信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 473-485.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.03.012
基于联邦学习和区块链技术的TAP规则处理系统
- 吉林大学计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
-
收稿日期:2023-12-20出版日期:2024-03-10发布日期:2024-04-03 -
通讯作者:王峰 E-mail:wangfeng12@mails.jlu.edu.cn -
作者简介:薛茗竹(1999—),女,吉林,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为区块链、隐私保护|胡亮(1968—),男,吉林,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为网络安全|王明(1998—),男,山西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为物联网数据挖掘|王峰(1987—),男,吉林,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为计算机系统架构、网络空间安全 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2017YFA0604500);吉林省科技发展计划(20220101115JC)
TAP Rule Processing System Based on Federated Learning and Blockchain Technology
XUE Mingzhu, HU Liang, WANG Ming, WANG Feng( )
)
- College of Computer Science and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
-
Received:2023-12-20Online:2024-03-10Published:2024-04-03 -
Contact:WANG Feng E-mail:wangfeng12@mails.jlu.edu.cn
摘要:
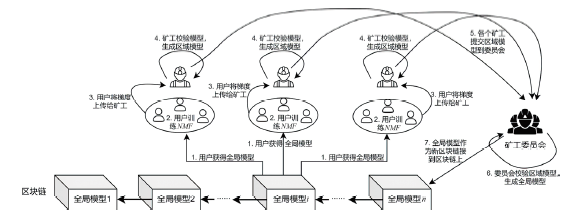
触发执行编程(Trigger-Action Programming,TAP)为用户联动物联网(Internet of Things,IoT)设备提供了便捷的编程范式。利用机器学习对用户已编辑的TAP规则进行分析,实现TAP规则推荐和生成等功能可以提升用户体验。但TAP规则可能包含个人隐私信息,用户对上传和分享TAP信息存在顾虑。文章提出了基于联邦学习和区块链技术的TAP规则处理系统,用户可在本地进行TAP模型训练,无需上传隐私数据。为解决集中式服务器单点故障和防范恶意模型参数上传的问题,文章利用区块链技术改进集中式TAP联邦学习架构。用户将本地模型更新的累积梯度传输给区块链中的矿工,进行异常识别和交叉验证。矿工委员会整合正常用户提供的累积梯度,得到的全局模型作为一个新区块的数据,链接到区块链上,供用户下载使用。文章采用轻量级无监督的非负矩阵分解方法验证了提出的基于联邦学习和区块链的分布式学习架构的有效性。实验证明该联邦学习架构能有效保护TAP数据中的隐私,并且区块链中的矿工能够很好地识别恶意模型参数,确保了模型的稳定性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
薛茗竹, 胡亮, 王明, 王峰. 基于联邦学习和区块链技术的TAP规则处理系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 473-485.
XUE Mingzhu, HU Liang, WANG Ming, WANG Feng. TAP Rule Processing System Based on Federated Learning and Blockchain Technology[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 473-485.
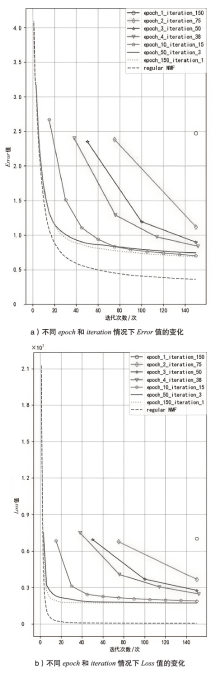
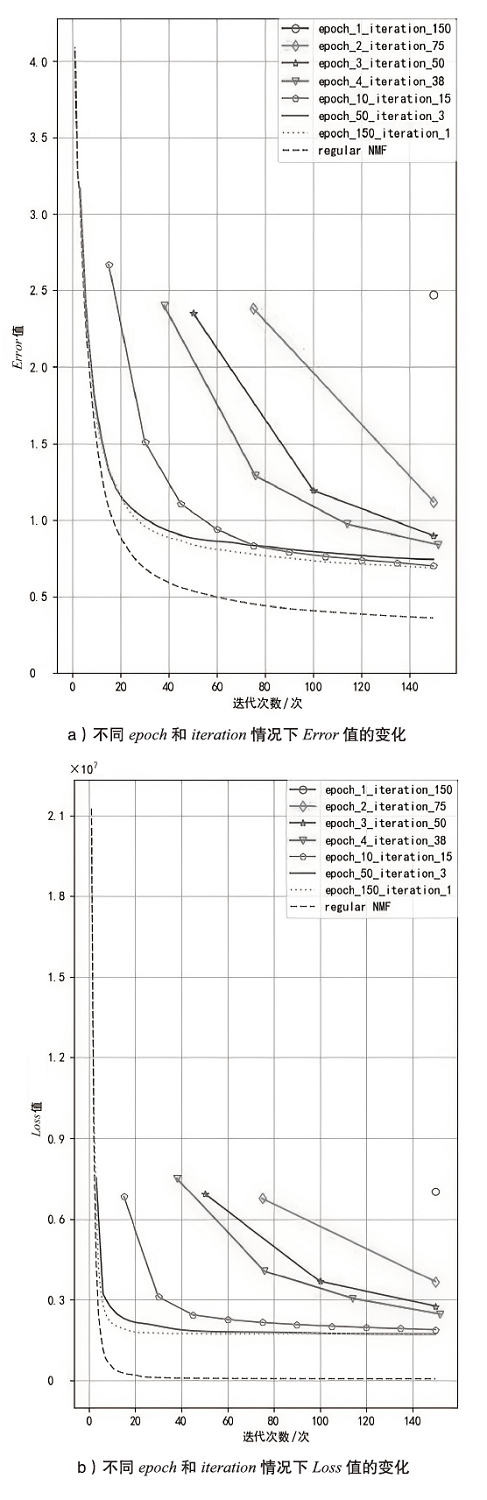
表1
验证用户的Error值
| 验证用户1 | 验证用户2 | 验证用户3 | 平均Error值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| epoch_1_iteration_150 | 2.73 | 2.9 | 2.81 | 2.81 |
| epoch_2_iteration_75 | 1.83 | 1.88 | 1.86 | 1.86 |
| epoch_3_iteration_50 | 1.64 | 1.64 | 1.65 | 1.64 |
| epoch_4_iteration_38 | 1.58 | 1.57 | 1.59 | 1.58 |
| epoch_10_iteration_15 | 1.51 | 1.48 | 1.50 | 1.5 |
| epoch_50_iteration_3 | 1.53 | 1.51 | 1.54 | 1.53 |
| epoch_150_iteration_1 | 1.51 | 1.48 | 1.51 | 1.5 |
| regular NMF | 1.53 | 1.52 | 1.52 | 1.52 |
| [1] | WANG Ming, XING Yongheng, WANG Feng. Unsupervised Matrix Factorization Based Trigger Action Programming Rules Recommendation[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(2): 96-103. |
| 王明, 邢永恒, 王峰. 基于无监督非负矩阵分解的TAP规则推荐[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 96-103. | |
| [2] |
CHAI Di, WANG Leye, CHEN Kai, et al. Secure Federated Matrix Factorization[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2020, 36(5): 11-20.
doi: 10.1109/MIS.2020.3014880 URL |
| [3] |
SHIN H, KIM S, SHIM J, et al. Privacy Enhanced Matrix Factorization for Recommendation with Local Differential Privacy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2018, 30(9): 1770-1782.
doi: 10.1109/TKDE.69 URL |
| [4] | KIM S, KIM J, KOO D, et al. Efficient Privacy-Preserving Matrix Factorization via Fully Homomorphic Encryption[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 11th ACM on Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 617-628. |
| [5] | GILLIS N. The Why and How of Nonnegative Matrix Factorization[J]. Regularization, Optimization, Kernels, and Support Vector Machines, 2014, 12(257): 257-291. |
| [6] | YANG Qiang, LIU Yang, CHEN Tianjian, et al. Federated Machine Learning: Concept and Applications[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2019, 10(2): 1-19. |
| [7] | FERNANDES E, RAHMATI A, JUNG J, et al. Decentralized Action Integrity for Trigger-Action IoT Platforms[C]// Internet Society. Proceedings 2018 Network and Distributed System Security Symposium. San Diego: Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, 2018: 1-16. |
| [8] | CHEN Yunang, CHOWDHURY A R, WANG Ruizhe, et al. Data Privacy in Trigger-Action Systems[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2021: 501-518. |
| [9] |
BREVE B, CIMINO G, DEUFEMIA V. Identifying Security and Privacy Violation Rules in Trigger-Action IoT Platforms with NLP Models[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 10(6): 5607-5622.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3222615 URL |
| [10] | MCMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data[C]// PMLR.Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. New York: PMLR, 2017: 1273-1282. |
| [11] |
SUN Rui, LI Chao, WANG Wei, et al. Research Progress of Blockchain-Based Federated Learning[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(11): 3413-3420.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021111934 |
|
孙睿, 李超, 王伟, 等. 基于区块链的联邦学习研究进展[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(11): 3413-3420.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021111934 |
|
| [12] |
AONO Y, HAYASHI T, WANG Lihua, et al. Privacy-Preserving Deep Learning via Additively Homomorphic Encryption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 13(5): 1333-1345.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2787987 URL |
| [13] |
KIM H, PARK J, BENNIS M, et al. Blockchained On-Device Federated Learning[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 24(6): 1279-1283.
doi: 10.1109/COML.4234 URL |
| [14] | BOGDANOV D, LAUR S, WILLEMSON J. Sharemind: A Framework for Fast Privacy-Preserving Computations[C]// ESORICS.Computer Security-ESORICS 2008: 13th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 192-206. |
| [15] | NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[EB/OL]. (2019-07-17)[2023-12-19]. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf. |
| [16] | XIAO Yang, ZHANG Ning, LOU Wenjing, et al. A Survey of Distributed Consensus Protocols for Blockchain Networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(2): 1432-1465. |
| [17] | SAAD S M S, RADZI R Z R M. Comparative Review of the Blockchain Consensus Algorithm between Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)[ J]. International Journal of Innovative Computing, 2020, 10(2): 27-32. |
| [18] |
LAMPORT L, SHOSTAK R, PEASE M. The Byzantine Generals Problem[J]. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems, 1982, 4(3): 382-401.
doi: 10.1145/357172.357176 URL |
| [19] | CASTRO M, LISKOV B. Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance[C]// USENIX. Proceedings of the Third Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation. Berkeley: USENIX, 1999: 173-186. |
| [20] | FURUKAWA J, LINDELL Y, NOF A, et al. High-Throughput Secure Three-Party Computation for Malicious Adversaries and an Honest Majority[C]// IACR. Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2017: 225-255. |
| [21] | KOGIAS E K, JOVANOVIC P, GAILLY N, et al. Enhancing Bitcoin Security and Performance with Strong Consistency via Collective Signing[C]// USENIX. 25th Usenix Security Symposium (Usenix Security 16). Berkeley: USENIX, 2016: 279-296. |
| [22] |
ZHENG Zibin, XIE Shaoan, DAI Hongning, et al. Blockchain Challenges and Opportunities: A Survey[J]. International Journal of Web and Grid Services, 2018, 14(4): 352-375.
doi: 10.1504/IJWGS.2018.095647 URL |
| [23] | ZHANG Yu, WEN Jiangtao. An IoT Electric Business Model Based on the Protocol of Bitcoin[C]// IEEE.2015 18th International Conference on Intelligence in Next Generation Networks. New York: IEEE, 2015: 184-191. |
| [24] | JIN Ming. Research on Key Technologies of Federated Learning Based on Blockchain[D]. Harbin:Harbin Engineering University, 2021. |
| 金明. 基于区块链的联邦学习关键技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2021. |
| [1] | 翟鹏, 何泾沙, 张昱. 物联网环境下基于SM9算法和区块链技术的身份认证方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 179-187. |
| [2] | 何业锋, 权家辉, 刘妍. 基于混合区块链的位置隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 229-238. |
| [3] | 林怡航, 周鹏远, 吴治谦, 廖勇. 基于触发器逆向的联邦学习后门防御方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 262-271. |
| [4] | 金志刚, 丁禹, 武晓栋. 融合梯度差分的双边校正联邦入侵检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 293-302. |
| [5] | 吴昊天, 李一凡, 崔鸿雁, 董琳. 基于零知识证明和区块链的联邦学习激励方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 1-13. |
| [6] | 朱郭诚, 何德彪, 安浩杨, 彭聪. 基于区块链和SM9数字签名的代理投票方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 36-47. |
| [7] | 赵佳, 杨博凯, 饶欣宇, 郭雅婷. 基于联邦学习的Tor流量检测算法设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 60-68. |
| [8] | 徐茹枝, 戴理朋, 夏迪娅, 杨鑫. 基于联邦学习的中心化差分隐私保护算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 69-79. |
| [9] | 赖成喆, 赵益宁, 郑东. 基于同态加密的隐私保护与可验证联邦学习方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 93-105. |
| [10] | 公鹏飞, 谢四江, 程安东. 基于HotStuff改进的多主节点共识算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 108-117. |
| [11] | 周权, 陈民辉, 卫凯俊, 郑玉龙. 基于SM9的属性加密的区块链访问控制方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 37-46. |
| [12] | 赵佳豪, 蒋佳佳, 张玉书. 基于动态默克尔哈希树的跨链数据一致性验证模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 95-107. |
| [13] | 邵震哲, 蒋佳佳, 赵佳豪, 张玉书. 面向跨链的改进加权拜占庭容错算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 109-120. |
| [14] | 覃思航, 代炜琦, 曾海燕, 顾显俊. 基于区块链的电力应用数据安全共享研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 52-65. |
| [15] | 彭翰中, 张珠君, 闫理跃, 胡成林. 联盟链下基于联邦学习聚合算法的入侵检测机制优化研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 76-85. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||