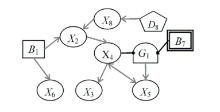
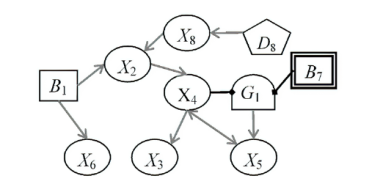
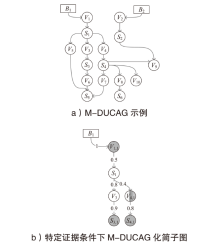
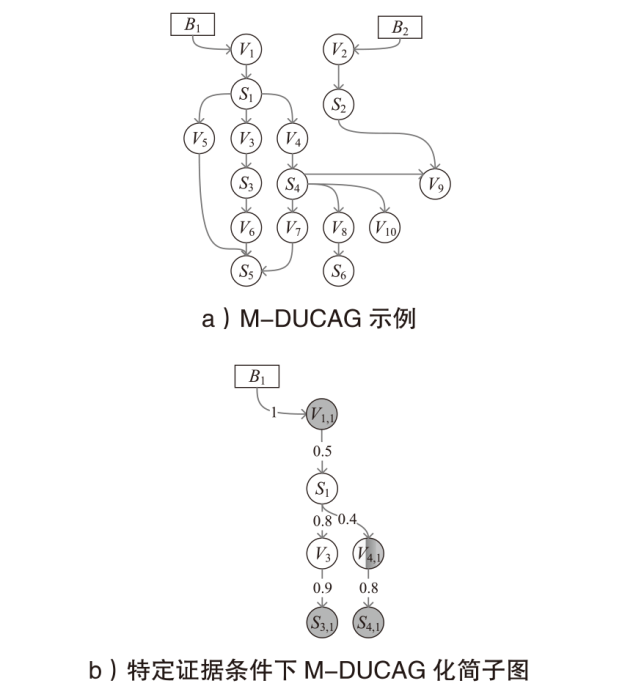
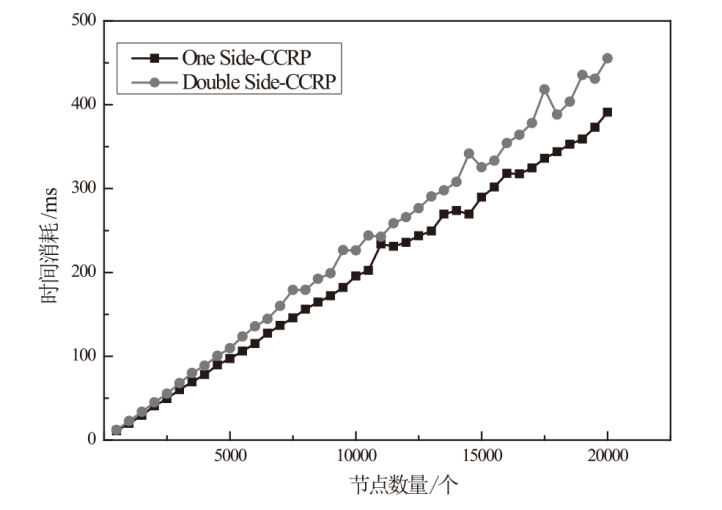
Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 778-793.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.05.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Multi-State Causal Representation and Inference Model in Uncertain Network Attack Scenarios
DONG Chunling( ), FENG Yu, FAN Yongkai
), FENG Yu, FAN Yongkai
- School of Computer and Cyber Sciences, Communication University of China, Beijing 100024, China
-
Received:2024-12-30Online:2025-05-10Published:2025-06-10
CLC Number:
Cite this article
DONG Chunling, FENG Yu, FAN Yongkai. Multi-State Causal Representation and Inference Model in Uncertain Network Attack Scenarios[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 778-793.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.05.010
| 节点 | D-CCRP因果链 | Pr (Xv) | O-CCRP因果链 | Pr (Xv) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1,1 | — | — | — | — |
| S1,2 | (AS1,2;V1,1+AV3;S1,2·AS3,1;V+ AV4;S1,2·AS4,1;V4)/3 | 0.73 | AS1,2;V1,1 | 0.5 |
| V3,0 | (AS1,2;V1,1·AV3,0;S1,2+AS3,1;V3,0)/2 | 0.5 | AS1,2;V1,1 | 0.1 |
| V3,1 | (AS1,2;V1,1·AV3,1;S1,2+AS3,1;V3,1)/2 | 0.65 | AS1,2;V1,1·AV3,1;S1,2 | 0.4 |
| V4,0 | (AS1,2;V1,1·AV4,0;S1,2+AS4,1;V4,0)/2 | 0.6 | AS1,2;V1,1·AV4,0;S1,2 | 0.4 |
| V4,1 | (AS1,2;V1,1·AV4,1;S1,2+AS4,1;V4,1)/2 | 0.45 | AS1,2;V1,1·AV4,1;S1,2 | 0.1 |
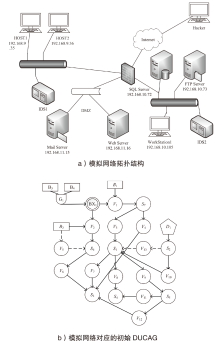
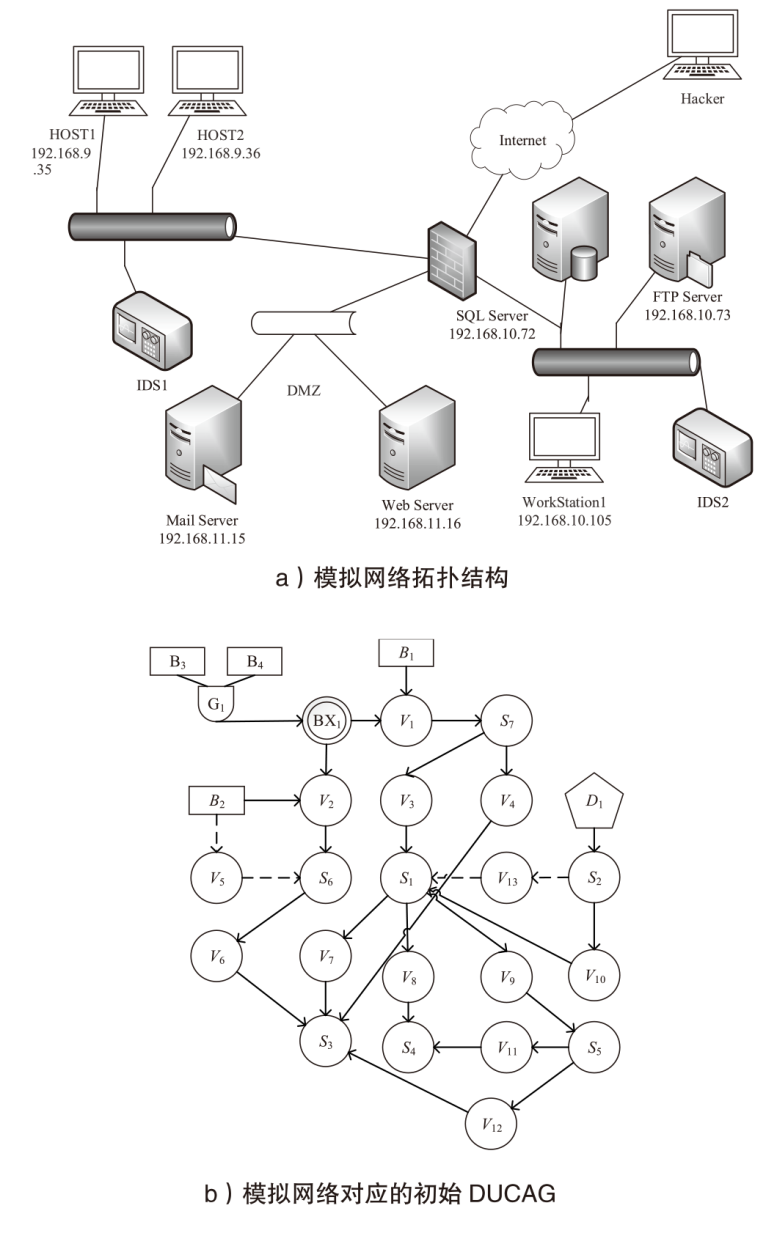
| ID | 描述信息 | IP地址 | 攻击行为节点 | 漏洞CVE编号 | 攻击发生概率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | HOST1 | 192.168.9.35 | V3, V10 | CVE-2013-3940 | 0.86 |
| CVE-2012-0002 | 0.86 | ||||
| V13 | 零日漏洞攻击 | 0.80 | |||
| S2 | HOST2 | 192.168.9.36 | D1 | Inside Attack | 1.00 |
| S3 | SQL Server | 192.168.10.72 | V4, V6, V7, V12 | CVE-2016-7253 | 0.80 |
| S4 | FTP Server | 192.168.10.73 | V8, V11 | CVE-2015-4108 | 0.86 |
| CVE-2019-10009 | 0.80 | ||||
| S5 | Workstation | 192.168.10.105 | V9 | CVE-2019-5541 | 0.80 |
| CVE-2019-5524 | 0.80 | ||||
| S6 | Mail Server | 192.168.11.15 | V2 | CVE-2020-14066 | 0.80 |
| V5 | 零日漏洞攻击 | 0.80 | |||
| S7 | Web Server | 192.168.11.16 | V1 | CVE-2017-12728 | 0.25 |
| 攻击序列 | 模拟攻击序列 | 攻击候选序列及其概率 |
|---|---|---|
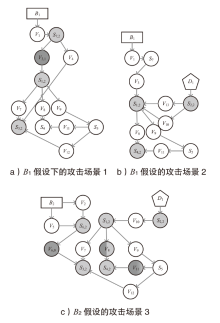
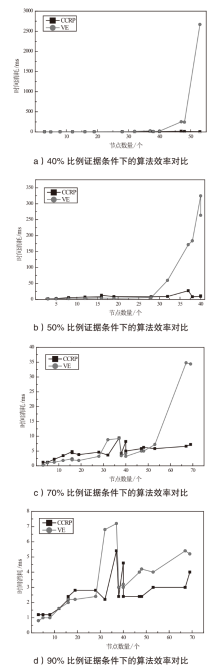
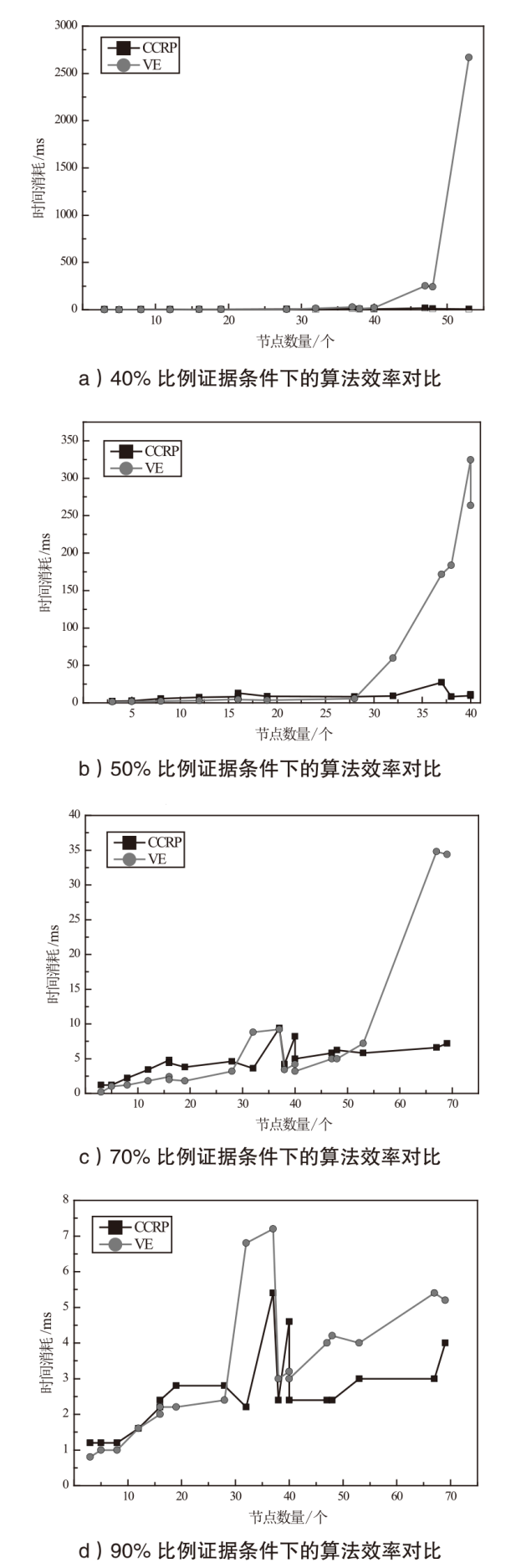
| 1 | B1→V1→S7→ V3→S1→V7→S3 | B1(BX1)→V1,0→S7,2→V3,1→S1,2→V7,0→ S3,2(0.2983) B1(BX1)→V1,0→S7,2→V4,0→S3,2(0.2983) BX1→V2,0→S6,2→V6,0→S3,2(0.3055) |
| 2 | D1→S2→V13→ S1→V8→S4 | D1→S2,2→V13,0→S1,2→V8→S4,2(0.4590) D1→S2,2→V13,0→S1,2→V9,1→S5,2→V11→ S4,2(0.1500) D1→S2,2→V10,1→S1,2→V8→S4,2(0.2870) |
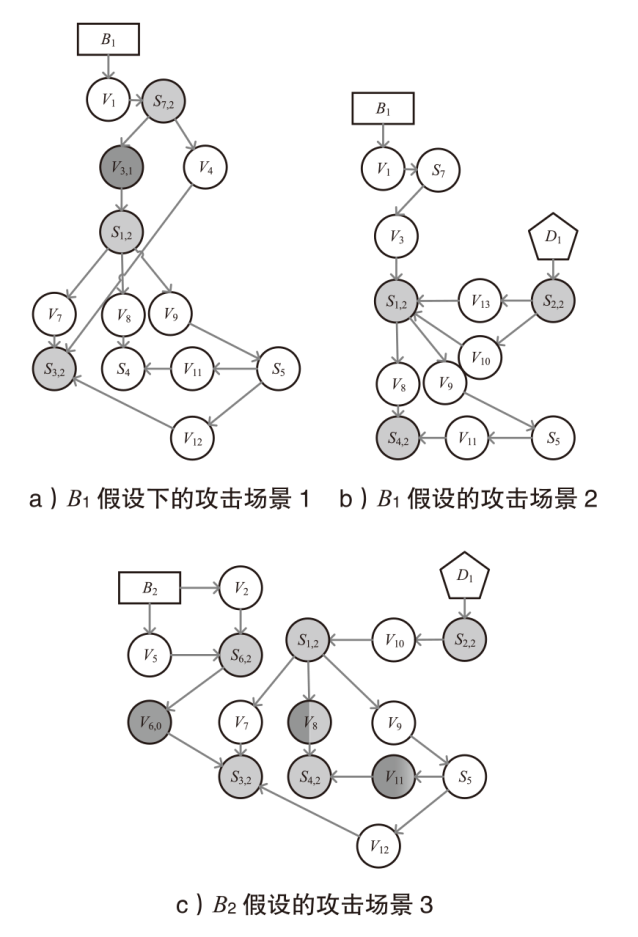
| 3 | 1)B2→V5→ S6→V6→S3 2)D1→S2→V10→ S1→V8→S4 | B2(BX1)→V2,0→S6,2→V6,0→S3,2(0.3732) B2(BX1)→V5,0→S6,2→V6,0→S3,2(0.3732) D1→S2,2→V10,1→S1,2→V8,0→S4,2(0.3420) D1→S2,2→V10,1→S1,2→V8,1→S4,2(0.3690) |
| [1] | PING Guolou, YE Xiaojun. A Survey of Research on Network Attack Model[J]. Journal of Information Security Research, 2020, 6(12): 1058-1067. |
| 平国楼, 叶晓俊. 网络攻击模型研究综述[J]. 信息安全研究, 2020, 6(12): 1058-1067. | |
| [2] | KONSTA A-M, LAFUENTE A L, SPIGA B, et al. Survey: Automatic Generation of Attack Trees and Attack Graphs[J]. Computer Security, 2024, 137(C): 103660-103672. |
| [3] | GADYATSKAYA O. How to Generate Security Cameras: Towards Defence Generation for Socio-Technical Systems[C]// Springer. Proceedings of the Graphical Models for Security:Second International Workshop(GraMSec 2015). Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 50-65. |
| [4] | IVANOVA M G, PROBST C W, HANSEN R R, et al. Transforming Graphical System Models to Graphical Attack Models[C]// Springer. Proceedings of the Graphical Models for Security:Second International Workshop(GraMSec 2015). Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 82-96. |
| [5] | LIU Xuejiao. Research on Network Vulnerability Assessment and Intrusion Alert Analysis Technology[D]. WuHan: HuaZhong Nornal University, 2011. |
| 刘雪娇. 网络脆弱性评估及入侵报警分析技术研究[D]. 武汉: 华中师范大学, 2011. | |
| [6] |
ZHONG Shangqin, XU Guosheng, YAO Wenbin, et al. Network Security Analysis Based on Host-Security-Group[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2012, 35(1): 19-23.
doi: 10.13190/jbupt.201201.19.zhongshq |
|
钟尚勤, 徐国胜, 姚文斌, 等. 基于主机安全组划分的网络安全性分析[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2012, 35(1): 19-23.
doi: 10.13190/jbupt.201201.19.zhongshq |
|
| [7] | ZENITANI K. From Attack Graph Analysis to Attack Function Analysis[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 650: 119703-119719. |
| [8] | MOHAMMADZAD M, KARIMPOUR J, MAHAN F. MAGD: Minimal Attack Graph Generation Dynamically in Cyber Security[J]. Computer Networks, 2023, 236: 110004-110019. |
| [9] | WANG Lingyu, YAO Chao, SINGHAL A, et al. Interactive Analysis of Attack Graphs Using Relational Queries[C]// Data and Applications Security XX. 20th Annual IFIP WG 113 Working Conference on Data and Applications Security. Heidelberg:Springer, 2006: 119-132. |
| [10] | WANG Shuo, TANG Guangming, KOU Guang, et al. An Attack Graph Generation Method Based on Heuristic Searching Strategy[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2016 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC). New York: IEEE, 2016: 1180-1185. |
| [11] | KAYNAR K, SIVRIKAYA F. Distributed Attack Graph Generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2015, 13(5): 519-532. |
| [12] | PU Junyan, LI Yahui, ZHOU Chunjie. Cross-Domain Dynamic Security Risk Analysis Method of Industrial Control System Based on Probabilistic Attack Graph[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(9): 85-94. |
| 浦珺妍, 李亚辉, 周纯杰. 基于概率攻击图的工控系统跨域动态安全风险分析方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 85-94. | |
| [13] | POOLSAPPASIT N, DEWRI R, RAY I. Dynamic Security Risk Management Using Bayesian Attack Graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2011, 9(1): 61-74. |
| [14] | ZHANG Kai, LIU Jingju. Network Attack Path Analysis Method Based on Vulnerability Dynamic Availability[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(4): 62-72. |
| 张凯, 刘京菊. 基于漏洞动态可利用性的网络入侵路径分析方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(4): 62-72. | |
| [15] |
WANG Yang, WU Jianying, HUANG Jinlei, et al. Network Intrusion Intention Recognition Method Based on Bayesian Attack Graph[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(22): 73-79.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1809-0081 |
|
王洋, 吴建英, 黄金垒, 等. 基于贝叶斯攻击图的网络入侵意图识别方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(22): 73-79.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1809-0081 |
|
| [16] |
WANG Wenjuan, DU Xuehui, SHAN Dibin. Construction Method of Attack Scenario in Cloud Environment Based on Dynamic Probabilistic Attack Graph[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(1): 1-17.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021004 |
|
王文娟, 杜学绘, 单棣斌. 基于动态概率攻击图的云环境攻击场景构建方法[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(1): 1-17.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021004 |
|
| [17] | MA Chunguang, WANG Chenghong, ZHANG Donghong, et al. A Dynamic Network Risk Assessment Model Based on Attacker’s Inclination[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 52(9): 2056-2068. |
| 马春光, 汪诚弘, 张东红, 等. 一种基于攻击意愿分析的网络风险动态评估模型[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 52(9): 2056-2068. | |
| [18] | GAO Qingguan, ZHANG Bo, FU Anmin. An Advanced Persistent Threat Detection Method Based on Attack Graph[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(12): 59-68. |
| 高庆官, 张博, 付安民. 一种基于攻击图的高级持续威胁检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12): 59-68. | |
| [19] | XIE PENG, LI J H, OU Xinming, et al. Using Bayesian Networks for Cyber Security Analysis[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/IFIP. International Conference on Dependable Systems & Networks (DSN). New York: IEEE, 2010: 211-220. |
| [20] | CHEN Xiaojun, SHI Jinqiao, XU Fei, et al. Algorithm of Optimal Security Hardening Measures Against Insider Threat[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2014, 51(7): 1565-1577. |
| 陈小军, 时金桥, 徐菲, 等. 面向内部威胁的最优安全策略算法研究[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2014, 51(7): 1565-1577. | |
| [21] | WANG Hui, CHEN Fuwang, WANG Zhe. Research on Internal Network Attack Graph Based on Strength Coefficient[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2018, 35(2): 515-520. |
| 王辉, 陈甫旺, 王哲. 基于强度系数的内部网络攻击图研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2018, 35(2): 515-520. | |
| [22] | LALLIE H S, DEBATTISTA K, BAL J. A Review of Attack Graph and Attack Tree Visual Syntax in Cyber Security[J]. Computer Science Review, 2020, 35: 100219-100260. |
| [23] | KEVIN P M. Dynamic Bayesian Networks:Representation, Inference and Learning[D]. Berkeley: University of California, 2002. |
| [24] | CAI Baoping, LIU Yu, XIE Min. A Dynamic-Bayesian-Network-Based Fault Diagnosis Methodology Considering Transient and Intermittent Faults[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2017, 14(1): 276-285. |
| [25] | ZHANG Qin, DONG Chunling, CUI Yan, et al. Dynamic Uncertain Causality Graph for Knowledge Representation and Probabilistic Reasoning: Statistics Base, Matrix, and Application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks & Learning Systems, 2014, 25(4): 645-663. |
| [26] | DONG Chunling, FENG Yu, SHANG Wenqian. A New Method of Dynamic Network Security Analysis Based on Dynamic Uncertain Causality Graph[J]. Journal of Cloud Computing, 2024, 13(1): 24-41. |
| [27] | DONG Chunling, ZHANG Qin. The Cubic Dynamic Uncertain Causality Graph: A Methodology for Temporal Process Modeling and Diagnostic Logic Inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(10): 4239-4253. |
| [28] | DONG Chunling, ZHOU Zhenxu, ZHANG Qin. Cubic Dynamic Uncertain Causality Graph: A New Methodology for Modeling and Reasoning About Complex Faults with Negative Feedbacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2018, 67(3): 920-932. |
| [29] | ISAAC M, JOHN M, SADEGH S, et al. Cyclic Bayesian Attack Graphs: A Systematic Computational Approach[C]// IEEE.Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom). New York: IEEE, 2020: 129-136. |
| [1] | WANG Jianxin, XU Hongke, XIAO Chaoen, ZHANG Lei. Research on Rowhammer Vulnerability Defense Method Based on Remapping Matrix [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 758-766. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xuewang, LU Hui, XIE Haofei. A Data Augmentation Method Based on Graph Node Centrality and Large Model for Vulnerability Detection [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(4): 550-563. |
| [3] | CHANG Zhenxuan, ZHENG Zhihan, MEI Aohan, TAN Yu’an. An Efficient Gray-Box Fuzzing Approach for Firmware Network Applications [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(4): 654-663. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yuxuan, HUANG Cheng, LIU Rong, LENG Tao. Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection Method Combining Prompt Tuning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(4): 664-673. |
| [5] | WANG Juan, ZHANG Boxian, ZHANG Zhijie, XIE Haining, FU Jintao, WANG Yang. Java Deserialization Vulnerability Mining Based on Fuzzing [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(1): 1-12. |
| [6] | ZHANG Liqiang, LU Mengjun, YAN Fei. A Cross-Contract Fuzzing Scheme Based on Function Dependencies [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(7): 1038-1049. |
| [7] | WANG Juan, GONG Jiaxin, LIN Ziqing, ZHANG Xiaojuan. Multidimensional Depth Oriented Fuzzing Method of Java Web Applications [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 282-292. |
| [8] | LI Pengchao, ZHANG Quantao, HU Yuan. Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection Method Based on Graph Convolutional Network with Dual Attention Mechanism [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(11): 1624-1631. |
| [9] | SHEN Qintao, LIANG Ruigang, WANG Baolin, ZHANG Jingcheng, CHEN Kai. Vulnerability Causation Analysis Based on Dynamic Execution Logging and Reverse Analysis [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(10): 1493-1505. |
| [10] | ZHANG Zhanpeng, WANG Juan, ZHANG Chong, WANG Jie, HU Yuyi. The Research on Efficient Web Fuzzing Technology Based on Graph Isomorphic Network [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(10): 1544-1552. |
| [11] | WANG Juan, ZHANG Chong, GONG Jiaxin, LI Jun’e. Review of Fuzzing Based on Machine Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 1-16. |
| [12] | ZHONG Yuanxin, LIU Jiayong, JIA Peng. Directed Fuzzing Based on Dynamic Time Slicing and Efficient Mutation [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 99-108. |
| [13] | JIA Fan, KANG Shuya, JIANG Weiqiang, WANG Guangtao. Vulnerability Similarity Algorithm Evaluation Based on NLP and Feature Fusion [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(1): 18-27. |
| [14] | ZHANG Guanghua, LIU Yongsheng, WANG He, YU Naiwen. Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection Scheme Based on BiLSTM and Attention Mechanism [J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(9): 46-54. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yujian, LIU Daifu, TONG Fei. Reentrancy Vulnerability Detection in Smart Contracts Based on Local Graph Matching [J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(8): 1-7. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||