信息网络安全 ›› 2022, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 11-20.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2022.02.002
对DSA和ECDSA的一种改进格攻击
- 1.武汉大学国家网络安全学院,武汉 430072
2.武汉大学空天信息安全与可信计算教育部重点实验室,武汉 430064
-
收稿日期:2021-09-23出版日期:2022-02-10发布日期:2022-02-16 -
通讯作者:贾耀民 E-mail:649154808@qq.com -
作者简介:余发江(1980—),男,湖北,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为可信计算、系统安全、密码学|贾耀民(1995—),男,湖北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为可信计算、系统安全、密码学 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61772384)
An Enhanced Lattice Attack to DSA and ECDSA Scheme
YU Fajiang1,2, JIA Yaomin1,2( )
)
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
2. Key Laboratory of Aerospace Information Security and Trusted Computing of Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430064, China
-
Received:2021-09-23Online:2022-02-10Published:2022-02-16 -
Contact:JIA Yaomin E-mail:649154808@qq.com
摘要:
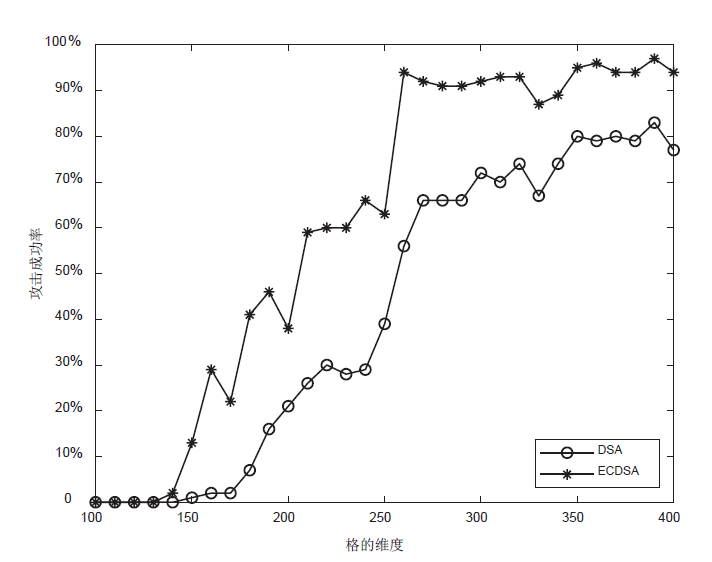
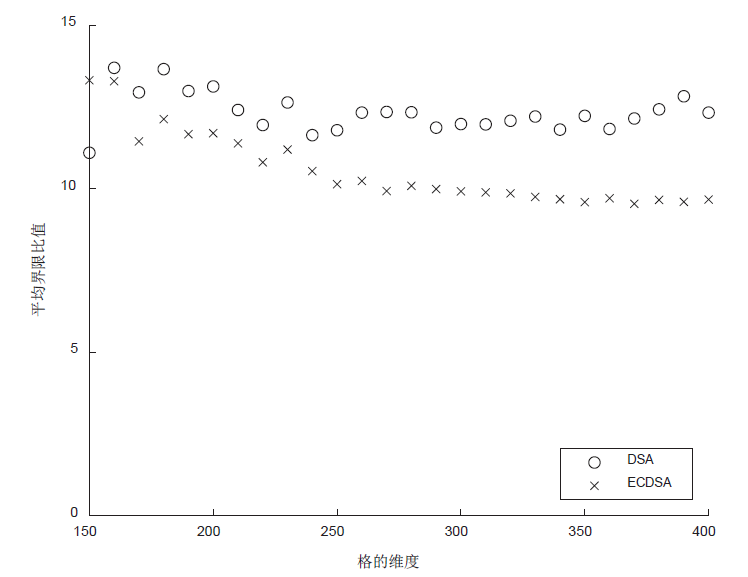
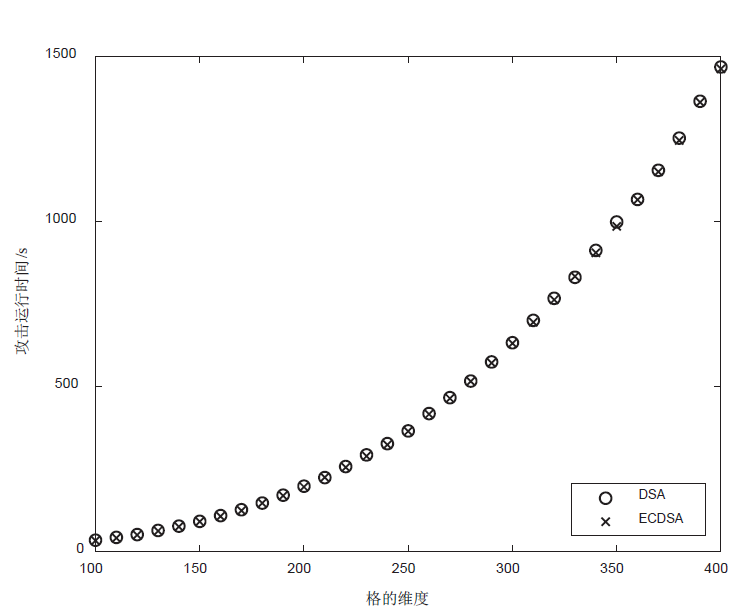
利用格攻击DSA和ECDSA的方法,通过构造同余方程组可以将隐藏数字问题转化为格中最近向量问题,当同余方程组至多有一个解小于给定界限时,可通过求解格中最近向量获取签名私钥。给定界限越大,对解向量的大小要求越宽松,攻击的难度也越低。文章提出一种新的给定界限,其大小是原有界限的6.92倍,显著降低了格攻击的难度。利用从OpenSSL收集到的DSA和ECDSA的签名数据,设计验证新界限的格攻击实验。实验结果表明,新界限对已知解向量元素的要求由最高比特位6位降低到3 位。对于DSA,当格的维度为350时,攻击成功率达80%;对于ECDSA,当格的维度为260时,攻击成功率达97%。通过解向量减去一个基准向量,可将对已知解向量元素的要求降低至1位,从而降低格攻击的难度。
中图分类号:
引用本文
余发江, 贾耀民. 对DSA和ECDSA的一种改进格攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 11-20.
YU Fajiang, JIA Yaomin. An Enhanced Lattice Attack to DSA and ECDSA Scheme[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(2): 11-20.
| [1] | FIPS PUB 186-4 Digital Signature Standard (DSS)[S]. USA: Department of Commerce/National Institute of Standards and Technology: Federal Information Processing Standards Publication, 2013. |
| [2] | ARANHA D F, NOVAES F R, TAKAHASHI A, et al. LadderLeak: Breaking ECDSA with Less than One Bit of Nonce Leakage[C]//ACM. 2020 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS’20), November 9-13, 2020, NY, USA. New York: ACM, 2020: 225-242. |
| [3] | MA Ziqiang, LI Bingyu, CAI Quanwei, et al. Applications and Developments of the Lattice Attack in Side Channel Attacks[C]//ACNS. ACNS 2020: Applied Cryptography and Network Security Workshops, February 5-9, 2020, New Orleans, USA. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 435-452. |
| [4] | BONEH D, VENKATESAN R. Hardness of Computing the Most Significant Bits of Secret Keys in Diffie-Hellman and Related Schemes[C]//Springer. CRYPTO’1996: Advances in Cryptology, August 18-22, 1996, California, USA. Heidelberg: Springer, 1996: 129-142. |
| [5] | MICCIANCIO D, GOLDWASSER S. Complexity of Lattice Problems[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2002. |
| [6] |
LENSTRA A K, LENSTRA H W, LOVÁSZ L. Factoring Polynomials with Rational Coefficients[J]. Mathematische Annalen, 1982, 261(4):515-534.
doi: 10.1007/BF01457454 URL |
| [7] |
BABAI L. On Lovasz’ Lattice Reduction and the Nearest Lattice Point Problem[J]. Combinatorica, 1986, 6(1):1-13.
doi: 10.1007/BF02579403 URL |
| [8] |
HOWGRAVE-GRAHAM N A, SMART N P. Lattice Attacks on Digital Signature Schemes[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2001, 23(3):283-290.
doi: 10.1023/A:1011214926272 URL |
| [9] |
NGUYEN P Q, SHPARLINSKI I E. The Insecurity of the Digital Signature Algorithm with Partially Known Nonces[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 2003, 15(3):151-176.
doi: 10.1007/s00145-002-0021-3 URL |
| [10] |
NGUYEN P Q, SHPARLINSKI I E. The Insecurity of the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm with Partially Known Nonces[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2001, 30(2):201-217.
doi: 10.1023/A:1025436905711 URL |
| [11] | HLAVAC M, ROSA T. Extended Hidden Number Problem and Its Cryptanalytic Applications[C]//Springer. SAC 2006: Selected Areas in Cryptography, August 17-18, 2006, Montreal, Canada. Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 114-133. |
| [12] | BENGER N, POL J V D, SMART N P, et al. Ooh Aah Just a Little Bit: A Small Amount of Side Channel Can Go a Long Way[C]//Springer. Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems-CHES 2014, September 23-26, 2014, Busan, Republic of Korea. Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 75-92. |
| [13] | POL J V D, SMART N P, YAROM Y. Just a Little Bit More[C]//Springer. Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA Conference (CT-RSA 2015), April 20-24, 2015, San Francisco, CA, USA. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 3-21. |
| [14] | FAN Shuqin, WANG Wenbo, CHENG Qingfeng. Attacking OpenSSL Implementation of ECDSA with a Few Signatures[C]//ACM. 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS’16), October 24-28, 2016, Vienna, Austria. New York: ACM, 2016: 1505-1515. |
| [15] | RYAN K. Return of the Hidden Number Problem: A Widespread and Novel Key Extraction Attack on ECDSA and DSA[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/346703657_Return_of_the_Hidden_Number_Problem_A_Widespread_and_Novel_Key_Extraction_Attack_on_ECDSA_and_DSA, , 2018-11-20. |
| [16] | ARANHA D F, FOUQUE P A, GÉRARD B, et al. GLV/GLS Decomposition, Power Analysis, and Attacks on ECDSA Signatures with Single-bit Nonce Bias[C]//Springer. International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security 2014, December 7-11, 2014, Taibei, Taiwan, China. Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 262-281. |
| [17] | GENKIN D, PACHMANOV L, PIPMAN I, et al. ECDSA Key Extraction from Mobile Devices via Nonintrusive Physical Side Channels[C]//ACM. 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS’16), October 24-28, 2016, Vienna, Austria. New York: ACM, 2016: 1626-1638. |
| [18] | BELGARRIC P, FOUQUE P A, MACARIO-RAT G, et al. Side-channel Analysis of Weierstrass and Koblitz Curve ECDSA on Android Smartphones[C]//Springer. Cryptographers’ Track at the RSA Conference 2016, February 29-March 4, 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 232-256. |
| [19] | ZHANG Kaiyu, XU Sen, GU Dawu, et al. Practical Partial-nonce-exposure Attack on ECC Algorithm[C]//IEEE. 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security (CIS), December 15-18, 2017, Hong Kong, China. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 248-252. |
| [20] | CAO Weiqiong, FENG Jingyi, CHEN Hua, et al. Two Lattice-based Differential Fault Attacks Against ECDSA with wNAF Algorithm[C]//Springer. Information Security and Cryptology-ICISC 2015, November 25-27, 2015, Seoul, Republic of Korea. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 297-313. |
| [21] | NGUYEN P Q, TIBOUCHI M. Fault Analysis in Cryptography[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2012. |
| [22] | BRUMLEY B B, TUVERI N. Remote Timing Attacks Are Still Practical[C]//Springer. Computer Security-ESORICS 2011, September 12-14, 2011, Leuven, Belgium. Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 355-371. |
| [23] | MOGHIMI D, SUNAR B, EISENBARTH T, et al. TPM-FAIL: TPM Meets Timing and Lattice Attacks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.05673, 2019-11-13. |
| [24] | TIBOUCHI M. Attacks on (EC) DSA with Biased Nonces[EB/OL]. https://ecc2017.cs.ru.nl/slides/ecc2017-tibouchi.pdf, 2017-11-13. |
| [25] | POULAKIS D. New Lattice Attacks on DSA Schemes[J]. Journal of Mathematical Cryptology, 2016, 10(2):135-144. |
| [26] | ADAMOUDIS M, DRAZIOTIS K A, POULAKIS D. Enhancing an Attack to DSA Schemes[C]//Springer. International Conference on Algebraic Informatics (CAI 2019), June 30-July 4, 2019, Niš, Serbia. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 13-25. |
| [27] | ADAMOUDIS M, DRAZIOTIS K A, POULAKIS D. Attacking (EC) DSA with Partially Known Multiples of Nonces[J]. IACR Cryptol ePrint Archive, 2021, 35(10):347-356. |
| [28] | SUN Chao, ESPITAU T, TIBOUCHI M, et al. Guessing Bits: Improved Lattice Attacks on (EC)DSA[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2021, 28(1):391-413. |
| [1] | 张光华, 闫风如, 张冬雯, 刘雪峰. 基于LSTM-Attention的内部威胁检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 1-10. |
| [2] | 王健, 张蕴嘉, 刘吉强, 陈志浩. 基于区块链的司法数据管理及电子证据存储机制[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 21-31. |
| [3] | 吴克河, 程瑞, 姜啸晨, 张继宇. 基于SDP的电力物联网安全防护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 32-38. |
| [4] | 刘峰, 杨成意, 於欣澄, 齐佳音. 面向去中心化双重差分隐私的谱图卷积神经网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 39-46. |
| [5] | 颜靖华, 侯毅, 辛浪. 基于IPSec VPN和多路径传输协议融合的应急通信策略研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 47-54. |
| [6] | 侯雨桐, 马兆丰, 罗守山. 基于区块链的数据安全共享与受控分发技术研究与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 55-63. |
| [7] | 夏强, 何沛松, 罗杰, 刘嘉勇. 基于普遍对抗噪声的高效载体图像增强算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 64-75. |
| [8] | 胡瑞钦, 谭晶磊, 彭心荷, 张红旗. 面向SDN数据层的双虚假IP地址动态跳变技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 76-85. |
| [9] | 易铮阁, 袁文勇, 李瑞峰, 杨晓元. 一种支持动态操作的身份基云存储方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 86-95. |
| [10] | 熊建英. 基于信息行为的社交网络节点信誉评估模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 51-59. |
| [11] | 李鹏超, 刘彦飞. 基于删除PE文件头的恶意代码内存取证方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 38-43. |
| [12] | 陈光宣, 吴家健, 操丹妮, 谢清泉. 一种基于Checkm8漏洞的iPhone取证方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 44-50. |
| [13] | 倪雪莉, 王群, 梁广俊. 微信证据的鉴真方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 60-69. |
| [14] | 张淑清, 蔡志文. 云数据下基于可问责属性即可撤销的加密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 70-77. |
| [15] | 高见, 王凯悦, 黄淑华. 面向视频监控网络的安全评估指标体系研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 78-85. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||