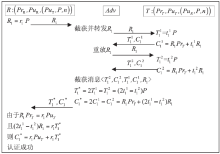
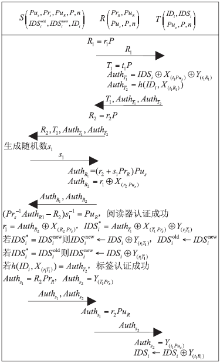
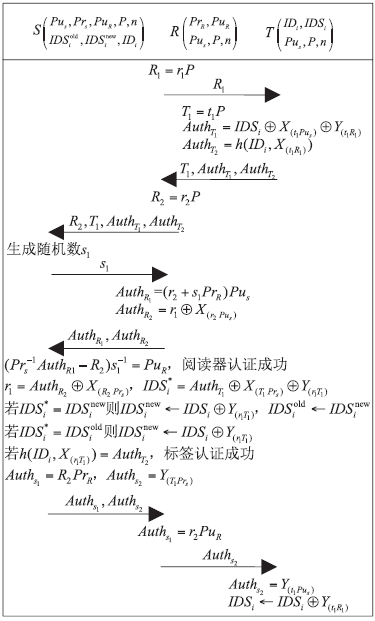
| [1] |
董晓蕾. 物联网隐私保护研究进展[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2015,52(10):2341-2352.
|
| [2] |
LEUNG J, CHEUNG W, CHU S C.Aligning RFID Applications with Supply Chain Strategies[J]. Information & Management, 2014, 51(2): 260-269.
|
| [3] |
NGAI E W T, GUNASEKARAN A. RFID Adoption: Issues and Challenges[J]. International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems, 2017, 5(1): 1-8.
|
| [4] |
张玉婷,严承华. 一种基于双向认证协议的RFID标签认证技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全,2016(1):64-69.
|
| [5] |
YU Yinhui, ZHANG Lei.Research on a Provable Security RFID Authentication Protocol Based on Hash Function[J]. Journal of China Universities of Posts & Telecommunications, 2016, 23(2): 31-37.
|
| [6] |
马庆,郭亚军,曾庆江,等. 一种新的超轻量级RFID双向认证协议[J]. 信息网络安全,2016(5):44-50.
|
| [7] |
SHI Leyi, JIA Cong, GONG Jian, et al.RFID Mutual Authentication Protocol on Pseudo-random Hash Function with Shared Secrets[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 38(2): 361-366.
|
| [8] |
杨玉龙,彭长根,郑少波,等. 基于移动智能终端的超轻量级移动RFID安全认证协议[J]. 信息网络安全,2017(5):22-27.
|
| [9] |
VAUDENAY S.On Privacy Models for RFID[C]//Springer. 2007 International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, December 2-6, 2007, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia. Heidelberg: Springer, 2007: 68-87.
|
| [10] |
HE D, ZEADALLY S.An Analysis of RFID Authentication Schemes for Internet of Things in Healthcare Environment Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2015, 2(1): 72-83.
|
| [11] |
LEE Y K, BATINA L, VERBAUWHEDE I. EC-RAC (ECDLP Based Randomized Access Control): Provably Secure RFID Authentication Protocol[C]//IEEE. 2008 IEEE International Conference on RFID, April 16-17, 2008, Las Vegas, NV, USA. New Jersey: IEEE, 2008: 97-104.
|
| [12] |
KI L Y, BATINA L, VERBAUWHEDE I.Untraceable RFID Authentication Protocols: Revision of EC-RAC[C]//IEEE. 2009 IEEE International Conference on RFID, April 27-28, 2009, Orlando, FL, USA. New Jersey: IEEE, 2009: 178-185.
|
| [13] |
LIAO Yipin, HSIAO C M.A Secure ECC-based RFID Authentication Scheme Integrated with ID-verifier Transfer Protocol[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2014, 18(7): 133-146.
|
| [14] |
ZHAO Zhenguo.A Secure RFID Authentication Protocol for Healthcare Environments Using Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2014, 38(5): 46.
|
| [15] |
FARASH M S, NAWAZ O, MAHMOOD K, et al.A Provably Secure RFID Authentication Protocol Based on Elliptic Curve for Healthcare Environments[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2016, 40(7): 1-7.
|
| [16] |
CHIEN H Y.Elliptic Curve Cryptography-based RFID Authentication Resisting Active Tracking[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2017, 94(4): 2925-2936.
|
| [17] |
CHOU J S.An Efficient Mutual Authentication RFID Scheme Based on Elliptic Curve Cryptography[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2014, 70(1): 75-94.
|
| [18] |
ZHANG Zezhong, QI Qingqing.An Efficient RFID Authentication Protocol to Enhance Patient Medication Safety Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2014, 38(5): 47-54.
|
| [19] |
夏戈明,史立哲, 周文,等. 轻量级RFID双向通信认证协议优化方案[J]. 信息网络安全,2014(2):58-62.
|
| [20] |
ALAMR A A, KAUSAR F, KIM J, et al.A Secure ECC-based RFID Mutual Authentication Protocol for Internet of Things[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2016, 8(2): 1-14.
|