信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 281-294.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.02.009
基于情感辅助多任务学习的社交网络攻击性言论检测技术研究
金地1,2,3, 任昊1,2,3, 唐瑞1,2,3, 陈兴蜀1,2,3, 王海舟1,2,3( )
)
- 1.四川大学网络空间安全学院,成都 610065
2.数据安全防护与智能治理教育部重点实验室,成都 610065
3.四川大学网络空间安全研究院,成都 610065
-
收稿日期:2024-12-10出版日期:2025-02-10发布日期:2025-03-07 -
通讯作者:王海舟 E-mail:whzh.nc@scu.edu.cn -
作者简介:金地(2001—),女,河南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络舆情分析|任昊(1991—),男,安徽,副研究员,博士,主要研究方向为数据安全和隐私保护、AI安全与治理、应用密码学|唐瑞(1990—),男,四川,助理研究员,博士,主要研究方向为人工智能安全、社交网络分析|陈兴蜀(1968—),女,贵州,教授,博士,主要研究方向为云计算安全、数据安全、威胁检测、开源情报和人工智能安全|王海舟(1986—),男,四川,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为网络舆情分析、开源情报分析 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2022YFC3303101);四川省科技厅重点研发计划(2023YFG0145)
Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning
JIN Di1,2,3, REN Hao1,2,3, TANG Rui1,2,3, CHEN Xingshu1,2,3, WANG Haizhou1,2,3( )
)
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China
2. Key Laboratory of Data Protection and Intelligent Management, Ministry of Education, Chengdu 610065, China
3. China Cyber Science Research Institute, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China
-
Received:2024-12-10Online:2025-02-10Published:2025-03-07
摘要:
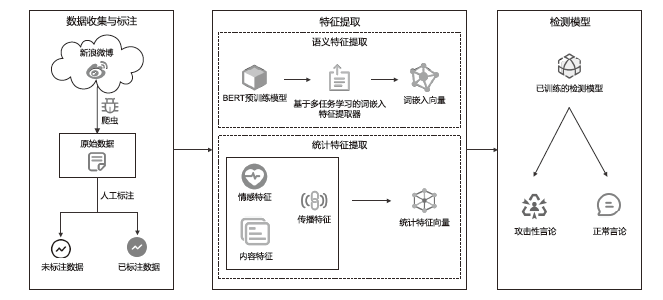
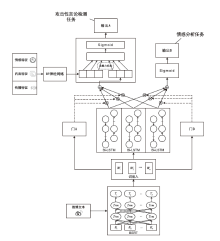
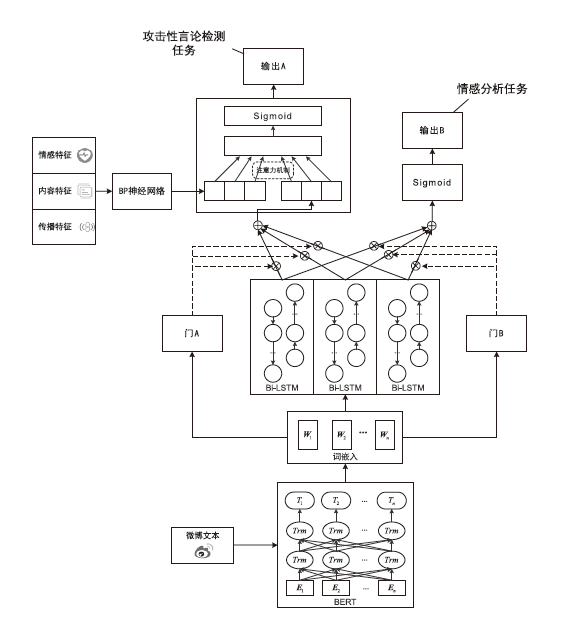
随着互联网和移动互联网技术的快速发展,越来越多的人们热衷于在社交网络上获取信息,表达自己的立场和观点。但近年来,社交网络上充斥着越来越多的攻击性言论及其他不良言论,网络暴力大量滋生。目前,攻击性言论检测研究大多集中在英文领域,面向中文攻击性言论检测的相关研究较少。针对该问题,首先,文章采集了新浪微博平台中大量的推文数据,并依据制定的标注规则对相关数据进行标注,构建了中文攻击性言论数据集;然后,文章提取了包括情感特征、内容特征、传播特征3个类别在内的统计特征;最后,文章构建了基于多任务学习的攻击性言论检测模型,引入辅助任务情感分析,利用两个任务之间的高度相关性提升模型的检测效果。实验结果表明,文章提出的检测模型对攻击性言论的检测效果优于其他常用检测方法。该研究工作为后续的面向社交网络的攻击性言论检测提供了方法和思路。
中图分类号:
引用本文
金地, 任昊, 唐瑞, 陈兴蜀, 王海舟. 基于情感辅助多任务学习的社交网络攻击性言论检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 281-294.
JIN Di, REN Hao, TANG Rui, CHEN Xingshu, WANG Haizhou. Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 281-294.
表3
常见文本分类模型对比实验
| 模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Macro-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TextCNN[ | 0.839 | 0.719 | 0.583 | 0.770 |
| TextRNN[ | 0.809 | 0.659 | 0.492 | 0.721 |
| TextRCNN[ | 0.818 | 0.658 | 0.568 | 0.745 |
| TextDPCNN[ | 0.826 | 0.782 | 0.422 | 0.721 |
| BERT[ | 0.827 | 0.654 | 0.653 | 0.769 |
| BERT-CNN | 0.829 | 0.680 | 0.600 | 0.763 |
| BERT-RNN | 0.824 | 0.672 | 0.583 | 0.755 |
| BERT-RCNN | 0.826 | 0.659 | 0.628 | 0.764 |
| BERT-DPCNN | 0.821 | 0.655 | 0.598 | 0.754 |
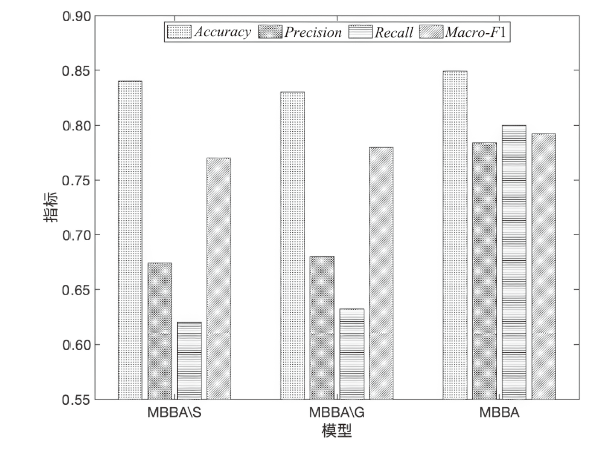
| MBBA(本文) | 0.849 | 0.784 | 0.800 | 0.792 |
表4
攻击性言论检测模型对比实验结果
| 模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Macro-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaiduTC | 0.571 | 0.298 | 0.525 | 0.380 |
| Qwen1.5-0.5B | 0.514 | 0.489 | 0.486 | 0.466 |
| Qwen-7B | 0.519 | 0.480 | 0.475 | 0.483 |
| LLaMA3-8B | 0.606 | 0.638 | 0.681 | 0.591 |
| Alpaca2-7B | 0.477 | 0.643 | 0.640 | 0.477 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 0.406 | 0.599 | 0.581 | 0.403 |
| GPT-4o | 0.757 | 0.705 | 0.754 | 0.716 |
| GPT-4-Turbo | 0.741 | 0.707 | 0.770 | 0.710 |
| COLDetector[ | 0.729 | 0.769 | 0.729 | 0.742 |
| MBBA(本文) | 0.849 | 0.784 | 0.800 | 0.792 |
表5
模型在COLDataset数据集上的泛化性实验结果
| 模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Macro-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaiduTC | 0.630 | 0.610 | 0.560 | 0.540 |
| Qwen1.5-0.5B | 0.496 | 0.385 | 0.457 | 0.417 |
| Qwen-7B | 0.617 | 0.511 | 0.749 | 0.607 |
| LLaMA3-8B | 0.615 | 0.601 | 0.603 | 0.601 |
| Alpaca2-7B | 0.676 | 0.695 | 0.700 | 0.676 |
| ChatGLM3-6B | 0.529 | 0.616 | 0.588 | 0.517 |
| GPT-4o | 0.767 | 0.784 | 0.725 | 0.734 |
| GPT-4-Turbo | 0.784 | 0.784 | 0.756 | 0.764 |
| COLDetector[ | 0.810 | 0.800 | 0.820 | 0.810 |
| MBBA(本文) | 0.831 | 0.840 | 0.831 | 0.832 |
| [1] | BURNAP P, WILLIAMS M L. Cyber Hate Speech on Twitter: An Application of Machine Classification and Statistical Modeling for Policy and Decision Making[J]. Policy & Internet, 2015, 7(2): 223-242. |
| [2] | Pew Research Center. Online Harassment 2017[EB/OL]. (2017-07-11)[2024-12-06]. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2017/07/11/online-harassment-2017. |
| [3] | Department for the Protection of Youth Rights and Interests of the Central Committee of the Communist Youth League, China Internet Network Information Centre (CNNIC). 2021 National Research Report on Minors’ Internet Usage[EB/OL]. (2022-11-30)[2024-12-06]. http://news.youth.cn/gn/202211/t20221130_14165457.htm. |
| 共青团中央维护青少年权益部, 中国互联网络信息中心. 2021年全国未成年人互联网使用情况研究报告[EB/OL]. (2022-11-30)[2024-12-06]. http://news.youth.cn/gn/202211/t20221130_14165457.htm. | |
| [4] | Secretary Bureau of the Office of the Central Cyberspace Affairs Commission. Notice of Effectively Strengthening the Governance of Cyber Violence[EB/OL]. (2022-11-04)[2024-12-06]. https://www.cac.gov.cn/2022-11/04/c_1669204414682178.htm. |
| 中央网信办秘书局. 关于切实加强网络暴力治理的通知[EB/OL]. (2022-11-04)[2024-12-06]. https://www.cac.gov.cn/2022-11/04/c_1669204414682178.htm. | |
| [5] | PATCHIN J W, HINDUJA S. Cyberbullying Among Tweens in the United States: Prevalence, Impact, and Helping Behaviors[J]. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 2022, 42(3): 414-430. |
| [6] | WATANABE H, BOUAZIZI M, OHTSUKI T. Hate Speech on Twitter: A Pragmatic Approach to Collect Hateful and Offensive Expressions and Perform Hate Speech Detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 13825-13835. |
| [7] | SU Huipo, HUANG Zhenjie, CHANG H T, et al. Rephrasing Profanity in Chinese Text[C]// ACL. The 1st Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 18-24. |
| [8] | YANG H, LIN Chuanjie. TOCP: A Dataset for Chinese Profanity Processing[C]// ELRA. The 2nd Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying. Paris: ELRA, 2020: 6-12. |
| [9] | DAVIDSON T, WARMSLEY D, MACY M, et al. Automated Hate Speech Detection and the Problem of Offensive Language[C]// AAAI. The 11th International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2017, 11(1): 512-515. |
| [10] | SWAMY S D, JAMATIA A, GAMBACK B, et al. NIT_Agartala_NLP_Team at SemEval-2019 Task 6: an Ensemble Approach to Identifying and Categorizing Offensive Language in Twitter Social Media Corpora[C]// ACL. The 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 696-703. |
| [11] | BALAKRISHNAN V, GOVINDAN V, GOVAICHELVAN K N. Tamil Offensive Language Detection: Supervised Versus Unsupervised Learning Approaches[J]. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing, 2023, 22(4): 1-14. |
| [12] | KIM Y. Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification[C]// ACL. The 19th Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2014: 1746-1751. |
| [13] | GAMBACK B, SIKDAR U K. Using Convolutional Neural Networks to Classify Hate-Speech[C]// ACL. The 1st Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 85-90. |
| [14] | PARK J H, FUNG P. One-Step and Two-Step Classification for Abusive Language Detection on Twitter[C]// ACL. The 1st Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 41-45. |
| [15] | SINGH V, VARSHNEY A, AKHTAR S S, et al. Aggression Detection on Social Media Text Using Deep Neural Networks[C]// ACL. The 2nd Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2018: 43-50. |
| [16] | BADJATIYA P, GUPTA S, GUPTA M, et al. Deep Learning for Hate Speech Detection in Tweets[C]// ACM. The 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion. New York: ACM, 2017: 759-760. |
| [17] | PAVLOPOULOS J, MALAKASIOTIS P, ANDROUTSOPOULOS I. Deep Learning for User Comment Moderation[C]// ACL. The 1st Workshop on Abusive Language Online. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 25-35. |
| [18] | PAVLOPOULOS J, MALAKASIOTIS P, ANDROUTSOPOULOS I. Deeper Attention to Abusive User Content Moderation[C]// ACL. The 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 1125-1135. |
| [19] | DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. Bert: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding[C]//ACL. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 4171-4186. |
| [20] | LIU Ping, LI Wen, ZOU Liang. NULI at SemEval-2019 Task 6: Transfer Learning for Offensive Language Detection Using Bidirectional Transformers[C]// ACL. The 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 87-91. |
| [21] | PARASCHIV A, CERCEL D C. UPB at GermEval-2019 Task 2: BERT-Based Offensive Language Classification of German Tweets[C]// GSCL. The 15th Conference on Natural Language Processing. Erlangen: GSCL, 2019: 396-402. |
| [22] | RISCH J, STOLL A, ZIEGELE M, et al. hpiDEDIS at GermEval 2019: Offensive Language Identification Using a German BERT Model[C]// GSCL. The 15th Conference on Natural Language Processing. Erlangen: GSCL, 2019: 405-410. |
| [23] | RAJAMANICKAM S, MISHRA P, YANNAKOUDAKIS H, et al. Joint Modelling of Emotion and Abusive Language Detection[C]// ACL. The 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2020: 4270-4279. |
| [24] | ZHOU Xianbing, YANG Yong, FAN Xiaochao, et al. Hate Speech Detection Based on Sentiment Knowledge Sharing[C]// ACL. The 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2021: 7158-7166. |
| [25] | YANG Chuanpeng, ZHU Fuqing, LIU Guihua, et al. Multimodal Hate Speech Detection via Cross-Domain Knowledge Transfer[C]// ACM. The 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2022: 4505-4514. |
| [26] | DENG Jiawen, ZHOU Jingyan, SUN Hao, et al. COLD: A Benchmark for Chinese Offensive Language Detection[C]// ACL. The 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2022: 11580-11599. |
| [27] | PAVLOPOULOS J, MALAKASIOTIS P, BAKAGIANNI J, et al. Improved Abusive Comment Moderation with User Embeddings[C]//ACL. The 2017 EMNLP Workshop:Natural Language Processing Meets Journalism. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 51-55. |
| [28] | QIAN Jing, ELSHERIEF M, BELDING E M, et al. Leveraging Intra-User and Inter-User Representation Learning for Automated Hate Speech Detection[C]//ACL. The 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2018: 118-123. |
| [29] | MISHRA P, DEL TREDICI M, YANNAKOUDAKIS H, et al. Author Profiling for Abuse Detection[C]// ACL. The 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2018: 1088-1098. |
| [30] | RIBEIRO M H, CALAIS P H, SANTOS Y A, et al. Characterizing and Detecting Hateful Users on Twitter[C]// AAAI. The 12th International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2018: 676-679. |
| [31] | MISHRA P, DEL TREDICI M, YANNAKOUDAKIS H, et al. Abusive Language Detection with Graph Convolutional Networks[C]//ACL. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 2145-2150. |
| [32] | ZHANG Yu, YANG Qiang. A Survey on Multi-Task Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2021, 34(12): 5586-5609. |
| [33] | ROSS B, RIST M, CARBONELL G, et al. Measuring the Reliability of Hate Speech Annotations: The Case of the European Refugee Crisis[C]// NLP4CMC III. The 3rd Workshop on Natural Language Processing for Computer-Mediated Communication. Bochum: Bochumer Linguistische Arbeitsberichte, 2016: 6-9. |
| [34] | WASEEM Z. Are You a Racist or am I Seeing Things? Annotator Influence on Hate Speech Detection on Twitter[C]// ACL. The 2016 EMNLP Workshop on Natural Language Processing and Computational Social Science. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2016: 138-142. |
| [35] | WASEEM Z, HOVY D. Hateful Symbols or Hateful People? Predictive Features for Hate Speech Detection on Twitter[C]//ACL. The 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2016: 88-93. |
| [36] | SINA Weibo. Weibo Community Convention[EB/OL]. (2021-05-27)[2024-12-06]. https://service.account.weibo.com/h5/roles/gongyue. |
| 新浪微博. 微博社区公约[EB/OL]. (2021-05-27)[2024-12-06]. https://service.account.weibo.com/h5/roles/gongyue. | |
| [37] | Zhihu. Zhihu Community Guidelines[EB/OL]. (2022-04-28)[2024-12-06]. https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/506696688. |
| 知乎. 知乎社区规范[EB/OL]. (2022-04-28)[2024-12-06]. https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/506696688. | |
| [38] | META. Community Standards[EB/OL]. (2024-11-12)[2024-12-06]. https://transparency.meta.com/zh-cn/policies/community-standards/. |
| META. 社群守则[EB/OL]. (2024-11-12)[2024-12-06]. https://transparency.meta.com/zh-cn/policies/community-standards/. | |
| [39] | X Corp. The X Roles[EB/OL]. (2023-07-01)[2024-12-06]. https://help.x.com/zh-cn/rules-and-policies/twitter-rules. |
| [40] | RODRIGUEZ A, ARGUETA C, CHEN Yiling. Automatic Detection of Hate Speech on Facebook Using Sentiment and Emotion Analysis[C]// IEEE. The 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication. New York: IEEE, 2019: 169-174. |
| [41] | LIU Pengfei, QIU Xipeng, HUANG Xuanjing. Recurrent Neural Network for Text Classification with Multi-Task Learning[C]// ACM. The 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2016: 2873-2879. |
| [42] | LAI Siwei, XU Liheng, LIU Kang, et al. Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Classification[C]// AAAI. The 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2015: 2267-2273. |
| [43] | JOHNSON R, ZHANG Tong. Deep Pyramid Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Categorization[C]// ACL. The 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2017: 562-570. |
| [1] | 李海龙, 崔治安, 沈燮阳. 网络流量特征的异常分析与检测方法综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [2] | 武浩莹, 陈杰, 刘君. 改进Simon32/64和Simeck32/64神经网络差分区分器[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [3] | 陈晓静, 陶杨, 吴柏祺, 刁云峰. 面向骨骼动作识别的优化梯度感知对抗攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [4] | 徐茹枝, 张凝, 李敏, 李梓轩. 针对恶意软件的高鲁棒性检测模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [5] | 田钊, 牛亚杰, 佘维, 刘炜. 面向车联网的车辆节点信誉评估方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [6] | 张光华, 刘亦纯, 王鹤, 胡勃宁. 基于JSMA对抗攻击的去除深度神经网络后门防御方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [7] | 徐子荣, 郭焱平, 闫巧. 基于特征恶意度排序的恶意软件对抗防御模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| [8] | 杨志鹏, 刘代东, 袁军翼, 魏松杰. 基于自注意力机制的网络局域安全态势融合方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 398-410. |
| [9] | 江荣, 刘海天, 刘聪. 基于集成学习的无监督网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [10] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [11] | 赵鹏程, 于俊清, 李冬. 一种基于深度学习的SRv6网络流量调度优化算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 272-281. |
| [12] | 金志刚, 丁禹, 武晓栋. 融合梯度差分的双边校正联邦入侵检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 293-302. |
| [13] | 张选, 万良, 罗恒, 杨阳. 基于两阶段图学习的僵尸网络自动化检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(12): 1933-1947. |
| [14] | 印杰, 陈浦, 杨桂年, 谢文伟, 梁广俊. 基于人工智能的物联网DDoS攻击检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1615-1623. |
| [15] | 魏金侠, 黄玺章, 付豫豪, 李婧, 龙春. 基于全局特征学习的挖矿流量检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1506-1514. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||