信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 20-29.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.04.003
基于多通道联合学习的自动调制识别网络
- 1.厦门大学信息学院,厦门 361005
2.西藏大学信息科技学院,拉萨 850000
3.北京大学武汉人工智能研究院,武汉 430023
-
收稿日期:2022-11-17出版日期:2023-04-10发布日期:2023-04-18 -
通讯作者:吴志强 E-mail:lightnesstibet@163.com -
作者简介:赵彩丹(1974—),女,福建,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为无线信号处理、深度学习和无线网络安全|陈璟乾(1999—),男,福建,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为无线信号处理和深度学习|吴志强(1973—),男,北京,教授,博士,主要研究方向为无线信号处理、深度学习和调制编码。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61971368);国家自然科学基金(61731012);国家自然科学基金委区域创新发展联合基金(U20A20162)
Automatic Modulation Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Channel Joint Learning
ZHAO Caidan1, CHEN Jingqian1, WU Zhiqiang2,3( )
)
- 1. School of Information Science and Technology, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361000, China
2. School of Information Science and Technology, Tibet University, Lhasa 850000, China
3. Peking University Institute for Artificial Intelligence, Beijing 100871, China
-
Received:2022-11-17Online:2023-04-10Published:2023-04-18 -
Contact:WU Zhiqiang E-mail:lightnesstibet@163.com
摘要:
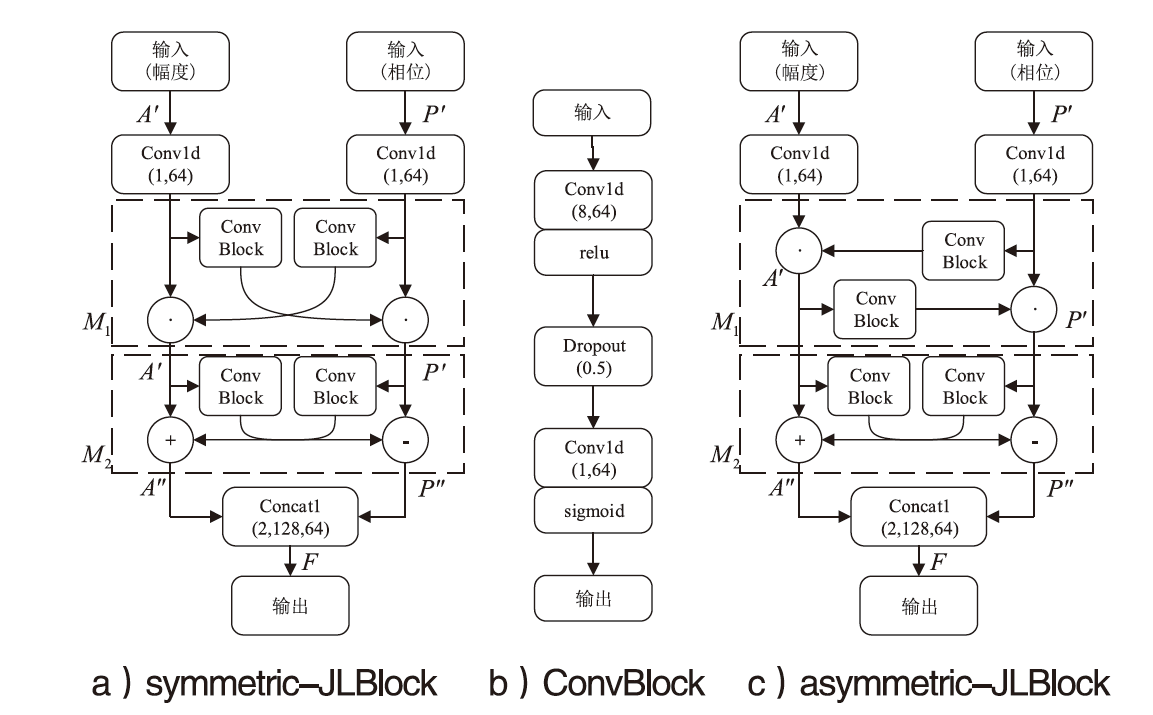
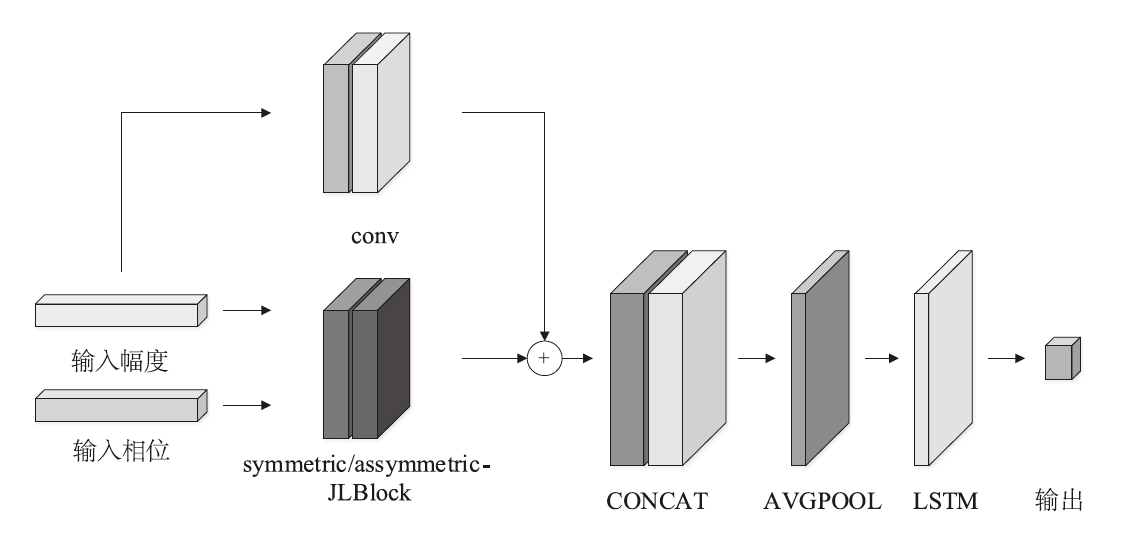
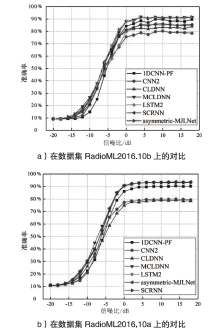
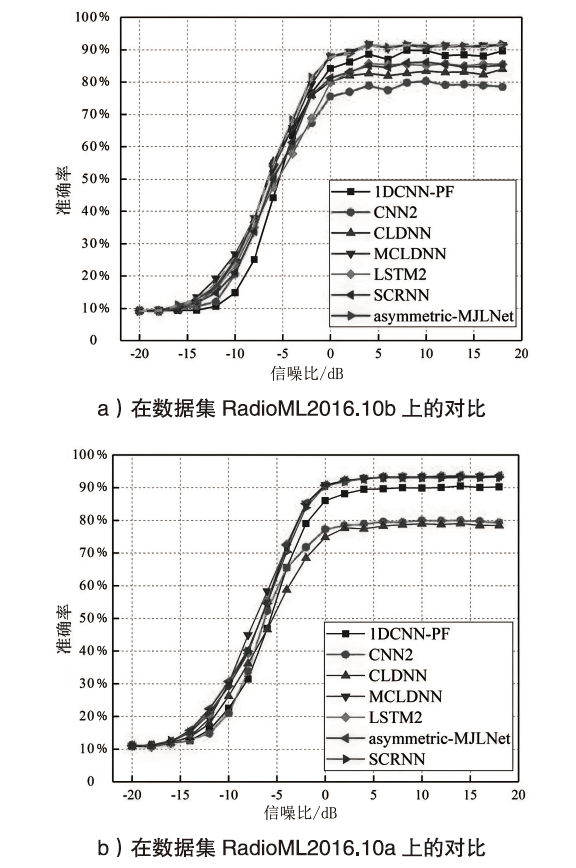
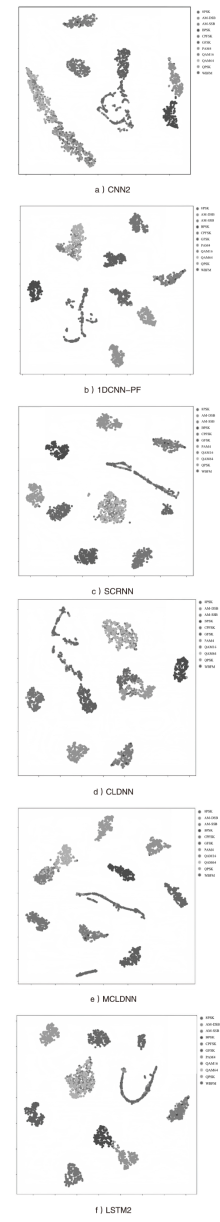
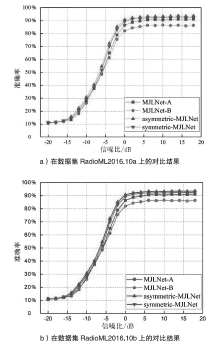
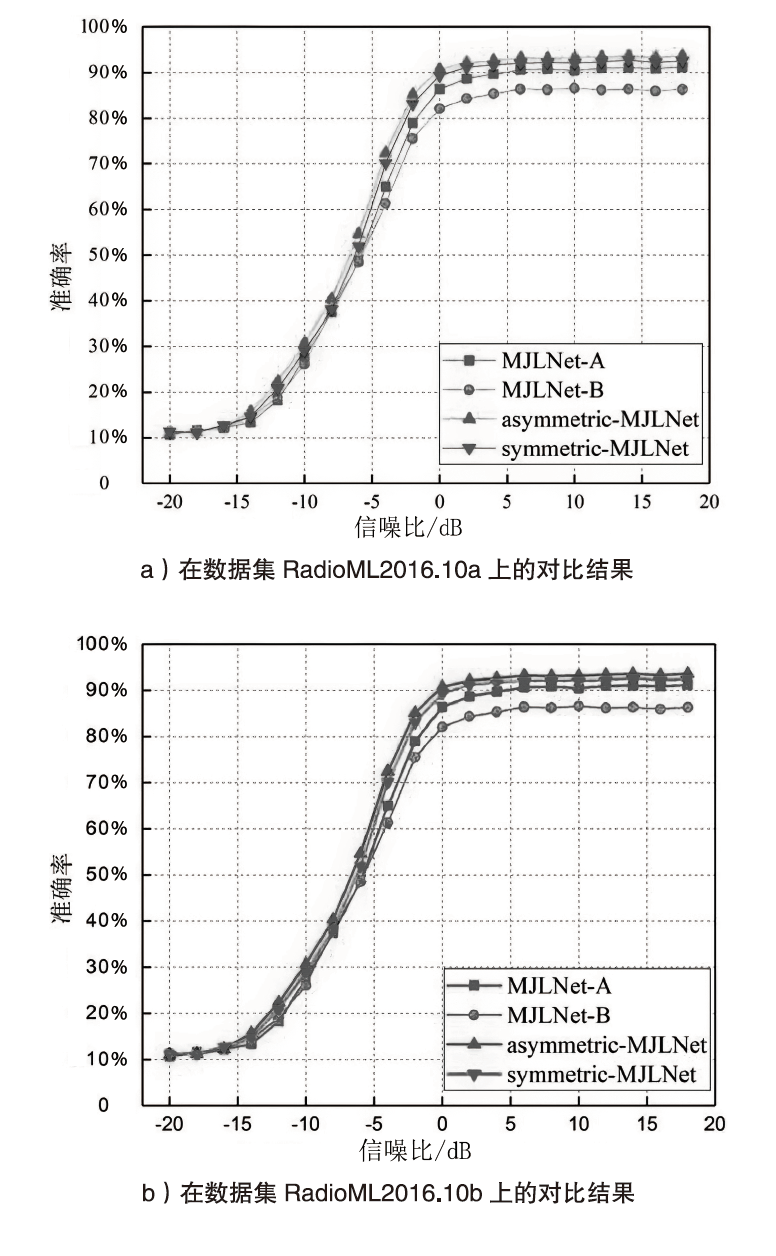
自动调制识别技术不仅可以提高频谱资源的利用率,而且是有效鉴别用户合法身份的方式之一。为进一步提高识别算法的性能,文章考虑幅度和相位特征之间的联系,提出了一种新的非对称多通道联合学习网络。该网络将幅度、相位以及两者的联合矩阵作为多通道输入端,在不改变参数量和计算速度的前提下利用非对称联合学习模块,较好地提取调制信号的幅度和相位中同质和异构特征,来实现自适应调制编码。实验结果表明,与其他深度学习网络相比,文章所提网络在基准开源数据集RadioML2016.10a和RadioML2016.10b上分别实现了91.73%和93.36%的识别精度。
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵彩丹, 陈璟乾, 吴志强. 基于多通道联合学习的自动调制识别网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 20-29.
ZHAO Caidan, CHEN Jingqian, WU Zhiqiang. Automatic Modulation Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Channel Joint Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(4): 20-29.
表2
SNR=0 dB时模型在RadioML2016.10a数据集上的性能
| 网络 调制 方式 | SCRNN | 1DCNN-PF | CNN2 | CLDNN | MCLDNN | LSTM2 | SCRNN | asymmetric-MJLNet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8PSK | 84% | 80% | 77% | 82% | 86% | 73% | 84% | 89% |
| AM-DSB | 86% | 99% | 99% | 87% | 89% | 93% | 86% | 90% |
| AM-SSB | 97% | 98% | 95% | 94% | 92% | 95% | 97% | 93% |
| BPSK | 99% | 98% | 98% | 99% | 99% | 94% | 99% | 99% |
| CPFSK | 100% | 100% | 98% | 96% | 100% | 99% | 100% | 100% |
| GFSK | 99% | 94% | 94% | 93% | 99% | 97% | 99% | 97% |
| PAM4 | 98% | 98% | 98% | 97% | 98% | 96% | 98% | 98% |
| QAM16 | 52% | 83% | 40% | 40% | 81% | 76% | 52% | 83% |
| QAM64 | 55% | 71% | 59% | 63% | 86% | 48% | 55% | 81% |
| QPSK | 82% | 95% | 40% | 74% | 96% | 86% | 82% | 97% |
| WBFM | 39% | 29% | 24% | 43% | 41% | 33% | 39% | 38% |
| [1] |
GUPTA A, JHA R K. A Survey of 5G Network: Architecture and Emerging Technologies[J]. IEEE Access, 2015, 3: 1206-1232.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2015.2461602 URL |
| [2] |
WANG Qun, SUN Haijian, HU R Q Y, et al. When Machine Learning Meets Spectrum Sharing Security: Methodologies and Challenges[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2022, 3: 176-208.
doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2022.3146364 URL |
| [3] |
LANZOLLA G, ANDERSON J A. Digital Transformation[J]. Business Strategy Review, 2008, 19(2): 72-76.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8616.2008.00539.x URL |
| [4] |
ZHANG Lin, XIAO Ming, WU Gang, et al. A Survey of Advanced Techniques for Spectrum Sharing in 5G Networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2017, 24(5): 44-51.
doi: 10.1109/MWC.2017.1700069 URL |
| [5] | ALARBI A, ALKISHRIWO O A S. Modulation Classification Based on Statistical Features and Artificial Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 1st International Maghreb Meeting of the Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering MI-STA. New York: IEEE, 2021: 748-751. |
| [6] | KIM K, POLYDOROS A. Digital Modulation Classification: The BPSK Versus QPSK Case[C]// IEEE. MILCOM 88, 21st Century Military Communications Conference. New York: IEEE, 1988: 431-436. |
| [7] |
JIANG Yuhan, ZOU Yulong, OUYANG Jian, et al. Secrecy Energy Efficiency Optimization for Artificial Noise Aided Physical-Layer Security in OFDM-Based Cognitive Radio Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(12): 11858-11872.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2876062 URL |
| [8] | LI Xiaofan, DONG Fangwei, ZHANG Sha, et al. A Survey on Deep Learning Techniques in Wireless Signal Recognition[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2019, 179: 1-12. |
| [9] |
WALENCZYKOWSKA M, KAWALEC A. Type of Modulation Identification Using Wavelet Transform and Neural Network[J]. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences Technical Sciences, 2016, 64(1): 257-261.
doi: 10.1515/bpasts-2016-0028 URL |
| [10] |
SWAMI A, SADLER B M. Hierarchical Digital Modulation Classification Using Cumulants[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2000, 48(3): 416-429.
doi: 10.1109/26.837045 URL |
| [11] | VUCIC D, VUKOTIC S, ERIC M. Cyclic Spectral Analysis of OFDM/OQAM Signals[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2017, 73: 139-143. |
| [12] |
OTTER D W, MEDINA J R, KALITA J K. A Survey of the Usages of Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(2): 604-624.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.5962385 URL |
| [13] |
KHAN M, SAJJAD M, KWON S. Clustering-Based Speech Emotion Recognition by Incorporating Learned Features and Deep BiLSTM[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 79861-79875.
doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639 URL |
| [14] | O’SHEA T J, CORGAN J, CLANCY T C. Convolutional Radio Modulation Recognition Networks[C]// Springer. International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks. Berlin:Springer, 2016: 213-226. |
| [15] | WEST N E, O'SHEA T. Deep Architectures for Modulation Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN). New York: IEEE, 2017: 1-7. |
| [16] |
RAJENDRAN S, MEERT W, GIUSTINIANO D, et al. Deep Learning Models for Wireless Signal Classification with Distributed Low-Cost Spectrum Sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2018, 4(3): 433-445.
doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2018.2835460 URL |
| [17] | PERENDA E, RAJENDRAN S, POLLIN S. Automatic Modulation Classification Using Parallel Fusion of Convolutional Neural Networks[C]// BalkanCom. Third International Balkan Conference on Communications and Networking. Istanbul: BalkanCom, 2019: 469-478. |
| [18] |
XU Jialang, LUO Chunbo, PARR G, et al. A Spatiotemporal Multi-Channel Learning Framework for Automatic Modulation Recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(10): 1629-1632.
doi: 10.1109/LWC.5962382 URL |
| [19] |
LIAO Kaisheng, ZHAO Yaodong, GU Jie, et al. Sequential Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks for Fast Automatic Modulation Classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 27182-27188.
doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639 URL |
| [20] |
HUYNH-THE T, PHAM Q V, NGUYEN T V, et al. Automatic Modulation Classification: A Deep Architecture Survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 142950-142971.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3120419 URL |
| [21] | LIU Minhao, ZENG Ailing, LAI Q, et al. Time Series is a Special Sequence: Forecasting with Sample Convolution and Interaction[EB/OL]. (2021-10-19)[2022-11-05]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3171665133. |
| [22] | O'SHEA T J, WEST N. Radio Machine Learning Dataset Generation with GNU Radio[EB/OL]. (2016-09-06)[2022-11-05]. https://pubs.gnuradio.org/index.php/grcon/article/view/11. |
| [23] | LAURENS V D M, GEOFFREY H. Visualizing Data Using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(11): 2579-2625. |
| [1] | 谭柳燕, 阮树骅, 杨敏, 陈兴蜀. 基于深度学习的教育数据分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 96-102. |
| [2] | 徐占洋, 程洛飞, 程建春, 许小龙. 一种使用Bi-ADMM优化深度学习模型的方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 54-63. |
| [3] | 陈得鹏, 刘肖, 崔杰, 仲红. 一种基于双阈值函数的成员推理攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 64-75. |
| [4] | 贾凡, 康舒雅, 江为强, 王光涛. 基于NLP及特征融合的漏洞相似性算法评估[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(1): 18-27. |
| [5] | 高博, 陈琳, 严迎建. 基于CNN-MGU的侧信道攻击研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 55-63. |
| [6] | 刘光杰, 段锟, 翟江涛, 秦佳禹. 基于多特征融合的移动流量应用识别[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 18-26. |
| [7] | 王浩洋, 李伟, 彭思维, 秦元庆. 一种基于集成学习的列车控制系统入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 46-53. |
| [8] | 郑耀昊, 王利明, 杨婧. 基于网络结构自动搜索的对抗样本防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 70-77. |
| [9] | 刘峰, 杨成意, 於欣澄, 齐佳音. 面向去中心化双重差分隐私的谱图卷积神经网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 39-46. |
| [10] | 郭森森, 王同力, 慕德俊. 基于生成对抗网络与自编码器的网络流量异常检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(12): 7-15. |
| [11] | 林发鑫, 张健. 虚拟化平台异常行为检测系统的设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11): 62-67. |
| [12] | 张郅, 李欣, 叶乃夫, 胡凯茜. 融合多重风格迁移和对抗样本技术的验证码安全性增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 129-135. |
| [13] | 高昌锋, 肖延辉, 田华伟. 基于多阶段渐进式神经网络的图像相机指纹提取算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 15-23. |
| [14] | 刘家银, 李馥娟, 马卓, 夏玲玲. 基于多尺度卷积神经网络的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 31-38. |
| [15] | 刘烁, 张兴兰. 基于双重注意力的入侵检测系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 80-86. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||