信息网络安全 ›› 2022, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (5): 11-20.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2022.05.002
以太坊智能合约定理证明中的形式化规约研究综述
- 南京大学计算机科学与技术系,南京 210023
-
收稿日期:2022-03-17出版日期:2022-05-10发布日期:2022-06-02 -
通讯作者:黄达明 E-mail:huangdm@nju.edu.cn -
作者简介:华景煜(1985—),男,江苏,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络安全与隐私保护|黄达明(1976—),男,江苏,讲师,硕士,主要研究方向为形式化验证、信息安全 -
基金资助:江苏省前沿引领技术基础研究专项(BK20202001)
Survey of Formal Specification Methods in Theorem Proving of Ethereum Smart Contract
- Department of Computer Science and Technology, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
-
Received:2022-03-17Online:2022-05-10Published:2022-06-02 -
Contact:HUANG Daming E-mail:huangdm@nju.edu.cn
摘要:
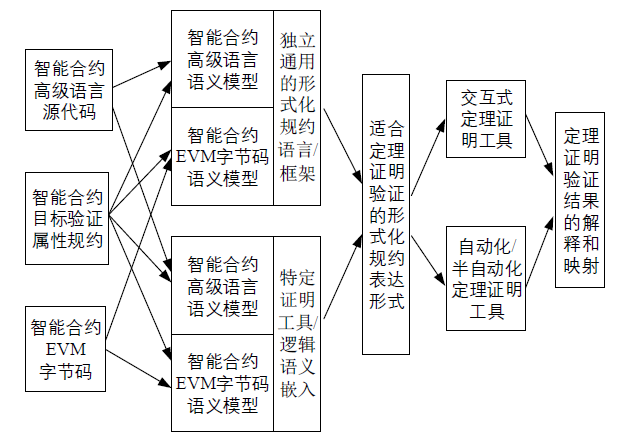
以太坊智能合约的形式化验证是目前的研究热点,在各种形式化验证方法中,定理证明方法具有误报少、可以处理大状态空间等优点。定理证明需要强大的形式化规约表达能力作为基础。文章对现有以太坊智能合约的定理证明研究中使用的形式化规约表达方法进行综述,从智能合约开发语言和区块链内生语义的建模、智能合约安全属性和功能属性的形式化规约表达、自动定理证明和交互式定理证明的选择等角度对形式化规约方法进行比较和讨论,并指出目前的困难和未来的研究方向。
中图分类号:
引用本文
华景煜, 黄达明. 以太坊智能合约定理证明中的形式化规约研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 11-20.
HUA Jingyu, HUANG Daming. Survey of Formal Specification Methods in Theorem Proving of Ethereum Smart Contract[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(5): 11-20.
| [1] | TOLMACH P, LI Yi, LIN Shangwei, et al. A Survey of Smart Contract Formal Specification and Verification[J]. ACM Computing Survey, 2022, 54(7): 1-38. |
| [2] |
ZHU Jian, HU Kai, ZHANG Bojun. Review on Formal Verification of Smart Contract[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(4): 792-804.
doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200723 |
|
朱健, 胡凯, 张伯钧. 智能合约的形式化验证方法研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(4):792-804.
doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200723 |
|
| [3] | WANG Runliu, WU Huaiguang, HE Yaqiong. Survey of Formal Verification Methods for Smart Contracts[J]. Cyberspace Security, 2021, 12(2): 73-79. |
| 王润六, 吴怀广, 何亚琼. 智能合约的形式化验证方法综述[J]. 网络空间安全, 2021, 12(2):73-79. | |
| [4] | HU Kai, BAI Xiaomin, GAO Lingchao, et al. Formal Verification Method of Smart Contract[J]. Journal of Information Securyity Research, 2016, 2(12): 1080-1089. |
| [5] | MAGAZZENI D, MCBURNEY P, NASH W. Validation and Verification of Smart Contracts: A Research Agenda[J]. IEEE Computer, 2017, 50(9): 50-57. |
| [6] | LIU Jing, LIU Zhentian. A Survey on Security Verification of Blockchain Smart Contracts[J]. IEEE Access, 2019(7): 77894-77904. |
| [7] | SINGH A, PARIZI R M, ZHANG Qi, et al. Blockchain Smart Contracts Formalization: Approaches and Challenges to Address Vulnerabilities[J]. Computers & Security, 2020, 88: 1-10. |
| [8] | MATSUO S. How Formal Analysis and Verification Add Security to Blockchain-Based Systems[C]// IEEE. 2017 Formal Methods in Computer Aided Design. New Jersey: IEEE, 2017: 1-4. |
| [9] | GARFATTA I, KLAI K, GAALOUL W, et al. A Survey on Formal Verification for Solidity Smart Contracts[C]// ACM. The Australasian Computer Science Week Multiconference. New York: ACM, 2021: 1-10. |
| [10] | WANG Hebin, ZHENG Changyou, HUANG Song, et al. Review: Secure Formal Verification Methods for Ethereum Smart Contracts[J]. Computer Technology and Development. 2021, 31(9): 104-111. |
| 王赫彬, 郑长友, 黄松, 等. 以太坊智能合约安全形式化验证方法研究进展[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2021, 31(9):104-111. | |
| [11] | AMANI S, BÉGEL M, BORTIN M, et al. Towards Verifying Ethereum Smart Contract Bytecode in Isabelle/HOL[C]// ACM. The 7th ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on Certified Programs and Proofs. New York: ACM, 2018: 66-77. |
| [12] | BRÄM C, EILERS M, MÜLLER P, et al. Rich Specifications for Ethereum Smart Contract Verification[J]. The ACM on Programming Languages, 2021, 5: 1-30. |
| [13] | DIKA A, NOWOSTAWSKI M. Security Vulnerabilities in Ethereum Smart Contracts[C]// IEEE. The IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things(iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications(GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing(CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data(SmartData). New Jersey: IEEE, 2018: 955-962. |
| [14] | WAN Zhiyuan, XIA Xin, LO D, et al. Smart Contract Security: A Practitioners' Perspective[C]// IEEE/ACM. The IEEE/ACM 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering. New Jersey: IEEE, 2021: 1410-1422. |
| [15] | SAYEED S, MARCO-GISBERT H, CAIRA T. Smart Contract: Attacks and Protections[J]. IEEE Access, 2020(8): 24416-24427. |
| [16] | SAMREEN N F, ALALFI M H. A Survey of Security Vulnerabilities in Ethereum Smart Contracts[C]// ACM. The 30th Annual International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2020: 73-82. |
| [17] | BECKERT B, SCHIFFL J, ULBRICH M. Smart Contracts: Application Scenarios for Deductive Program Verification[C]// Springer. FM 2019 International Workshops. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 293-298. |
| [18] |
MULLIGAN D P, OWENS S, GRAY K E, et al. Lem: Reusable Engineering of Real-World Semantics[J]. ACM SIGPLAN Notices, 2014, 49(9): 175-188.
doi: 10.1145/2692915.2628143 URL |
| [19] |
ROSU G, SERBÃNUTÃ T F. An Overview of the K Semantic Framework[J]. Journal of Logic and Algebraic Programming, 2010, 79(6): 397-434.
doi: 10.1016/j.jlap.2010.03.012 URL |
| [20] | Formal Systems Lab, UIUC. The K Framework[EB/OL]. [2021-12-11]. http://kframework.org. |
| [21] | SWAMY N, HRITCU C, KELLER C, et al. Dependent Types and Multi-Monadic Effects in F*[C]// ACM. The 43rd Annual ACM SIGPLAN-SIGACT Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages. New York: ACM, 2016: 256-270. |
| [22] | BHARGAVAN K, DELIGNAT-LAVAUD A, FOURNET C. et al. Formal Verification of Smart Contracts: Short Paper[C]// ACM. The 2016 ACM Workshop on Programming Languages and Analysis for Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 91-96. |
| [23] | GRISHCHENKO I, MAFFEI M, SCHNEIDEWIND C. A Semantic Framework for the Security Analysis of Ethereum Smart Contracts[C]// Springer. International Conference on Principles of Security and Trust. Heidelberg: Springer, 2018: 243-269. |
| [24] | NEHAÏ Z, BOBOT F. Deductive Proof of Industrial Smart Contracts Using Why3[C]// ACM. FM 2019 International Workshops. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 299-311. |
| [25] | HAJDU A, JOVANOVIC D. Solc-Verify: A Modular Verifier for Solidity Smart Contracts[C]// Springer. The 2019 Working Conference on Verified Software:Theories, Tools, and Experiments. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 161-179. |
| [26] | SCHIFFL J, GRUNDMANN M, LEINWEBER M, et al. Towards Correct Smart Contracts: A Case Study on Formal Verification of Access Control[C]// ACM. 26th ACM Symposium on Access Control Models and Technologies. New York: ACM, 2021: 125-130. |
| [27] | ZHENG Yang, HANG Lei. Lolisa: Formal Syntax and Semantics for a Subset of the Solidity Programming Language in Mathematical Tool Coq[EB/OL]. [2021-12-20]. https://ideas.repec.org/a/hin/jnlmpe/6191537.html. |
| [28] | ZHENG Yang, HANG Lei. FEther: An Extensible Definitional Interpreter for Smart-Contract Verifications in Coq[J]. IEEE Access, 2019(7): 37770-37791. |
| [29] | SUN Tianyu, YU Wensheng. A Formal Verification Framework for Security Issues of Blockchain Smart Contracts[EB/OL]. (2020-02-03) [2021-12-22]. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9020255. |
| [30] | SERGEY I, KUMAR A, HOBOR A. Scilla: A Smart Contract Intermediate-Level LAnguage[EB/OL]. [2021-12-22]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1801.00687. |
| [31] | SERGEY I, NAGARAJ V, JOHANNSEN J, et al. Safer Smart Contract Programming with Scilla[J]. ACM on Programming Languages, 2019, 3: 1-30. |
| [32] | ANNENKOV D, NIELSEN J B, SPITTERS B. ConCert: A Smart Contract Certification Framework in Coq[C]// ACM. The 9th ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on Certified Programs and Proofs. New York: ACM, 2020: 215-228. |
| [33] | HIRAI Y. Defining the Ethereum Virtual Machine for Interactive Theorem Provers[C]// Springer. International Conference on Financial Cryprography and Data Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2017: 520-535. |
| [34] | HILDENBRANDT E, SAXENA M, RODRIGUES N, et al. KEVM: A Complete Formal Semantics of the Ethereum Virtual Machine[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE 31st Computer Security Foundations Symposium. New Jersey: IEEE, 2018: 204-217 |
| [35] | DAEJUN P, ZHANG Yi, MANASVI S, et al. A Formal Verification Tool for Ethereum VM bytecode[C]// ACM. The 26th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2018: 912-915. |
| [36] | LE T C, XU Lei, CHEN Lin, et al. Proving Conditional Termination for Smart Contracts[C]// ACM. The 2nd ACM Workshop on Blockchains, Cryptocurrencies, and Contracts. New York: ACM, 2018: 57-59. |
| [37] | ZHANG Fan, CECCHETTI E, CROMAN K, et al. Town Crier: An Authenticated Data Feed for Smart Contracts[C]// ACM. The 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 270-282. |
| [1] | 冯景瑜, 张琪, 黄文华, 韩刚. 基于跨链交互的网络安全威胁情报共享方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 21-29. |
| [2] | 李鹏, 郑田甜, 徐鹤, 朱枫. 基于区块链技术的RFID安全认证协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(5): 1-11. |
| [3] | 王健, 于航, 韩臻, 韩磊. 基于智能合约的云存储共享数据访问控制方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(11): 40-47. |
| [4] | 于克辰, 郭莉, 姚萌萌. 基于区块链的高价值数据共享系统设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(11): 75-84. |
| [5] | 边玲玉, 张琳琳, 赵楷, 石飞. 基于LightGBM的以太坊恶意账户检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 73-80. |
| [6] | 姜楠, 王玮琦, 王健. 基于智能合约的个人隐私数据保护方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(11): 22-31. |
| [7] | 周元健, 秦冬梅, 刘忆宁, 吕松展. 基于区块链的可信仓单系统设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(6): 84-90. |
| [8] | 王文明, 施重阳, 王英豪, 危德健. 基于区块链技术的交易及其安全性研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(5): 1-9. |
| [9] | 黑一鸣, 刘建伟, 张宗洋, 喻辉. 基于区块链的可公开验证分布式云存储系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(3): 52-60. |
| [10] | 李佩丽, 徐海霞, 马添军, 穆永恒. 区块链技术在网络互助中的应用及用户隐私保护[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(9): 60-65. |
| [11] | 马春光, 安婧, 毕伟, 袁琪. 区块链中的智能合约[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(11): 8-17. |
| [12] | 章玥;郭建;朱晓冉. 基于模型的开发方法在多应用智能卡中的应用[J]. , 2013, 13(12): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||