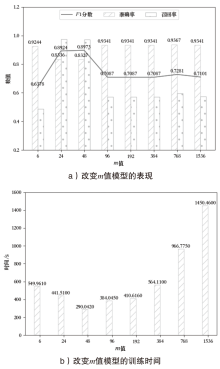
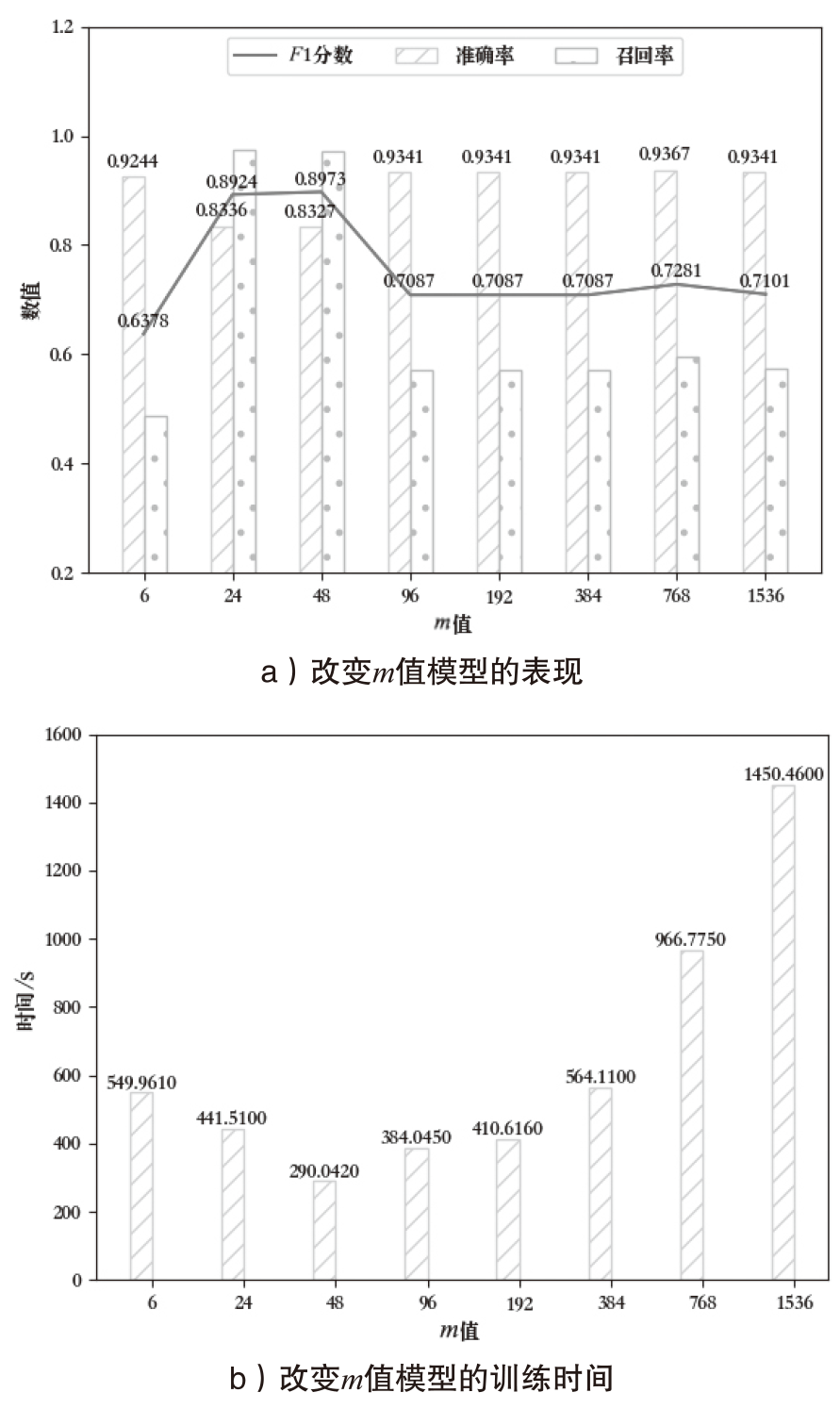
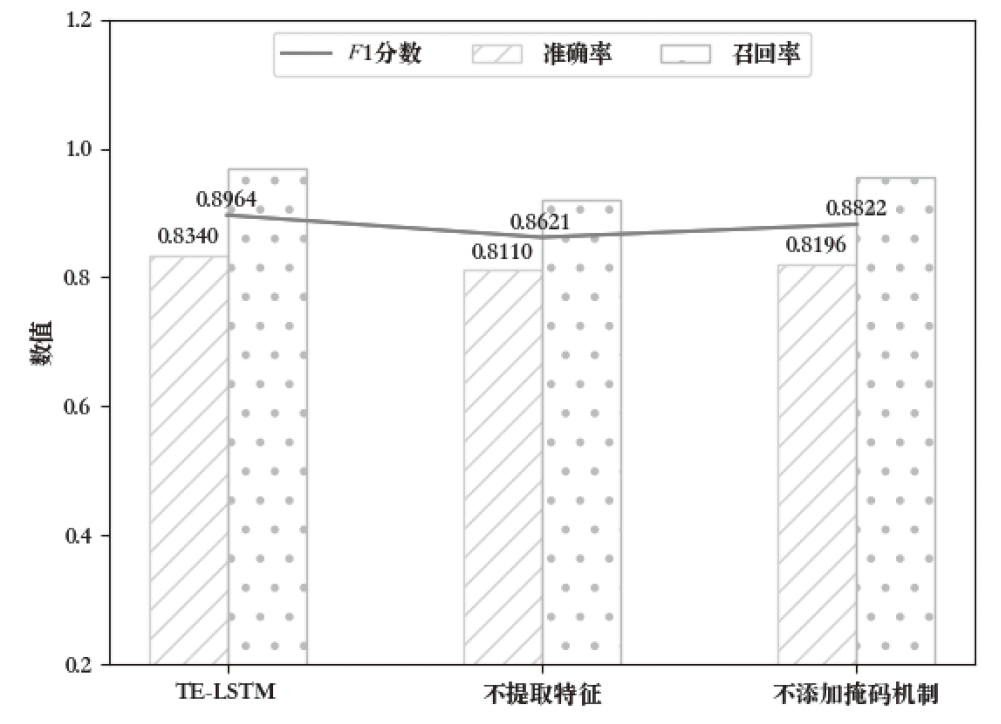
| [1] |
LIANG Xiao, GUI Xiaolin, DAI Haojun, et al. Research on Cache Side Channel Attack Technology of Virtual Machines in Cloud Environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(2): 317-336.
|
| [2] |
Verizon. 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. https://www.verizon.com/business/resources/T2b1/reports/2023-data-breach-investigations-report-dbir.pdf.
|
| [3] |
AKASH T, JAYAN A, GAUR N, et al. Identifying Insider Cyber Threats Using Behaviour Modelling and Analysis[C]// IEEE. 2023 OITS International Conference on Information Technology (OCIT). New York: IEEE, 2023: 35-40.
|
| [4] |
LE D C, ZINCIR-HEYWOOD A N. Evaluating Insider Threat Detection Workflow Using Supervised and Unsupervised Learning[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW). New York: IEEE, 2018: 270-275.
|
| [5] |
MENG Fanzhi, LU Peng, LI Junhao, et al. GRU and Multi-Autoencoder Based Insider Threat Detection for Cyber Security[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Data Science in Cyberspace (DSC). New York: IEEE, 2021: 203-210.
|
| [6] |
TIAN Zhihong, SHI Wei, TAN Zhiyuan, et al. Deep Learning and Dempster-Shafer Theory Based Insider Threat Detection[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020: 1-10.
|
| [7] |
YUAN Shuhan, WU Xintao. Deep Learning for Insider Threat Detection: Review, Challenges and Opportunities[EB/OL]. (2021-05-01)[2025-01-20]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102221.
|
| [8] |
TUOR A, KAPLAN S, HUTCHINSON B, et al. Deep Learning for Unsupervised Insider Threat Detection in Structured Cybersecurity Data Streams[EB/OL]. (2017-10-02)[2025-01-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.00811.
|
| [9] |
ELDARDIRY H, BART E, LIU Juan, et al. Multi-Domain Information Fusion for Insider Threat Detection[C]// IEEE. 2013 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops. New York: IEEE, 2013: 45-51.
|
| [10] |
ZHANG Lili, XIE Yuxiang, LUAN Xidao, et al. Multi-Source Heterogeneous Data Fusion[C]// IEEE. 2018 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Big Data (ICAIBD). New York: IEEE, 2018: 47-51.
|
| [11] |
LEE S, PARK S, HONG K. RDFNet: RGB-D Multi-Level Residual Feature Fusion for Indoor Semantic Segmentation[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). New York: IEEE, 2017: 4990-4999.
|
| [12] |
BILINSKI P, PRISACARIU V. Dense Decoder Shortcut Connections for Single-Pass Semantic Segmentation[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 6596-6605.
|
| [13] |
LE V H, ZHANG Hongyu. Log-Based Anomaly Detection without Log Parsing[C]// IEEE. 2021 36th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE). New York: IEEE, 2021: 492-504.
|
| [14] |
LIU Shuo, XU Liwen, WANG Jinru, et al. LCR-GAN: Learning Crucial Representation for Anomaly Detection[C]// ACM. 2021 5th International Conference on Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2021: 162-167.
|
| [15] |
WU Shuguang, WANG Hongyan, WANG Yu, et al. Technology Analysis of Network Anomalous Behavior Detection Based on Machine Learning[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE). New York: IEEE, 2022: 730-737.
|
| [16] |
MAO Sheng, GUO Jiansheng, GU Taoyong, et al. Dis-AE-LSTM: Generative Adversarial Networks for Anomaly Detection of Time Series Data[C]// IEEE. 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering (ICAICE). New York: IEEE, 2020: 330-336.
|
| [17] |
SAID E M, LE-KHAC N A, DEV S, et al. Network Anomaly Detection Using LSTM Based Autoencoder[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 16th ACM Symposium on QoS and Security for Wireless and Mobile Networks. New York: ACM, 2020: 37-45.
|
| [18] |
XUE Yapeng. Research on Time Series Anomaly Detection Based on Graph Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Automation and Computer Engineering (ICEACE). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1670-1674.
|
| [19] |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All you Need[J]. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: 5998-6008.
|
| [20] |
YIN Chuanlong, ZHU Yuefei, FEI Jinlong, et al. A Deep Learning Approach for Intrusion Detection Using Recurrent Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 21954-21961.
|
| [21] |
XU Wei, HUANG Ling, FOX A, et al. Detecting Large-Scale System Problems by Mining Console Logs[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the ACM SIGOPS 22nd Symposium on Operating Systems Principles. New York: ACM, 2009: 117-132.
|
| [22] |
XU Wei, HUANG Ling, FOX A, et al. Online System Problem Detection by Mining Patterns of Console Logs[C]// IEEE. 2009 Ninth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. New York: IEEE, 2009: 588-597.
|
| [23] |
LOU Jianguang, FU Qiang, YANG Shengqi, et al. Mining Invariants from Console Logs for System Problem Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2010, 59(6): 759-774.
|
| [24] |
OLINER A, STEARLEY J. What Supercomputers Say: A Study of Five System Logs[C]// IEEE. The 37th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN’07). New York: IEEE, 2007: 575-584.
|
| [25] |
DU Min, LI Feifei, ZHENG Guineng, et al. DeepLog: Anomaly Detection and Diagnosis from System Logs through Deep Learning[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 1285-1298.
|
| [26] |
AUDIBERT J, MICHIARDI P, GUYARD F, et al. USAD: UnSupervised Anomaly Detection on Multivariate Time Series[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2020: 3395-3404.
|
| [27] |
LI Sainan, YIN Qilei, LI Guoliang, et al. Unsupervised Contextual Anomaly Detection for Database Systems[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Management of Data. New York: ACM, 2022: 788-802.
|
| [28] |
SOWMYA K, RAMESH K. Enhancing Anomaly Detection in Multivariate Time Series with Stacked Transformer Encoders and Adaptive Positional Embeddings[EB/OL]. (2024-12-06)[2025-01-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-09821-w.
|
 ), HU Aiqun1,2,3
), HU Aiqun1,2,3