信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (8): 66-75.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.08.006
基于对抗性机器学习的网络入侵检测方法研究
- 西北工业大学深圳研究院,深圳 518057
-
收稿日期:2023-01-19出版日期:2023-08-10发布日期:2023-08-08 -
通讯作者:郭森森 E-mail:guosensen@mail.nwpu.edu.cn -
作者简介:沈华(1982—),男,甘肃,高级工程师,博士研究生,主要研究方向为网络空间安全|田晨(1998—),男,陕西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络空间安全|郭森森(1990—),男,河南,博士,主要研究方向为网络空间安全、对抗机器学习|慕志颖(1994—),女,山东,博士研究生,主要研究方向为数据挖掘和社交网络舆论对抗 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62272389)
Research on Adversarial Machine Learning-Based Network Intrusion Detection Method
SHEN Hua, TIAN Chen, GUO Sensen( ), MU Zhiying
), MU Zhiying
- Shenzhen Research Institute of Northwestern Polytechnical University, Shenzhen 518057, China
-
Received:2023-01-19Online:2023-08-10Published:2023-08-08 -
Contact:GUO Sensen E-mail:guosensen@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
摘要:
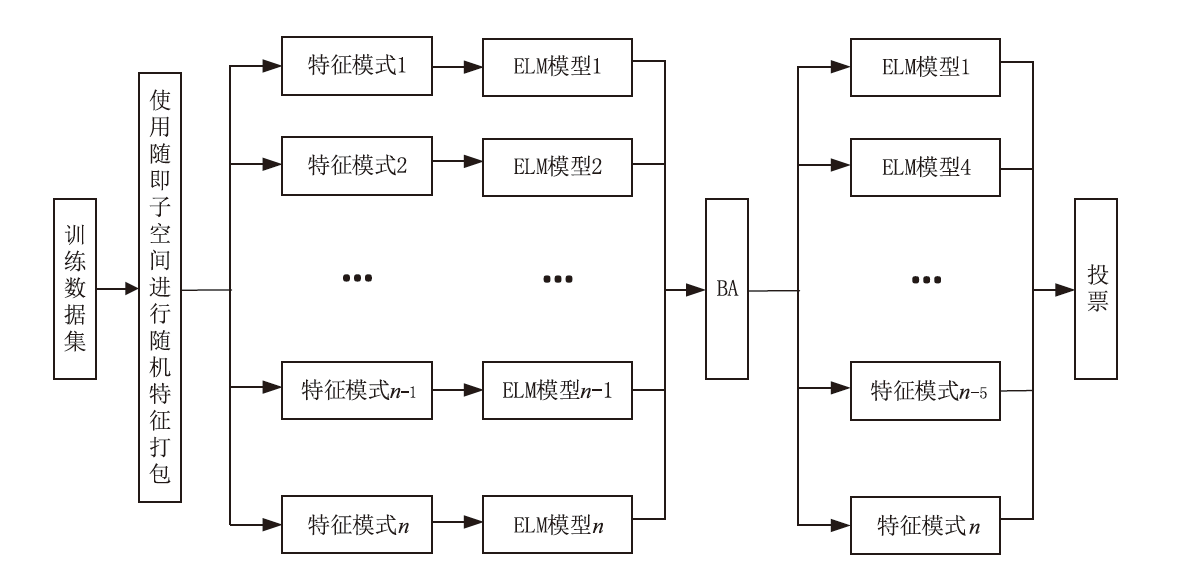
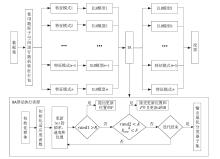
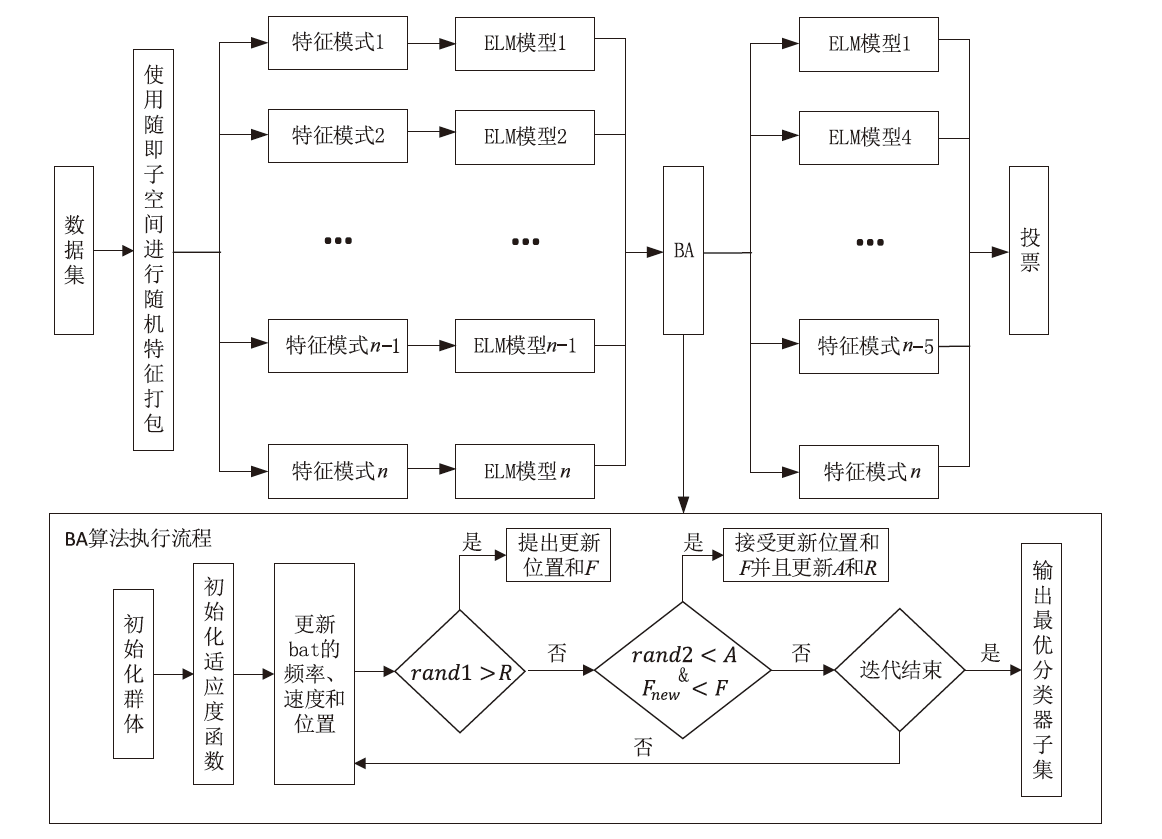
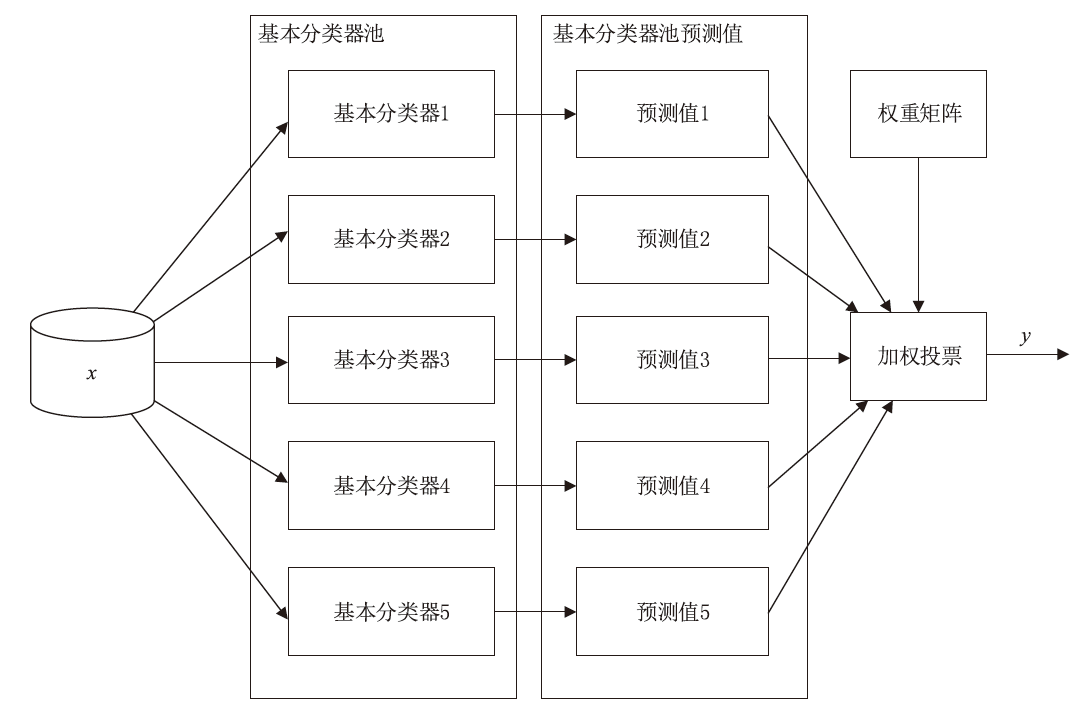
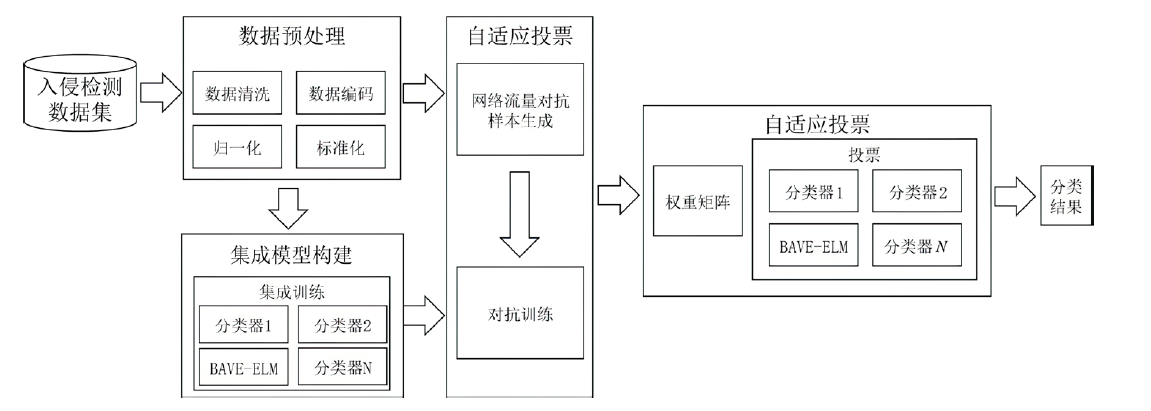
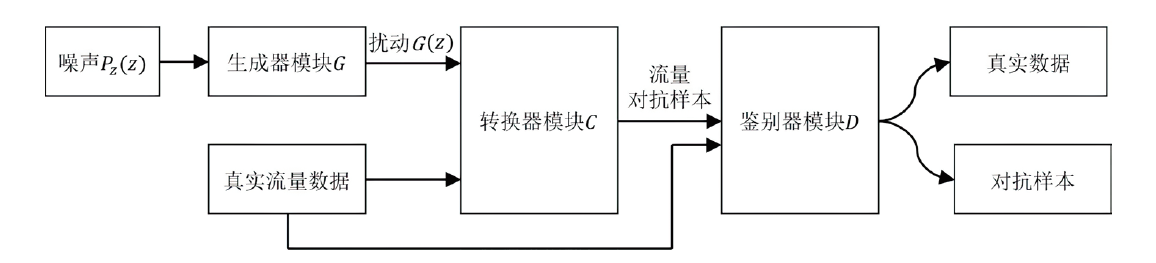
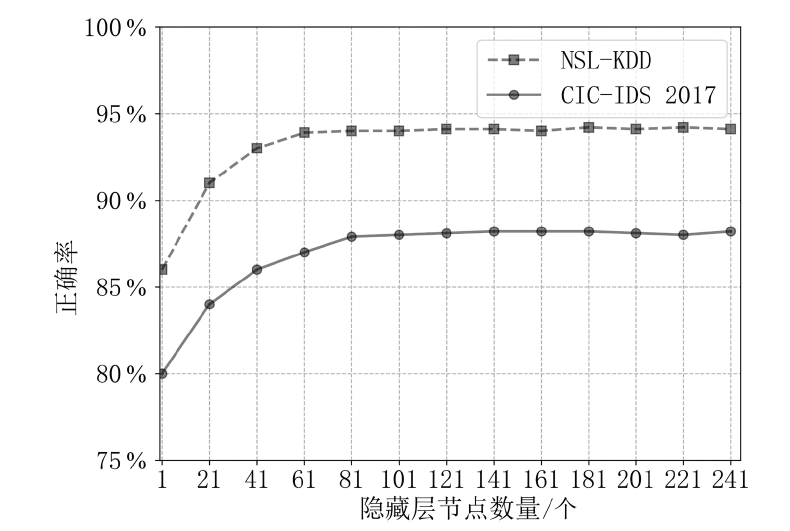
网络攻击数据中攻击类别多样、数量分布不均等问题,导致现有基于机器学习的网络入侵检测模型对部分攻击类型的泛化能力较弱,并且由于深度学习模型容易受到对抗样本的攻击,使得深度学习模型在网络入侵检测方面的应用存在诸多约束。对此,文章首先提出了基于随机子空间的入侵检测模型—BAVE-ELM(Bat Algorithm Voting Ensemble Extreme Learning Machines),该方法较好地平衡了模型的泛化能力和虚警率;然后,以BAVE-ELM作为一种基分类器,提出了一种基于自适应集成的网络入侵检测系统(Ensemble Adaptive Network Intrusion Detection System,EA-NIDS),通过集成多种类型的机器学习模型,显著提高了检测模型针对各种攻击类型的泛化能力;最后,文章提出了基于对抗性机器学习的网络入侵检测方法,通过在EA-NIDS中引入对抗训练,显著提升了模型在对抗样本攻击下的鲁棒性。实验结果表明,文章所提出的方法有效提高了网络入侵检测的检测性能以及泛化性,并且在不影响模型准确率的前提下,可显著提升基于机器学习的网络入侵检测模型在对抗性环境中的鲁棒性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
沈华, 田晨, 郭森森, 慕志颖. 基于对抗性机器学习的网络入侵检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 66-75.
SHEN Hua, TIAN Chen, GUO Sensen, MU Zhiying. Research on Adversarial Machine Learning-Based Network Intrusion Detection Method[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 66-75.
表2
不同算法在CIC-IDS2017数据集上的性能
| 算法 | Acc | FPR | DR | Cost | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 决策树 | 87.92 % | 1.96 % | 87.35 % | 4.04 % | 45.82 % |
| 随机森林 | 88.48 % | 2.32 % | 89.52 % | 4.82 % | 53.43 % |
| KNN | 86.36 % | 3.04 % | 86.84 % | 5.94 % | 92.61 % |
| 支持向量机 | 81.29 % | 3.84 % | 83.07 % | 10.62 % | 2006.31 % |
| Adaboost | 83.47 % | 6.93 % | 81.49 % | 8.72 % | 559.47 % |
| LR | 78.36 % | 2.59 % | 80.04 % | 6.82 % | 76.88 % |
| DNN | 89.36 % | 0.81 % | 88.17 % | 2.04 % | 316.14 % |
| BAVE-ELM | 89.15 % | 1.03 % | 89.74 % | 2.92 % | 150.68 % |
表3
各模型在CIC-IDS2017数据集和NSL-KDD数据集上的性能
| 数据集 | NSL-KDD | CIC-IDS2017 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 指标 | Acc | FPR | DR | Cost | Acc | FPR | DR | Cost |
| EA-NIDS | 96.84 % | 0.39 % | 96.83 % | 1.31 % | 92.67 % | 1.64 % | 93.07 % | 2.85 % |
| BAVE-ELM | 95.54 % | 0.84 % | 94.08 % | 2.39 % | 89.15 % | 1.93 % | 89.74 % | 3.92 % |
| ELM-KNN[ | 90.37 % | 2.91 % | 88.43 % | 8.47 % | 84.33 % | 4.63 % | 85.54 % | 13.51 % |
| CNN[ | 89.18 % | 2.88 % | 89.76 % | 8.97 % | 81.48 % | 3.21 % | 80.72 % | 11.29 % |
| LSSVMIDS[ | 83.69 % | 4.36 % | 81.31 % | 20.35 % | 74.08 % | 4.84 % | 75.97 % | 17.14 % |
| NB Tree[ | 78.04 % | 10.09 % | 79.47 % | 40.09 % | 65.14 % | 9.06 % | 67.88 % | 35.82 % |
表4
EA-NIDS模型对各类型攻击的检测准确率
| 算法 | BENIGN | DoS | Brute Force SSH | Botnet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 决策树 | 96.51 % | 88.43 % | 5.96 % | 1.91 % |
| 随机森林 | 95.17 % | 86.86 % | 2.82 % | 2.93 % |
| KNN | 96.49 % | 87.18 % | 20.58 % | 6.72 % |
| 支持向量机 | 96.06 % | 79.37 % | 13.72 % | 1.86 % |
| Adaboost | 93.68 % | 80.64 % | 3.94 % | 3.04 % |
| BAVE-ELM | 97.06 % | 87.69 % | 50.6 % | 46.87 % |
| LR | 90.48 % | 79.91 % | 2.06 % | 1.48 % |
| DNN | 93.92 % | 87.35 % | 32.75 % | 9.07 % |
| EA-NIDS | 96.36 % | 87.04 % | 60.93 % | 63.42 % |
| [1] | IMRAN M, HAIDER N, SHOAIB M, et al. An Intelligent and Efficient Network Intrusion Detection System Using Deep Learning[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2022, 99: 764-772. |
| [2] | DIXIT P, SILAKARI S. Deep Learning Algorithms for Cybersecurity Applications: A Technological and Status Review[J]. Computer Science Review, 2021, 39: 317-328. |
| [3] |
SARANYA T, SRIDEVI S, DEISY C, et al. Performance Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms in Intrusion Detection System: A Review[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 171: 1251-1260.
doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2020.04.133 URL |
| [4] |
INJADAT M N, MOUBAYED A, NASSIF A B, et al. Machine Learning Towards Intelligent Systems: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2021, 54: 3299-3348.
doi: 10.1007/s10462-020-09948-w |
| [5] |
FARNAAZ N, JABBAR M. Random Forest Modeling for Network Intrusion Detection System[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 89: 213-217.
doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.06.047 URL |
| [6] |
JIANG Hui, HE Zheng, YE Gang, et al. Network Intrusion Detection Based on PSO-XGBoost Model[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 58392-58401.
doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639 URL |
| [7] |
WISANWANICHTHAN T, THAMMAWICHAI M. A Double-Layered Hybrid Approach for Network Intrusion Detection System Using Combined Naive Bayes and SVM[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 138432-138450.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3118573 URL |
| [8] | YANG Junzheng, LIU Feng, ZHAO YuanJie, et al. An Ensemble Learning Based Non-Intrusive Network Security Risk Assessment Prediction Model[C]//IEEE. 2022 7th IEEE International Conference on Data Science in Cyberspace (DSC). New York: IEEE, 2022: 17-23. |
| [9] |
RING M, WUNDERLICH S, SCHEURING D, et al. A Survey of Network-Based Intrusion Detection Data Sets[J]. Computers & Security, 2019, 86: 147-167.
doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2019.06.005 URL |
| [10] | VOROBEYCHIK Y, KANTARCIOGLU M. Adversarial Machine Learning[J]. Synthesis Lectures on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, 2018, 12(3): 160-169. |
| [11] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[C]//ICLR. The 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations. New York: ICLR, 2014: 189-201. |
| [12] | GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[C]//ICLR. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. New York: ICLR, 2015: 371-384. |
| [13] | CARLINI N, WAGNER D. Towards Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2017: 39-57. |
| [14] | MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, FROSSARD P. Deepfool:A Simple and Accurate Method to Fool Deep Neural Networks[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 2574-2582. |
| [15] | DONG Yingpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting Adversarial Attacks with Momentum[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 9185-9193. |
| [16] | MARDRY A, MAKELOV A, SCHMIDT L, et al. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks[C]// ICLR. The 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. New York: ICLR, 2018: 211-220. |
| [17] | MOGHADDASI S S, FARAJI N. A Hybrid Algorithm Based on Particle Filter and Genetic Algorithm for Target Tracking[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 147: 188-199. |
| [18] |
LIU Feng, WANG Hanyang, Zhang Jiaohao, et al. EvoGAN: An Evolutionary Computation Assisted GAN[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 469: 81-90.
doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.10.060 URL |
| [19] | FERRAG M A, MAGLARAS L, MOSCHOYIANNIS S, et al. Deep Learning for Cyber Security Intrusion Detection: Approaches, Datasets, and Comparative Study[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2020, 50: 419-430. |
| [20] |
LATAH M, TOKER L. An Efficient Flow-Based Multi-Level Hybrid Intrusion Detection System for Software-Defined Networks[J]. CCF Transactions on Networking, 2020, 3(3-4): 261-271.
doi: 10.1007/s42045-020-00040-z |
| [21] |
WU Kehe, CHEN Zuge, LI Wei. A Novel Intrusion Detection Model for a Massive Network Using Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 50850-50859.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2868993 URL |
| [22] |
AMBUSAIDI MA, HE XiangJian, NANDA P, et al. Building an Intrusion Detection System Using a Filter-Based Feature Selection Algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(10): 2986-2998.
doi: 10.1109/TC.2016.2519914 URL |
| [1] | 李晨蔚, 张恒巍, 高伟, 杨博. 基于AdaN自适应梯度优化的图像对抗迁移攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 64-73. |
| [2] | 蒋曾辉, 曾维军, 陈璞, 武士涛. 面向调制识别的对抗样本研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 74-90. |
| [3] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王斌君, 翟晗名. 融合对抗增强和多任务优化的恶意短信检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 21-30. |
| [4] | 胡卫, 赵文龙, 陈璐, 付伟. 基于Logits向量的JSMA对抗样本攻击改进算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 62-69. |
| [5] | 郑耀昊, 王利明, 杨婧. 基于网络结构自动搜索的对抗样本防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 70-77. |
| [6] | 夏强, 何沛松, 罗杰, 刘嘉勇. 基于普遍对抗噪声的高效载体图像增强算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 64-75. |
| [7] | 张郅, 李欣, 叶乃夫, 胡凯茜. 融合多重风格迁移和对抗样本技术的验证码安全性增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 129-135. |
| [8] | 于克辰, 郭莉, 姚萌萌. 基于空间及能量维度的黑盒对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 72-78. |
| [9] | 仝鑫, 王罗娜, 王润正, 王靖亚. 面向中文文本分类的词级对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 12-16. |
| [10] | 李红娇, 陈红艳. 基于WGAN的移动恶意对抗样本生成研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(11): 51-58. |
| [11] | 饶绪黎, 徐彭娜, 陈志德, 许力. 基于不完全信息的深度学习网络入侵检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(6): 53-60. |
| [12] | 魏书宁, 陈幸如, 焦永, 王进. AR-OSELM算法在网络入侵检测中的应用研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(6): 1-6. |
| [13] | 杨晶, 赵鑫, 芦天亮. 基于logs2intrusions与Web Log Explorer的综合取证分析研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(3): 33-38. |
| [14] | 程晋;严承华;樊攀星. 基于RBR和CBR的网络入侵检测系统模型[J]. , 2013, 13(7): 0-0. |
| [15] | 陈斌. 构建安全可靠的网络入侵检测系统[J]. , 2010, (5): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||