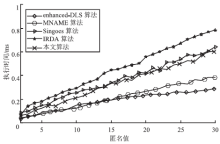
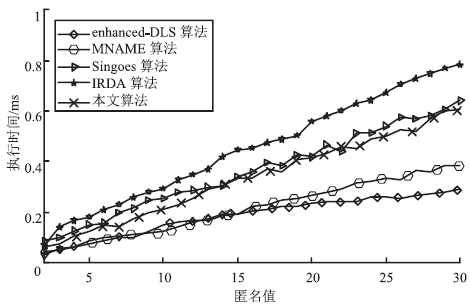
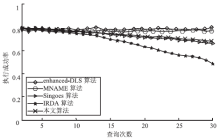
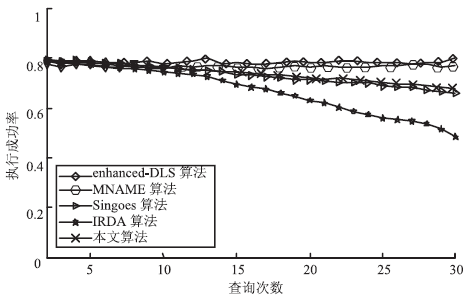
Netinfo Security ›› 2018, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (5): 12-12.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2018.05.002
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
A Markov Prediction-based Algorithm for Continuous Query Privacy Protection
Lei ZHANG1,2, Bin WANG1,2, Lili YU2( )
)
- 1. College of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin Heilongjiang 150001, China
2. College of Information Science and Electronic Technology, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi Heilongjiang 154007, China
-
Received:2017-12-22Online:2018-05-15Published:2020-05-11
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lei ZHANG, Bin WANG, Lili YU. A Markov Prediction-based Algorithm for Continuous Query Privacy Protection[J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(5): 12-12.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2018.05.002
| [1] | NIU Ben, LI Qinghua, ZHU Xiaoyan, et al.Achieving k-anonymity in Privacy-aware Location-based Services[J]. Journal of Graph Algorithms & Applications, 2014, 20(2): 363-410. |
| [2] | NIU Ben, LI Qinghua, ZHU Xiaoyan, et al.Enhancing Privacy through Caching in Location-based Services[C]//IEEE. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, April 26-May 1, 2015, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China. New Jersey: IEEE, 2015: 1017-1025. |
| [3] | SUN Yanming, CHEN Min, HU Long, et al. ASA: against Statistical Attacks for Privacy-aware Users in Location Based Service[EB/OL]. ,2017-11-20. |
| [4] | XU Yan.Research on Network Link Prediction Based on Data Mining[J]. Netinfo Security, 2017(6): 30-34. |
| 徐燕. 基于数据挖掘的网络链接预测研究[J]. 信息网络安全,2017(6):30-34. | |
| [5] | GRUTESER M, GRUNWALD D.Anonymous Usage of Location-based Services through Spatial and Temporal Cloaking[C]//ACM. 1st International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications and Services, May 5-8, 2003, San Francisco, California. New York: ACM, 2003: 31-42. |
| [6] | GEDIK B, LIU Ling.Location Privacy in Mobile Systems: a Personalized Anonymization Model[C]//IEEE. 25th IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, June 6-10, 2005, Columbus, OH, USA. New Jersey: IEEE, 2005: 620-629. |
| [7] | TALUKDER N, AHAMED S I.Preventing Multi-query Attack in Location-based Services[C]//ACM. 3rd ACM Conference on Wireless Network Security, March 22-24, 2010, Hoboken, New Jersey, USA. ACM: New York: 2010, 25-35. |
| [8] | XUE Jiao, LIU Xiangyu, YANG Xiaochun, et al.A Location Privacy Preserving Approach on Road Network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2011, 34(5): 865-878. |
| 薛姣,刘向宇,杨晓春,等. 一种面向公路网络的位置隐私保护方法[J]. 计算机学报,2011,34(5):865-878. | |
| [9] | SCHLEGEL R, CHOW C Y, HUANG Q, et al.User-defined Privacy Grid System for Continuous Location-based Services[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2015, 14(10): 2158-2172. |
| [10] | CHE Yanzhe, HE Qinming, HONG Xiaoyan, et al.X-Region: a Framework for Location Privacy Preservation in Mobile Peer-to-Peer Networks[J]. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2015, 28(1): 167-186. |
| [11] | YIU M L, JENSEN C S, HUANG Xuegang, et al.SpaceTwist: Managing the Trade-offs among Location Privacy, Query Performance, and Query Accuracy in Mobile Services[C]//IEEE. IEEE 24th International Conference on Data Engineering, April 7-12, 2008, Cancun, Mexico. New Jersey: IEEE, 2008: 366-375. |
| [12] | YIU M L, JENSEN C S, MOLLER J, et al.Design and Analysis of a Ranking Approach to Private Location-based Services[J]. ACM Transactions on Database Systems, 2011, 36(2): 475-486. |
| [13] | MA Chunguang, ZHOU Changli, YANG Songtao.A Voronoi-based Location Privacy-preserving Method for Continuous Query in LBS[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2015, 11(3): 1-17. |
| [14] | PENG Tao, LIU Qin, WANG Guojun.Enhanced Location Privacy Preserving Scheme in Location-based Services[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2017, 11(1): 219-230. |
| [15] | BAMBA B, LIU Ling, PESTI P, et al.Supporting Anonymous Location Queries in Mobile Environments with Privacygrid[C]//ACM. 17th International Conference on World Wide Web, April 21-25, 2008, Beijing, China. New York: ACM, 2008: 237-246. |
| [16] | XIAO Zheng, XU Jianliang, MENG Xiaofeng. p-Sensitivity: a Semantic Privacy-protection Model for Location-based Services[C]//IEEE. 9th International Conference on Mobile Data Management Workshops, April 27-30, 2008, Beijing, China. New Jersey: IEEE, 2008: 47-54. |
| [17] | LIU Fuyu, HUA K A, CAI Ying.Query l-diversity in Location-based Services[C]//IEEE. 10th International Conference on Mobile Data Management: Systems, Services and Middleware, May 18-20, 2009, Taiwan, China. New Jersey: IEEE, 2009: 436-442. |
| [18] | CHOW C Y, MOKBEL M F, LIU Xuan.A Peer-to-Peer Spatial Cloaking Algorithm for Anonymous Location-based Service[C]//ACM. 14th Annual ACM International Symposium on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, November 10-11, 2006, Arlington, Virginia, USA. New York: ACM, 2006: 171-178. |
| [19] | MA Chunguang, ZHANG Lei, YANG Songtao.Review on Location Trajectory Privacy Protection[J]. Netinfo Security, 2015(10): 24-31. |
| 马春光,张磊,杨松涛. 位置轨迹隐私保护综述[J]. 信息网络安全,2015(10):24-31. | |
| [20] | REBOLLO-MONEDERO D, FORNE J, DOMINGO-FERRER J.Query Profile Obfuscation by Means of Optimal Query Exchange between Users[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2012, 9(5): 641-654. |
| [21] | NIU Ben, ZHU Xiaoyan, LI Qinghua, et al. A Novel Attack to Spatial Cloaking Schemes in Location-based Services[EB/OL]. , 2017-11-20. |
| [22] | ZHANG Haichuan, ZHAO Zemao, TIAN Yujie, et al.Research on Optimization Selection of Personalized Space Anonymous Algorithm[J]. Netinfo Security, 2015(3): 23-27. |
| 张海川,赵泽茂,田玉杰,等. 基于个性化的空间匿名算法最优化选择研究[J]. 信息网络安全,2015(3):23-27. | |
| [23] | MA Chunguang, ZHANG Lei, YANG Songtao, et al.Achieve Personalized Anonymity through Query Blocks Exchanging[J]. China Communications, 2016, 13(11): 106-118. |
| [24] | MA Chunguang, ZHANG Lei, YANG Songtao, et al. Hiding Yourself Behind Collaborative Users When Using Continuous Location-based Services[EB/OL]. , 2017-11-20. |
| [25] | HWANG R H, HSUEH Y L, CHUNG H W.A Novel Time-obfuscated Algorithm for Trajectory Privacy Protection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2014, 7(2): 126-139. |
| [26] | ZHANG Lei, MA Chunguang, YANG Songtao, et al.Location Privacy Protection Model and Algorithm Based on Profiles Generalization[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(12): 2894-2900. |
| 张磊,马春光,杨松涛,等. 基于轮廓泛化的位置隐私保护模型及方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术,2016,38(12):2894-2900. | |
| [27] | WANG Yong, GAO Shimeng, NIE Xiao, et al.A LBSs Cloaking Algorithm Based on Velocity Dynamic Variation[J]. Netinfo Security, 2015(4): 28-35. |
| 王勇,高诗梦,聂肖,等. 基于速度动态差异的位置服务匿名算法[J]. 信息网络安全,2015(4):28-35. | |
| [28] | ZHANG Lei, MA Chunguang, YANG Songtao.Location Association Similar Based Anonymus Algorithm[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2016, 11(2): 197-201, 213. |
| 张磊,马春光,杨松涛. 基于位置关联相似性的匿名算法[J]. 中国科技论文,2016,11(2):197-201,213. | |
| [29] | ZHANG Lei, MA Chunguang, YANG Songtao, et al.CP-ABE Based Users Collaborative Privacy Protection Scheme for Continuous Query[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(9): 76-85. |
| 张磊,马春光,杨松涛,等. 基于属性基加密的用户协作连续查询隐私保护策略[J]. 通信学报,2017,38(9):76-85. | |
| [30] | ANDRÉS M E, BORDENABE N E, CHATZIKOKOLAKIS K, et al. Geo-indistinguishability: Differential Privacy for Location-based Systems[C]//ACM. 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security, ACM, November 4-8, 2013, Berlin, Germany. New York: ACM, 2013: 901-914. |
| [31] | BORDENABE N E, CHATZIKOKOLAKIS K, PALAMIDESSI C.Optimal Geo-indistinguishable Mechanisms for Location Privacy[C]//ACM. 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, November 3-7, 2014, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA. New York: ACM, 2014: 251-262. |
| [32] | WU Shasha, XIONG Jinbo, YE Guohua, et al.Research on Location Privacy Protection Based on Dummy Locations in Mobile Internet Environment[J]. Netinfo Security, 2016(10): 54-59. |
| 吴莎莎, 熊金波,叶帼华,等. 移动互联网环境下基于假位置的位置隐私保护研究[J]. 信息网络安全,2016(10):54-59. |
| [1] | Wenjiang HAO, Yun LIN. Research on Social Responsibility of Internet Enterprises and Its Enlightenment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2019, 19(9): 130-133. |
| [2] | Quan ZHOU, Shumei XU, Ningbin YANG. A Privacy Protection Scheme for Smart Grid Based on Attribute-based Group Signature [J]. Netinfo Security, 2019, 19(7): 25-30. |
| [3] | Yanming FU, Zhenduo LI. Research on k-means++ Clustering Algorithm Based on Laplace Mechanism for Differential Privacy Protection [J]. Netinfo Security, 2019, 19(2): 43-52. |
| [4] | Ronglei HU, Yanqiong HE, Ping ZENG, Xiaohong FAN. Design and Implementation of Medical Privacy Protection Scheme in Big Data Environment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(9): 48-54. |
| [5] | Peili LI, Haixia XU, Tianjun MA, Yongheng MU. The Application of Blockchain Technology in Network Mutual Aid and User Privacy Protection [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(9): 60-65. |
| [6] | Rong MA, Xiuhua CHEN, Hui LIU, Jinbo XIONG. Research on User Privacy Measurement and Privacy Protection in Mobile Crowdsensing [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(8): 64-72. |
| [7] | Le WANG, Zherong YANG, Rongjing LIU, Xiang WANG. A CP-ABE Privacy Preserving Method for Wearable Devices [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(6): 77-84. |
| [8] | Lei ZHANG, Bin WANG, Lili YU. A Hash Function-based Attribute Generalization Privacy Protection Scheme [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(3): 14-25. |
| [9] | Liang LI, Yinghui ZHANG, Kaixin DENG, Tiantian ZHANG. Privacy-aware Power Injection in 5G Smart Grid [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(12): 87-92. |
| [10] | Na ZHAO, Hui LONG, Jinshu SU. A Scheme for Anonymous Authentication and Privacy Protection in the Internet of Things Environment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(11): 1-7. |
| [11] | Chunming TANG, Weiming WEI. Regression Algorithm with Privacy Based on Secure Two-party Computation [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(10): 10-16. |
| [12] | ZHAO Kuo, XING Yongheng. Security Survey of Internet of Things Driven by Block Chain Technology [J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(5): 1-6. |
| [13] | YANG Yulong, PENG Changgen, ZHENG Shaobo, ZHU Yijie. Ultra-lightweight Security Authentication Protocol for Mobile RFID Systems Based on Mobile Smart Terminal [J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(5): 22-27. |
| [14] | ZHANG Jianhong, LI Pengyan. An Efficient Data Integrity Verification Scheme for Cloud Storage [J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(3): 1-5. |
| [15] | FANG Yuejian, ZHU Jinzhong, ZHOU Wen, LI Tongliang. A Survey on Data Mining Privacy Protection Algorithms [J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(2): 6-11. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||