信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (10): 21-30.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.10.004
融合对抗增强和多任务优化的恶意短信检测方法
- 1.中国人民公安大学信息网络安全学院,北京 100038
2.公安部第三研究所,上海 200031
-
收稿日期:2023-05-06出版日期:2023-10-10发布日期:2023-10-11 -
通讯作者:金波 E-mail:jinbo@gass.cn -
作者简介:仝鑫(1995—),男,河南,博士研究生,CCF会员,主要研究方向为网络空间安全和自然语言处理|金波(1972—),男,上海,研究员,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为网络空间安全|王斌君(1962—),男,北京,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为人工智能安全|翟晗名(1997—),女,河北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为自然语言处理
A Malicious SMS Detection Method Blending Adversarial Enhancement and Multi-Task Optimization
TONG Xin1, JIN Bo1,2( ), WANG Binjun1, ZHAI Hanming1
), WANG Binjun1, ZHAI Hanming1
- 1. School of Information Network Security, Beijing 100038, China
2. The Third Research Institute of Ministry of Public Security, Shanghai 200031, China
-
Received:2023-05-06Online:2023-10-10Published:2023-10-11
摘要:
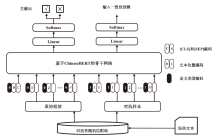
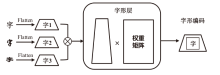
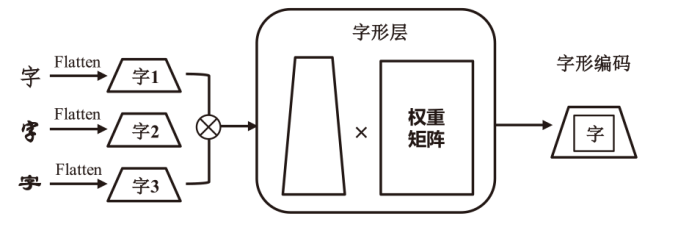
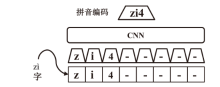
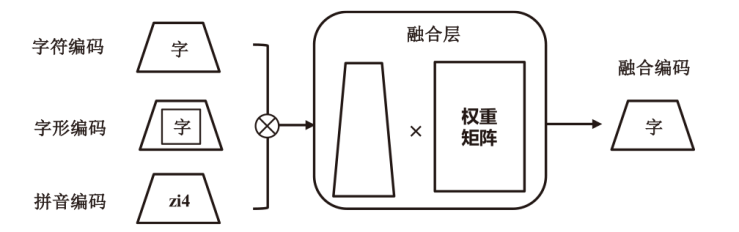
现有恶意短信检测方法往往聚焦于提升检测准确率或速度,而忽略了模型自身的安全问题,因此,在真实场景中可能会遭受对抗样本攻击。为了解决上述问题,文章提出了一种融合对抗增强和多任务优化的恶意短信检测模型。在输入阶段,利用随机匹配池生成“原始文本-对抗样本”对作为输入,并且引入语义类型编码技术帮助模型区分数据边界。然后,使用基于ChineseBERT的单塔神经网络作为主干模型对短信的语义、拼音和字形特征进行挖掘。在输出阶段,使用监督的分类交叉熵损失和无监督的输入一致性损失作为多任务优化目标,以帮助模型学习文本对内在的关联特征并完成分类。基于公开数据集的实验结果表明,该方法的准确率和鲁棒性优于多种机器学习和深度学习检测方法。
中图分类号:
引用本文
仝鑫, 金波, 王斌君, 翟晗名. 融合对抗增强和多任务优化的恶意短信检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 21-30.
TONG Xin, JIN Bo, WANG Binjun, ZHAI Hanming. A Malicious SMS Detection Method Blending Adversarial Enhancement and Multi-Task Optimization[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(10): 21-30.
表3
基于常规短信数据集的检测效果对比
| 方法 | 模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 机器 学习 | NB | 95.28% | 93.07% | 97.84% | 95.40% |
| DT | 94.14% | 94.09% | 94.20% | 94.14% | |
| RF | 95.86% | 97.75% | 93.88% | 95.78% | |
| SVM | 96.16% | 99.57% | 92.72% | 96.02% | |
| KNN | 85.22% | 95.88% | 73.60% | 83.28% | |
| 深度 学习 | Word-TextCNN | 97.26% | 99.87% | 94.64% | 97.19% |
| Word-BiLSTM | 97.48% | 99.62% | 95.32% | 97.42% | |
| Char-TextCNN | 96.64% | 98.58% | 94.64% | 96.57% | |
| Char -BiLSTM | 96.14% | 96.01% | 96.28% | 96.15% | |
| BERT | 98.60% | 99.31% | 97.88% | 98.59% | |
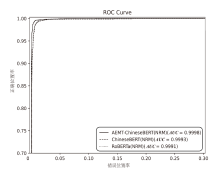
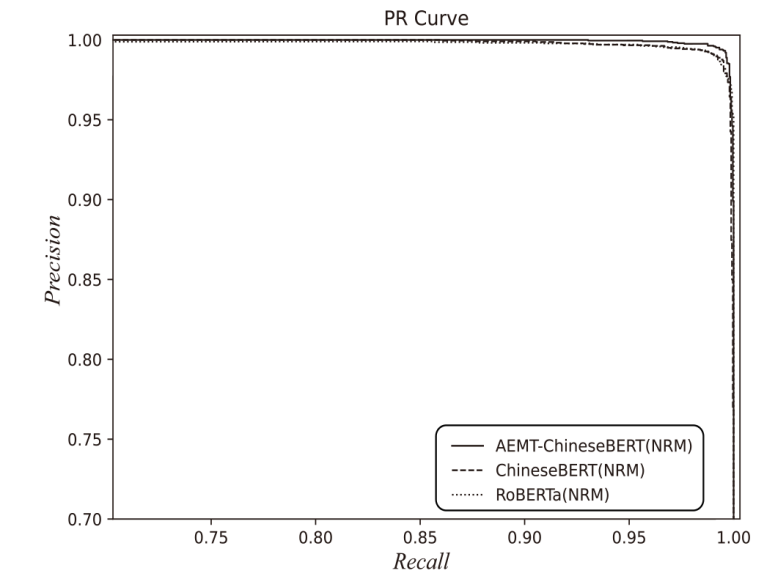
| RoBERTa | 99.02% | 99.16% | 98.88% | 99.02% | |
| XLNet | 98.34% | 97.34% | 99.40% | 98.36% | |
| ChineseBERT | 99.12% | 98.77% | 99.48% | 99.12% | |
| AEMT-ChineseBERT | 99.42% | 99.52% | 99.32% | 99.42% |
表4
基于对抗性短信数据集的检测效果对比
| 方法 | 模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 机器 学习 | NB | 88.46% | 83.33% | 96.16% | 89.29% |
| DT | 78.06% | 91.98% | 61.48% | 73.70% | |
| RF | 77.52% | 97.25% | 56.64% | 71.59% | |
| SVM | 80.18% | 98.96% | 61.00% | 75.48% | |
| KNN | 76.18% | 94.86% | 55.36% | 69.92% | |
| 深度 学习 | Word-TextCNN | 63.76% | 100.0% | 27.52% | 43.16% |
| Word-BiLSTM | 64.58% | 100.0% | 29.16% | 45.15% | |
| Char-TextCNN | 91.14% | 98.31% | 83.72% | 90.43% | |
| Char -BiLSTM | 90.54% | 96.47% | 84.16% | 89.90% | |
| BERT | 92.24% | 96.89% | 87.28% | 91.84% | |
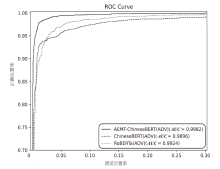
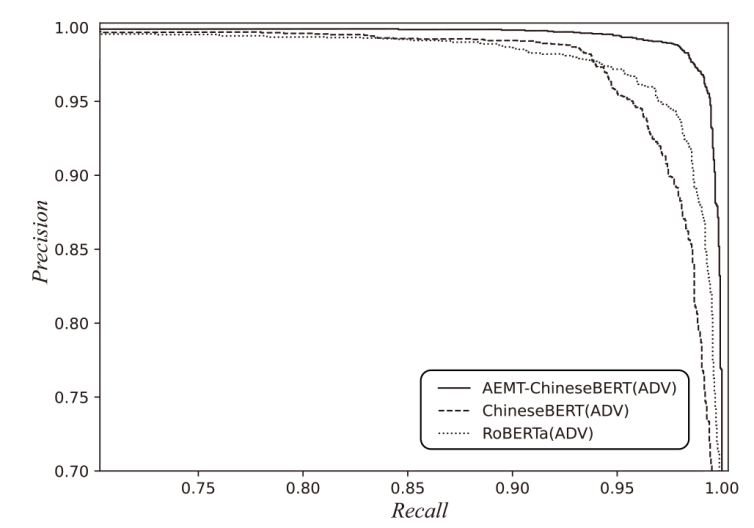
| RoBERTa | 95.38% | 98.13% | 92.52% | 95.24% | |
| XLNet | 94.02% | 92.47% | 95.84% | 94.13% | |
| ChineseBERT | 95.88% | 98.64% | 93.04% | 95.76% | |
| AEMT-ChineseBERT | 98.18% | 98.98% | 97.36% | 98.16% |
表5
消融实验结果
| 部分 | 细节 | Ori.Acc | Adv.Acc | Decrease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 99.42% | 98.18% | 1.24% | |
| 模型输入 | AEMT-ChineseBERT w/o TE | 下降0.40% | 下降0.56% | 上升0.16% |
| AEMT-ChineseBERT w NA | 下降0.36% | 下降1.24% | 上升0.88% | |
| AEMT-ChineseBERT w AN | 下降0.52% | 下降0.84% | 上升0.32% | |
| 训练目标 | AEMT-ChineseBERT w/o MT | 下降0.66% | 下降1.36% | 上升0.70% |
| Adv-ChineseBERT | 下降0.78% | 下降1.50% | 上升0.72% | |
| 主干网络 | AEMT-RoBERTa | 下降0.28% | 下降0.32% | 上升0.04% |
| AEMT-ChineseBERT w/o PT | 下降1.60% | 下降1.32% | 下降0.28% | |
| [1] | Beijing Qihoo Technology Co., Ltd. 2022 China Mobile Phone Security Status Report[EB/OL]. (2023-03-02) [2023-03-16]. https://pop.shouji.360.cn/safe_report/Mobile-Security-Report-202212.pdf. |
| 北京奇虎科技有限公司. 2022年度中国手机安全状况报告[EB/OL]. (2023-03-02) [2023-03-16]. https://pop.shouji.360.cn/safe_report/Mobile-Security-Report-202212.pdf. | |
| [2] | SUN Zijun, LI Xiaoya, SUN Xiaofei, et al. ChineseBERT: Chinese Pretraining Enhanced by Glyph and Pinyin Information[C]// ACL. Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. New York: ACL, 2021: 2065-2075. |
| [3] |
TAUFIQ N M, LEE C, ABDULLAH M F A, et al. Simple SMS Spam Filtering on Independent Mobile Phone[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2012, 5(10): 1209-1220.
doi: 10.1002/sec.v5.10 URL |
| [4] | HO T P, KANG H S, KIM S R. Graph-Based KNN Algorithm for Spam SMS Detection[J]. Journal of Universal Computerence, 2013, 19(16): 2404-2419. |
| [5] | HASSANI Z, HAJIHASHEMI V, BORNA K, et al. A Classification Method for E-Mail Spam Using a Hybrid Approach for Feature Selection Optimization[J]. Journal of Sciences, 2020, 31(2): 165-173. |
| [6] |
ILHAN T Z, YILDIRAK K, ALADAG C H. An Enhanced Random Forest Approach Using CoClust Clustering: MIMIC-III and SMS Spam Collection Application[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2023, 10(1): 38-47.
doi: 10.1186/s40537-023-00720-9 |
| [7] |
ABID M A, ULLAH S, SIDDIQUE M A, et al. Spam SMS Filtering Based on Text Features and Supervised Machine Learning Techniques[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(28): 39853-39871.
doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12991-0 |
| [8] |
XIA Tian, CHEN Xuemin. A Discrete Hidden Markov Model for SMS Spam Detection[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(14): 5011-5020.
doi: 10.3390/app10145011 URL |
| [9] |
XIA Tian, CHEN Xuemin. A Weighted Feature Enhanced Hidden Markov Model for Spam SMS Filtering[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 444(15): 48-58.
doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.02.075 URL |
| [10] |
GIANNELLA C R, WINDER R, WILSON B. Supervised SMS Text Message SPAM Detection[J]. Natural Language Engineering, 2015, 21(4): 553-567.
doi: 10.1017/S1351324914000102 URL |
| [11] | ABAYOMI A O, MISRA S, ABAYOMI A A. A Deep Learning Method for Automatic SMS Spam Classification: Performance of Learning Algorithms on Indigenous Dataset[J]. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2022, 34(17): 69-89. |
| [12] |
ROY P K, SINGH J P, BANERJEE S. Deep Learning to Filter SMS Spam[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 102(1): 524-533.
doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.09.001 URL |
| [13] | WAJA G, PATIL G, MEHTA C, et al. How AI Can be Used for Governance of Messaging Services: A Study on Spam Classification Leveraging Multi-Channel Convolutional Neural Network[J]. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 2023, 3(1): 147-160. |
| [14] |
LIU Xiaoxu, LU Haoye, NAYAK A. A Spam Transformer Model for SMS Spam Detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9(5): 80253-80263.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3081479 URL |
| [15] | OSWALD C, SIMON S E, BHATTACHARYA A. SpotSpam: Intention Analysis-Driven SMS Spam Detection Using BERT Embeddings[J]. ACM Transactions on the Web (TWEB), 2022, 16(3): 1-27. |
| [16] | ZHANG Jiliang, LI Chen. Adversarial Examples: Opportunities and Challenges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 31(7): 2578-2593. |
| [17] | GAO Ji, LANCHANTIN J, SOFFA ML, et al. Black-Box Generation of Adversarial Text Sequences to Evade Deep Learning Classifiers[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SP Workshops 2018). New York: IEEE, 2018: 50-56. |
| [18] | WANG Wenqi, WANG Run, WANG Lina, et al. Adversarial Examples Generation Approach for Tendency Classification on Chinese Texts[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(8): 2415-2427. |
| 王文琦, 汪润, 王丽娜, 等. 面向中文文本倾向性分类的对抗样本生成方法[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(8): 2415-2427. | |
| [19] | HU Mianning, LI Xin, LI Mingfeng, et al. Research on Multi-Strategy Data Enhancement Technology for Fraud Short Message Identification[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(10): 121-128. |
| 胡勉宁, 李欣, 李明锋, 等. 面向诈骗短信息识别的融合多策略数据增强技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 121-128. | |
| [20] | TONG Xin, WANG Jingya, WANG Binjun, et al. CSMTP: An RL-Based Adversarial Examples Generation Method for Chinese Social Media Texts Classification Models[J]. International Journal of Network Security, 2023, 25(1): 48-60. |
| [21] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[C]// IEEE. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017). New York: IEEE, 2017: 5998-6008. |
| [22] | DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Under-Standing[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Com-Putational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. New York: IEEE, 2019: 4171-4186. |
| [23] | LIU Yinhan, OTT M, GOYAL N, et al. Roberta: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach[EB/OL]. (2019-07-26) [2023-03-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692v1. |
| [24] | YANG Zhilin, DAI Zihang, YANG Yiming, et al. XLNet: Generalized Auto-Regressive Pretraining for Language Understanding[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2019: 5753-5763. |
| [25] | LIU Zejian, LI Fanrong, LI Gang, et al. EBERT: Efficient BERT Inference with Dynamic Structured Pruning[C]// ACL. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics:ACL-IJCNLP 2021. New York: ACL, 2021: 4814-4823. |
| [26] |
GOU Jianping, YU Baosheng, MAYBANK S J, et al. Knowledge Distillation: A Survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(3): 1789-1819.
doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01453-z |
| [1] | 沈华, 田晨, 郭森森, 慕志颖. 基于对抗性机器学习的网络入侵检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 66-75. |
| [2] | 李晨蔚, 张恒巍, 高伟, 杨博. 基于AdaN自适应梯度优化的图像对抗迁移攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 64-73. |
| [3] | 蒋曾辉, 曾维军, 陈璞, 武士涛. 面向调制识别的对抗样本研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 74-90. |
| [4] | 胡卫, 赵文龙, 陈璐, 付伟. 基于Logits向量的JSMA对抗样本攻击改进算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 62-69. |
| [5] | 郑耀昊, 王利明, 杨婧. 基于网络结构自动搜索的对抗样本防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 70-77. |
| [6] | 夏强, 何沛松, 罗杰, 刘嘉勇. 基于普遍对抗噪声的高效载体图像增强算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 64-75. |
| [7] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王靖亚, 杨莹. 一种面向Android恶意软件的多视角多任务学习检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 1-7. |
| [8] | 张郅, 李欣, 叶乃夫, 胡凯茜. 融合多重风格迁移和对抗样本技术的验证码安全性增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 129-135. |
| [9] | 于克辰, 郭莉, 姚萌萌. 基于空间及能量维度的黑盒对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 72-78. |
| [10] | 仝鑫, 王罗娜, 王润正, 王靖亚. 面向中文文本分类的词级对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 12-16. |
| [11] | 李红娇, 陈红艳. 基于WGAN的移动恶意对抗样本生成研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(11): 51-58. |
| [12] | 李宏军, 郎为民, 邓刚. 一种高效的大数据中心完整性检查方案研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(5): 1-8. |
| [13] | 苏娇娆. 多水印技术及其在数字作品交易中的应用[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(2): 71-76. |
| [14] | 何冰;苏变玲. 基于Krawtchouk不变矩的零水印算法研究[J]. , 2013, 13(7): 0-0. |
| [15] | 李馥娟. 从频发的信息泄露事件分析Web服务安全[J]. , 2012, 12(7): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||