信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 10-19.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.04.002
面向车联网环境的异常行为检测机制研究综述
- 1.武汉大学国家网络安全学院,武汉 430040
2.国家工业信息安全发展研究中心,北京 100040
-
收稿日期:2022-10-14出版日期:2023-04-10发布日期:2023-04-18 -
通讯作者:吕臣臣 E-mail:lvbuer@whu.edu.cn -
作者简介:曹越(1984—),男,湖北,教授,博士,主要研究方向为智能交通系统、车联网安全|吕臣臣(1998—),男,河南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为车联网异常行为检测|孙娅苹(1986—),女,北京,高级工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为车联网、数据安全技术防护与测评|张宇昂(2000—),男,河南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为车联网异常行为检测。 -
基金资助:湖北省国际科技合作计划(2021EHB012);武汉市知识创新专项(2022010801010117);中央高校基本科研业务费专项(2042022rc0020)
Review of Research on Misbehavior Detection in VANET
CAO Yue1, LYU Chenchen1( ), SUN Yaping2, ZHANG Yu’ang1
), SUN Yaping2, ZHANG Yu’ang1
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430040, China
2. CIC Industry and Information Security, Beijing 100040, China
-
Received:2022-10-14Online:2023-04-10Published:2023-04-18 -
Contact:LYU Chenchen E-mail:lvbuer@whu.edu.cn
摘要:
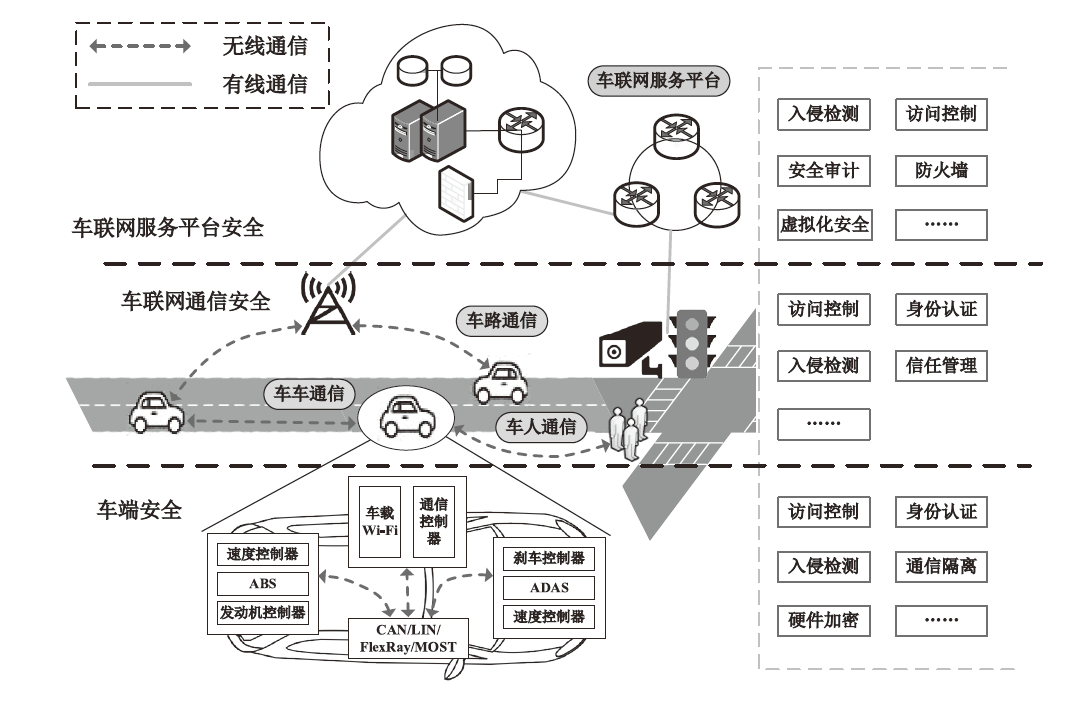
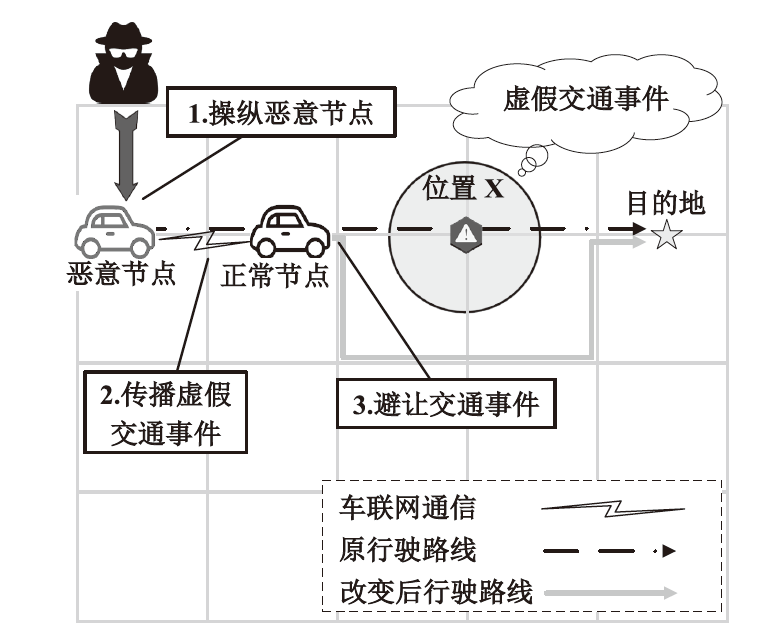
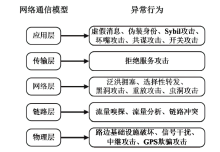
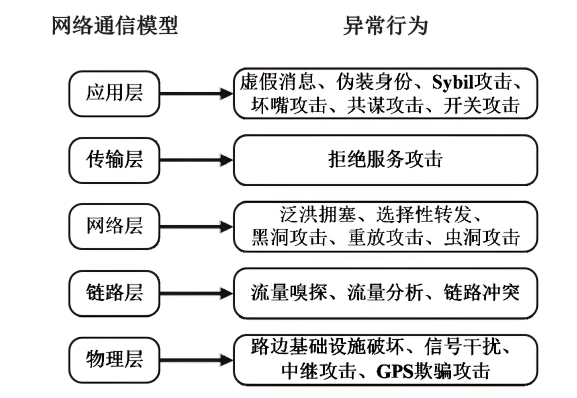
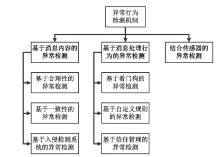
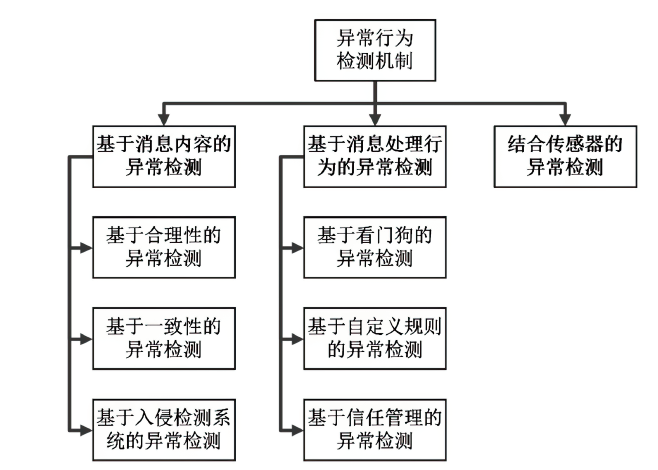
以智能网联汽车为核心的下一代智能交通系统逐渐深入城市居民生活,但也暴露出如远程恶意控制车辆、泄露车主个人信息等安全威胁。相较于车端设备与车联网服务平台层面的安全问题,文章重点关注车联网通信层面面临的安全问题。基于此,文章对近年来车联网环境中异常行为检测机制的相关研究进行了梳理。首先,分析了异常行为定义,并总结了常见威胁模型;然后,从基于消息内容的异常检测、基于消息处理行为的异常检测和结合传感器的异常检测3个方面,讨论了异常行为检测机制的分类;最后,总结了当前车联网通信异常行为检测机制中尚未解决的技术问题和未来研究趋势。
中图分类号:
引用本文
曹越, 吕臣臣, 孙娅苹, 张宇昂. 面向车联网环境的异常行为检测机制研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 10-19.
CAO Yue, LYU Chenchen, SUN Yaping, ZHANG Yu’ang. Review of Research on Misbehavior Detection in VANET[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(4): 10-19.
表1
基于消息内容的异常检测
| 方案 | 类别 | 安全威胁 | 威胁对应 网络模型 | 突出特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 基于合理性的 异常检测 | 异常数据 | 应用层 | 预定义规则检测较快,且易于扩展和修改规则 |
| 文献[ | 基于合理性的 异常检测 | 虚假消息 | 应用层 | 卡尔曼滤波能从一组有限的且包含噪声的数据中预测节点的移动位置 |
| 文献[ | 基于合理性的 异常检测 | 虚假消息 | 应用层 | 结合多方面的特征构建集成学习模型 |
| 文献[ | 基于合理性的 异常检测 | 虚假消息 | 应用层 | 构建历史合法轨迹数据库以检测虚假位置构成的虚假轨迹 |
| 文献[ | 基于一致性的 异常检测 | 虚假消息 | 应用层 | 通过假设检验严格检测不一致数据,具有较高的可靠性 |
| 文献[ | 基于一致性的 异常检测 | 虚假消息 | 应用层 | 利用基数估计的方法减小广播事件消息的开销 |
| 文献[ | 基于一致性的 异常检测 | 虚假消息 | 应用层 | 通过将车辆按地理位置分组的方式减小广播事件消息的开销 |
| 文献[ | 基于一致性的 异常检测 | 黑洞攻击 | 网络层 | 基于非参数的统计方法检测和识别恶意节点 |
| 文献[ | 基于入侵检测系统的异常检测 | 异常数据 | 应用层 | 节点只进行预处理,学习和分类在可信第三方和服务提供者进行,降低了对节点性能的要求 |
| 文献[ | 基于入侵检测系统的异常检测 | 异常数据 | 应用层 | 通过将数据收集、存储和分析过程限制在可代表集群的一组节点的方式减少SVM训练集的大小 |
| 文献[ | 基于入侵检测系统的异常检测 | 异常数据 | 应用层 | 基于深度生成模型和分布式SDN协作检测整个网络的异常行为 |
表2
基于消息处理行为的异常检测
| 方案 | 类别 | 安全威胁 | 威胁对应 网络模型 | 突出特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ 方案 | 看门狗系统 | 黑洞攻击 | 网络层 | 基于相遇历史评估节点的信誉,并引入相遇节点的本地信誉作为间接信誉 |
| 文献[ 方案 | 看门狗系统 | 黑洞攻击 | 网络层 | 基于与相遇节点的社交关系识别正常节点、个人自私节点和社交自私节点 |
| 文献[ 方案 | 看门狗系统 | 贪婪攻击 | 链路层 | 基于贪婪行为的特征检测异常行为,此类特征难以隐藏,具有较高的可靠性 |
| 文献[ 方案 | 自定义规则 | 泛洪攻击 | 网络层 | 通过限制速率的方式检测泛洪攻击 |
| 文献[ 方案 | 自定义规则 | 泛洪攻击 | 网络层 | 扩展了速率限制,允许合理突发流量情况发生 |
| 文献[ 方案 | 信任管理 | 坏嘴攻击和开关攻击 | 应用层 | 基于节点间直接交互构建本地信任,分析链接本地信任以生成全局信任 |
| 文献[ 方案 | 信任管理 | 黑洞攻击、消息篡改和身份伪造 | 网络层 应用层 | 评估节点行为以生成观察证据,随后基于观察证据识别恶意节点 |
| 文献[ 方案 | 信任管理 | 坏嘴攻击和开关攻击 | 应用层 | 结合节点可信度(基于功能信任度和推荐信任度)和数据信任(基于多节点数据)识别异常行为 |
| [1] | MITCHELL R, CHEN I R. A Survey of Intrusion Detection Techniques for Cyber-Physical Systems[J]. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2014, 46(4): 1-29. |
| [2] | EZE E C, ZHANG Sijiang, LIU Enjie. Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANETs):Current State, Challenges, Potentials and Way Forward[C]// IEEE. 2014 20th International Conference on Automation and Computing. New York: IEEE, 2014: 176-181. |
| [3] | LIN Xiufan. Research on Legal Issues of Tort Liability of Autopilot Cars[D]. Baoding: Hebei University, 2019. |
| 林秀繁. 自动驾驶汽车侵权责任法律问题研究[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2019. | |
| [4] | SHANG Xun. China FAW and Alibaba Strategic Cooperation: Join Hands to Build Intelligent Connected Vehicles[J]. Commercial Vehicle, 2020(1): 10. |
| 商讯. 中国一汽与阿里巴巴战略合作:携手打造智能网联汽车[J]. 商用汽车, 2020(1): 10. | |
| [5] | TIAN Ye. Huawei Builds Smart Car Solutions[J]. Intelligent Connected Vehicles, 2022(1): 68-69. |
| 田野. 华为打造智能汽车解决方案[J]. 智能网联汽车, 2022(1): 68-69. | |
| [6] | China Academy for Information and Communications Technology. White Paper on Cybersecurity of VANETs[EB/OL]. (2017-09-21)[2022-05-06]. http://www.caict.ac.cn/kxyj/qwfb/bps/201804/P020170921430215345026.pdf. |
| 中国信息通信研究院. 车联网网络安全白皮书[EB/OL]. (2017-09-21)[2022-05-06]. http://www.caict.ac.cn/kxyj/qwfb/bps/201804/P020170921430215345026.pdf. | |
| [7] | REN/ITS-0010089 Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Part 2: Specification of Cooperative Awareness Basic Service, V1.4.1[S]. Nice: ETSI, 2019. |
| [8] | REN/ITS-0010090 Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Part 3: Specifications of Decentralized Environmental Notification Basic Service, V1.3.1[S]. Nice: ETSI, 2019. |
| [9] | MCGURRIN M. Vehicle Information Exchange Needs for Mobility Applications[EB/OL]. (2012-08-01)[2022-05-06]. https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/3365. |
| [10] | SAE J2735_201603 Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) Message Set Dictionary[S]. Nice: ETSI, 2016. |
| [11] | CHANDOLA V, BANERJEE A, KUMAR V. Anomaly Detection: A Survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2009, 41(3): 1-58. |
| [12] | HEIJDEN R W, DIETZEL S, LEINMÜLLER T, et al. Survey on Misbehavior Detection in Cooperative Intelligent Transportation Systems[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 21(1): 779-811. |
| [13] | JIANG Jinfang, HAN Guangjie. Survey of Trust Management Mechanism in Wireless Sensor Network[J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(4): 12-20. |
| 江金芳, 韩光洁. 无线传感器网络中信任管理机制研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 12-20. | |
| [14] | LO N W, TSAI H C. Illusion Attack on Vanet Applications—A Message Plausibility Problem[C]// IEEE. 2007 IEEE Globecom Workshops. New York: IEEE, 2007: 1-8. |
| [15] |
JAEGER A, BIMEYER N, STUBING H, et al. A Novel Framework for Efficient Mobility Data Verification in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, 2012, 10(1): 11-21.
doi: 10.1007/s13177-011-0038-9 URL |
| [16] |
GHALEB F A, MAAROF M A, ZAINAL A, et al. Ensemble-Based Hybrid Context-Aware Misbehavior Detection Model for Vehicular Ad Hoc Network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(23): 2852-2880.
doi: 10.3390/rs11232852 URL |
| [17] | LE A, MAPLE C. Shadows Don’t Lie: n-Sequence Trajectory Inspection for Misbehaviour Detection and Classification in VANETs[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1-6. |
| [18] |
ZAIDI K, MILOJEVIC M B, RAKOCEVIC V, et al. Host-Based Intrusion Detection for VANETs: A Statistical Approach to Rogue Node Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 65(8): 6703-6714.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2480244 URL |
| [19] | HSIAO H C, STUDER A, DUBEY R, et al. Efficient and Secure Threshold-Based Event Validation for VANETs[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Fourth ACM Conference on Wireless Network Security. New York: ACM, 2011: 163-174. |
| [20] |
MOLINA-GIL J, CABALLERO-GIL P, CABALLERO-GIL C. Aggregation and Probabilistic Verification for Data Authentication in VANETs[J]. Information Sciences, 2014, 262: 172-189.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2013.07.036 URL |
| [21] |
ANTONOPOULOS A, VERIKOUKIS C. Cops: Cooperative Statistical Misbehavior Mitigation in Network-Coding-Aided Wireless Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 14(4): 1436-1446.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2754579 URL |
| [22] |
ALOQAILY M, OTOUM S, AL Ridhawi I, et al. An Intrusion Detection System for Connected Vehicles in Smart Cities[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2019, 90: 101842-101855.
doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2019.02.001 URL |
| [23] |
WAHAB O A, MOURAD A, OTROK H, et al. CEAP: SVM-Based Intelligent Detection Model for Clustered Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 50: 40-54.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.12.006 URL |
| [24] |
SHU Jiangang, ZHOU Lei, ZHANG Weizhe, et al. Collaborative Intrusion Detection for VANETs: A Deep Learning-Based Distributed SDN Approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 22(7): 4519-4530.
doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3027390 URL |
| [25] |
DIAS J F, RODRIGUES P C, XIA Feng, et al. A Cooperative Watchdog System to Detect Misbehavior Nodes in Vehicular Delay-Tolerant Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(12): 7929-7937.
doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2425357 URL |
| [26] |
JEDARI B, XIA Feng, CHEN Honglong, et al. A Social-Based Watchdog System to Detect Selfish Nodes in Opportunistic Mobile Networks[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 92: 777-788.
doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.10.049 URL |
| [27] |
MEJRI M N, BEN-OTHMAN J. GDVAN: A New Greedy Behavior Attack Detection Algorithm for VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2016, 16(3): 759-771.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2577035 URL |
| [28] |
LI Qinghua, GAO Wei, ZHU Sencun, et al. To Lie or to Comply: Defending Against Flood Attacks in Disruption Tolerant Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2012, 10(3): 168-182.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2012.84 URL |
| [29] |
PHAM T D, YEO C K, YANAI N, et al. Detecting Flooding Attack and Accommodating Burst Traffic in Delay-Tolerant Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 67(1): 795-808.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2748345 URL |
| [30] |
XIAO Yonggang, LIU Yanbing. BayesTrust and VehicleRank: Constructing an Implicit Web of Trust in VANET[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(3): 2850-2864.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2894056 URL |
| [31] | GE Chunpeng, ZHOU Lu, HANCKE G P, et al. A Provenance-Aware Distributed Trust Model for Resilient Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 16(8): 12481-12489. |
| [32] |
LI Wenjia, SONG Houbing. ART: An Attack-Resistant Trust Management Scheme for Securing Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 17(4): 960-969.
doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2494017 URL |
| [33] |
YAO Yuan, XIAO Bin, WU Gaofei, et al. Multi-Channel Based Sybil Attack Detection in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Using RSSI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 18(2): 362-375.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2833849 URL |
| [34] | ERCAN S, AYAIDA M, MESSAI N. New Features for Position Falsification Detection in VANETs Using Machine Learning[C]// IEEE. ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2021: 1-6. |
| [35] | SUN Mingshun, LI Ming, GERDES R. A Data Trust Framework for VANETs Enabling False Data Detection and Secure Vehicle Tracking[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS). New York: IEEE, 2017: 1-9. |
| [36] | HEIJDEN R W, LUKASEDER T, KARGL F. VeReMi: A Dataset for Comparable Evaluation of Misbehavior Detection in VANETs[C]// EAI. International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Systems. Berlin:Springer, 2018: 318-337. |
| [37] |
SOMMER C, GERMAN R, DRESSLER F. Bidirectionally Coupled Network and Road Traffic Simulation for Improved IVC Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2010, 10(1): 3-15.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.2010.133 URL |
| [38] | KAMEL J, WOLF M, HEIJDEN R W, et al. VeReMi Extension: A Dataset for Comparable Evaluation of Misbehavior Detection in VANETs[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC2020). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-6. |
| [1] | 胡艺, 佘堃. 基于区块链和智能合约的双链车联网系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 26-35. |
| [2] | 林发鑫, 张健. 虚拟化平台异常行为检测系统的设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11): 62-67. |
| [3] | 刘忻, 王家寅, 杨浩睿, 张瑞生. 一种基于区块链和secGear框架的车联网认证协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 27-36. |
| [4] | 王湘懿, 张健. 基于图像和机器学习的虚拟化平台异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 92-96. |
| [5] | 荆涛, 万巍. 面向属性迁移状态的P2P网络行为分析方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(1): 16-25. |
| [6] | 汪金苗, 王国威, 王梅, 朱瑞瑾. 面向雾计算的隐私保护与访问控制方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 41-45. |
| [7] | 吴志红, 赵建宁, 朱元, 陆科. 国密算法和国际密码算法在车载单片机上应用的对比研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(8): 68-75. |
| [8] | 袁超, 张浩, Gulliver Thomas Aaron. 车联网中协作车--车通信系统在N-Rayleigh信道下ASEP性能分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(3): 40-46. |
| [9] | 徐凌伟, 张浩, 王景景, 吴春雷. 车联网中车—车通信系统在n-Rayleigh信道下的性能分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2014, 14(12): 65-70. |
| [10] | 郎为民. 物联网安全技术的相关研究与发展[J]. , 2011, 11(3): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||