBAS S G, HASHMAT F, SHAH G A, et al. Generic Signature Development for IoT Botnet Families[EB/OL]. (2021-09-01)[2024-02-25]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2666281721001323. |
| [7] | BLAISE A, BOUET M, CONAN V, et al. Detection of Zero-Day Attacks: An Unsupervised Port-Based Approach[EB/OL]. (2020-10-01)[2024-02-25]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1389128620300761. |
| [8] | PANDA M, ABD ALLAH A M, HASSANIEN A E. Developing an Efficient Feature Engineering and Machine Learning Model for Detecting IoT-Botnet Cyber Attacks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 91038-91052. |
| [9] | SAFITRI W A, AHMAD T, HOSTIADI D P. Analyzing Machine Learning-Based Feature Selection for Botnet Detection[C]// IEEE. 2022 1st International Conference on Information System & Information Technology (ICISIT). New York: IEEE, 2022: 386-391. |
| [10] | LEFOANE M, GHAFIR I, KABIR S, et al. Machine Learning for Botnet Detection: An Optimized Feature Selection Approach[C]// ACM. The 5th International Conference on Future Networks & Distributed Systems. New York: ACM, 2022: 195-200. |
| [11] | NIMBALKAR P, KSHIRSAGAR D. Feature Selection for Intrusion Detection System in Internet-of-Things (IoT)[J]. ICT Express, 2021, 7(2): 177-181. |
| [12] | BAHSI H, NOMM S, TORRE F B L. Dimensionality Reduction for Machine Learning Based IoT Botnet Detection[C]// IEEE. 2018 15th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV). New York: IEEE, 2018: 1857-1862. |
| [13] | GUERRA M A, BAHSI H, NOMM S. Hybrid Feature Selection Models for Machine Learning Based Botnet Detection in IoT Networks[C]// IEEE. 2019 International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW). New York: IEEE, 2019: 324-327. |
| [14] | SHAFIQ M, TIAN Zhihong, BASHIR A K, et al. CorrAUC: A Malicious Bot-IoT Traffic Detection Method in IoT Network Using Machine-Learning Techniques[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 8(5): 3242-3254. |
| [15] | LEE J, PARK D, LEE C. Feature Selection Algorithm for Intrusions Detection System Using Sequential forward Search and Random Forest Classifier[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems (TIIS), 2017, 11(10): 5132-5148. |
| [16] | ALAM T, QAMARS, DIXIT A, et al. Genetic Algorithm: Reviews, Implementations, and Applications[EB/OL]. (2020-06-05)[2024-02-25]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.12673. |
| [17] | LIU Xiangyu, DU Yanhui. Towards Effective Feature Selection for IoT Botnet Attack Detection Using a Genetic Algorithm[EB/OL]. (2023-02-07)[2024-02-25]. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/12/5/1260. |
| [18] | DESAI M G, SHI Yong, SUO Kun. IoT Bonet and Network Intrusion Detection Using Dimensionality Reduction and Supervised Machine Learning[C]// IEEE. 2020 11th IEEE Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON). New York: IEEE, 2020: 316-322. |
| [19] | SOE Y N, FENG Yaokai, SANTOSA P I, et al. Machine Learning-Based IoT-Botnet Attack Detection with Sequential Architecture[EB/OL]. (2020-08-05)[2024-02-25]. https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/20/16/4372. |
| [20] | ALSHEHRI M S, AHMAD J, ALMAKDI S, et al. SkipGateNet: A Lightweight CNN-LSTM Hybrid Model with Learnable Skip Connections for Efficient Botnet Attack Detection in IoT[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12(12): 35521-35538. |
| [21] | LUU C D, NGUYEN V Q, PHAM T S, et al. A Zero-Shot Deep Learning Approach for Unknown IoT Botnet Attack Detection[C]// IEEE. 2023 RIVF International Conference on Computing and Communication Technologies (RIVF). New York: IEEE, 2023: 278-283. |
| [22] | XU Zhaozhao, SHEN Derong, NIE Tiezheng, et al. Hybrid Feature Selection Algorithm Combining Information Gain Ratio and Genetic Algorithm[J]. Journal or Software, 2022, 33(3): 1128-1140. |
| 许召召, 申德荣, 聂铁铮, 等. 融合信息增益比和遗传算法的混合式特征选择算法[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(3): 1128-1140. | |
| [23] |
PAUL A, MUKHERJEE D P, DAS P, et al. Improved Random Forest for Classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(8): 4012-4024.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2834830 pmid: 29993742 |
| [24] | KE Guolin, MENG Qi, FINLEY T, et al. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree[EB/OL]. (2017-12-04)[2024-02-25]. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/hash/6449f44a102fde848669bdd9eb6b76fa-Abstract.html. |
| [25] | GOPIKA N, ME A M K. Correlation Based Feature Selection Algorithm for Machine Learning[C]// IEEE. 2018 3rd International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES). New York: IEEE, 2018: 692-695. |
| [26] | VERGARA J R, ESTEVEZ P A. A Review of Feature Selection Methods Based on Mutual Information[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2014, 24: 175-186. |
| [27] | LYU Yang, FENG Yaokai, SAKURAI K. A Survey on Feature Selection Techniques Based on Filtering Methods for Cyber Attack Detection[EB/OL]. (2023-03-15)[2024-02-25]. https://www.mdpi.com/2078-2489/14/3/191. |
| [28] | HUANG C L, WANG C J. A GA-Based Feature Selection and Parameters Optimization for Support Vector Machines[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2006, 31(2): 231-240. |
| [29] | ALEJANDRE F V, CORTES N C, ANAYA E A. Feature Selection to Detect Botnets Using Machine Learning Algorithms[C]// IEEE. 2017 International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Computers (CONIELECOMP). New York: IEEE, 2017: 1-7. |
| [30] | WIYONO R T, CAHYANI N D W. Performance Analysis of Decision Tree C4.5 as a Classification Technique to Conduct Network Forensics for Botnet Activities in Internet of Things[C]// IEEE. 2020 International Conference on Data Science and Its Applications (ICoDSA). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-5. |
| [31] | IFTIKHAR S, AL-MADANI D, ABDULLAH S, et al. A Supervised Feature Selection Method for Malicious Intrusions Detection in IoT Based on Genetic Algorithm[J]. International Journal of Computer Science & Network Security, 2023, 23(3): 49-56. |
| [32] | AN Ting. Application of Genetic Algorithm Based on F-Ratio Rule in Signal Feature Selection[C]// IEEE. 2017 10th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID). New York: IEEE, 2017: 492-495. |
| [33] | LI Juan. A Feature Subset Selection Algorithm Based on Feature Activity and Improved GA[C]// IEEE. 2015 11th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security (CIS). New York: IEEE, 2015: 206-210. |
| [34] | ABDI H, WILLIAMS L J. Normalizing Data[J]. Encyclopedia of Research Design, 2010, 1: 935-938. |
| [35] | CHEN Tianqi, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM,2016: 785-794. |
| [36] | HAN Lu, LI Wenjun, SU Zhi. An Assertive Reasoning Method for Emergency Response Management Based on Knowledge Elements C4.5 Decision Tree[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 122: 65-74. |
| [37] | MEIDAN Y, BOHADANA M, MATHOV Y, et al. N-Baiot—Network-Based Detection of IoT Botnet Attacks Using Deep Autoencoders[J]. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 2018, 17(3): 12-22. |
| [1] | 顾国民, 陈文浩, 黄伟达. 一种基于多模型融合的隐蔽隧道和加密恶意流量检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 694-708. |
| [2] | 屠晓涵, 张传浩, 刘孟然. 恶意流量检测模型设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 520-533. |
| [3] | 徐子荣, 郭焱平, 闫巧. 基于特征恶意度排序的恶意软件对抗防御模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| [4] | 钟静, 方冰, 朱江. 基于稀疏矩阵结构的特征选择算法现状研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 352-362. |
| [5] | 杨杰超, 胡汉平, 帅燕, 邓宇昕. 基于时变互耦合双混沌系统的轻量级序列密码[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 385-397. |
| [6] | 张强, 何俊江, 李汶珊, 李涛. 基于深度度量学习的异常流量检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 462-472. |
| [7] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [8] | 翟鹏, 何泾沙, 张昱. 物联网环境下基于SM9算法和区块链技术的身份认证方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 179-187. |
| [9] | 王君艳, 伊鹏, 贾洪勇, 张建辉. 基于改进CAE的物联网终端风险评估模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 150-159. |
| [10] | 张伟, 李子轩, 徐晓瑀, 黄海平. SDP-CoAP:基于软件定义边界的安全增强CoAP通信框架设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 17-31. |
| [11] | 刘宇啸, 陈伟, 张天月, 吴礼发. 基于稀疏自动编码器的可解释性异常流量检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 74-85. |
| [12] | 李志华, 王志豪. 基于LCNN和LSTM混合结构的物联网设备识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 43-54. |
| [13] | 郭瑞, 魏鑫, 陈丽. 工业物联网环境下可外包的策略隐藏属性基加密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 1-12. |
| [14] | 彭诚, 范伟, 朱大立, 杨芬. 基于加权贝叶斯分类器的LTE接入网中间人攻击检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 1-10. |
| [15] | 郇鑫焘, 缪凯焘, 陈稳, 吴畅帆. 基于自主舍弃与校准的鲁棒物联网设备无线密钥生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 17-26. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||