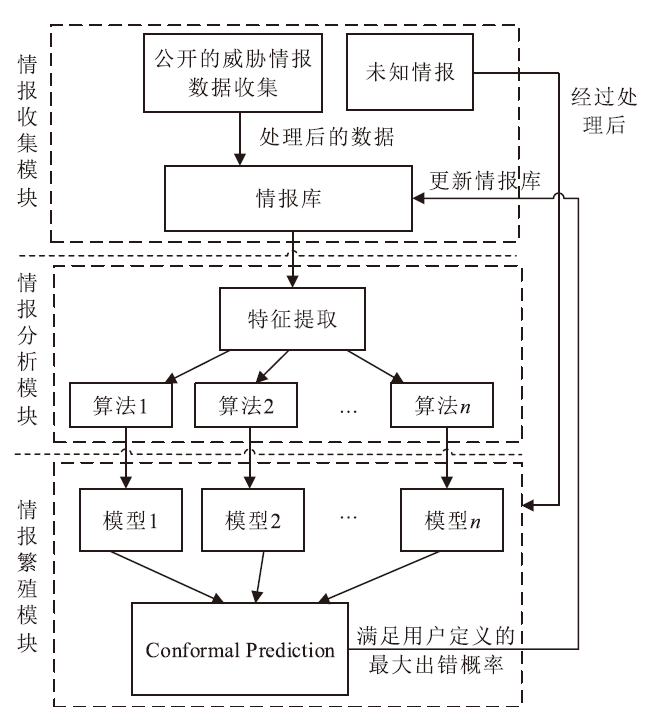
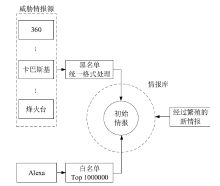
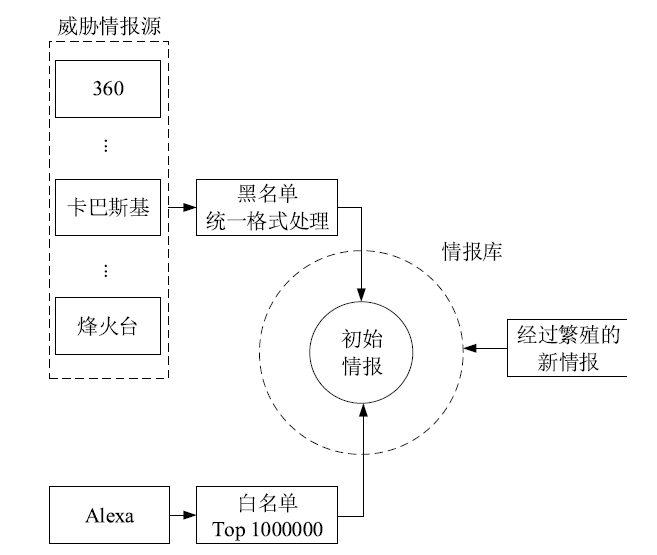
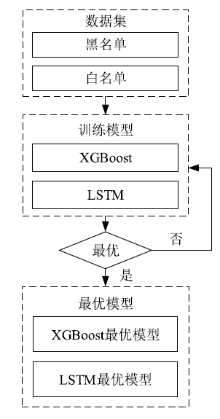
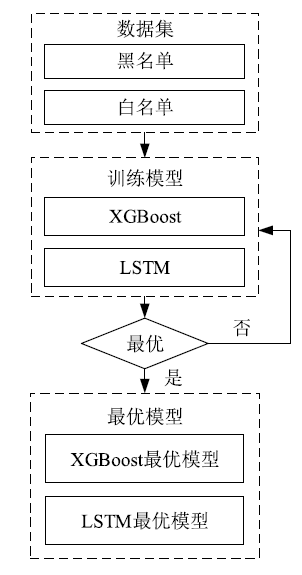
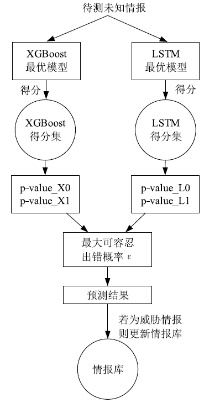
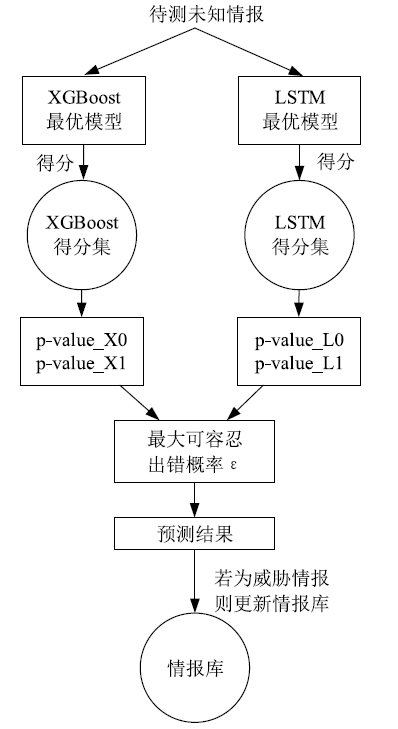
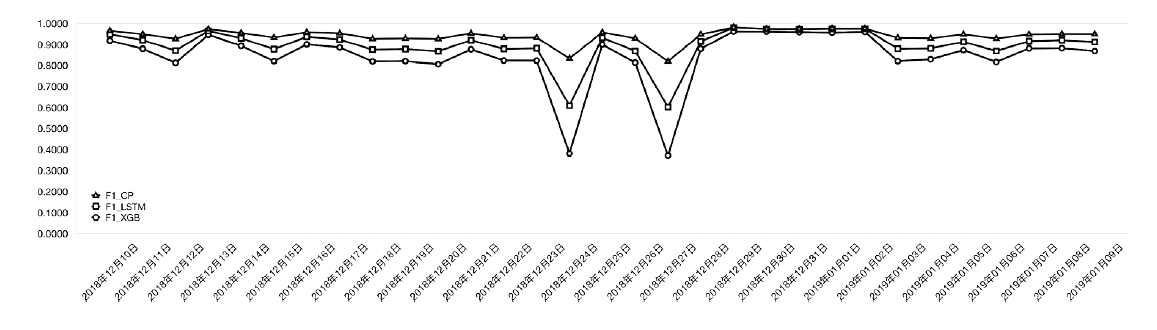
| [1] |
WIEM T, HELMI R. A Survey on Technical Threat Tntelligence in the Age of Sophisticated Cyber Attacks[J]. Computer and Security, 2018,72(C):212-233.
|
| [2] |
SAMUEL S, DOMINIK T, PATRICK H. FANCI: Feature-based Automated NXDomain Classification and Intelligence [C]//USENIX. The 27th USENIX Security Symposium, August 15-17, 2018, Baltimore, MD, USA. Berkeley: USNIX Association, 2018: 1165-1181.
|
| [3] |
ZHANG Y, EGELMAN S, CRANOR L, et al. Phinding Phish: Evaluating Anti-phishing Tools[R]. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: CMU, CMU-CyLab-06-018, 2006.
|
| [4] |
SAHOO D, LIU C, HOI S C H. Malicious URL Detection Using Machine Learning: a Survey[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1701.07179.pdf, 2020 -2-12.
|
| [5] |
WOODBRIDGE J, ANDERSON H S, AHUJA A, et al. Predicting Domain Generation Algorithms with Long Short-term Memory Networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.00791.pdf, 2020 -2-11.
|
| [6] |
DAVUTH N, KIM S R. Classification of Malicious Domain Names using Support Vector Machine and Bi-gram Method[J]. International Journal of Security and Its Applications, 2013,7(1):51-58.
|
| [7] |
SAXE J, BERLIN K. eXpose: A Character-level Convolutional Neural Network with Embeddings for Detecting Malicious URLs, file paths and registry keys[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.08568.pdf, 2020 -2-11.
|
| [8] |
SHI Yong, CHEN Gong, LI Juntao. Malicious Domain Name Detection Based on Extreme Machine Learning[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2018,48(3):1347-1357.
|
| [9] |
HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long Short-term Memory[J]. Neural computation, 1997,9(8):1735-1780.
URL
pmid: 9377276
|
| [10] |
ROBERTO J, KUMAR S, SANTANU K D, et al. Transcend: Detecting Concept Drift in Malware Classification Models [C]//USENIX. The 26th USENIX Security Symposium, August 16-18, 2017, Vancouver, BC, Canada. Berkeley: USNIX Association, 2017: 625-642.
|
 ), WU Yijie2, DU Zhenhua3
), WU Yijie2, DU Zhenhua3