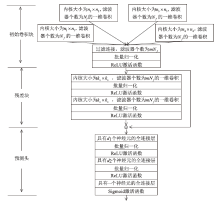
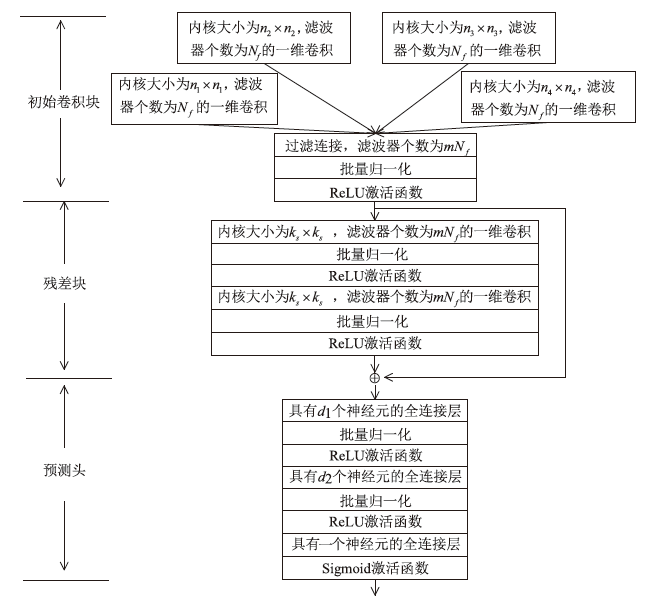
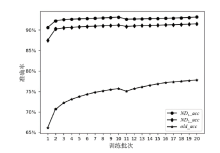
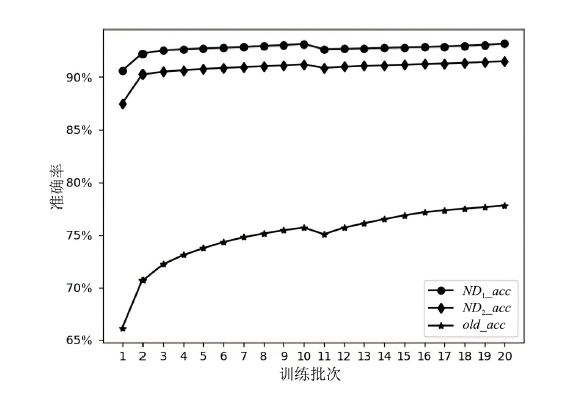
Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 249-259.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.02.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
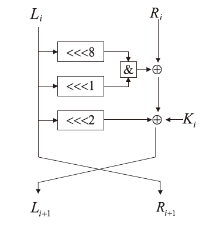
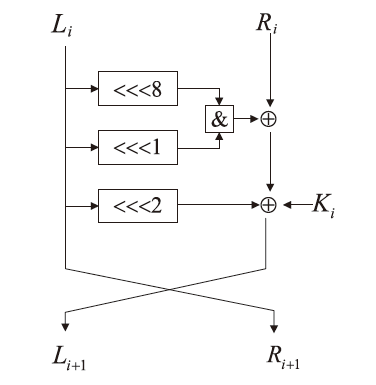
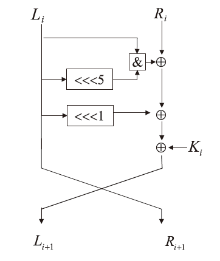
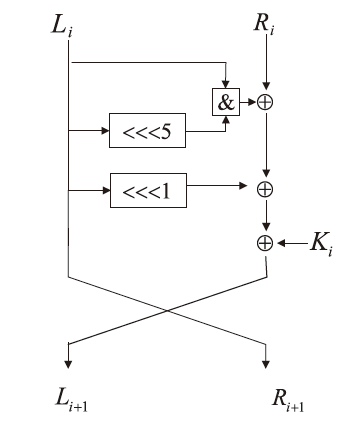
Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64
WU Haoying1, CHEN Jie1,2( ), LIU Jun3
), LIU Jun3
- 1. School of Telecommunications Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
2. Henan Key Laboratory of Network Cryptography Technology, Zhengzhou 450001, China
3. School of Computer Science, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an 710119, China
-
Received:2024-05-22Online:2025-02-10Published:2025-03-07
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WU Haoying, CHEN Jie, LIU Jun. Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 249-259.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.02.006
| 密码 | 轮数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simon32/64 | 7 | 96.73 % | 99.22 % | 99.51 % | 99.16 % | 99.12 % |
| Simon32/64 | 8 | 76.76 % | 77.36 % | 80.38 % | 85.46 % | 89.21 % |
| Simon32/64 | 9 | 62.70 % | 64.38 % | 67.17 % | 62.84 % | 62.50 % |
| Simeck32/64 | 7 | 98.75 % | 99.78 % | 99.81 % | 99.96 % | 99.99 % |
| Simeck32/64 | 8 | 86.77 % | 91.38 % | 97.13 % | 97.31 % | 97.92 % |
| Simeck32/64 | 9 | 67.26 % | 68.58 % | 67.95 % | 66.98 % | 66.90 % |
| 密码 | 轮数 | 数据复杂度 | 计算复杂度 | 攻击成功率 | 结果来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simon32/64 | 11 | 100% (1000次攻击) | 文献[ | ||
| Simon32/64 | 11 | — | 95.6% (1000次攻击) | 文献[ | |
| Simon32/64 | 12 | 86% (100次攻击) | 本文 | ||
| Simeck32/64 | 10 | 80% (50次攻击) | 文献[ | ||
| Simeck32/64 | 12 | 97% (100次攻击) | 本文 |
| [1] | BOGDANOV A, KNUDSEN L R, LEANDER G, et al. PRESENT: An Ultra-Lightweight Block Cipher[C]// Springer. Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems-CHES 2007. Heidelberg: Springer, 2007: 450-466. |
| [2] | WU Wenling, ZHANG Lei. LBlock: A Lightweight Block Cipher[C]// Springer. Applied Cryptography and Network Security (ACNS 2011). Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 327-344. |
| [3] | BEAULIEU R, SHORS D, SMITH J, et al. The Simon and Speck Families of Lightweight Block Ciphers[C]// IEEE. 2015 52nd ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-6. |
| [4] | YANG Gangqiang, ZHU Bo, SUDER V, et al. The Simeck Family of Lightweight Block Ciphers[C]// Springer. Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems-CHES 2015. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 307-329. |
| [5] | WANG Meiqin. Differential Cryptanalysis of Reduced-Round PRESENT[C]// Springer. Progress in Cryptology-AFRICACRYPT 2008. Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 40-49. |
| [6] | WANG Ning, WANG Xiaoyun, JIA Keting. Improved Impossible Differential Attack on Reduced-Round LBlock[C]// Springer. Information Security and Cryptology-ICISC 2015. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 136-152. |
| [7] | LI Mingming, GUO Jiansheng, CUI Jingyi, et al. Impossible Differential Cryptanalysis of SPECK[C]// Springer. Trusted Computing and Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 16-31. |
| [8] | SUN Ling, FU Kai, WANG Meiqin. Improved Zero-Correlation Cryptanalysis on SIMON[C]// Springer. Information Security and Cryptology. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 125-143. |
| [9] | QIAO Kexin, HU Lei, SUN Siwei. Differential Analysis on Simeck and SIMON with Dynamic Key-Guessing Techniques[C]// Springer. Information Systems Security and Privacy. Heidelberg: Springer, 2017: 64-85. |
| [10] | GOHR A. Improving Attacks on Round-Reduced Speck32/64 Using Deep Learning[C]// Springer. Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO 2019. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 150-179. |
| [11] | PAL D, MANDAL U, DAS A, et al. Deep Learning Based Differential Classifier of PRIDE and RC5[C]// Springer. Applications and Techniques in Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2023: 46-58. |
| [12] | JAIN A, KOHLI V, MISHRA G. Deep Learning-Based Differential Distinguisher for Lightweight Cipher PRESENT[EB/OL]. (2020-07-12)[2024-04-30]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/846, 2020-07-12/2023-1-17. |
| [13] | HOU Zezhou, CHEN Shaozhen, REN Jiongjiong. Research and Application of Deep Learning on Differential Distinguisher of Block Cipher[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(5): 1893-1906. |
| 侯泽洲, 陈少真, 任炯炯. 深度学习在分组密码差分区分器上的研究应用[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(5): 1893-1906. | |
| [14] | ZHANG Liu, WANG Zilong, WANG Baocang. Improving Differential-Neural Cryptanalysis with Inception[EB/OL]. (2022-02-20)[2024-04-30]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2022/183, 2022-02-10/2023-1-17. |
| [15] | BENAMIRA A, GERAULT D, PEYRIN T, et al. A Deeper Look at Machine Learning-Based Cryptanalysis[C]// Springer. Cryptology-EUROCRYPT 2021. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 805-835. |
| [16] | BAKSI A. Machine Learning-Assisted Differential Distinguishers for Lightweight Ciphers[C]// Springer. Classical and Physical Security of Symmetric Key Cryptographic Algorithms. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 141-162. |
| [17] | HOU Zezhou, REN Jiongjiong, CHEN Shaozhen. Improve Neural Distinguisher for Cryptanalysis[EB/OL]. (2021-08-06)[2024-04-30]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2021/1017, 2021-08-06/2023-1-17. |
| [18] | CHEN Yi, SHEN Yantian, YU Hongbo, et al. A New Neural Distinguisher Considering Features Derived from Multiple Ciphertext Pairs[J]. The Computer Journal, 2023, 66(6): 1419-1433. |
| [19] | FU Chaohui, DUAN Ming, WEI Qiang, et al. Polytopic Differential Attack Based on Deep Learning and Its Application[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2021, 8(4): 591-600. |
| [20] | BIHAM E, SHAMIR A. Differential Cryptanalysis of DES-Like Cryptosystems[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 1991, 4(1): 63-72. |
| [21] | TIESSEN T. Polytopic Cryptanalysis[C]// Springer. Cryptology-EUROCRYPT 2016. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 214-239. |
| [22] | SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going Deeper with Convolutions[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-9. |
| [23] | YANG Xiaoxue, CHEN Jie, HAN Lidong. Application of Deep Learning in Differential Cryptanalysis of ARX Block Ciphers[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2022, 9(5): 923-935. |
| [24] | SU Hengchuan, ZHU Xuanyong, MING Duan.Polytopic Attack on Round-Reduced Simon32/64 Using Deep Learning[C]// Springer. Information Security and Cryptology. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 3-20. |
| [1] | LI Hailong, CUI Zhian, SHEN Xieyang. Overview of Anomaly Analysis and Detection Methods for Network Traffic [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [2] | JIN Di, REN Hao, TANG Rui, CHEN Xingshu, WANG Haizhou. Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [3] | CHEN Xiaojing, TAO Yang, WU Baiqi, DIAO Yunfeng. Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [4] | XU Ruzhi, ZHANG Ning, LI Min, LI Zixuan. Research on a High Robust Detection Model for Malicious Software [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [5] | TIAN Zhao, NIU Yajie, SHE Wei, LIU Wei. A Reputation Evaluation Method for Vehicle Nodes in V2X [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [6] | ZHANG Guanghua, LIU Yichun, WANG He, HU Boning. Defense Scheme for Removing Deep Neural Network Backdoors Based on JSMA Adversarial Attacks [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [7] | XU Zirong, GUO Yanping, YAN Qiao. Malicious Software Adversarial Defense Model Based on Feature Severity Ranking [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| [8] | YANG Zhipeng, LIU Daidong, YUAN Junyi, WEI Songjie. Research on Network Local Security Situation Fusion Method Based on Self-Attention Mechanism [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 398-410. |
| [9] | JIANG Rong, LIU Haitian, LIU Cong. Unsupervised Network Intrusion Detection Method Based on Ensemble Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [10] | FENG Guangsheng, JIANG Shunpeng, HU Xianlang, MA Mingyu. New Research Progress on Intrusion Detection Techniques for the Internet of Things [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [11] | ZHAO Pengcheng, YU Junqing, LI Dong. An Optimal Algorithm for Traffic Scheduling in SRv6 Network Based on Deep Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 272-281. |
| [12] | JIN Zhigang, DING Yu, WU Xiaodong. Federated Intrusion Detection Algorithm with Bilateral Correction Merging Gradient Difference [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 293-302. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xuan, WAN Liang, LUO Heng, YANG Yang. Automated Botnet Detection Method Based on Two-Stage Graph Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(12): 1933-1947. |
| [14] | YIN Jie, CHEN Pu, YANG Guinian, XIE Wenwei, LIANG Guangjun. Detection of DDoS Attacks in the Internet of Things Based on Artificial Intelligence [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(11): 1615-1623. |
| [15] | WEI Jinxia, HUANG Xizhang, FU Yuhao, LI Jing, LONG Chun. Mining Traffic Detection Method Based on Global Feature Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(10): 1506-1514. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||