信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1627-1638.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.013
C/C++代码跨形态相似性检测技术研究
- 四川大学网络空间安全学院,成都 610065
-
收稿日期:2025-05-10出版日期:2025-10-10发布日期:2025-11-07 -
通讯作者:贾鹏 E-mail:pengjia@scu.edu.cn -
作者简介:王彦昕(2000—),男,广西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为二进制安全|贾鹏(1988—),男,河南,副研究员,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为漏洞挖掘、软件动静态分析|范希明(1993—),男,新疆,博士研究生,主要研究方向为二进制软件漏洞挖掘、人工智能安全|彭熙(1994—),男,湖南,博士研究生,主要研究方向为二进制安全、系统安全、人工智能 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFB3101803)
Research on Cross Form Similarity Detection for C/C++ Code
WANG Yanxin, JIA Peng( ), FAN Ximing, PENG Xi
), FAN Ximing, PENG Xi
- School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China
-
Received:2025-05-10Online:2025-10-10Published:2025-11-07 -
Contact:JIA Peng E-mail:pengjia@scu.edu.cn
摘要:
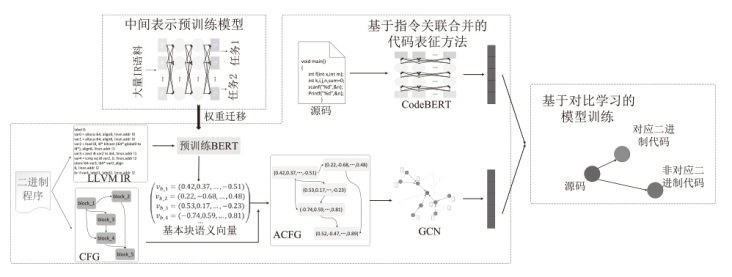
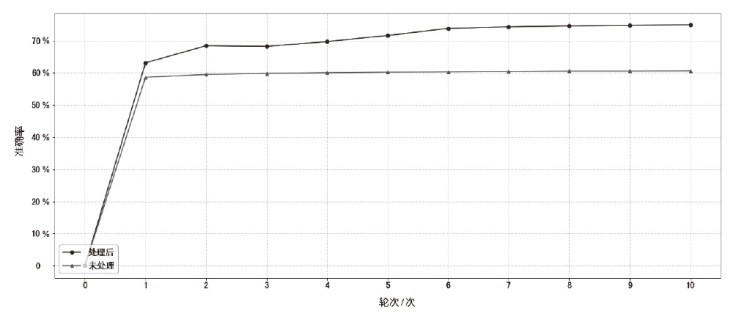
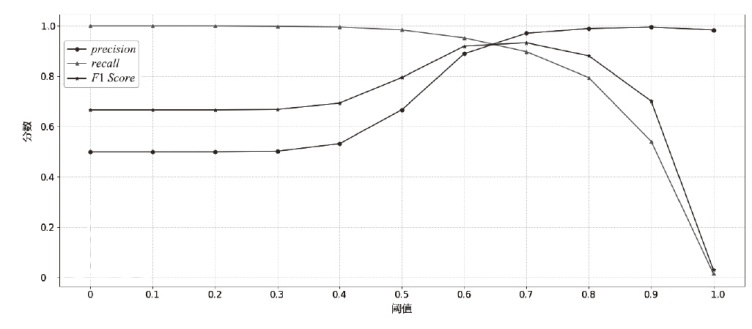
源码二进制相似性检测在软件开发和软件安全相关的任务中起着重要的作用,如逆向工程、版权侵权检测等。目前,源码二进制相似性检测方法虽然取得了不错的效果,但大多局限在相同架构、编译器、优化级别下的二进制代码与源代码进行相似性检测。而在实际检测中,被检测的二进制文件常常是不同架构、编译器和优化级别的,若对此进行区分再进行检测会带来额外的时间开销,同时会给特征设计提取带来额外的挑战。为此,文章提出了一种基于中间表示的跨架构、编译器和优化级别的源码二进制相似性检测方法,该检测方法在二进制端将二进制转换为能在不同平台和编程语言之间进行代码转换的中间表示,以减少不同编译情况下同源二进制文件的语义差距,使用CodeBERT模型提取源码特征,使用BERT模型和GCN模型提取二进制文件特征,由余弦相似性计算两端相似性。为了验证该检测方法的有效性,文章通过不同编译器、优化级别和编译架构将7个组件编译成二进制文件并构造数据集,在数据集上进行了一对一检测和一对多检测两项任务,并探究了预训练、合并指令、阈值等因素对识别准确性产生的影响。实验结果和分析表明,文章提出的基于中间表示的源码二进制相似性检测方法能够有效解决多种编译情况下同源二进制函数与源码的相似性检测问题。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王彦昕, 贾鹏, 范希明, 彭熙. C/C++代码跨形态相似性检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1627-1638.
WANG Yanxin, JIA Peng, FAN Ximing, PENG Xi. Research on Cross Form Similarity Detection for C/C++ Code[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1627-1638.
表2
一对一检测结果
| 场景 | 本文方法 | B2SFinder | BinPro | XLIR | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 精确率 | 召回率 | F1值 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1值 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1值 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1值 | |
| XO | 97.1% | 90.2% | 93.5% | 76.7% | 8.7% | 15.6% | 98.6% | 34.2% | 50.8% | 89.6% | 88.9% | 89.2% |
| XA | 96.8% | 90.9% | 93.7% | 83.3% | 6.5% | 12.1% | 97.8% | 22.4% | 36.5% | 89.1% | 88.2% | 88.6% |
| XC | 96.4% | 91.1% | 93.7% | 74.2% | 8.7% | 15.6% | 99.1% | 38.2% | 55.2% | 88.6% | 89.2% | 88.9% |
| XO+XA | 96.9% | 89.7% | 93.1% | 80.6% | 6.3% | 11.7% | 97.6% | 23.5% | 37.9% | 88.7% | 88.5% | 88.6% |
| XO+XC | 97.0% | 90.0% | 93.4% | 67.2% | 8.5% | 15.1% | 98.9% | 37.0% | 53.8% | 89.2% | 87.9% | 88.5% |
| XA+XC | 97.1% | 90.8% | 93.9% | 78.9% | 6.3% | 11.7% | 97.9% | 31.6% | 47.8% | 88.3% | 87.6% | 87.9% |
| XO+XA+ XC | 97.1% | 89.8% | 93.3% | 72.0% | 6.2% | 11.4% | 98.5% | 35.3% | 51.9% | 87.7% | 87.6% | 87.6% |
表3
一对多检测结果
| 场景 | 本文方法 | B2SFinder | BinPro | XLIR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s2b | b2s | s2b | b2s | s2b | b2s | s2b | b2s | |
| XO | 80.2% | 82.5% | 23.8% | 25.7% | 27.4% | 18.8% | 75.6% | 78.9% |
| XA | 81.1% | 83.5% | 33.2% | 21.7% | 24.4% | 19.8% | 76.1% | 78.9% |
| XC | 80.1% | 83.3% | 23.1% | 25.7% | 23.6% | 19.0% | 75.9% | 78.7% |
| XO+XA | 76.9% | 81.8% | 28.9% | 21.7% | 26.1% | 18.7% | 74.5% | 78.5% |
| XO+XC | 76.5% | 82.2% | 20.6% | 25.7% | 26.2% | 18.2% | 74.6% | 78.3% |
| XA+XC | 77.1% | 83.2% | 30.0% | 22.6% | 23.6% | 18.8% | 74.1% | 78.6% |
| XO+XA+XC | 74.4% | 82.0% | 28.5% | 22.6% | 25.0% | 18.1% | 73.3% | 78.2% |
表4
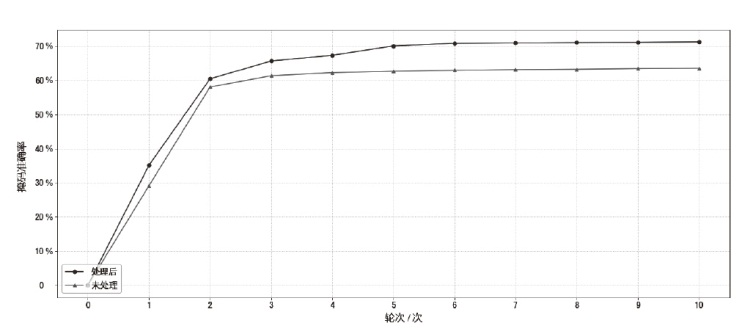
有无预训练对比结果
| 场景 | 无预训练 | 有预训练 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 精确率 | 召回率 | F1值 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1值 | |
| XO | 92.8% | 88.0% | 91.8% | 97.1% | 90.2% | 93.5% |
| XA | 94.1% | 89.5% | 91.8% | 96.8% | 90.9% | 93.7% |
| XC | 92.8% | 89.5% | 91.1% | 96.4% | 91.1% | 93.7% |
| XO+XA | 92.4% | 87.9% | 90.1% | 96.9% | 89.7% | 93.1% |
| XO+XC | 92.6% | 88.4% | 90.4% | 97.0% | 90.0% | 93.4% |
| XA+XC | 92.9% | 89.4% | 91.1% | 97.1% | 90.8% | 93.9% |
| XO+XA+XC | 92.9% | 88.3% | 90.6% | 97.1% | 89.8% | 93.3% |
| [1] | MIYANI D, HUANG Zhen, LIE D. Binpro: A Tool for Binary Source Code Provenance[EB/OL]. (2017-11-02)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.00830. |
| [2] | SHAHKAR A. On Matching Binary to Source Code[D]. Montreal: Concordia University, 2016. |
| [3] | ASLANYAN H, MOVSISYAN H, ARUTUNIAN M, et al. Bin2Source: Matching Binary to Source Code[C]// IEEE. 2021 Ivannikov ISPRAS Open Conference (ISPRAS). New York: IEEE, 2021: 3-7. |
| [4] | DUAN Ruian, BIJLANI A, XU Meng, et al. Identifying Open-Source License Violation and 1-Day Security Risk at Large Scale[C]// ACM. The 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 2169-2185. |
| [5] | WANG Wenhan, LI Ge, MA Bo, et al. Detecting Code Clones with Graph Neural Network and Flow-Augmented Abstract Syntax Tree[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE 27th International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER). New York: IEEE, 2020: 261-271. |
| [6] | ZHAO Gang, HUANG J. Deepsim: Deep Learning Code Functional Similarity[C]// ACM. The 2018 26th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2018: 141-151. |
| [7] | CHANDRAMOHAN M, XUE Yinxing, XU Zhengzi, et al. Bingo: Cross-Architecture Cross-OS Binary Search[C]// ACM. The 2016 24th ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Foundations of Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2016: 678-689. |
| [8] | ZUO Fei, LI Xiaopeng, YOUNG P, et al. Neural Machine Translation Inspired Binary Code Similarity Comparison beyond Function Pairs[EB/OL]. (2018-08-08)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.04706. |
| [9] | YU Zeping, ZHENG Wenxin, WANG Jiaqi, et al. Codecmr: Cross-Modal Retrieval for Function-Level Binary Source Code Matching[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 3872-3883. |
| [10] | GUI Yi, WAN Yao, ZHANG Hongyu, et al. Cross-Language Binary-Source Code Matching with Intermediate Representations[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER). New York: IEEE, 2022: 601-612. |
| [11] | JIANG Ling, AN Junwen, HUANG Huihui, et al. BinaryAI: Binary Software Composition Analysis via Intelligent Binary Source Code Matching[C]// ACM. The IEEE/ACM 46th International Conference on Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2024: 1-13. |
| [12] | PHAN H N, PHAN H N, NGUYEN T N, et al. Repohyper: Better Context Retrieval is All You Need for Repository-Level Code Completion[EB/OL]. (2024-08-14)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.06095. |
| [13] | EGHBALI A, PRADEL M. De-Hallucinator: Iterative Grounding for LLM-Based Code Completion[EB/OL]. (2024-06-19)[2025-03-05]. https://jespereggers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/De-Hallucinator-Iterative-Grounding-for-LLM-Based-Code-1.pdf. |
| [14] | ZHANG Fengji, CHEN Bei, ZHANG Yue, et al. Repocoder: Repository-Level Code Completion through Iterative Retrieval and Generation[EB/OL]. (2023-10-20)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12570. |
| [15] | GU Xiaodong, ZHANG Hongyu, KIM S. Deep Code Search[C]// ACM. The 40th International Conference on Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2018: 933-944. |
| [16] | HUSAIN H, WU H H, GAZIT T, et al. Codesearchnet Challenge: Evaluating the State of Semantic Code Search[EB/OL]. (2020-06-08)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.09436. |
| [17] | ZHANG Xiaochuan, SUN Wenjie, PANG Jianmin, et al. Similarity Metric Method for Binary Basic Blocks of Cross-Instruction Set Architecture[EB/OL]. (2020-02-23)[2025-03-05]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/bar2020-23002.pdf. |
| [18] | TANG Ze, SHEN Xiaoyu, LI Chuan, et al. Ast-Trans: Code Summarization with Efficient Tree-Structured Attention[C]// ACM. The 44th International Conference on Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2022: 150-162. |
| [19] | JOHNSON R, ZHANG Tong. Deep Pyramid Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Categorization[EB/OL]. [2025-03-05]. https://aclanthology.org/P17-1052/. |
| [20] | FENG Zhangyin, GUO Daya, TANG Duyu, et al. Codebert: A Pre-Trained Model for Programming and Natural Languages[EB/OL]. (2020-09-18)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08155. |
| [21] | DING Yangruibo, CHAKRABORTY S, BURATTI L, et al. CONCORD: Clone-Aware Contrastive Learning for Source Code[C]// ACM. The 32nd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis. New York: ACM, 2023: 26-38. |
| [22] | NIU Chang’an, LI Chuanyi, NG V, et al. Spt-Code: Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-Training for Learning Source Code Representations[C]// ACM. The 44th International Conference on Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2022: 2006-2018. |
| [23] | ZHANG Jian, WANG Xu, ZHANG Hongyu, et al. A Novel Neural Source Code Representation Based on Abstract Syntax Tree[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/ACM 41st International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE). New York: ACM, 2019: 783-794. |
| [24] | GUO Daya, REN Shuo, LU Shuai, et al. GraphCodeBert: Pre-Training Code Representations with Data Flow[EB/OL]. (2021-09-13)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.08366. |
| [25] | LIU Jiahao, ZENG Jun, WANG Xiang, et al. Learning Graph-Based Code Representations for Source-Level Functional Similarity Detection[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE/ACM 45th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE). New York: IEEE, 2023: 345-357. |
| [26] | FENG Qian, ZHOU Rundong, XU Chengcheng, et al. Scalable Graph-Based Bug Search for Firmware Images[C]// ACM. The 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 480-491. |
| [27] | XU Xiaojun, LIU Chang, FENG Qian, et al. Neural Network-Based Graph Embedding for Cross-Platform Binary Code Similarity Detection[C]// ACM. The 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 363-376. |
| [28] | YU Zeping, CAO Rui, TANG Qiyi, et al. Order Matters: Semantic-Aware Neural Networks for Binary Code Similarity Detection[C]// AAAI. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2020: 1145-1152. |
| [29] | KIM G, HONG S, FRANZ M, et al. Improving Cross-Platform Binary Analysis Using Representation Learning via Graph Alignment[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 31st ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis. New York: ACM, 2022: 151-163. |
| [30] | SHALEV N, PARTUSH N. Binary Similarity Detection Using Machine Learning[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 13th Workshop on Programming Languages and Analysis for Security. New York: ACM, 2018: 42-47. |
| [31] | Zynamics. BinDiff[EB/OL]. [2025-03-05]. https://www.zynamics.com/bindiff.html. |
| [32] | PEI Kexin, XUAN Zhou, YANG Junfeng, et al. Trex: Learning Execution Semantics from Micro-Traces for Binary Similarity[EB/OL]. (2021-03-26)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.08680. |
| [33] | LUO Zhenhao, WANG Pengfei, WANG Baosheng, et al. VulHawk: Cross-Architecture Vulnerability Detection with Entropy-Based Binary Code Search[EB/OL]. (2023-02-27)[2025-03-05]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/ndss2023_f415_paper.pdf. |
| [34] | JI Yuede, CUI Lei, HUANG H H. Buggraph: Differentiating Source-Binary Code Similarity with Graph Triplet-Loss Network[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2021: 702-715. |
| [35] | TEHRANIJAMSAZ A, CHEN Hanze, JANNESARI A. Graphbinmatch: Graph-Based Similarity Learning for Cross-Language Binary and Source Code Matching[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW). New York: IEEE, 2024: 506-515. |
| [36] | Hugging Face. Hugging Face[EB/OL]. [2025-03-05]. https://huggingface.co/. |
| [37] | ALLAMANIS M. Graph Neural Networks in Program Analysis[EB/OL]. (2022-01-03)[2025-03-05]. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-16-6054-2_22. |
| [38] | ALLAMANIS M, BROCKSCHMIDT M, KHADEMI M. Learning to Represent Programs with Graphs[EB/OL]. (2018-05-04)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.00740. |
| [39] | CUMMINS C, FISCHES Z V, BEN-NUN T, et al. Programl: Graph-Based Deep Learning for Program Optimization and Analysis[EB/OL]. (2020-03-23)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10536. |
| [40] | KIPF T N, WELLING M. Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks[EB/OL]. (2017-02-22)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.02907. |
| [41] | MARCELLI A, GRAZIANO M, UGARTE-PEDRERO X, et al. How Machine Learning is Solving the Binary Function Similarity Problem[C]// USENIX. The 31st USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security’22). Berkeley: USENIX, 2022: 2099-2116. |
| [42] | POWERS D M W. Evaluation: from Precision, Recall and F-Measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness and Correlation[EB/OL]. (2020-10-11)[2025-03-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.16061. |
| [43] | YUAN Zimu, FENG Muyue, LI Feng, et al. B2sfinder: Detecting Open-Source Software Reuse in Cots Software[C]// IEEE. 2019 34th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1038-1049. |
| [1] | 胡斌, 黑一鸣, 吴铁军, 郑开发, 刘文忠. 大模型安全检测评估技术综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1477-1492. |
| [2] | 张大龙, 丁曙光, 韩志龙, 付守利, 唐志青, 石磊. 网络韧性评估框架和方法综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1493-1505. |
| [3] | 兰佳晨, 陈夏润, 周杨凯, 文伟平. 多模态网络中的路由技术与协议研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1506-1522. |
| [4] | 余发江, 王朝州. TrustZone半虚拟化与容器化实现机制[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1523-1536. |
| [5] | 陶慈, 王逸, 张蕾, 陈平. 面向云边协同场景中固件的模糊测试方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1537-1545. |
| [6] | 谢四江, 冯雁, 阎亚龙, 宁飞. 基于密钥双同步的量子密钥通用服务模式研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1546-1553. |
| [7] | 李古月, 张子豪, 毛承海, 吕锐. 基于累积量与深度学习融合的水下调制识别模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1554-1569. |
| [8] | 胡隆辉, 宋虹, 王伟平, 易佳, 张智雄. 大语言模型在安全托管服务误报处理中的应用研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1570-1578. |
| [9] | 王友贺, 孙奕. 基于CNN-BiLSTM-CBAM的多特征融合恶意PDF文档检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1579-1588. |
| [10] | 张璐, 贾鹏, 刘嘉勇. 基于多元语义图的二进制代码相似性检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1589-1603. |
| [11] | 梁凤梅, 潘正豪, 刘阿建. 基于共性伪造线索感知的物理和数字人脸攻击联合检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1604-1614. |
| [12] | 李涛, 程柏丰. 基于图神经网络的网络资产主动识别技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(10): 1615-1626. |
| [13] | 詹东阳, 黄子龙, 谭凯, 俞兆丰, 贺铮, 张宏莉. 面向Serverless应用的跨函数行为分析与约束技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1329-1337. |
| [14] | 曹骏, 向尕, 任亚唯, 谭自程, 杨群生. 基于大模型的少样本APT攻击事件抽取方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1338-1347. |
| [15] | 胡雨翠, 高浩天, 张杰, 于航, 杨斌, 范雪俭. 车联网安全自动化漏洞利用方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1348-1356. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||