Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 281-294.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.02.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning
JIN Di1,2,3, REN Hao1,2,3, TANG Rui1,2,3, CHEN Xingshu1,2,3, WANG Haizhou1,2,3( )
)
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China
2. Key Laboratory of Data Protection and Intelligent Management, Ministry of Education, Chengdu 610065, China
3. China Cyber Science Research Institute, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China
-
Received:2024-12-10Online:2025-02-10Published:2025-03-07
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIN Di, REN Hao, TANG Rui, CHEN Xingshu, WANG Haizhou. Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 281-294.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.02.009
| 模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Macro-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TextCNN[ | 0.839 | 0.719 | 0.583 | 0.770 |
| TextRNN[ | 0.809 | 0.659 | 0.492 | 0.721 |
| TextRCNN[ | 0.818 | 0.658 | 0.568 | 0.745 |
| TextDPCNN[ | 0.826 | 0.782 | 0.422 | 0.721 |
| BERT[ | 0.827 | 0.654 | 0.653 | 0.769 |
| BERT-CNN | 0.829 | 0.680 | 0.600 | 0.763 |
| BERT-RNN | 0.824 | 0.672 | 0.583 | 0.755 |
| BERT-RCNN | 0.826 | 0.659 | 0.628 | 0.764 |
| BERT-DPCNN | 0.821 | 0.655 | 0.598 | 0.754 |
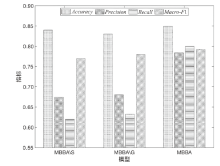
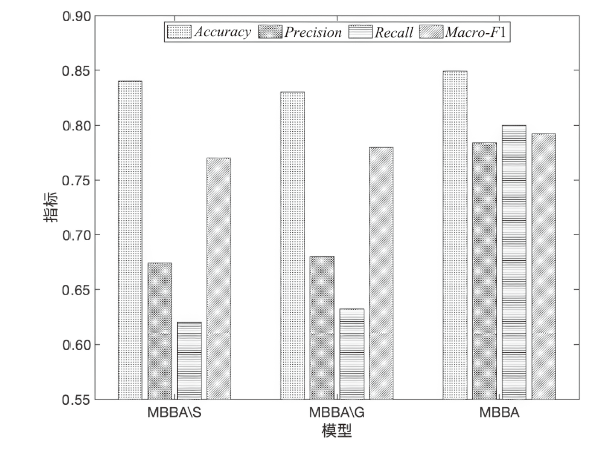
| MBBA(本文) | 0.849 | 0.784 | 0.800 | 0.792 |
| 模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Macro-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaiduTC | 0.571 | 0.298 | 0.525 | 0.380 |
| Qwen1.5-0.5B | 0.514 | 0.489 | 0.486 | 0.466 |
| Qwen-7B | 0.519 | 0.480 | 0.475 | 0.483 |
| LLaMA3-8B | 0.606 | 0.638 | 0.681 | 0.591 |
| Alpaca2-7B | 0.477 | 0.643 | 0.640 | 0.477 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 0.406 | 0.599 | 0.581 | 0.403 |
| GPT-4o | 0.757 | 0.705 | 0.754 | 0.716 |
| GPT-4-Turbo | 0.741 | 0.707 | 0.770 | 0.710 |
| COLDetector[ | 0.729 | 0.769 | 0.729 | 0.742 |
| MBBA(本文) | 0.849 | 0.784 | 0.800 | 0.792 |
| 模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Macro-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaiduTC | 0.630 | 0.610 | 0.560 | 0.540 |
| Qwen1.5-0.5B | 0.496 | 0.385 | 0.457 | 0.417 |
| Qwen-7B | 0.617 | 0.511 | 0.749 | 0.607 |
| LLaMA3-8B | 0.615 | 0.601 | 0.603 | 0.601 |
| Alpaca2-7B | 0.676 | 0.695 | 0.700 | 0.676 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 0.529 | 0.616 | 0.588 | 0.517 |
| GPT-4o | 0.767 | 0.784 | 0.725 | 0.734 |
| GPT-4-Turbo | 0.784 | 0.784 | 0.756 | 0.764 |
| COLDetector[ | 0.810 | 0.800 | 0.820 | 0.810 |
| MBBA(本文) | 0.831 | 0.840 | 0.831 | 0.832 |
| [1] | BURNAP P, WILLIAMS M L. Cyber Hate Speech on Twitter: An Application of Machine Classification and Statistical Modeling for Policy and Decision Making[J]. Policy & Internet, 2015, 7(2): 223-242. |
| [2] | Pew Research Center. Online Harassment 2017[EB/OL]. (2017-07-11)[2024-12-06]. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2017/07/11/online-harassment-2017. |
| [3] | Department for the Protection of Youth Rights and Interests of the Central Committee of the Communist Youth League, China Internet Network Information Centre (CNNIC). 2021 National Research Report on Minors’ Internet Usage[EB/OL]. (2022-11-30)[2024-12-06]. http://news.youth.cn/gn/202211/t20221130_14165457.htm. |
| 共青团中央维护青少年权益部, 中国互联网络信息中心. 2021年全国未成年人互联网使用情况研究报告[EB/OL]. (2022-11-30)[2024-12-06]. http://news.youth.cn/gn/202211/t20221130_14165457.htm. | |
| [4] | Secretary Bureau of the Office of the Central Cyberspace Affairs Commission. Notice of Effectively Strengthening the Governance of Cyber Violence[EB/OL]. (2022-11-04)[2024-12-06]. https://www.cac.gov.cn/2022-11/04/c_1669204414682178.htm. |
| 中央网信办秘书局. 关于切实加强网络暴力治理的通知[EB/OL]. (2022-11-04)[2024-12-06]. https://www.cac.gov.cn/2022-11/04/c_1669204414682178.htm. | |
| [5] | PATCHIN J W, HINDUJA S. Cyberbullying Among Tweens in the United States: Prevalence, Impact, and Helping Behaviors[J]. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 2022, 42(3): 414-430. |
| [6] | WATANABE H, BOUAZIZI M, OHTSUKI T. Hate Speech on Twitter: A Pragmatic Approach to Collect Hateful and Offensive Expressions and Perform Hate Speech Detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 13825-13835. |
| [7] | SU Huipo, HUANG Zhenjie, CHANG H T, et al. Rephrasing Profanity in Chinese Text[C]// ACL. The 1st Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 18-24. |
| [8] | YANG H, LIN Chuanjie. TOCP: A Dataset for Chinese Profanity Processing[C]// ELRA. The 2nd Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying. Paris: ELRA, 2020: 6-12. |
| [9] | DAVIDSON T, WARMSLEY D, MACY M, et al. Automated Hate Speech Detection and the Problem of Offensive Language[C]// AAAI. The 11th International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2017, 11(1): 512-515. |
| [10] | SWAMY S D, JAMATIA A, GAMBACK B, et al. NIT_Agartala_NLP_Team at SemEval-2019 Task 6: an Ensemble Approach to Identifying and Categorizing Offensive Language in Twitter Social Media Corpora[C]// ACL. The 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 696-703. |
| [11] | BALAKRISHNAN V, GOVINDAN V, GOVAICHELVAN K N. Tamil Offensive Language Detection: Supervised Versus Unsupervised Learning Approaches[J]. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing, 2023, 22(4): 1-14. |
| [12] | KIM Y. Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification[C]// ACL. The 19th Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2014: 1746-1751. |
| [13] | GAMBACK B, SIKDAR U K. Using Convolutional Neural Networks to Classify Hate-Speech[C]// ACL. The 1st Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 85-90. |
| [14] | PARK J H, FUNG P. One-Step and Two-Step Classification for Abusive Language Detection on Twitter[C]// ACL. The 1st Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 41-45. |
| [15] | SINGH V, VARSHNEY A, AKHTAR S S, et al. Aggression Detection on Social Media Text Using Deep Neural Networks[C]// ACL. The 2nd Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2018: 43-50. |
| [16] | BADJATIYA P, GUPTA S, GUPTA M, et al. Deep Learning for Hate Speech Detection in Tweets[C]// ACM. The 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion. New York: ACM, 2017: 759-760. |
| [17] | PAVLOPOULOS J, MALAKASIOTIS P, ANDROUTSOPOULOS I. Deep Learning for User Comment Moderation[C]// ACL. The 1st Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 25-35. |
| [18] | PAVLOPOULOS J, MALAKASIOTIS P, ANDROUTSOPOULOS I. Deeper Attention to Abusive User Content Moderation[C]// ACL. The 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 1125-1135. |
| [19] | DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. Bert: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding[C]//ACL. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 4171-4186. |
| [20] | LIU Ping, LI Wen, ZOU Liang. NULI at SemEval-2019 Task 6: Transfer Learning for Offensive Language Detection Using Bidirectional Transformers[C]// ACL. The 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 87-91. |
| [21] | PARASCHIV A, CERCEL D C. UPB at GermEval-2019 Task 2: BERT-Based Offensive Language Classification of German Tweets[C]// GSCL. The 15th Conference on Natural Language Processing. Erlangen: GSCL, 2019: 396-402. |
| [22] | RISCH J, STOLL A, ZIEGELE M, et al. hpiDEDIS at GermEval 2019: Offensive Language Identification Using a German BERT Model[C]// GSCL. The 15th Conference on Natural Language Processing. Erlangen: GSCL, 2019: 405-410. |
| [23] | RAJAMANICKAM S, MISHRA P, YANNAKOUDAKIS H, et al. Joint Modelling of Emotion and Abusive Language Detection[C]// ACL. The 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2020: 4270-4279. |
| [24] | ZHOU Xianbing, YANG Yong, FAN Xiaochao, et al. Hate Speech Detection Based on Sentiment Knowledge Sharing[C]// ACL. The 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2021: 7158-7166. |
| [25] | YANG Chuanpeng, ZHU Fuqing, LIU Guihua, et al. Multimodal Hate Speech Detection via Cross-Domain Knowledge Transfer[C]// ACM. The 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2022: 4505-4514. |
| [26] | DENG Jiawen, ZHOU Jingyan, SUN Hao, et al. COLD: A Benchmark for Chinese Offensive Language Detection[C]// ACL. The 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2022: 11580-11599. |
| [27] | PAVLOPOULOS J, MALAKASIOTIS P, BAKAGIANNI J, et al. Improved Abusive Comment Moderation with User Embeddings[C]//ACL. The 2017 EMNLP Workshop:Natural Language Processing Meets Journalism. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 51-55. |
| [28] | QIAN Jing, ELSHERIEF M, BELDING E M, et al. Leveraging Intra-User and Inter-User Representation Learning for Automated Hate Speech Detection[C]//ACL. The 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2018: 118-123. |
| [29] | MISHRA P, DEL TREDICI M, YANNAKOUDAKIS H, et al. Author Profiling for Abuse Detection[C]// ACL. The 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2018: 1088-1098. |
| [30] | RIBEIRO M H, CALAIS P H, SANTOS Y A, et al. Characterizing and Detecting Hateful Users on Twitter[C]// AAAI. The 12th International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2018: 676-679. |
| [31] | MISHRA P, DEL TREDICI M, YANNAKOUDAKIS H, et al. Abusive Language Detection with Graph Convolutional Networks[C]//ACL. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 2145-2150. |
| [32] | ZHANG Yu, YANG Qiang. A Survey on Multi-Task Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2021, 34(12): 5586-5609. |
| [33] | ROSS B, RIST M, CARBONELL G, et al. Measuring the Reliability of Hate Speech Annotations: The Case of the European Refugee Crisis[C]// NLP4CMC III. The 3rd Workshop on Natural Language Processing for Computer-Mediated Communication. Bochum: Bochumer Linguistische Arbeitsberichte, 2016: 6-9. |
| [34] | WASEEM Z. Are You a Racist or am I Seeing Things? Annotator Influence on Hate Speech Detection on Twitter[C]// ACL. The 2016 EMNLP Workshop on Natural Language Processing and Computational Social Science. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2016: 138-142. |
| [35] | WASEEM Z, HOVY D. Hateful Symbols or Hateful People? Predictive Features for Hate Speech Detection on Twitter[C]//ACL. The 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2016: 88-93. |
| [36] | SINA Weibo. Weibo Community Convention[EB/OL]. (2021-05-27)[2024-12-06]. https://service.account.weibo.com/h5/roles/gongyue. |
| 新浪微博. 微博社区公约[EB/OL]. (2021-05-27)[2024-12-06]. https://service.account.weibo.com/h5/roles/gongyue. | |
| [37] | Zhihu. Zhihu Community Guidelines[EB/OL]. (2022-04-28)[2024-12-06]. https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/506696688. |
| 知乎. 知乎社区规范[EB/OL]. (2022-04-28)[2024-12-06]. https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/506696688. | |
| [38] | META. Community Standards[EB/OL]. (2024-11-12)[2024-12-06]. https://transparency.meta.com/zh-cn/policies/community-standards/. |
| META. 社群守则[EB/OL]. (2024-11-12)[2024-12-06]. https://transparency.meta.com/zh-cn/policies/community-standards/. | |
| [39] | X Corp. The X Roles[EB/OL]. (2023-07-01)[2024-12-06]. https://help.x.com/zh-cn/rules-and-policies/twitter-rules. |
| [40] | RODRIGUEZ A, ARGUETA C, CHEN Yiling. Automatic Detection of Hate Speech on Facebook Using Sentiment and Emotion Analysis[C]// IEEE. The 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication. New York: IEEE, 2019: 169-174. |
| [41] | LIU Pengfei, QIU Xipeng, HUANG Xuanjing. Recurrent Neural Network for Text Classification with Multi-Task Learning[C]// ACM. The 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2016: 2873-2879. |
| [42] | LAI Siwei, XU Liheng, LIU Kang, et al. Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Classification[C]// AAAI. The 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2015: 2267-2273. |
| [43] | JOHNSON R, ZHANG Tong. Deep Pyramid Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Categorization[C]// ACL. The 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 562-570. |
| [1] | LI Hailong, CUI Zhian, SHEN Xieyang. Overview of Anomaly Analysis and Detection Methods for Network Traffic [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [2] | WU Haoying, CHEN Jie, LIU Jun. Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64 [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [3] | CHEN Xiaojing, TAO Yang, WU Baiqi, DIAO Yunfeng. Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [4] | XU Ruzhi, ZHANG Ning, LI Min, LI Zixuan. Research on a High Robust Detection Model for Malicious Software [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [5] | TIAN Zhao, NIU Yajie, SHE Wei, LIU Wei. A Reputation Evaluation Method for Vehicle Nodes in V2X [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [6] | ZHANG Guanghua, LIU Yichun, WANG He, HU Boning. Defense Scheme for Removing Deep Neural Network Backdoors Based on JSMA Adversarial Attacks [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [7] | XU Zirong, GUO Yanping, YAN Qiao. Malicious Software Adversarial Defense Model Based on Feature Severity Ranking [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| [8] | YANG Zhipeng, LIU Daidong, YUAN Junyi, WEI Songjie. Research on Network Local Security Situation Fusion Method Based on Self-Attention Mechanism [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 398-410. |
| [9] | JIANG Rong, LIU Haitian, LIU Cong. Unsupervised Network Intrusion Detection Method Based on Ensemble Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [10] | FENG Guangsheng, JIANG Shunpeng, HU Xianlang, MA Mingyu. New Research Progress on Intrusion Detection Techniques for the Internet of Things [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [11] | ZHAO Pengcheng, YU Junqing, LI Dong. An Optimal Algorithm for Traffic Scheduling in SRv6 Network Based on Deep Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 272-281. |
| [12] | JIN Zhigang, DING Yu, WU Xiaodong. Federated Intrusion Detection Algorithm with Bilateral Correction Merging Gradient Difference [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 293-302. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xuan, WAN Liang, LUO Heng, YANG Yang. Automated Botnet Detection Method Based on Two-Stage Graph Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(12): 1933-1947. |
| [14] | YIN Jie, CHEN Pu, YANG Guinian, XIE Wenwei, LIANG Guangjun. Detection of DDoS Attacks in the Internet of Things Based on Artificial Intelligence [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(11): 1615-1623. |
| [15] | WEI Jinxia, HUANG Xizhang, FU Yuhao, LI Jing, LONG Chun. Mining Traffic Detection Method Based on Global Feature Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(10): 1506-1514. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||