信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (11): 104-117.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.11.011
基于BiTCN-DLP的恶意代码分类方法
- 1.空军工程大学防空反导学院,西安 710051
2.空军工程大学研究生院,西安 710051
-
收稿日期:2023-08-25出版日期:2023-11-10发布日期:2023-11-10 -
通讯作者:宋亚飞yafei_song@163.com -
作者简介:李思聪(2000—),女,陕西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络空间安全和恶意代码检测|王坚(1982—),男,陕西,副教授,硕士,主要研究方向为智能信息处理和恶意软件检测|宋亚飞(1988—),男,河南,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为机器学习及其在目标识别和入侵检测等领域中的应用|黄玮(1998—),男,江西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络空间安全和恶意代码检测 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61806219);国家自然科学基金(61703426);国家自然科学基金(61876189);陕西省科学基金(2021JM-226);陕西省高校科协青年人才托举计划(20190108);陕西省高校科协青年人才托举计划(20220106);陕西省创新能力支撑计划(2020KJXX-065)
Malicious Code Classification Method Based on BiTCN-DLP
LI Sicong1,2, WANG Jian1, SONG Yafei1( ), HUANG Wei1,2
), HUANG Wei1,2
- 1. Air and Missile Defense College, Air Force Engineering University, Xi’an 710051, China
2. Graduate School of Air Force Engineering University, Xi’an 710051, China
-
Received:2023-08-25Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-11-10
摘要:
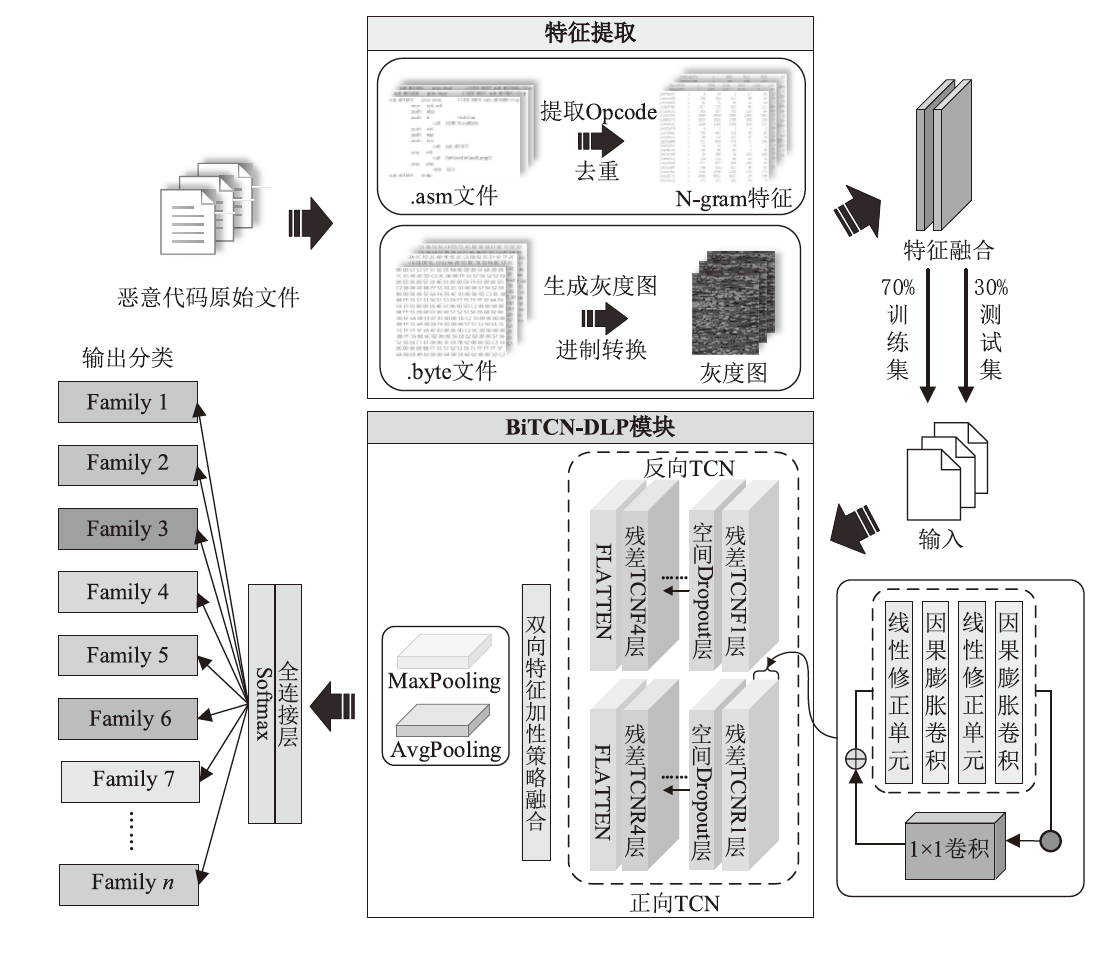
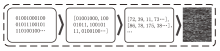
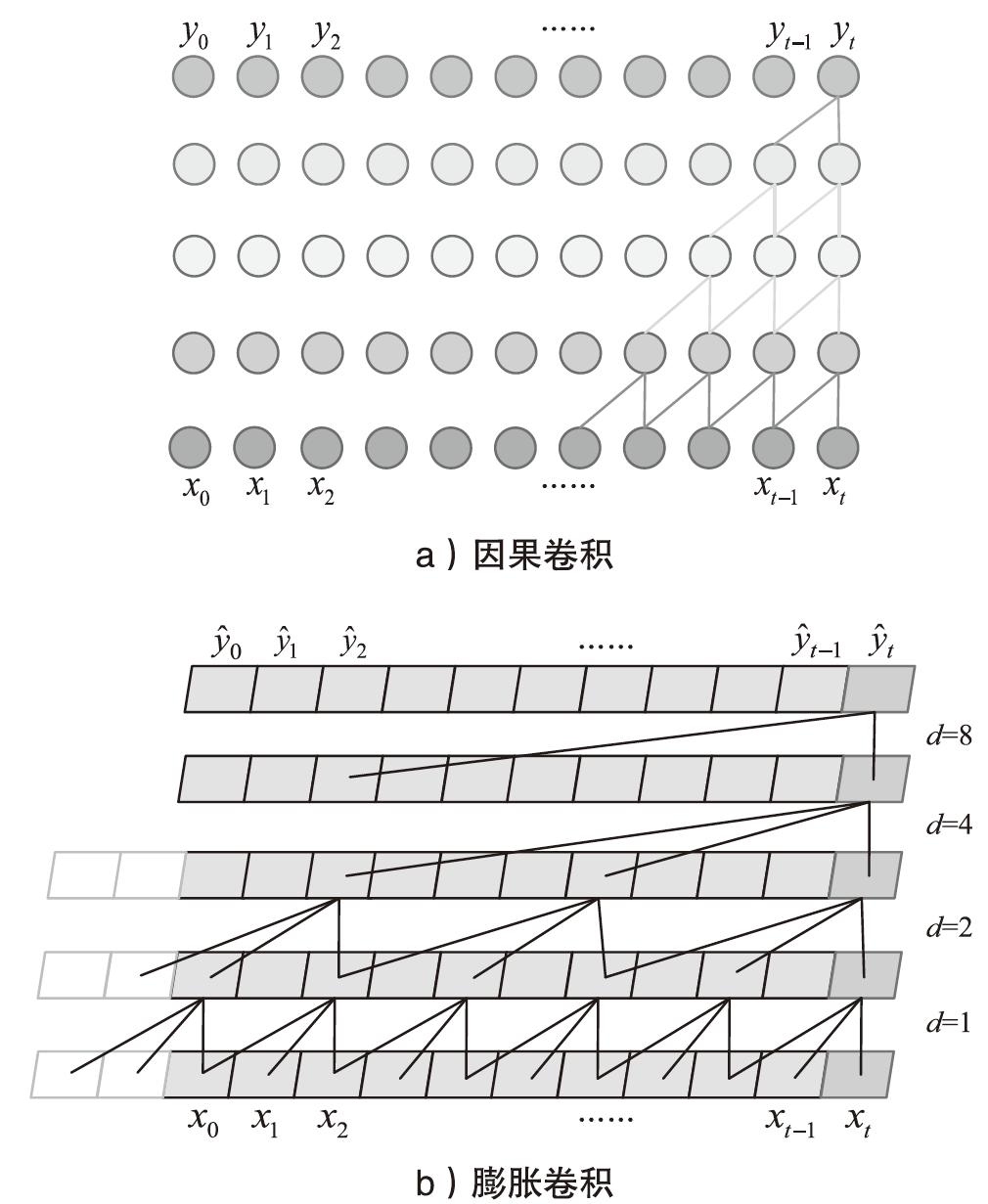
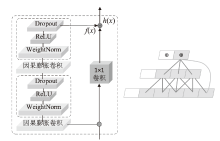
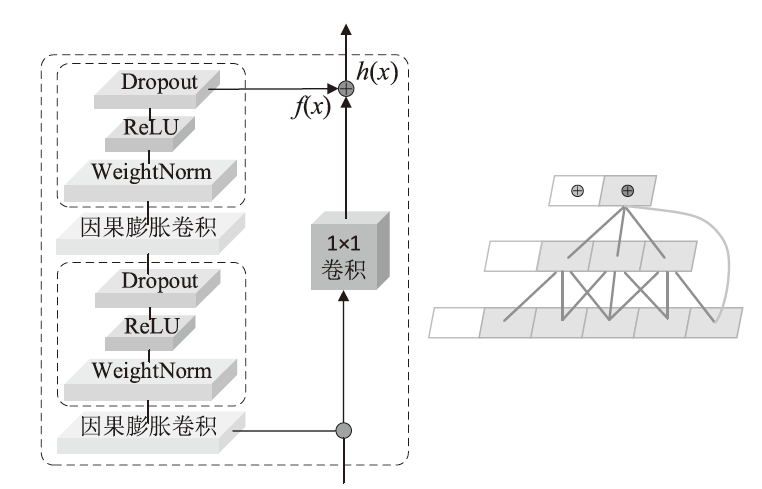
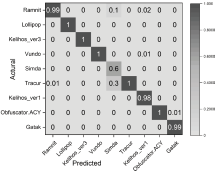
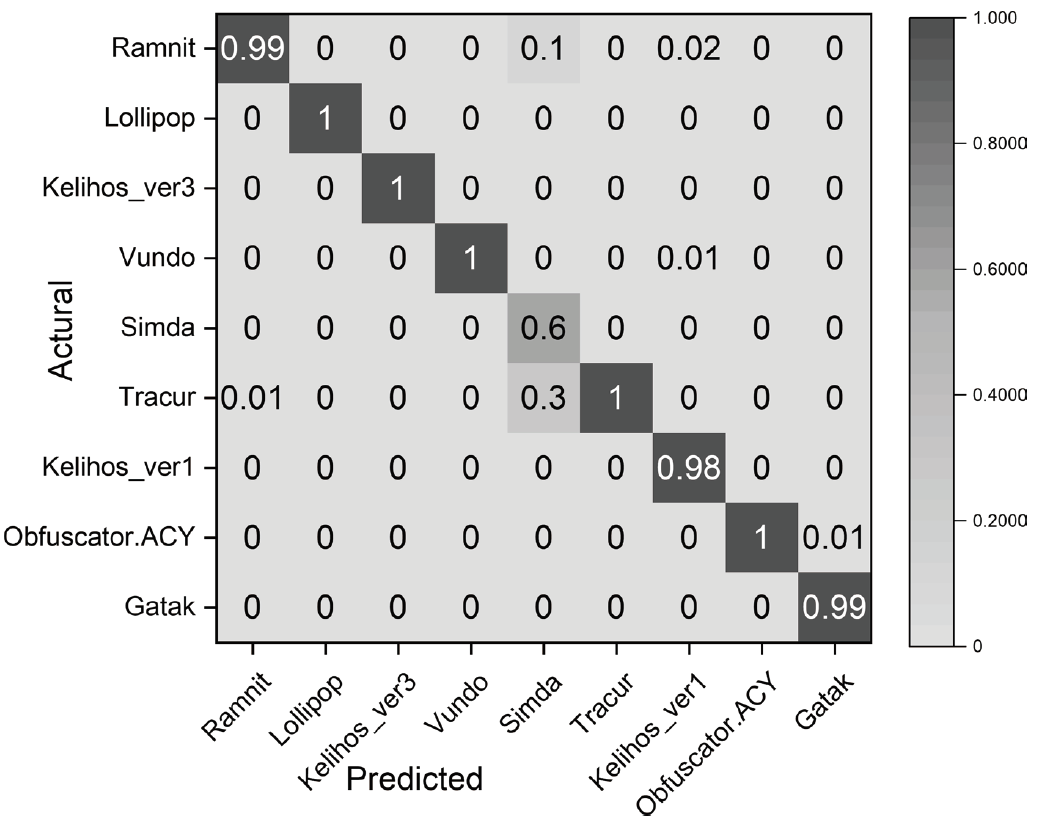
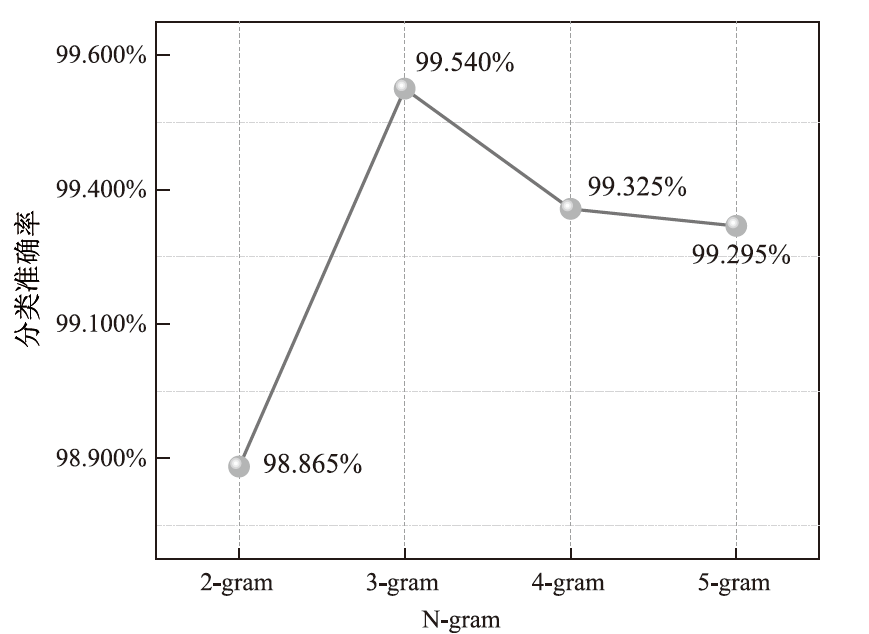
为应对不断升级的恶意代码变种,针对现有恶意代码分类方法对特征提取能力不足、分类准确率下降的问题,文章提出了基于双向时域卷积网络(Bidirectional Temporal Convolution Network,BiTCN)和池化融合(Double Layer Pooling,DLP)的恶意代码分类方法(BiTCN-DLP)。首先,该方法融合恶意代码操作码和字节码特征以展现不同细节;然后,构建BiTCN模型充分利用特征的前后依赖关系,引入池化融合机制进一步挖掘恶意代码数据内部深层的依赖关系;最后,文章在Kaggle数据集上对模型进行验证,实验结果表明,基于BiTCN-DLP的恶意代码分类准确率可达99.54%,且具有较快的收敛速度和较低的分类误差,同时,文章通过对比实验和消融实验证明了该模型的有效性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李思聪, 王坚, 宋亚飞, 黄玮. 基于BiTCN-DLP的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 104-117.
LI Sicong, WANG Jian, SONG Yafei, HUANG Wei. Malicious Code Classification Method Based on BiTCN-DLP[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(11): 104-117.
表7
不同模型性能实验结果对比
| 模型 | 特征 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 | 参数量/M | 检测 时间/ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-class SVM[ | Opcode+ 灰度图 | 74.40 % | — | — | — | — | — |
| 文献[ | CFG+DGCNN | 94.40 % | 94.18 % | 93.68 % | 93.93 % | — | — |
| PCA and KNN[ | 灰度图 | 96.60 % | — | — | — | — | — |
| 文献[ | Mcs-ResNet | 97.21 % | 96.55 % | 96.24 % | 96.39 % | — | 150.75 |
| 文献[ | 灰度图 | 97.49 % | — | — | 94.00 % | — | — |
| 文献[ | A-GCN | 98.03 % | — | — | 93.80 % | — | — |
| Strand Gene Sequence[ | .asm序列 | 98.53 % | 97.42 % | — | — | — | 28.91 |
| RSGC[ | Opcode+ 灰度图 | 98.90 % | — | — | — | — | — |
| MCSC[ | 灰度图 | 98.86 % | — | — | 98.07 % | — | — |
| ID-CNN-IMIR[ | 灰度图 | 98.94 % | — | — | — | — | — |
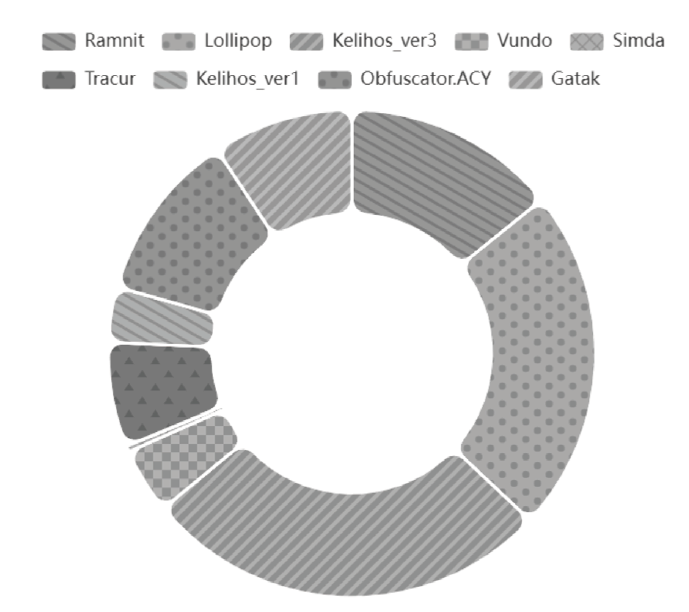
| TI-MVD[ | SCC-GRU | 99.10 % | 97.50 % | 98.65 % | — | — | — |
| Orthrus[ | 字节+ Opcode | 99.26 % | 98.86 % | — | 90.67 % | — | — |
| BiTCN-SA[ | Opcode+ 灰度图 | 99.75 % | 99.69 % | 99.66 % | 99.63 % | 12.64 | 20.92 |
| BiTCN-DLP | Opcode+ 灰度图 | 99.54 % | 99.61 % | 99.42 % | 99.49 % | 3.86 | 4.34 |
| [1] | Internet Development Research. The 51st Statistical Report on the Development of the Internet in China[EB/OL]. (2023-03-02)[2023-07-10]. https://www.cnnic.cn/n4/2023/0302/c199-10755.html. |
| 互联网发展研究. 《中国互联网络发展状况统计报告》[EB/OL]. (2023- 03-02)[2023-07-10]. https://www.cnnic.cn/n4/2023/0302/c199-10755.html. | |
| [2] | Kaspersky Security Network. IT Threat Evolution in Q3 2021[EB/OL]. (2022-05-27)[2023-07-10]. https://securelist.com/it-threat-evolution-in-q1-2022-mobile-statistics/10658. |
| [3] |
KIM S, YEOM S, OH H, et al. Automatic Malicious Code Classification System through Static Analysis Using Machine Learning[J]. Symmetry, 2020, 13(1): 35-45.
doi: 10.3390/sym13010035 URL |
| [4] | NATARAJ L, KARTHIKEYAN S, JACOB G, et al. Malware Images: Visualization and Automatic Classification[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Visualization for Cyber Security. New York: ACM, 2011: 1-7. |
| [5] |
CUI Zhihua, DU Lei, WANG Penghong, et al. Malicious Code Detection Based on CNNs and Multi-Objective Algorithm[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2019, 129: 50-58.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2019.03.010 |
| [6] | GAYATHRI S, GOPI V P, PALANISAMY P. A Lightweight CNN for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification from Fundus Images[EB/OL]. (2020-08-11)[2023-07-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102115. |
| [7] | REZENDE E, RUPPERT G, CARVALHO T, et al. Malicious Software Classification Using VGG16 Deep Neural Network’s Bottleneck Features[C]// Latifi, Shahram. Information Technology-New Generations:15th International Conference on Information Technology. Berlin:Springer International Publishing, 2018: 51-59. |
| [8] | XU Mingdi, TONG Hui, JIN Chaoyang, et al. Malicious Code Detection Method Based on Multiple Features[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics and Communication Engineering (ICECE). New York: IEEE, 2021: 8-15. |
| [9] | ZHAO Yuntao, XU Chunyu, BO Bo, et al. Maldeep: A Deep Learning Classification Framework against Malware Variants Based on Texture Visualization[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2019, 2019(8): 1-11. |
| [10] |
DAMODARAN A, TROIA F D, VISAGGIO C A, et al. A Comparison of Static, Dynamic, and Hybrid Analysis for Malware Detection[J]. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, 2017, 13: 1-12.
doi: 10.1007/s11416-015-0261-z URL |
| [11] | VENKATRAMAN S, ALAZAB M. Use of Data Visualisation for Zero-Day Malware Detection[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2018, 2018: 1-13. |
| [12] |
ALAZAB M. Profiling and Classifying the Behavior of Malicious Codes[J]. Journal of Systems and Software, 2015, 100: 91-102.
doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.10.031 URL |
| [13] | SEBASTIO S, BARANOV E, BIONDI F, et al. Optimizing Symbolic Execution for Malware Behavior Classification[EB/OL]. (2020-03-12)[2023-07-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2020.101775. |
| [14] | WANG Kun, SONG Tao, LIANG Alei. Mmda: Metadata Based Malware Detection on Android[C]// IEEE. 2016 12th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security (CIS). New York: IEEE, 2016: 598-602. |
| [15] |
VENKATRAMAN S, ALAZAB M, VINAYAKUMAR R. A Hybrid Deep Learning Image-Based Analysis for Effective Malware Detection[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2019, 47: 377-389.
doi: 10.1016/j.jisa.2019.06.006 URL |
| [16] | ABOU-ASSALEH T, CERCONE N, KESELJ V, et al. N-gram-Based Detection of New Malicious Code[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 28th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference(COMPSAC). New York: IEEE, 2004: 41-42. |
| [17] | MOSKOVITCH R, FEHER C, TZACHAR N, et al. Unknown Malcode Detection Using Opcode Representation[C]// Springer.European Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics. Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 204-215. |
| [18] |
SANTOS I, BREZO F, UGARTE-PEDRERO X, et al. Opcode Sequences as Representation of Executables for Data-Mining-Based Unknown Malware Detection[J]. Information Sciences, 2013, 231: 64-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2011.08.020 URL |
| [19] | KANG B J, YERIMA S Y, MCLAUGHLIN K, et al. N-Opcode Analysis for Android Malware Classification and Categorization[C]// IEEE.2016 International Conference on Cyber Security and Protection of Digital Services (Cyber Security). New York: IEEE, 2016: 1-7. |
| [20] |
NATARAJ L, MANJUNATH B S. Spam: Signal Processing to Analyze Malware[Applications Corner][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2016, 33(2): 105-117.
doi: 10.1109/MSP.2015.2507185 |
| [21] | JIANG Ruilin, QIN Renchao. Multi-Neural Network Malicious Code Detection Model Based on Depth-Separable Convolution[J]. Computer Applications, 2023, 43(5): 1527-1533. |
|
蒋瑞林, 覃仁超. 基于深度可分离卷积的多神经网络恶意代码检测模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(5):1527-1533.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022050716 |
|
| [22] | WEI Lizhuo, SHI Chunzhu, XU Fengkai, et al. Static Detection Technique of Malicious Code Based on Feature Sequences[J]. Network Security and Data Governance, 2022, 41(10): 56-64. |
| 魏利卓, 石春竹, 许凤凯, 等. 基于特征序列的恶意代码静态检测技术[J]. 网络安全与数据治理, 2022, 41(10):56-64. | |
| [23] | LIU Zixuan, WANG Chen. BiLSTM Malicious Code Classification Based on Multi-Feature Fusion[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2022, 30(18): 67-72. |
| 刘紫煊, 王晨. 基于多特征融合的BiLSTM恶意代码分类[J]. 电子设计工程, 2022, 30(18):67-72. | |
| [24] | WANG Degang, SUN Yi, ZHOU Chuanxin, et al. A Model Similarity-Based Approach for Model Malicious Code Entrapment Detection[J]. Journal of Network and Information Security, 2023, 9(4): 90-103. |
| 汪德刚, 孙奕, 周传鑫, 等. 基于模型相似度的模型恶意代码夹带检测方法[J]. 网络与信息安全学报, 2023, 9(4):90-103. | |
| [25] | LIU Chen, LI Bo, ZHAO Jun, et al. TI-MVD: A Temporal Interaction-Enhanced Model for Malware Variants Detection[EB/OL]. (2023-08-18)[2023-08-20]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110850. |
| [26] | BU S J, CHO S B. Malware Classification with Disentangled Representation Learning of Evolutionary Triplet Network[EB/OL]. (2023-07-01)[2023-08-20]. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:259645678. |
| [27] | BAI Shaojie, KOLTER J Z, KOLTUN V. An Empirical Evaluation of Generic Convolutional and Recurrent Networks for Sequence Modeling[EB/OL]. (2018-04-19)[2023-07-10]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1803.01271. |
| [28] |
ZHAO Wentian, GAO Yanyun, JI Tingxiang, et al. Deep Temporal Convolutional Networks for Short-Term Traffic Flow Forecasting[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 114496-114507.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935504 |
| [29] |
BAI Jinrong, WANG Junfeng. Improving Malware Detection Using Multi-View Ensemble Learning[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2016, 9(17): 4227-4241.
doi: 10.1002/sec.v9.17 URL |
| [30] |
WANG Shuo, WANG Jian, WANG Yanan, et al. A Fast Detection Method for Malicious Code Based on Feature Fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics, 2023, 51(1): 57-66.
doi: 10.1080/00207218108901299 URL |
|
王硕, 王坚, 王亚男, 等. 一种基于特征融合的恶意代码快速检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(1):57-66.
doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211701 |
|
| [31] |
FAN Yuying, LI Chengjuan, YI Qiang, et al. Classification of Field Moving Targets Based on Improved TCN Network[J]. Computer Engineering, 2021, 47: 106-112.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0058750 |
| [32] |
Hewage P, Behera A, Trovati M, et al. Temporal Convolutional Neural (TCN) Network for an Effective Weather Forecasting Using Time-Series Data from the Local Weather Station[J]. Soft Computing, 2020, 24: 16453-16482.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-020-04954-0 |
| [33] | KOCHER G, KUMAR G. Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms with Feature Selection for Intrusion Detection Using UNSW-NB15 Dataset[J]. International Journal of Network Security & Its Applications, 2021, 13(1): 21-31. |
| [34] | D’HOOGE L, WAUTERS T, VOLCKAERT B, et al. Inter-Dataset Generalization Strength of Supervised Machine Learning Methods for Intrusion Detection[EB/OL]. (2020-06-15)[2023-07-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2020.102564. |
| [35] | WANG Shuo, WANG Jian, SONG Yafei, et al. Malware Variants Detection Model Based on MFF-HDBA[EB/OL]. (2022-09-24)[2023-07-10]. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199593. |
| [36] | BIG 2015, Microsoft Malware Protection Center, Microsoft Azure Machine Learning, et al. Kaggle BIG 2015 Dataset[EB/OL]. (2019-03-28) [2023-07-10]. https://www.kaggle.com/c/malware-classification. |
| [37] | ANANDHI V, VINOD P, MENON V G. Malware Visualization and Detection Using DenseNets[EB/OL]. (2021-07-01)[2023-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-021-01581-w. |
| [38] | HAMAD N, ULLAH F, NAEEM M, et al. Malware Detection in Industrial Internet of Things Based on Hybrid Image Visualization and Deep Learning Model[EB/OL]. (2020-08-01)[2023-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2020.102154. |
| [39] |
XIAO Guoqing, LI Jingning, CHEN Yuedan, et al. MalFCS: An Effective Malware Classification Framework with Automated Feature Extraction Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2020, 141: 49-58.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2020.03.012 URL |
| [40] | KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization[EB/OL]. (2017-01-30)[2023-07-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980. |
| [41] | BURNAEV E, SMOLYAKOV D. One-Class SVM with Privileged Information and Its Application to Malware Detection[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW). New York: IEEE, 2016: 273-280. |
| [42] | YAN Jiaqi, YAN Guanhua, JIN Dong. Classifying Malware Represented as Control Flow Graphs Using Deep Graph Convolutional Neural Network[C]// IEEE.2019 49th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN). New York: IEEE, 2019: 52-63. |
| [43] | NARAYANAN B N, DJANEYE-BOUNDJOU O, KEBEDE T M. Performance Analysis of Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition Algorithms for Malware Classification[C]// IEEE.2016 IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON) and Ohio Innovation Summit (OIS). New York: IEEE, 2016: 338-342. |
| [44] | SHAO Yanli, LU Yang, WEI Dan, et al. Malicious Code Classification Method Based on Deep Residual Network and Hybrid Attention Mechanism for Edge Security[EB/OL]. (2022-07-07)[2023-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3301718. |
| [45] |
GIBERT D, MATEU C, PLANES J, et al. Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Classification of Malware Represented as Images[J]. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, 2019, 15: 15-28.
doi: 10.1007/s11416-018-0323-0 |
| [46] | LU Yang. Research on the Classification Method of Malicious Code Variants Based on Deep Neural Network[D]. Hangzhou: Hangzhou University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2022. |
| 陆洋. 基于深度神经网络的恶意代码变种分类方法研究[D]. 杭州: 杭州电子科技大学, 2022. | |
| [47] |
DREW J, HAHSLER M, MOORE T. Polymorphic Malware Detection Using Sequence Classifcation Methods and Ensembles[J]. EURASIP Journal on Information Security, 2017, 2017(1): 1-12.
doi: 10.1186/s13635-016-0053-0 URL |
| [48] |
CHEN Xiaohan, WEI Shuning, QIN Zhengze. Malware Family Classification Based on Deep Learning Visualization[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(22): 131-138.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2007-0291 |
|
陈小寒, 魏书宁, 覃正泽. 基于深度学习可视化的恶意软件家族分类[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(22):131-138.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2007-0291 |
|
| [49] |
NI Sang, QIAN Quan, ZHANG Rui. Malware Identification Using Visualization Images and Deep Learning[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 77: 871-885.
doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2018.04.005 URL |
| [50] | WANG Dong, YANG Ke, XUAN Jiaxing, et al. A Multi-Classification Method for Malicious Code Families Based on One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2021, 38(12): 332-340. |
| 王栋, 杨珂, 玄佳兴, 等. 基于一维卷积神经网络的恶意代码家族多分类方法研究[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(12):332-340. | |
| [51] | GIBERT D, MATEU C, PLANES J. Orthrus: A Bimodal Learning Architecture for Malware Classification[C]// IEEE. 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-8. |
| [52] | HUANG Wei, WANG Jian, WU Xuan, et al. Malicious Code Classification Method Based on BiTCNSA[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University, 2023, 24(4): 77-84. |
| 黄玮, 王坚, 吴暄, 等. 基于 BiTCNSA 的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 空军工程大学学报, 2023, 24(4):77-84. |
| [1] | 姚远, 樊昭杉, 王青, 陶源. 基于多元时序特征的恶意域名检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 1-8. |
| [2] | 刘光杰, 段锟, 翟江涛, 秦佳禹. 基于多特征融合的移动流量应用识别[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 18-26. |
| [3] | 林伟. 基于多特征融合的区块链异常交易检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 24-30. |
| [4] | 刘家银, 李馥娟, 马卓, 夏玲玲. 基于多尺度卷积神经网络的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 31-38. |
| [5] | 潘孝勤, 杜彦辉. 基于混合特征和多通道GRU的伪造语音鉴别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 1-7. |
| [6] | 朱朝阳, 周亮, 朱亚运, 林晴雯. 基于行为图谱筛的恶意代码可视化分类算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 54-62. |
| [7] | 谭茹涵, 左黎明, 刘二根, 郭力. 基于图像特征融合的恶意代码检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 90-95. |
| [8] | 顾兆军, 郝锦涛, 周景贤. 基于改进双线性卷积神经网络的恶意网络流量分类算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(10): 67-74. |
| [9] | 李振军;程杰仁. 基于多特征分布式拒绝服务攻击的检测[J]. , 2013, 13(5): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||