信息网络安全 ›› 2022, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (12): 47-56.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2022.12.006
基于零知识证明的区块链方案研究进展
- 1.桂林电子科技大学计算机与信息安全学院,桂林 541004
2.广西密码学与信息安全重点实验室,桂林 541004
-
收稿日期:2022-08-29出版日期:2022-12-10发布日期:2022-12-30 -
通讯作者:陈莉杰 E-mail:cecilia_clj@163.com -
作者简介:王勇(1977—),男,湖北,副研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为信息安全与密码学|陈莉杰(1998—),女,河南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全与区块链|钟美玲(1997—),女,四川,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全与区块链 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61962012)
Progress in Blockchain Solutions Based on Zero-Knowledge Proof
WANG Yong1,2, CHEN Lijie1,2( ), ZHONG Meiling1,2
), ZHONG Meiling1,2
- 1. School of Computer Science and Information Security, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin 541004, China
2. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Cryptography and Information Security, Guilin 541004, China
-
Received:2022-08-29Online:2022-12-10Published:2022-12-30 -
Contact:CHEN Lijie E-mail:cecilia_clj@163.com
摘要:
匿名性是区块链的一个重要特性,随着区块链应用到溯源系统、身份认证、拍卖系统、物联网等多个领域,区块链去匿名化的风险极大增加,数据的隐私保护和审计监管问题亟待解决。一些研究人员已经在密码学领域找到一种高级加密原语(零知识证明)来增强区块链的匿名性和隐私性,目前已有突破性进展。文章对基于零知识证明的区块链方案进行分析研究,首先介绍了零知识证明的原理机制;然后将相关方案进行全面分析和对比,划分出隐私支付、隐私计算及审计监管3类研究重点,并分析了针对这3类重点方案的研究目标及进展情况,总结了已有工作的优点与不足;最后对基于零知识证明的区块链方案存在的局限性和挑战进行分析,阐述了未来研究方向。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王勇, 陈莉杰, 钟美玲. 基于零知识证明的区块链方案研究进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(12): 47-56.
WANG Yong, CHEN Lijie, ZHONG Meiling. Progress in Blockchain Solutions Based on Zero-Knowledge Proof[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(12): 47-56.
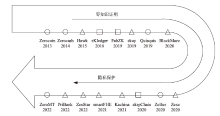
表2
基于零知识证明的区块链方案比较
| 方案 | 原理机制 | 模型 | 优点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zerocoin[ | ZKP | UTXO | 内部不可链接性、防盗窃、防DoS攻击 |
| Zerocash[ | zk-SNARKs | UTXO | 隐藏所有交易信息,强匿名性 |
| Hawk[ | MPC+zk-SNARKs | UTXO | 自动编译加密协议、惩戒机制、独立隐私性 |
| zKLedger[ | NIZK+MapReduce | UTXO | 提供快速和丰富的审计,具有完整性 |
| ZeeStar[ | NIZK+ 同态加密 | 账户 | 结合多方的私有价值和外部价值,性能良好且实用性强 |
| FabZK[ | NIZK+ 范围证明 | 账户 | 支持自动审计、轻量级、可编程性强 |
| Quisquis[ | DDH[ | UTXO+账户 | 交易小、验证快、防盗、安全性高 |
| Zether[ | zk-SNARKs | 账户 | 隐藏交易金额、不可链接性 |
| BlockMaze[ | NIZK+Bulletproofs | 账户 | 支持多领域应用,平衡了透明性和隐私性 |
| smartFHE[ | NIZK+Bulletproofs | 账户 | 不会发生用户过载情况,执行速度快 |
| Zexe[ | zk-SNARKs | UTXO | 隐藏脚本和脚本本身的输入,实现了离线计算 |
| Zkay[ | NIZK | 账户 | 可编程智能合约,动态映射和公共循环的显式函数编码 |
| zkrpChain[ | Bulletproofs | UTXO | 证明可批量验证,适用于审计监管系统 |
| Kachina[ | NIZK | 账户 | 实现了智能合约的并发交互,预测用户信息泄露行为 |
| 方案 | 匿名性 | 可信 设置 | 缺点 |
| Zerocoin[ | 较低 | √ | 金额不能任意拆分和组合,不能隐藏交易金额和接收地址,验证时间长 |
| Zerocash[ | 较高 | √ | 匿名交易花费时间长 |
| Hawk[ | 较高 | √ | 打破了去中心化特性,合约成本高 |
| zKLedger[ | 中等 | ? | 不能实现事务回滚,交易吞吐量低、延迟高 |
| ZeeStar[ | 中等 | √ | 不适用实际应用场景,加密和解密成本较高 |
| FabZK[ | 较高 | ? | 易发生无效交易、证明成本高、交易延迟高 |
| Quisquis[ | 较低 | ? | 交易生成速度慢、通信成本高 |
| Zether[ | 较高 | √ | 存储和时间成本高 |
| BlockMaze[ | 中等 | ? | 交易成本较高,证明被接收之前需要锁定账户 |
| smartFHE[ | 中等 | ? | 交易成本较高 |
| Zexe[ | 中等 | √ | 生成证明成本高,只能面向密码学专业人员操作 |
| Zkay[ | 较低 | √ | 操作复杂,容易使用户过载 |
| zkrpChain[ | 中等 | ? | 易受到安全攻击 |
| Kachina[ | 较高 | ? | 目前不适用于实际场景 |
| [1] | NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[EB/OL]. (2008-11-01) [2022-07-20]. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf. |
| [2] | KELLERMANN T, MURPHY R. Modern Bank Heists 5.0[EB/OL]. (2022-05-06) [2022-07-20]. https://vmware.com/content/dam/learn/en/pdf/carbonblack/Modern%20Bank%20Heists%205.0%20Report.pdf. |
| [3] | ERMILOV D, PANOV M, YANOVICH Y. Automatic Bitcoin Address Clustering[C]// IEEE. 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications(ICMLA). New York: IEEE, 2017: 461-466. |
| [4] | NOETHER S, NOETHER S. Monero is not that Mysterious[EB/OL]. (2014-09-25) [2022-07-20]. https://web.getmonero.org/ru/resources/research-lab/pubs/MRL-0003.pdf. |
| [5] | HOPWOOD D, BOWE S, HORNBY T, et al. Zcash Protocol Specification[EB/OL]. (2014-05-18) [2022-07-20]. https://zips.z.cash/protocol/protocol.pdf. |
| [6] | GOLDWASSER S, MICALI S, RACKOFF C. The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof Systems[C]// ACM. 17th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 1985: 291-304. |
| [7] | ABDALLA M, AN J H, BELLARE M, et al. From Identification to Signatures via the Fiat-Shamir Transform: Minimizing Assumptions for Security and Forward-Security[C]// Springer. International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2002: 418-433. |
| [8] | BLUM M, FELDMAN P, MICALI S. Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge and Its Applications[C]// ACM. The Twentieth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 1988: 103-112. |
| [9] | MEIKLEJOHN S, POMAROLE M, JORDAN G, et al. A Fistful of Bitcoins: Characterizing Payments Among Men with no Names[C]// ACM. 2013 Conference on Internet Measurement Conference. New York: ACM, 2013: 127-140. |
| [10] | SHAO Jun, CAO Zhenfu. CCA-Secure Proxy Re-Encryption without Pairings[C]// Springer. International Workshop on Public Key Cryptography. Heidelberg: Springer, 2009: 357-376. |
| [11] | BOUDOT F. Efficient Proofs that A Committed Number Lies in An Interval[C]// Springer. International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2000: 431-444. |
| [12] | PEDERSEN T P. Non-Interactive and Information-Theoretic Secure Verifiable Secret Sharing[C]// Springer. Annual International Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 1991: 129-140. |
| [13] | BÜNZ B, BOOTLE J, BONEH D, et al. Bulletproofs: Short Proofs for Confidential Transactions and More[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy(SP). New York: IEEE, 2018: 315-334. |
| [14] | WANG Ting. A Review of Secure Multiparty Computation Theory Research[J]. Information Security and Technology, 2014, 5(5): 41-44. |
| [15] | GROTH J. Short Pairing-Based Non-Interactive Zero-Knowledge Arguments[C]// Springer. International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2010: 321-340. |
| [16] | GENNARO R, GENTRY C, PARNO B, et al. Quadratic Span Programs and Succinct NIZKs without PCPs[C]// Springer. Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 626-645. |
| [17] | SIMPSON W. The Quadratic Assignment Procedure(QAP)[C]// Stata. North American STATA Users’ Group Meeting. Texas: Stata, 2001: 12-13. |
| [18] | MALLER M, BOWE S, KOHLWEISS M, et al. Sonic: Zero-Knowledge SNARKs from Linear-Size Universal and Updatable Structured Reference Strings[C]// ACM. 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 2111-2128. |
| [19] | GABIZON A, WILLIAMSON Z J, CIOBOTARU O. Plonk: Permutations over Lagrange-Bases for Oecumenical Noninteractive Arguments of Knowledge[EB/OL]. (2019-08-21) [2022-07-20]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2019/953.pdf. |
| [20] | GROTH J. On the Size of Pairing-Based Non-Interactive Arguments[C]// Springer. Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 305-326. |
| [21] | RAHIMI A, MA MADDAH-ALI. Multi-Party Proof Generation in Qap-Based zk-Snarks[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory. New York: IEEE, 2021: 931-941. |
| [22] | LIPMAA H. Succinct non-Interactive Zero Knowledge Arguments from Span Programs and Linear Error-Correcting Codes[C]// Springer. International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 41-60. |
| [23] | BITANSKY N, CHIESA A, ISHAI Y, et al. Succinct non-Interactive Arguments via Linear Interactive Proofs[C]// Springer. Theory of Cryptography Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 315-333. |
| [24] | PARNO B, HOWELL J, GENTRY C, et al. Pinocchio: Nearly Practical Verifiable Computation[C]// IEEE. 2013 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2013: 238-252. |
| [25] | BEN-SASSON E, CHIESA A, GENKIN D, et al. SNARKs for C: Verifying Program Executions Succinctly and in Zero Knowledge[C]// Springer. Annual Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 90-108. |
| [26] | BEN-SASSON E, CHIESA A, TROMER E, et al. Succinct non-Interactive Arguments for a von Neumann Architecture[EB/OL]. (2013-12-30) [2022-07-20]. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.650.9468&rep=rep1&type=pdf. |
| [27] | BEN-SASSON E, BENTOV I, HORESH Y, et al. Scalable, Transparent, and Post-Quantum Secure Computational Integrity[EB/OL]. (2018-03-06) [2022-07-20]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/046.pdf. |
| [28] | MCCURLEY K S. The Discrete Logarithm Problem[C]// American Mathematical Society. Symposia in Applied Mathematics. Washington: American Mathematical Society, 1990: 49-74. |
| [29] | CANETTI R, CHEN Y, HOLMGREN J, et al. Fiat-Shamir: from Practice to Theory[C]// ACM. The 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 2019: 1082-1090. |
| [30] | MONTGOMERY P L. A Survey of Modern Integer Factorization Algorithms[J]. CWI Quarterly, 1994, 7(4): 337-366. |
| [31] | HUANG Xueyuan. The Use of Chinese Residue Theorem In Cryptography[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2006. |
| 黄学渊. 中国剩余定理在密码技术中的运用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2006. | |
| [32] | PEDERSEN T P. Non-Interactive and Information-Theoretic Secure Verifiable Secret Sharing[C]// Springer. Annual International Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 1991: 129-140. |
| [33] | BOOTLE J, CERULLI A, CHAIDOS P, et al. Efficient Zero-Knowledge Arguments for Arithmetic Circuits in the Discrete Log Setting[C]// Springer. Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 327-357. |
| [34] | MIERS I, GARMAN C, GREEN M, et al. Zerocoin: Anonymous Distributed E-Cash from Bitcoin[C]// IEEE. 2013 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2013: 397-411. |
| [35] | SASSON E B, CHIESA A, GARMAN C, et al. Zerocash: Decentralized Anonymous Payments from Bitcoin[C]// IEEE. 2014 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2014: 459-474. |
| [36] | FAUZI P, MEIKLEJOHN S, MERCER R, et al. Quisquis: A New Design for Anonymous Cryptocurrencies[C]// Springer. International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security. New York: Springer, 2019: 649-678. |
| [37] | BÜNZ B, AGRAWAL S, ZAMANI M, et al. Zether: Towards Privacy in a Smart Contract World[C]// Springer. International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 423-443. |
| [38] | CORRADINI F, MOSTARDA L, SCALA E. ZeroMT: Multi-Transfer Protocol for Enabling Privacy in off-Chain Payments[C]// Springer. International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 611-623. |
| [39] | DELGADO P, DINU F, KERMARREC A M, et al. Hawk: Hybrid Datacenter Scheduling[C]// USENIX. 2015 USENIX Annual Technical Conference(USENIX ATC 15). Berkeley: USENIX, 2015: 499-510. |
| [40] | STEFFEN S, BICHSEL B, GERSBACH M, et al. Zkay: Specifying and Enforcing Data Privacy in Smart Contracts[C]// ACM. The 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 1759-1776. |
| [41] |
GUAN Zhangshuang, WAN Zhiguo, YANG Yang, et al. BlockMaze: An Efficient Privacy-Preserving Account-Model Blockchain Based on zk-SNARKs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2020, 19(3): 1446-1463.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2020.3025129 URL |
| [42] | BOWE S, CHIESA A, GREEN M, et al. Zexe: Enabling Decentralized Private Computation[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy(SP). New York: IEEE, 2020: 947-964. |
| [43] | KERBER T, KIAYIAS A, KOHLWEISS M. Kachina-Foundations of Private Smart Contracts[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 34th Computer Security Foundations Symposium(CSF). New York: IEEE, 2021: 1-16. |
| [44] | SOLOMON R, ALMASHAQBEH G. SmartFHE: Privacy-Preserving Smart Contracts from Fully Homomorphic Encryption[EB/OL].(2021-02-10) [2022-07-20]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2021/133.pdf. |
| [45] | STEFFEN S, BICHSEL B, BAUMGARTNER R, et al. ZeeStar: Private Smart Contracts by Homomorphic Encryption and Zero-Knowledge Proofs[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy(SP). New York: IEEE, 2022: 1543-1543. |
| [46] | GJØSTEEN K, RAIKWAR M, WU Shuang. PriBank: Confidential Blockchain Scaling Using Short Commit-and-Proof NIZK Argument[C]// Springer. Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 589-619. |
| [47] | NARULA N, VASQUEZ W, VIRZA M. zkLedger: Privacy-Preserving Auditing for Distributed Ledgers[C]// USENIX. 15th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation(NSDI 18). Berkeley:USENIX, 2018: 65-80. |
| [48] | KANG Hui, DAI Ting, JEAN-LOUIS N, et al. Fabzk: Supporting Privacy-Preserving, Auditable Smart Contracts in Hyperledger Fabric[C]// IEEE. 2019 49th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks(DSN). New York: IEEE, 2019: 543-555. |
| [49] |
XU Shiwei, CAI Xiaowen, ZHAO Yizhi, et al. zkrpChain: Towards Multi-Party Privacy-Preserving Data Auditing for Consortium Blockchains Based on Zero-Knowledge Range Proofs[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2022, 128: 490-504.
doi: 10.1016/j.future.2021.09.034 URL |
| [50] | BONEH D. The Decision Diffie-Hellman Problem[C]// Springer. International Algorithmic Number Theory Symposium. Heidelberg: Springer, 1998: 48-63. |
| [51] | WATERS B R, FELTEN E W, SAHAI A. Receiver Anonymity via Incomparable Public Keys[C]// ACM. The 10th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2003: 112-121. |
| [52] | LV Haifeng, DING Yong, DAI Hongyan, et al. Survey on LWE-Based Fully Homomorphic Encryption Scheme[J]. Netinfo Security, 2015, 15(1): 32-38. |
| 吕海峰, 丁勇, 代洪艳, 等. LWE上的全同态加密方案研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(1):32-38. | |
| [53] | CHIESA A, HU Yuncong, MALLER M, et al. Marlin: Preprocessing zkSNARKs with Universal and Updatable SRS[C]// Springer. Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 738-768. |
| [54] | CAMENISCH J, KIAYIAS A, YUNG M. On the Portability of Generalized Schnorr Proofs[C]// Springer. Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2009: 425-442. |
| [55] | ANDROULAKI E, KARAME G O, ROESCHLIN M, et al. Evaluating User Privacy in Bitcoin[C]// Springer. International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 34-51. |
| [56] | REID F, HARRIGAN M. Security and Privacy in Social Networks[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2013. |
| [57] | LIAO K, ZHAO Ziming, DOUPÉ A, et al. Behind Closed Doors: Measurement and Analysis of CryptoLocker Ransoms in Bitcoin[C]// IEEE. 2016 APWG Symposium on Electronic Crime Research(eCrime). New York: IEEE, 2016: 1-13. |
| [58] | BIRYUKOV A, PUSTOGAROV I. Bitcoin over Tor isn’t a Good Idea[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2015: 122-134. |
| [59] | BISSIAS G, OZISIK A P, LEVINE B N, et al. Sybil-Resistant Mixing for Bitcoin[C]// ACM. The 13th Workshop on Privacy in the Electronic Society. New York: ACM, 2014: 149-158. |
| [60] | THOMAS S, SCHWARTZ E. A Protocol for Interledger Payments[EB/OL]. (2018-10-05) [2022-07-20]. https://interledger.org/interledger.pdf. |
| [61] | FRAUENTHALER P, SIGWART M, SPANRING C, et al. ETH Relay: A Cost-Efficient Relay for Ethereum-Based Blockchains[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain(Blockchain). New York: IEEE, 2020: 204-213. |
| [62] | POON J, DRYJA T. The Bitcoin Lightning Network: Scalable off-Chain Instant Payments[EB/OL]. (2016-01-14) [2022-07-20]. https://www.bitcoinlightning.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/lightning-network-paper.pdf. |
| [1] | 于晶, 袁曙光, 袁煜琳, 陈驰. 基于k匿名数据集的鲁棒性水印技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(9): 11-20. |
| [2] | 佟晓筠, 毛宁, 张淼, 王翥. 基于Henon映射与改进的提升小波变换图像加密算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(9): 31-39. |
| [3] | 张光华, 刘永升, 王鹤, 于乃文. 基于BiLSTM和注意力机制的智能合约漏洞检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(9): 46-54. |
| [4] | 张学旺, 刘宇帆. 可追踪身份的物联网感知层节点匿名认证方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(9): 55-62. |
| [5] | 胡艺, 佘堃. 基于区块链和智能合约的双链车联网系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 26-35. |
| [6] | 黄保华, 赵伟宏, 彭丽, 谢统义. 基于MPT索引的高效链上PKI模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 72-80. |
| [7] | 王健, 黄俊. 基于智能合约的日志安全存储与公平访问方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 27-36. |
| [8] | KELEKET GOMA Christy Junior Yannick, 易文哲, 王鹃. 一种基于SGX的轻量Fabric链码可信执行环境构建方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 73-83. |
| [9] | 秦宝东, 余沛航, 郑东. 基于双陷门同态加密的决策树分类模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 9-17. |
| [10] | 王圣雯, 胡爱群. 基于SM9算法的邮件加密系统设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(6): 53-60. |
| [11] | 王姝爽, 马兆丰, 刘嘉微, 罗守山. 区块链跨链安全接入与身份认证方案研究与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(6): 61-72. |
| [12] | 于克辰, 郭莉, 阴宏伟, 燕雪松. 面向数据中心场景的基于区块链与博弈论的高价值数据共享模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(6): 73-85. |
| [13] | 冯景瑜, 张琪, 黄文华, 韩刚. 基于跨链交互的网络安全威胁情报共享方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 21-29. |
| [14] | 刘嘉微, 马兆丰, 王姝爽, 罗守山. 基于区块链的隐私信用数据受限共享技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 54-63. |
| [15] | 崔皓宇, 马利民, 王佳慧, 张伟. 基于区块链的属性加密多授权机构安全模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 84-93. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||