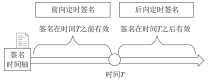
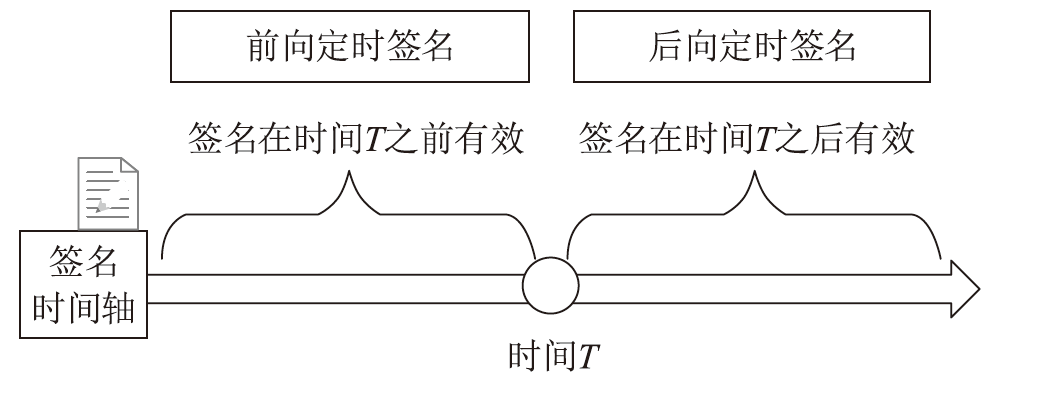
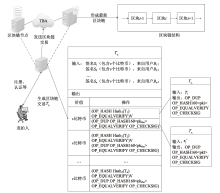
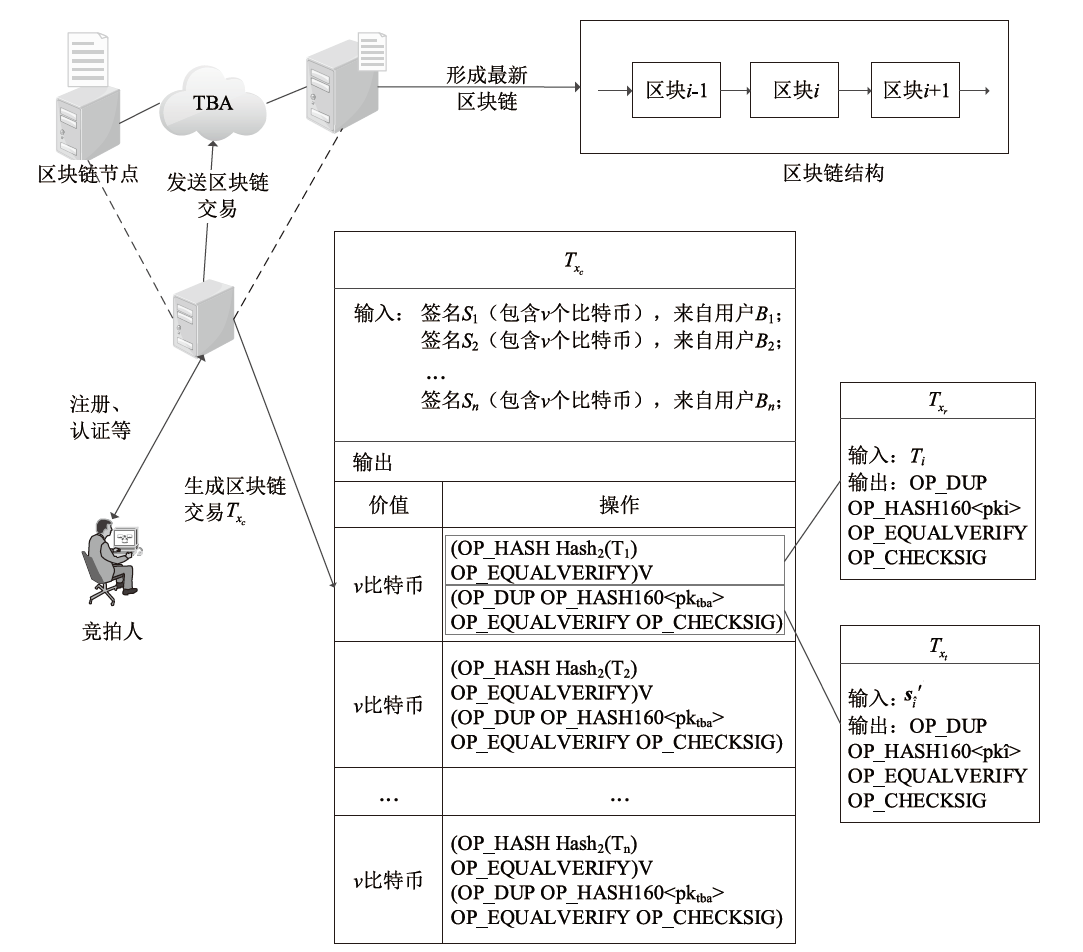
| [1] |
RIVEST R L, SHAMIR A, WAGNER D A. Time-Lock Puzzles and Timed-Release Crypto[EB/OL]. (2023-03-29)[2024-05-22]. https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/149822?show=full.
|
| [2] |
MALAVOLTA G, THYAGARAJAN S A K. Homomorphic Time-Lock Puzzles and Applications[C]// Springer. 39th Annual International Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 620-649.
|
| [3] |
LIU Yi, WANG Qi, YIU S M. Towards Practical Homomorphic Time-Lock Puzzles: Applicability and Verifiability[C]// Springer. 27th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 424-443.
|
| [4] |
DUJMOVIC J, GARG R, MALAVOLTA G. Time-Lock Puzzles with Efficient Batch Solving[C]// Springer. 43th Annual International Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2024: 311-341.
|
| [5] |
CHVOJKA P, JAGER T, SLAMANIG D, et al. Versatile and Sustainable Timed-Release Encryption and Sequential Time-Lock Puzzles[C]// Springer. 26th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 64-85.
|
| [6] |
LOE A, MEDLEY L, O’CONNELL C, et al. Applications of Timed-Release Encryption with Implicit Authentication[C]// Springer. 14th International Conference on Cryptology in Africa. Heidelberg: Springer, 2023: 490-515.
|
| [7] |
BONEH D, NAOR M. Timed Commitments[C]// Springer. 20th Annual International Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2000: 236-254.
|
| [8] |
KATZ J, LOSS J, XU Jiayu. On the Security of Time-Lock Puzzles and Timed Commitments[C]// Springer. Theory of Cryptography:18th International Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 390-413.
|
| [9] |
ARUN A, BONNEAU J, CLARK J. Short-Lived Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Signatures[C]// Springer. 28th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 487-516.
|
| [10] |
THYAGARAJAN S A K, BHAT A, MALAVOLTA G, et al. Verifiable Timed Signatures Made Practical[C]// ACM. 2020 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2020: 1733-1750.
|
| [11] |
MALAVOLTA G, MORENO-SANCHEZ P, KATE A, et al. Concurrency and Privacy with Payment-Channel Networks[C]// ACM. 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 455-471.
|
| [12] |
BONEH D, DRIJVERS M, NEVEN G. Compact Multi-Signatures for Smaller Blockchains[C]// Springer. 24th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2018: 435-464.
|
| [13] |
BENTOV I, KUMARESAN R. How to Use Bitcoin to Design Fair Protocols[C]// Springer. 34th Annual Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 421-439.
|
| [14] |
THYAGARAJAN S A K, MALAVOLTA G, SCHMID F, et al. Verifiable Timed Linkable Ring Signatures for Scalable Payments for Monero[C]// Springer. 27th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 467-486.
|
| [15] |
ZHOU Xiaotong, HE Debiao, NING Jianting, et al. Efficient Construction of Verifiable timed Signatures and Its Application in Scalable Payments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18: 5345-5358.
|
| [16] |
HOU Huiying, NING Jianting, HUANG Xinyi, et al. Verifiable Attribute-Based Timed Signatures and Its Applications[J]. Journal of Software, 2023, 34(5): 2465-2481.
|
|
侯慧莹, 宁建廷, 黄欣沂, 等. 可验证的属性基定时签名方案及其应用[J]. 软件学报, 2023, 34(5):2465-2481.
|
| [17] |
BAO Zijian, HE Debiao, FENG Qi, et al. Constant-Size Verifiable Timed Signatures from RSA Group for Bitcoin-Based Voting Protocols[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2024, 17(4): 1414-1425.
|
| [18] |
GOLDREICH O, GOLDWASSER S, HALEVI S. Public-Key Cryptosystems from Lattice Reduction Problems[C]// Springer. 17th Annual International Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 1997: 112-131.
|
| [19] |
NIST. NIST Announces First Four Quantum-Resistant Cryptographic Algorithms[EB/OL]. (2022-07-05)[2024-05-20]. https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2022/07/nist-announces-first-four-quantum-resistant-cryptographic-algorithms.
|
| [20] |
SHAMIR A. Identity-Based Cryptosystems and Signature Schemes[C]// Springer. Annual International Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 1985: 47-53.
|
| [21] |
RAJABI B, ESLAMI Z. A Verifiable Threshold Secret Sharing Scheme Based on Lattices[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 501: 655-661.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.11.004
|
| [22] |
ISHAI Y, SU Hang, WU D J. Shorter and Faster Post-Quantum Designated-Verifier zkSNARKs from Lattices[C]// ACM. 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2021: 212-234.
|
| [23] |
DUCAS L, DURMUS A, LEPOINT T, et al. Lattice Signatures and Bimodal Gaussians[C]// Springer. 33rd Annual Cryptology Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 40-56.
|
| [24] |
BERT P, FOUQUE P A, ROUX-LANGLOIS A, et al. Practical Implementation of Ring-SIS/LWE Based Signature and IBE[C]// Springer. Post-Quantum Cryptography:9th International Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2018: 271-291.
|
| [25] |
BELLARE M, NEVEN G. Multi-Signatures in the Plain Public-Key Model and a General Forking Lemma[C]// ACM. 13th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2006: 390-399.
|
| [26] |
GENTRY C, PEIKERT C, VAIKUNTANATHAN V. How to Use a Short Basis: Trapdoors for Hard Lattices and New Cryptographic Constructions[C]// ACM. The 40th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 2008: 197-206.
|
| [27] |
GENISE N, LI Baiyu. Gadget-Based iNTRU Lattice Trapdoors[C]// Springer. 21st International Conference on Cryptology in India. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 601-623.
|
 ), WANG Qingnan1, TAN Shuncong1, XIE Huiqin1, YAO Yunfei1,2
), WANG Qingnan1, TAN Shuncong1, XIE Huiqin1, YAO Yunfei1,2